We have provided CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper with solutions below. These Sample guess papers have been prepared as per the latest examination guidelines and paper pattern issued by CBSE. Students of Class 11 should practice all practice papers for Class 11 Chemistry given below as it will help them top improve their understanding of the subject. Please click on the links below to access free sample paper for Chemistry Class 11.
Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry
| CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Term 2 Sample Paper |
| CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Term 2 Sample Paper Set A |
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Term 2 Sample Paper Set A
SECTION – A
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
Le-Chatelier’s principle allows us to predict the effects of changes in temperature, pressure and concentration on a system at equilibrium. It states that if a system at equilibrium experiences a change, the system will shift its equilibrium to try to compensate for the change.
Increasing the volume has the same effect as decreasing the pressure and vice-versa. When we increase the pressure, the system will shift so the least number of gas molecules are formed because the more gas molecules there are, the more collisions there are. These collisions and the presence of gas molecules are what cause the pressure to increase. Likewise, when we decrease the pressure, the system will shift so the higher number of gas molecules are produced.
A reaction is endothermic if it takes heat from its surroundings. On the other hand, a reaction is exothermic if it gives heat to the surroundings. If we increase the temperature, then the endothermic reaction will be favoured because that will take in some of the excess heat. If we decrease the temperature, the exothermic reaction will be favoured because it will produce the heat that was lost. A catalyst increases the speed in which a reaction takes place, however it never has any effect on the equilibrium.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer :
(i) The equilibrium constant of a reaction is 300. If the volume of a reaction flask is tripled, the equilibrium constant will be
(a) 300
(b) 100
(c) 600
(d) 150
Answer
A
(ii) In N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3 reversible reaction, increase in pressure will favour
(a) reversible reaction
(b) forward direction
(c) irreversible reaction
(d) backward direction.
Answer
B
(iii) Which of the following information can be obtained on the basis of Le-Chatelier’s principle?
(a) Equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction
(b) Dissociation constant of a weak acid
(c) Entropy change in a reaction
(d) All of these
Answer
A
(iv) Of the following which change will shift the reaction towards the product?
I2(g) ⇌ 2I(g), ΔH° (298 K) = +150 kJ
(a) Increase in concentration of I
(b) Decrease in concentration of I2
(c) Increase in temperature
(d) Increase in total pressure
Answer
C
OR
The role of a catalyst in a reversible reaction is
(a) to increase the rate of forward reaction
(b) to alter the equilibrium constant of the reaction
(c) to decrease the rate of backward reaction
(d) to allow the equilibrium to be achieved quickly.
Answer
D
Following questions (Q. No. 2-6) are multiple choice questions carrying 1 mark each :
2. Two vessels of volumes 16.4 L and 5 L contain two ideal gases of molecular existence at the respective temperature of 27°C and 227°C and exert 1.5 and 4.1 atmospheres respectively. The ratio of the number of molecules of the former to that of the latter is
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 1/2
(d) 1/3
Answer
A
3. For the properties mentioned, the correct trend for the different species is in
(a) strength as Lewis acid – BCl3 > AlCl3 > GaCl3
(b) inert pair effect – Al > Ga > In
(c) oxidising property – Al3+ > In3+ > Tl3+
(d) first ionization enthalpy – B > Al > Tl A
OR
The stability of dihalides of Si, Ge, Sn and Pb increases steadily in the sequence
(a) PbX2 << SnX2 << GeX2 << SiX2
(b) GeX2 << SiX2 << SnX2 << PbX2
(c) SiX2 << GeX2 << PbX2 << SnX2
(d) SiX2 << GeX2 << SnX2 << PbX2.
Answer
D
4. Which of the following compounds will not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction with benzene?

Answer
B
5. What should be the correct order of lattice energy values of the following alkali halides?
LiCl, KI, KCl and NaCl
(a) KI > KCl > NaCl < LiCl
(b) NaCl > KCl > LiCl > KI
(c) LiCl > KCl > KI > NaCl
(d) LiCl > NaCl > KCl > KI
Answer
D
OR
The correct order of first ionisation enthalpies of the following elements is
(a) Be > Mg > Ca > Sr > Ra > Ba
(b) Ra > Ba > Sr > Ca > Mg > Be
(c) Be > Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba > Ra
(d) Ra > Sr > Ba > Mg > Ca > Be
Answer
A
6. 2-Hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment with which of the following reagents?
(i) Li/NH3
(ii) Pd/BaSO4
(iii) LiAlH4
(iv) Pt/H2
(a) Only (ii)
(b) Both (ii) and (iii)
(c) Both (i) and (iii)
(d) All of these
Answer
C
In the following questions (Q. No. 7 and 8), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
7. Assertion : Boron differs from aluminium and other members of group 13 in a number of properties.
Reason : Boron shows anomalous behaviour.
Answer
B
OR
Assertion : The relative strength of the various boron trihalides increase in the order BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 < BI3.
Reason : The trihalides of boron are planar molecules in which the central B atom is sp3 hybridized.
Answer
C
8. Assertion : Propene reacts with HBr to give isopropyl bromide.
Reason : Addition of hydrogen halide to alkenes follows Markownikoff’s rule.
Answer
A
SECTION – B
The following questions Q. No. 9-12 are short answer type and carry 2 marks each.
9. For the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g), at 400 K, KP = 41. Find the value of KP for each of the following reactions at the same temperature
(i) 2NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3H2(g)
(ii) 1/2 N2(g) + 3/2 H2(g) ⇌ NH3(g)
Answer :
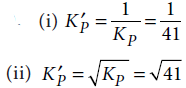
10. Discuss the trend of ionisation energy of the elements of group 14.
Answer : Ionization energy of carbon is quite high due to small size of the carbon atom. It then decreases to silicon due to the increase in size of silicon atom. Then there is a decrease in ionization energy from Si to Sn. This is because the ‘d’ electrons which are present in the inner configuration of Ge, and Sn shield the nuclear charge less effectively than is done by s-and p-electrons. The outer electrons are held strongly by the nucleus and there is only a small decrease in ionization energy
as we move from Si to Sn. In the case of Pb, there is only a marginal increase of atomic radius as we move from Sn to Pb and also there are f-electrons in the inner configuration which shield the nuclear charge less effectively than the d-electrons. So, the ionization energy instead of decreasing, shows a marginal increase.
11. What happens when
(i) sodium metal is dropped in water?
(ii) sodium metal is heated in free supply of air?
Answer : (i) Sodium metal catches fire and hydrogen gas is evolved.
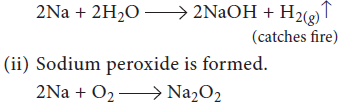
OR
On combustion Li forms Li2O; sodium gives the peroxide, Na2O2; and potassium, rubidium and caesium give superoxides, MO2. Why Li does not form a peroxide?
Answer :

The normal oxides contain O2– ion, the peroxides contain O22– ion and superoxides contain O2– ion. The peroxides and superoxides become more stable with increase in atomic number of the alkali metal. The formation and stability of these oxides can be explained on the basis of lattice energy effects. Li+ ion being a small ion has a strong positive field around it and can stabilise only a small anion, O2– whereas Na+ being a large cation can stabilise a large ion and so on.

12. F3C—CH CH2 gives anti-Markownikoff product. Why?
Answer : If the given compound follows Markownikoff’s rule,
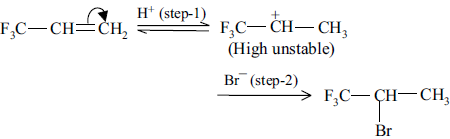
The carbocation produced in step-1 is highly unstable due to strong electron withdrawing group, hence it does not follow Markownikoff’s rule.
OR
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C—C, eight C—H σ bonds and one C—C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two
moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Answer : Alkene A contains 3C—C, 8C—H and one C = C bonds. An aldehyde containing one —CHO group and having molar mass of 44 amu has to be CH3CHO and since two moles of CH3CHO are obtained by ozonolysis of alkene A, the alkene has to be joined by two CH3CH— groups by a double bond. It has to be CH3—CH = CH—CH3, i.e., but-2-ene. But-2-ene contains 3C—C σ bonds, 8C—H σ bonds and one C = C bond.
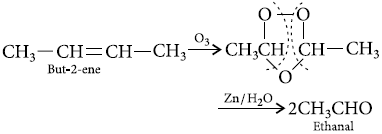
SECTION – C
Q. No. 13 and 14 are short answer type II carrying 3 marks each :
13. (a) 22 g of dry ice is placed in an evacuated bottle of 1 litre capacity and tightly stoppered. What would be the pressure inside the bottle, when it is heated to 37°C?
(b) 3.12 g of sulphur is vapourised at 427°C and 760 mm pressure, when the vapours occupy a volume of 700 mL. Find the molecular formula of sulphur. (atomic mass of sulphur = 32).
Answer : (a) W = 22 g CO2, V = 1 L, M = 44, T = 37 + 273 = 310 K, P = ?
Dry ice is solid CO2, which when heated in an evacuated bottle it is converted into gaseous CO2.
From ideal gas equation,

As atomic mass = 32, so no. of atoms in one molecule of sulphur = 255.84/32. = 8
Hence, molecular formula of sulphur is S8.
OR
An evacuated glass vessel weighs 50.0 g when empty, 148.0 g when filled with a liquid of density 0.98 g mL–1 and 50.5 g when filled with an ideal gas at 760 mm Hg at 300 K. Determine the molar mass of the gas.
Answer : From the given data, we have,
Weight of the liquid = (148 – 50 g) = 98 g
Volume of the liquid = 98/0.98 = 100 mL = Volume of vessel
∴ The vessel of 100 mL contains ideal gas at 760 mm of Hg and 300 K.
Now weight of the gas = (50.5 – 50) = 0.5 g
Using ideal gas equation, PV = nRT, we get,
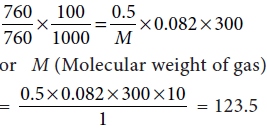
14. (a) Which hydrocarbon can’t be prepared by Kolbe’s electrolytic method?
C2H6, C2H4, CH4
(b) What happens when sodium acetate is heated with sodalime?
(c) An alkene (C5H10) on ozonolysis yielded two products. Both of them gave iodoform test, but only one responds to Tollen’s test. Identify the hydrocarbon.
Answer : (a) CH4 (methane) can’t be prepared by Kolbe’s electrolytic method, as in this method two alkyl radicals join together at anode.
(b) Methane gas is produced, when sodium acetate is heated with sodalime.
CH3—COONa + NaOH →CaO CH4 + Na2CO3
Sodium acetate Methane
(c) The ozonolysis products of the alkene respond to iodoform test, but one of them only responds to Tollen’s test. This shows one is acetaldehyde (which responds to both iodoform and Tollen’s test) and the other is 2-ketone (which responds only to iodoform test).
As the molecular formula of hydrocarbon is C5H10, so the ketone is acetone (CH3—CO—CH3). Hence the hydrocarbon is 2-methyl-but-2-ene.
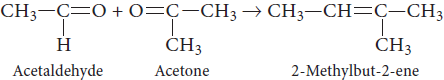
SECTION – D
Q. No. 15 and 16 are long answer type carrying 5 marks each.
15. (a) A gas expands from 3 dm3 to 5 dm3 against a constant pressure of 3 atm. The work done during expansion is used to heat 10 mole of water at 290 K. Calculate final temperature of water. Specific heat of water = 4.184 Jg–1 K–1
(b) Given the following standard enthalpies of reactions:
(i) Enthalpy of formation of water = –285.8 kJ mol–1
(ii) Enthalpy of combustion of acetylene = –1299.6 kJ mol–1
(iii) Enthalpy of combustion of ethylene = –1410.8 kJ mol–1
Calculate the heat of reaction for the hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene at constant volume (25°C).
Answer : (a) Work done is against constant external pressure, hence process is irreversible.

OR
(a) For a reaction, M2O(s) → 2M(s) + 1/2 O2(g), ΔH = 30 kJ mol–1 and ΔS = 0.07 kJ K–1 mol–1 at 1 atm. Calculate upto which temperature the reaction would not be spontaneous.
(b) Calculate the free energy change when 1 mole of NaCl is dissolved in water at 298 K.
Given :
(i) Lattice energy of NaCl = 778 kJ mol–1
(ii) Hydration energy of NaCl = –774.3 kJ mol–1
(iii) Entropy change at 298 K = 43 J mol–1
Answer :


16. (a) (i) What are the products formed when alkali metal oxide (M2O), peroxide (M2O2) and superoxide (MO2) hydrolysed by water?
(ii) List two properties showing similarity between lithium and magnesium.
(b) (i) Mg form Mg2+, but Na2+ does not exist. Explain.
(ii) Write balanced equations for the reactions between :
(I) Na2O2 and H2O
(II) KO2 and H2O.
Answer : (a) (i) Alkali metal oxide, peroxide and superoxide are easily hydrolysed by water to form the hydroxides according to the following reactions:
M2O + H2O → 2M+ + 2OH–
M2O2 + 2H2O → 2M+ + 2OH– + H2O2
2MO2 + 2H2O → 2M+ + 2OH– + H2O2 + O2
(ii) Both lithium and magnesium are harder and lighter than other elements in respective groups.
The oxides, Li2O and MgO do not combine with excess oxygen to give any superoxide.
(b) (i) Mg atom after losing one electron does not attain noble gas configuration whereas Na metal after the loss of one electron attains a noble gas configuration of neon. Therefore, the removal of second electron is energetically not favorable. Hence, Na2+ does not exist.
(ii) (I) Na2O2 + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2O2
(II) 2KO2 + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2O2 + O2
OR
(a) Halides of Be dissolve in organic solvents while those of Ba do not. Why is it so?
(b) Why are compounds of beryllium much more covalent than other group 2 elements?
(c) What is milk of magnesia? Give its one use.
(d) Solubility of MgCl2 is greater than that of MgF2. Why ?
(e) Why is BeCO3 stored in carbon dioxide atmosphere?
Answer : (a) This is because halides of Be are covalent while those of Ba are ionic.
(b) The extremely small size and high charge of Be2+ makes it strongly polarizing so that Be (II) compounds are almost covalent in nature.
(c) A suspension of magnesium hydroxide in water is called milk of magnesia. It is used as an antacid to neutralize excess of acid in the stomach.
(d) Because the fluorides are relatively less soluble than the chlorides owing to their high lattice energies.
(e) Beryllium carbonate is unstable and can be kept only in the atmosphere of CO2.
BeCO3 → BeO + CO2


