Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Amines Chapter 13 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 13 Amines Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Amines Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Methylamine reacts with HNO2 to form _________.
(A) CH3 — O — N = O
(B) CH3 — O — CH3
(C) CH3OH
(D) CH3CHO
Answer
C
Question. IUPAC name of product formed by reaction of methyl amine with two moles of ethyl chloride
(A) N,N-Dimethylethanamine
(B) N,N-Diethylmethanamine
(C) N-Methyl ethanamine
(D) N-Ethyl – N-methylethanamine
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following amines can be prepared by Gabriel synthesis ?
(A) Isobutyl amine
(B) Toluene
(C) N-methylbenzylamine
(D) Aniline
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following reagents would not be a good choice for reducing an aryl nitro compound to an amine ?
(A) H2(excess)/Pt
(B) LiAlH4 in ether
(C) Fe and HCl
(D) Sn and HCl
Answer
B
Question. The best reagent for converting 2–phenylpropanamide into 2-phenylpropanamine is _____.
(A) excess H2
(B) Br2 in aqueous NaOH
(C) Iodine in the presence of red phosphorus
(D) LiAlH4 in ether
Answer
D
Question. CH3CONH2 on reaction with NaOH and Br2 in alcoholic medium gives:
(A) CH3CH2NH2
(B) CH3CH2Br
(C) CH3NH2
(D) CH3COONa
Answer
C
Question. The best method for preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without changing the number of carbon atoms in the chain is:
(A) Hoffmann Bromamide reaction
(B) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
(C) Sandmeyer reaction
(D) Reaction with NH3
Answer
B
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength:
Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine
(A) Aniline < p-Nitroaniline < p-Toluidine
(B) Aniline < p-Toluidine < p-Nitroaniline
(C) p-Toluidine < p-Nitroaniline < Aniline
(D) p-Nitroaniline < Aniline < p-Toluidine
Answer
D
Question. Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
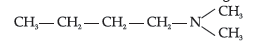
(A) N,N-Dimethylpropanamine
(B) 1,1-Dimethylbutanamine
(C) N-Methylpentan-1-amine
(D) N,N-Dimethylbutan-1-amine
Answer
D
Question. The correct IUPAC name for CH2 = CHCH2NHCH3 is:
(A) Allylmethylamine
(B) 2-amino-4-pentene
(C) 4-aminopent-1-ene
(D) N-methylprop-2-en-1-amine
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following should be most volatile ?
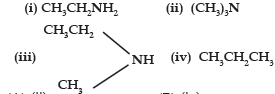
(A) (ii)
(B) (iv)
(C) (i)
(D) (iii)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a 3° amine ?
(A) 1-methylcyclohexylamine
(B) Triethylamine
(C) tert-butylamine
(D) N-methylaniline
Answer
B
Question. The gas evolved when methylamine reacts with nitrous acid is:
(A) NH3
(B) N2
(C) H2
(D) C2H6
Answer
B
Question. The correct increasing order of basic strength for the following compounds is __________
(A) II<III< I
(B) III < I < II
(C) III < II < I
(D) II < I < III
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following species are involved in the carbylamine test ?
(A) R—NC
(B) COCl2
(C) NaNO2 + HCl
(D) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Propanamide on reaction with bromine in aqueous NaOH gives:
(A) Propanamine
(B) Ethanamine
(C) N-Methyl ethanamine
(D) Propanenitrile
Answer
B
Question. Hinsberg’s reagent which is used to test amines is
(A) Benzene sulphonamide
(B) Benzene diazonium chloride
(C) Benzene sulphonyl chloride
(D) Acetanilide
Answer
C
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): Acetanilide is less basic than aniline.
Reason (R): Acetylation of aniline results in decrease of electron density on nitrogen.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Solubility of amines in water decreases with increase in molar mass.
Reason (R): Intermolecular H bonds formed by the higher amines are weaker.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): N, N-Diethylbenzene sulphonamide is insoluble in alkali.
Reason (R): Sulphonyl group attached to nitrogen atom is strong electron withdrawing group.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Aromatic 1° amines can be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
Reason (R): Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product whereas alkylation of amines gives poly substituted product.
Reason (R): Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups.
Answer
C
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion (A): Amines behave as a Lewis base.
Reason (R): Amines have an unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): (C2H5) 2NH > (C2H5) 3N > C2H5NH2 > NH3 is the order of basic strength in case of ethyl substituted amines.
Reason (R): The change of nature of the alkyl group, does not result in change of the order of basic strength.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3 is the order of basic strength in case of methyl substituted amines.
Reason (R): The inductive effect, solvation effect and steric hindrance of the alkyl group decide the basic strength of alkyl amines in the aqueous state.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger is the corresponding amine as a base.
Reason (R): The order of basicity of aliphatic amines is: primary > secondary > tertiary.
Answer
C
II. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion (A): The amino group of aniline is acetylated before bromination.
Reason (R): It is due to the strong deactivating effect of –NH2 group.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): In aniline –NH2 group facilitates the electrophilic attack.
Reason (R): It is due to decrease in electron density on the ring.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Benzene ring of aniline is highly deactivated.
Reason (R): In aniline, the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring increases the electron density on the ring.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): In aniline, the substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions.
Reason (R): The electron density is more at ortho and para positions.
Answer
A
III. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity.
Substitution tends to occur at ortho and parapositions.
To prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, the activating affect of –NH2 group be controlled. This can be done by protecting the – NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride,then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Question. Give the major product of the following reaction:
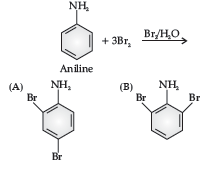

Answer
C
Question. Why is the activating effect of -NHCOCH3 group in the above reaction less than the activating effect of amino group?
(A) Due to mesomeric effect of benzene ring.
(B) Due to inductive effect of alkyl group.
(C) Due to resonance effect of acetanilide.
(D) All of the above
Answer
C
Question.Aniline is a resonance hybrid of:
(A) 3 resonating structures
(B) 6 resonating structures
(C) 2 resonating structures
(D) 5 resonating structures
Answer
D
Question. What is the major product A of the following reaction?

Answer
B
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) Write an isomer of C3H9N which gives foul smell of isocyanide when treated with chloroform and ethanolic NaOH
(ii) Write an isomer of C3H9N which does not react with Hinsberg reagent.
Answer. (i) Isomer of C3H9N is CH3CH2CH2NH2 , gives foul smell of isocyanides. (because primary amine Propan-1-amine
gives carbylamine reaction.)
(ii) Isomer of C3H9N which does not react with Hinsberg reagent is (CH3)3N i.e., tertiary amine.
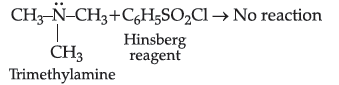
Question. (i) Arrange the following in decreasing order of solubility in water:
(CH3)3N,(CH3)2NH,CH3NH2
(ii) Arrange the following in decreasing order of the basic character:
C6H5NH2, (CH3)3N, C2H5NH2
Answer. (i) CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
(ii) (CH3)3N > C2H5NH2 > C6H5NH2
C6H5NH2 is least basic due to presence of -I group i.e., – C6H5 group that withdraws unshared pair of electrons present on N-atom of –NH2 group due to which it does not undergo protonation easily;
whereas (CH3)3N is most basic due to strong +I effect of –CH3 groups which release their bonding electrons towards N-atom and it undergoes protonation easily.
Hence, the decreasing order of the basic character is – (CH3)3N > C2H5NH2 > C6H5NH2.
Question. (i) Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points.
(CH3)3N, C2H5OH, C2H5NH2
(ii) Arrange the following in increasing order of base strength in gas phase:
(C2H5)3N, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH
Answer. (i) (CH3)3N < C2H5NH2 < C2H5OH
(ii) C2H5 NH2 < (C2H5 )2N < (C2H5 )3N Base strength is the ability to donate lone pair.
Due to inductive +I effect of C2H5 , the negative charge density on nitrogen atom increases.
Therefore, lone pair is easily available for donation.
C2H5H5NH2 < (C2H5)2 NH < (C2H5)3N
Question. (i) Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
(CH3CH2)2NCH3
(ii) Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH3NHCH(CH3)2
Answer. (i) N-Ethyl–N–methylethanamine.
(ii) N-Methylpropan-2-amine.
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of
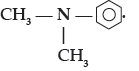
(ii) Out of (CH3)3N and (CH3)2NH, which one is more basic in aqueous solution?
Answer. (i) N, N – dimethylbenzenamine.
(ii) (CH3)2NH = Secondary amine
(CH3)3–N = Tertiary amine Secondary amines are more basic than tertiary amines in aqueous solution due to steric factor. So, (CH3)2NH is more basic in aqueous solution.
Question. (i) Arrange the following in increasing order of pKb values:
C6H5CH2NH2 ,C6H5NHCH3, C6H5NH2
(ii) Arrange the following in decreasing order of solubility in water:
(C2H5)2NH, C2H5NH2, C6H5NH2
Answer. (i) C6H5CH2NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5NH2 Greater the basic nature of amine, lesser will be the pKb value of amine. Since, C6H5CH2NH2 is most basic, so, it possesses least pKb value, while,C6H5NH2 is least basic, so, it possesses highest pKb value. Hence, the increasing order of pKb values is.
C6H5CH2NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 <C6H5NH2
(ii) C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2NH > C6H5NH2 (C2H5)2NH and C2H5NH2 are aliphatic amines and C6H5NH2is aromatic amine. Lower aliphatic amines can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Therefore, such amines are soluble in water. When number of alkyl groups (hydrophobic) increases then molar mass of amines increases. This usually results in a decrease in its solubility in water. Hence,C2H5NH2 is more soluble in water than (C2H5)2NH.
Whereas, aromatic amines are insoluble in water because of large hydrocarbon part (hydrophobic) which retards the formation of hydrogen bonding.
Question. Write the chemical equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Hoffmann-bromamide degradation reaction,
(ii) Carbylamine reaction.
Answer.
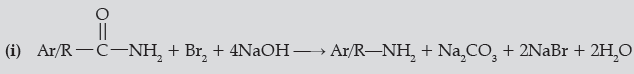
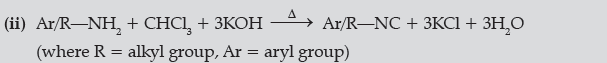
Question. Why does acetylation of —NH2 group of aniline reduce its activating effect ?
Answer. Direct nitration of aniline is not possible on account of –NH2 group present. However, nitration can be carried out after protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation to give acetanilide which is then nitrated and finally hydrolysed to give o- and p-nitroanilines. The acetyl group being electron withdrawing attracts the lone pair of electrons of the N – atom towards carbonyl group.
As a result, the activation effect of –NH2 group is reduced, that is, that lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance. Therefore, activating effect of NHCOCH3 group is less than that of NH2 group.
Question. Give reasons:
(i) Electrophilic substitution in aromatic amines takes place more readily than benzene.
(ii) CH3CONH2 is a weaker base than CH3CH2NH2.
Answer. (i) —NH2 group of aromatic amines strongly activates the aromatic ring through delocalisation of the lone pair of electrons of the N-atom over the aromatic ring.
Due to the strong activating effect of the —NH2 group, aromatic amines undergo electrophilic substitution reactions readily than benzene.
(ii) Due to resonance, the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in CH3CONH2 is delocalised over the keto group.
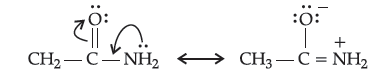
As a result, electron density on the N-atom in CH3CONH2 decreases. On the other hand, in C2H5NH2, due to +I effect of the ethyl group, the electron density on the N-atom increases consequently, CH3CONH2 is a weaker base than CH3CH2NH2.
Question. How do you convert the following :
(a) N-phenylethanamide to p-bromoaniline
(b) Benzoic acid to aniline
Answer.

Question. Give reasons:
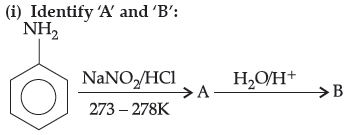
(ii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel Crafts reaction.
Answer.
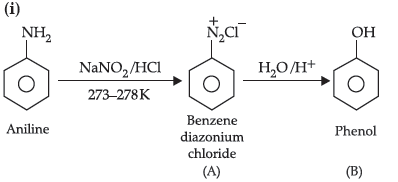
(ii) A Friedel–Crafts reaction is carried out in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3. But AlCl3, used as catalyst is acidic in nature i.e., Lewis acid whereas aniline is a strong Lewis base. Thus, aniline reacts with AlCl3 to form a salt.

Due to the positive charge on the N–atom, electrophilic substitution in the benzene ring is deactivated. Hence, aniline does not undergo Friedel–Crafts reaction.
Question. Complete the following reactions :
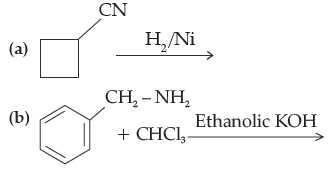
Answer.

Question. Give reasons:
(i) Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine.
(ii) It is difficult to prepare pure amines by ammonolysis of alkyl halides.
Answer. (i) Cyclohexylamine is more basic than aniline because aniline is a resonance hybrid of various resonance structures. As a result, in aniline the electron donating capacity of nitrogen for protonation is considerably decreased.
(ii) Ammonolysis of alkyl halides does not give single amine but gives a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
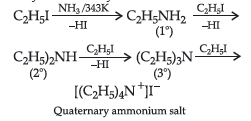
Question. Give two chemical tests to identify primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer. Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines:

Question. (i) Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
(CH3)2N — CH2CH3
(ii) Complete the following reaction equation:
C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O → …………………..
Answer. (i) N, N-Dimethylethanamine
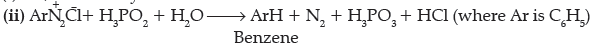
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in the following reactions:

Answer. (a) (A) CH3CONH2
(B) CH3NH2
(C) CH3NC

Question. Arrange the following compounds as directed:
(i) In increasing order of solubility in water:
(CH3)2NH, CH3NH2, C6H5NH2
(ii) In decreasing order of basic strength in aqueous solution:
(CH3)3N, (CH3)2NH, CH3NH2
(iii) In increasing order of boiling point:
(C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, C2H5NH2
Answer. (i) Increasing order of solubility in water:
C6H5NH2 < (CH3)2 NH < CH3NH2
(ii) Decreasing order of basic strength in aqueous solution:
(CH3)2NH > (CH3)3 N > CH3NH2
(iii) Increasing order of boiling point:
(C2H5)3 N < (C2H5)2 NH < C2H5NH2
Question. An aromatic compound ‘A’ on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘B’ of molecular formula C6H7N which on reacting with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces a foul smelling compound ‘C’. Write the structure and IUPAC names of compound A, B and C.
Answer.

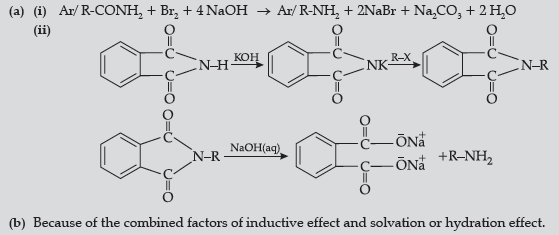
Question. (a) Write the reactions involved in the following:
(i) Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction
(ii) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
(b) Give reason:
(CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Answer.
Question. Give reasons:
(i) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
(ii) CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
(iii) Although –NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline.
Answer. (i) Due to the resonance, the electron pair of nitrogen atom gets delocalised towards carbonyl group / resonating structures.
(ii) Because of +I effect in methylamine electron density at nitrogen increases whereas in aniline resonance takes place and electron density on nitrogen decreases / resonating structures.
(iii) Due to protonation of aniline / formation of anilinium ion.
Question. Write the structures of A, B and C in the following:
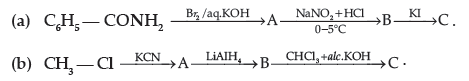
Answer. (a) C6H5NH2, C6H5N2+Cl–, C6H5I
(b) CH3CN, CH3CH2NH2, CH3 CH2NC
Question. Give reasons:
(i) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(ii) Aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel’s phthalimide synthesis.
(iii) Aliphatic amines are stronger base than ammonia.
Answer. (i) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction because aniline being a Lewis base forms a complex with AlCl3 which is a Lewis acid. The amino group is not in a position to activate the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution. Therefore the reaction is not possible.
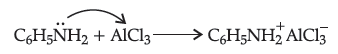
(ii) Aromatic primary amines can not be prepared by Gabriel’s phthalimide synthesis because haloarenes have to react with potassium phthalimide and they are least reactive. So, the
bond cleavage does not take place.
(iii) Aliphatic amines are stronger base than ammonia because the alkyl group in aliphatic amines has +I effect. So, the alkyl group tends to increase the electron density on the nitrogen atom whereas the electron releasing tendency of amines becomes more than that of ammonia.
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of property specified:
(i) Aniline, ethanamine, 2-ethylethanamine (solubility in water)
(ii) Ethanoic acid, ethanamine, ethanol (boiling point)
(iii) Methanamine, N, N- dimethylmethanamine and N- methylmethanamine (basic strength in aqueous phase)
Answer. (i) Aniline, N-ethylethanamine, Etanamine
(ii) Ethanamine, ethanol, ethanoic acid
(iii) N, N dimethylmethanamine, methanamine,N-methylmethanamine
Question. Give the str ucture of A, B and C in the following r eactions:

Answer.
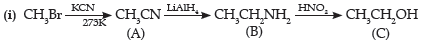
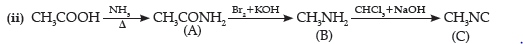
Question. (i) Give a chemical test to distinguish between N-methylethanamine and N,N-dimethyl ethanamine.
(ii) Write the reaction for catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene followed by reaction of product so formed with bromine water.
(iii) Out of butan-1-ol and butan-1-amine, which will be more soluble in water and why?
Answer. (i) N-methylethanamine is a secondary amine.
When it reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride, it forms N- Ethyl -N methyl sulphonamide and N, N-dimethyl ethanamine is a tertiary amine it does not react with benzenesulphonyl chloride.

(iii) Butan-1-ol
Alcohol forms stronger hydrogen bonds with water than formed by amine due to higher electronegativity of O in alcohol than N in amine.
Question. Give reasons for the following:
(i) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction,
(ii) (CH3)2 NH is more basic than (CH3)3 N in an aqueous solution.
(iii) Primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines.
Answer. (i) Aniline is a Lewis base while AlCl3 is lewis acid. They com bine to form a salt.
(ii) Due to combined + I and solvation effects.
(iii) Due to presence of H-bonding in primary amines.
Question. How will you convert the following:
(i) Nitrobenzene into aniline,
(ii) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
(iii) Aniline to N-phenylethanamide.
(Write the chemical equations involved.)
Answer. (i) Nitrobenzene into aniline

(ii) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
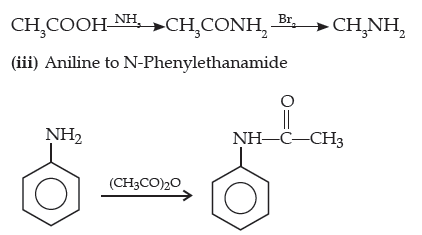
Long Answer Type Questions
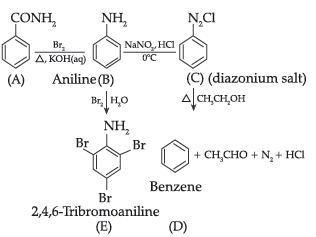
Question. An organic compound A with molecular formula C7H7NO reacts with Br2/aq. KOH to give compound B, which upon reaction with NaNO2 and HCl at 0°C gives C. Compound C on heating with CH3CH2OH gives a hydrocarbon D. Compound B on further reaction with Br2 water gives white precipitate of compound E. Identify the compound A, B, C, D and E; also justify your answer by giving relevant chemical equations.
Answer.
Question. Write the structure of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions:
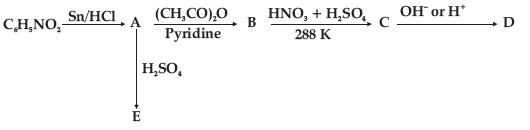
Answer.

Question. (i) Write the structures of main products when benzenediazonium chloride reacts with the following reagents:
(a) H3PO2 + H2O
(b) CuCN/KCN
(c) H2O
(ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their basic character in an aqueous solution:
C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N
(iii) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
C6H5 – NH2 and C6H5 – NH – CH3
Answer.

ii) C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)3N < (C2H5)2NH
(iii) Add CHCl3 and alc. KOH, C6H5–NH2 gives foul smell of isocyanide whereas C6H5–NH–CH3 does not .
Question. (a) Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions:

(b) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish be tween aniline and N,N-dimethylaniline.
(c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their pKb values:
C6H5NH2, C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3
Answer. (a) (i) C6H5NHCOCH3
(ii) C6H5SO2N(CH3)2
(iii) C6H5CH2NH2
(b) Add chloroform in the presence of KOH and heat, then, aniline gives a offensive smell while N, N dimethylaniline does not. (or any other test)
(c) C2H5NH2< C6H5NHCH3< C6H5NH2
Question. Predict the reagent or the product in the following reaction sequence:
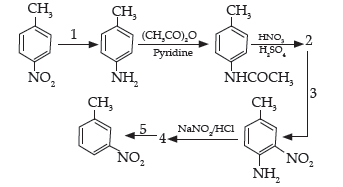
Answer.
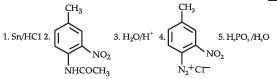
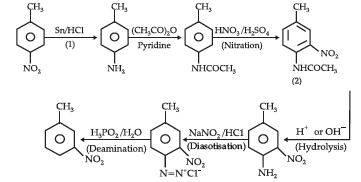
Question. (i) Write the structures of main products when aniline reacts with the following reagents:
(a) Br2 water
(b) HCl
(c) (CH3CO)2O / pyridine
(ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point:
C2H5NH2, C2H5OH, (CH3)3N
(iii) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
(CH3)2NH and (CH3)3N
Answer.


(iii) (CH3)2NH reacts with nitrous acid to form an oily layer of N-nitrosoamines which is insoluble in aqueous mineral acids.
