Please refer to Respiration in Plants Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Respiration in Plants
Objective Question
Question. Which one of the following is essential for the respiration as well as photosynthesis ?
(a) Ubiquinone
(b) Cytochrome
(c) RuBisCO
(d) Plastocyanin
Answer
B
Question. Citrate synthase, an enzyme of TCA cycle is located in
(a) cytosol in prokaryotes.
(b) mitochondrial matrix in eukaryotes.
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of the above
Answer
C
Question. Out of 38 ATP molecules produced per glucose, 32 ATP molecules are formed from NADH/FADH2 in
(a) respiratory chain
(b) Krebs cycle
(c) oxidative decarboxylation
(d) EMP
Answer
A
Question. Total number of ATP consumed during Kreb’s cycle is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer
A
Question. In the electron transport system, the final acceptor of proton is
(a) cytochrome b
(b) cytochrome a3
(c) oxygen
(d) ubiquinone (substance A)
Answer
C
Question. A major site for synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi is
(a) F1 headpiece in mitochondria.
(b) F0.
(c) F1 – F0.
(d) mitochondria.
Answer
A
Question. How many ATP molecules can be produced through oxidative phosphorylation of 2NADH2 and 3 FADH2?
(a) 15
(b) 24
(c) 6
(d) 12
Answer
D
Question. Chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in the chloroplasts and mitochondria is based on the
(a) membrane potential.
(b) accumulation of Na ions.
(c) accumulation of K ions.
(d) proton gradient.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is amphibolic in nature?
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
(c) TCA cycle
(d) Oxidative phosphorylation
Answer
C
Question. If R. Q. is less than 1.0 in a respiratory metabolism, it means that
(a) carbohydrates are used as respiratory substrate.
(b) organic acids are used as respiratory substrate.
(c) the oxidation of the respiratory substrate consumed more oxygen than the amount of CO2 released.
(d) the oxidation of the respiratory substrate consumed less oxygen than the amount of CO2 released.
Answer
C
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statement regarding the process of glycolysis is correct?
(a) Glucose undergoes complete oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid.
(b) Glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form one molecule of pyruvic acid.
(c) Glucose undergoes complete oxidation to form one molecule of pyruvic acid.
(d) Glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid.
Answer
D
Question. Select the incorrect statement about NADH during cellular respiration.
(a) It is synthesized in glycolysis.
(b) It is transferred into the mitochondria.
(c) It undergoes oxidative phosphorylation.
(d) It is reduced to NAD+.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement about cellular energy harvesting pathway is incorrect?
(a) Pyruvate oxidation can only occur under aerobic conditions.
(b) Autotrophs can produce their own food but must obtain energy from it by glycolysis & cellular
respiration.
(c) Fermentation usually occurs under aerobic conditions.
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a more accurate statement about respiration ?
(a) O2 must always be available for respiration.
(b) O2 combines with carbon to form CO2.
(c) O2 combines with hydrogen to form H2O.
(d) Air is inhaled and exhaled only from stomata.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement is/are the correct events in aerobic respiration?
(i) The complete oxidation of pyruvate by the stepwise removal of all the hydrogen atoms, leaving three
molecules of O2.
(ii). The complete oxidation of pyruvate by the stepwise removal of all the hydrogen atoms, leaving three
molecules of CO2.
(iii) The passing on of the electrons removed as part of the hydrogen atoms to molecular O2 with
simultaneous synthesis of ATP.
(iv) The passing on of the electrons removed as part of the hydrogen atoms to molecular O2 with
simultaneous synthesis of ADP.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match the column-I with column-II and choose the correct combination from the options given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Inner mitochondrial membrane | I. Krebs cycle |
| B. Pyruvic acid is converted into CO2 and ethanol. | II. ETC |
| C. Cytoplasm | III. Fermentation |
| D. Mitochondrial matrix | IV. Glycolysis |
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(b) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
D
Question. Match the number of carbon atoms given in column – I with that of the compounds given in column – II and select the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. 4C compound | I. Acetyl CoA |
| B. 2C compound | II. Pyruvate |
| C. 5C compound | III. Citric acid |
| D. 3C compound | IV. α – ketoglutaric acid |
| V. Malic acid |
(a) A – II; B – V; C – III; D – I
(b) A – V; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(c) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(d) A – V; B – III; C – I; D – II
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Respiration substrates are
(i) the compounds that are oxidized to utilise energy.
(ii) the compounds that are reduced to utilise energy.
(iii) the compounds that are oxidized to release energy.
(iv) the compounds that are reduce to release energy.
(a) (i) only
(b) both (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) only
(d) Both (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Energy accumulate in ATP in
(a) disulphide bond
(b) hydrogen bonds
(c) high energy phosphate bond
(d) ester bond
Answer
C
Question. What is the function of molecular oxygen in cellular respiration?
(a) It causes the breakdown of citric acid.
(b) It combines with glucose to produce carbon dioxide.
(c) It combines with carbon from organic molecules to produce carbon dioxide.
(d) It combines with hydrogen from organic molecules to produce water.
Answer
D
Question. Which one is correct sequence in glycolysis?
(a) G 6-P → PEP → 3-PGAL → 3-PGA
(b) G 6-P → 3-PGAL → 3-PGA → PEP
(c) G 6-P → PEP → 3-PGA → 3-PGAL
(d) G 6-P → 3-PGA → 3-PGAL → PEP
Answer
B
Question. In glycolysis, there is one step where NADH + H+ is formed from NAD+, this is when 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL) is converted to 1, 3- bisphosphyglycerate (BPGA). This reaction shows
(a) oxidative dehydrogenation
(b) oxidative phosphorylation
(c) oxidative dehydration
(d) oxidation reduction
Answer
A
Question. How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one mole of glucose to CO2 and H2O yields 686 kcal and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one mole of ATP is 12 kcal ?
(a) Thirty
(b) Fifty seven
(c) One
(d) Two
Answer
B
Question. The reasons for the involvement of different enzyme in each step of glycolysis is that
(a) each step occurs in a different compartment of a cell.
(b) each step occurs in a different cells.
(c) each step involves a different chemical reaction.
(d) each step involves a different change in potential energy.
Answer
C
Question. In alcoholic fermentation, NAD+ is produced during the
(a) reduction of acetyldehyde to ethanol.
(b) oxidation of glucose.
(c) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl coA.
(d) hydrolysis of ATP to ADP.
Answer
A
Question. In the conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl coenzyme A, NAD+ is
(a) oxidized
(b) reduced
(c) broken into one-carbon units
(d) isomerized
Answer
B
Question. End products of Krebs cycle from one molecule of glucose is
(a) 2ATP, 2NADH, 2FADH2, CO2 and H2O
(b) 2ATP, 8NADH, 2FADH2, CO2 and H2O
(c) 8ATP, 4NADH, FADH2, CO2 and H2O
(d) ATP, 4NADH, FADH2, CO2 and H2O
Answer
B
Question. Single turn of citric acid cycle yields
(a) 2FADH2, 2NADH2, 2GTP
(b) 1FADH2, 2NADH2, 1GTP
(c) 1FADH2, 4NADH2, 1GTP
(d) 1FADH2, 1NADH2, 2GTP
Answer
C
Question. O2 is used by
(a) citric acid cycle
(b) electron transport chain
(c) substrate level phosphorylation
(d) ATP synthase
Answer
D
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The given figure shows the few steps of the pathway are indicated by P, Q, R and S major pathway of anaerobic respiration.

Identify P, Q, R and S.

Answer
A
Question. Refer the figure and identify X, Y and Z
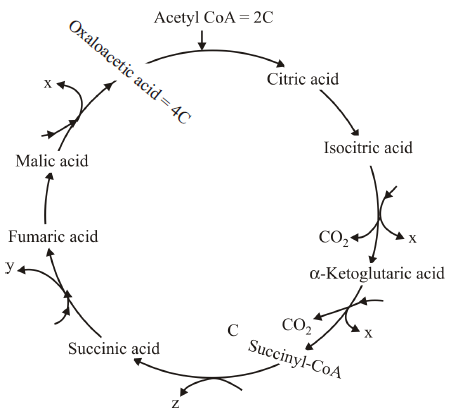
| X | Y | Z |
| (a) GTP | NADH2 | CO2 |
| (b) FADH2 | NADH2 | GTP |
| (c) NADH2 | FADH2 | GTP |
| (d) CO2 | NADH2 | ADP |
Answer
C
Question. The given figure represents the interelationship among metabolic pathways showing the respiration mediated breakdown of different organic molecules to CO2 and H2O.
Now identify A to D.

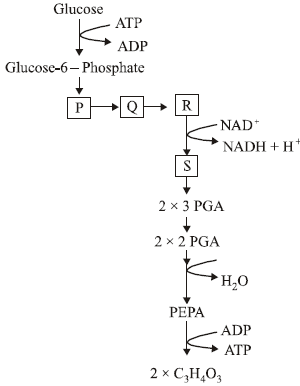
| P | Q | R | S |
| (a) 1,3 di PGA | 3 PGA | Fr.1,6 di P | Fr. 6 P |
| (b) 3 PGA | 1,3 di PGA | Fr. 1,6 di P | Fr.6 P |
| (c) Fr. 1,6 di P | Fr. 6 P | 3 PGA | 1,3 di PGA |
| (d) Fr.6 P | Fr. 1,6 di P | 3 PGA | 1,3 di PGA |
Answer
B


