Please refer to Coordination Compounds HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with solutions. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Coordination Compounds Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Question. For which of the following ligands magnitude of the crystal field splitting (Δo)will be greater than pairing energy (P)?
(a) Cl–
(b) SCN–
(c) CO
(d) S2–
Answer
C
Question. The charge on the central metal ion in the complex [Ni(CO)4] is
(a) + 2
(b) + 4
(c) 0
(d) + 3
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is incorrect regarding spectrochemical series?
(a) NH3 > H2O
(b) F– > C2O4
(c) NCS– > SCN–
(d) en > edta4–
Answer
B
Question. The unpaired electrons in Ni(CO)4 are
(a) zero
(b) one
(c) three
(d) four
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements related to crystal field splitting in octahedral coordination entities is incorrect?
(a) The dx2–y2 and dz2 orbitals has more energy ascompared to dxy, dyz and dxz orbitals.
(b) Crystal field spitting energy (Δo) depends directly on the charge of the metal ion and on the field produced by the ligand.
(c) In the presence of Br– as a ligand the distribution of electrons for d4 configuration will be t23g , eg1,
(d) In the presence of CN– as a ligand Δo< P.
Answer
D
Question. For [Co2(CO)8], what is the total number of metal – carbon bonds and number of metal–metal bonds.
(a) 10 ,1
(b) 8, 2
(c) 8, 1
(d) 10, 0
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is the correct order of field strength of ligands in spectrochemical series?
(a) I– < Cl– < F– < H2O < CN–
(b) F– < H2O < I– < CN– < Cl–
(c) CN– < I– < F– < Cl– < H2O
(d) H2O < F– < CN– < Cl– < I–
Answer
A
Question. Violet colour of [Ti(H2O)6]Cl3 on heating changes to___.
(a) Green
(b) Colourless
(c) White
(d) Red
Answer
B
Question. Calculate the value of log K3 when log values of K2, K1, K4 and β4 respectively are 4.0, 3.20, 4.0 and 11.9 ?
(a) 2.0
(b) 2.7
(c) 3.0
(d) 2.5
Answer
B
Question. For the reaction of the type M + 4L ⇌ ML4
(a) larger the stability constant, lower the proportion of ML4 that exists in solution
(b) larger the stability constant, higher the proportion of ML4 that exists in solution
(c) smaller the stability constant, higher the proportion of ML4 that exists in solution
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Arrange the following complexes in increasing order toward the wavelength of light they absorb? Where M is metal ion.
[M(NH3)]3+ = a, [M(CN)6]3– = b, [M(C2O4)3]3– = c, [MF6]3– = d,
(a) d, c, a, b
(b) d, a, c, b
(c) b, a, c, d
(d) a, b, c, d
Answer
C
Question. The colour of the coordination compounds depends on the crystal field splitting. What will be the correct order of absorption of wavelength of light in the visible region, for the complexes,
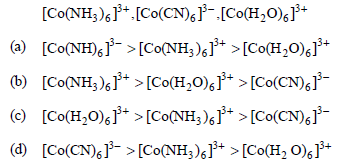
Answer
C
Question. In Fe(CO)5, the Fe – C bond possesses
(a) ionic character
(b) σ-character only
(c) Π-character
(d) both Π and σ characters
Answer
D
Question. If magnetic moment of [MnBr4]2– is 5.9 BM. Predict the number of electrons?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) 5
Answer
D
Question. The correct structure of Fe(CO)5 is (Z=26 for Fe)
(a) octahedral
(b) tetrahedral
(c) square pyramidal
(d) trigonal pyramidal
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the limitation of crystal field theory?
(i) Ligands are assumed as point charges.
(ii) It does not accounts for the covalent character of bonding between the ligand and the central atom.
(iii) It does not explain how colour of coordination compounds depends on ligand attached to central metal atom/ion.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) only (d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. Coordination compounds have great importance in biological systems. In this context which of the following statements is incorrect ?
(a) Cyanocobalamin is B12 and contains cobalt
(b) Haemoglobin is the red pigment of blood and contains iron
(c) Chlorophylls are green pigments in plants and contain calcium
(d) Carboxypeptidase – A is an exzyme and contains zinc.
Answer
C
Question.139. Consider the following reactions.
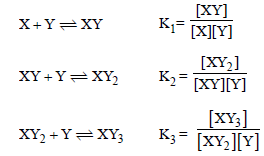
On the basis of reactions above which of the following is incorrect?
(a) Overall stability constant = K1K2K3
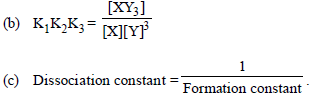
(d) All of the above are correct.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following coordination compounds is used to inhibit the growth of tumours?
(a) Trans-platin
(b) EDTA complex of calcium
(c) [(Ph3P)3RhCl]
(d) Cis-platin
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following does not have a metal- carbon bond?
(a) Al(OC2H5)3
(b) C2H5MgBr
(c) K[Pt(C2H4)Cl3]
(d) Ni(CO)4
Answer
A
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the complex species given in Column-I with the isomerism exhibited in Column-II and assign the correct code:
Column-I Column-II
(Complex species) (Isomerism)
(A) [Co[NH3)4Cl2]+ (p) optical
(B) cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ (q) ionisation
(C) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 (r) coordination
(D) [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6] (s) geometrical
(a) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r)
(b) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s)
(c) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(d) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
Answer
D
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(Coordination compound) (Central metal atom)
(A) Chlorophyll (p) Rhodium
(B) Blood pigment (q) Cobalt
(C) Wilkinson catalyst (r) Calcium
(D) Vitamin B12 (s) Iron
(t) Magnesium
(a) A – (t), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
(b) A – (s), B – (q), C – (p), D – (r)
(c) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(d) A – (r), B – (t), C – (p), D – (q)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(A) [Ni(CN)4]2– (p) Ti4+
(B) Chlorophyll (q) sp3; paramagnetic
(C) Ziegler – Natta (r) Non-planar
catalyst
(D) [NiCl4]2– (s) Mg2+
(E) Deoxyhaemoglobin (t) Planar
(u) dsp2; diamagnetic
(a) A – (u), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q), E – (r)
(b) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (u), E – (r)
(c) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (u), E – (t)
(d) A – (u), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q), E – (t)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(Ligand) (Type of ligand)
(A) Triphenylphosphine (p) Unidenate
(B) BF3 (q) Didentate
(C) Ethylenediamine (r) Not a ligand
(D) Ethylenediaminetetracetateion (s) Hexadenate
(a) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s)
(b) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(c) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s)
(d) A – (p), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-I
(A) Estimation of (p) [Ag(CN)2]–
water hardness.
(B) Extraction of silver. (q) [Ni(CO)4]
(C) Hydrogenation of (r) Na2EDTA
alkenes.
(D) Photography (s) [(Ph3P)3RhCl]
(E) Purification of (t) [Ag(S2O3)2]3–
Nickel.
(a) A – (r) , B – (p), C – (s), D – (t), E– (q)
(b) A – (p) , B – (r), C – (s), D – (t), E– (q)
(c) A – (r) , B – (s), C – (p), D – (t), E– (q)
(d) A – (r) , B – (p), C – (s), D – (q), E– (t)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns.
Column-I Column-II
(Complexes) (Absorbed Light)
(A) [Ni(H2O)4(en)]2+(aq) (p) Yellow Orange
(B) [Ni(H2O)4(en)2]2+(aq) (q) Blue–Green
(C) [Ni(en)3]2+(aq) (r) Red
(a) A – (r), B – (q), C – (p)
(b) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q)
(c) A – (q), B – (r), C – (p)
(d) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q)
Answer
D
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : [Fe(CN)6]3– is weakly paramagnetic while [Fe(CN)6]4– is diamagnetic.
Reason : [Fe(CN)6]3– has +3 oxidation state while [Fe(CN)6]4– has +2 oxidation state.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : [Ti(H2O)6]3+ is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless.
Reason : d-d transition is not possible in [Sc(H2O)6]3+.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3.
Reason : NF3 ionizes to give F– ions in aqueous solution.
Answer
C
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Which one of the following complexes is an outer orbital complex ?
(a) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(b) [Mn(CN)6]4–
(c) [Fe(CN)6]4–
(d) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
(Atomic nos. : Mn = 25; Fe = 26; Co = 27, Ni = 28)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following will give a pair of enantiomorphs?
(a) [Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6]
(b) [Co(en)2Cl2]Cl
(c) [Pt(NH3)4] [PtCl6]
(d) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO2
(en =NH2CH2CH2NH2)
Answer
B
Question. Correct statements about the following complexes [MnCl6]3– and [Mn(CN)6]3– respectively are.
(a) Magnetic moment is 4.8 and 2.8
(b) inner sphere and outer sphere complexes.
(c) sp3d2 and d2sp3 complexes.
(d) Both (a) and (c).
Answer
D
Question. The formula for the complex, dichlorobis (urea) copper (II) is
(a) [Cu{O = C (NH2)2}] Cl2
(b) [Cu{O = C (NH2)2}Cl]Cl
(c) [CuCl2 {O = C(NH2)2}2]
(d) [CuCl2] [{O = C (NH2)2}]2
Answer
C
Question. The total number of possible isomers for the complex compound [CuII (NH3)4] [PtII Cl4]
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 4
Answer
D
Question. A co-ordination complex compound of cobalt has the molecular formula containing five ammonia molecules, one nitro group and two chlorine atoms for one cobalt atom.One mole of this compound produces three mole ions in an aqueous solution. On reacting this solution with excess of AgNO3 solution, we get two moles of AgCl precipitate. The ionic formula for this complex would be
(a) [Co(NH3)4 (NO2) Cl] [(NH3) Cl]
(b) [Co (NH3)5 Cl] [Cl (NO2)]
(c) [Co (NH3)5 (NO2)] Cl2
(d) [Co (NH3)5] [(NO2)2Cl2]
Answer
C
Question. The existence of two different coloured complexes with the composition of + [Co(NH3)4Cl2 ] is due to :
(a) linkage isomerism
(b) geometrical isomerism
(c) coordination isomerism
(d) ionization isomerism
Answer
B
Question. The d electron configurations of Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Ni2+ are 3d4, 3d5, 3d6 and 3d8 respectively. Which one of the following aqua complexes will exhibit the minimum paramagnetic behaviour?
(a) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(b) [Ni(H2O)6]2+
(c) [Cr(H2O)6]2+
(d) [Mn(H2O)6]2+
(At. No. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Ni = 28)
Answer
B
Question. Among the following complexes, optical activity is possible in
(a) [Co(NH3)6 ]3+
(b) [Co(H2O)2 (NH3 )2Cl2 ]+
(c) [Cr(H2O)2Cl2 ]+
(d) [Co(CN)5NC]
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following complex ions is expected to absorb visible light?
(a) [Ti (en)2(NH3)2]4 +
(b) [Cr (NH3)6]3 +
(c) [Zn (NH3)6]2 +
(d) [Sc (H2O)3 (NH3)3]3+
(At. no. Zn = 30, Sc = 21, Ti = 22, Cr = 24)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds exhibits linkage isomerism ?
(a) [Co(en)2]Cl3
(b) [Co(NH3)6][Cr(en)3]
(c) [Co(en)2NO2Cl]Br
(d) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Br2
Answer
C
Question. Identify the optically active compounds from the following :
(i) [Co(en)3 ]3+
(ii) trans -[Co(en)2Cl2 ]+
(iii) cis -[Co(en)2Cl2 ]+
(iv) [Cr(NH3 )5 Cl]
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Crystal field stabilization energy for high spin d 4 octahedral complex is:
(a) – 1.8 Δ0
(b) – 1.6 Δ0 + P
(c) – 1.2 Δ0
(d) – 0.6 Δ0
Answer
D
Question. For which value of the x, and y, the following square planar compound shows geometrical isomers [Pt (Cl)x(Br)y]2–
(a) 1, 3
(b) 3, 1
(c) 2, 2
(d) 1, 1
Answer
B
Question. Suppose someone made aqueous solution of NiCl2 and recrystallized its aqueous solution in excess of water and if two moles of precipitate AgCl was formed on treatment with AgNO3, what is the most probable structure of the compound ?
(a) [Ni(Cl)2(H2O)4]
(b) [Ni (H2O)6]Cl2
(c) [Ni(H2O)5Cl]
(d) [Ni (H2O)4Cl2].2H2O
Answer
B
Question. Using valence bond theory, the complex [Cr(H2O)6]3+ can be described as
(a) sp3d2, outer orbital complex, paramagnetic
(b) dsp2, inner orbital complex, diamagnetic
(c) d2sp3, inner orbital complex, paramagnetic
(d) d2sp3, outer orbital complex, diamagnetic.
Answer
C
Question. Mark the correct statements regarding the geometry of complex ions.
(i) The geometry of the complex ion depends upon the coordination number.
(ii) If coordination number is 6, the complex is octahedral.
(iii) If coordination number is 4, the geometry of the complex may be tetrahedral or square planar.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii) only
(c) (i) and (iii) only
(d) (ii) and (iii) only
Answer
A
Question. [Fe(CN)6]4– and [Fe(H2O)6]2+ show different colours in dilute solution because
(a) CN– is a strong field ligand and H2O is a weak field ligand hence magnitude of CFSE is different
(b) both CN– and H2O absorb same wavelength of energy
(c) complexes of weak field ligands are generally colourless
(d) the sizes of CN– and H2O are different hence their colours are also different.
Answer
A
Question. Electronic configuration of [Cu(NH3)6]2+ on the basis of crystal field splitting theory is

Answer
B
Question. Ms. Anjali class 12th chemistry teacher explained IUPAC nomenclature of coordination compounds in her class. Then she asked students to write the names of 5 coordination compounds.Kavya written these five names :
[Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3 – Triamminetriaqua chromium(III)chloride, [Ag(NH3)2][Ag(CN)2] Diamminesilver(I) dicyanidosilver(I)
[CoCl2(en)2]Cl-Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diammine) cobalt (III) chloride K3[Al(C2O4)3] – Potassium trioxalatoaluminium (III) [Ni(CO)4]-Tetracarbonylnickel(0) Few names given by her were not correct as she didn’t follow one rule while naming these compounds. That one rule is
(a) the ligands are name in an alphabetical order before the name of central atom/ion.
(b) prefixes mono, di, tri etc. are used to indicate the number of individual ligands in the coordination entity.
(c) if the complex ion is cation, the metal is named same as the element.
(d) if the complex ion is anion, the metal ends with suffix – ate.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following primary and secondary valencies are not correctly marked against the compound?
(a) [Cr(NH3)6]Cl3 p = 3, s = 6
(b) K2[PtCl4] p = 2, s = 4
(c) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] p = 2, s = 4
(d) [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 p = 4, s = 4
Answer
D
Question. Fex+ + SCN– → Octahedral complex Fey+ + CN– →Octahedral complex (x and y may or may not be equal)
The difference between the spin-only magnetic moments is 4.2 B.M. approximately. The reason for this difference in magnetic moment is
(a) CN– is a strong ligand while SCN– is a weak ligand
(b) Fe is present in O.S. I in complex with SCN– while in O.S. III in complex with CN–
(c) SCN– is a strong ligand while CN– is a weak ligand
(d) x is 3 while y is 1.
Answer
A
Question. In coordination compounds metals show two type of linkages : primary and secondary. Primary valency is ionisable and corresponds to conductivity. Several coordination compounds are formed by Co(III) with ligand NH3 and Cl– both.
Conductivity of complex I corresponds to 1 : 3 electrolyte, conductivity of complex II corresponds to 1 : 2 electrolyte while conductivity of complex 3 and 4 corresponds to 1 : 1 electrolyte. So correct option about these complexes is
(a) complex I is [(Co(NH3)6]Cl3 with purple colour
(b) complex II is [(Co(NH3)6]Cl3 with purple colour
(c) complex III is [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl with violet colour
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. When excess of ammonia is added to copper sulphate solution, the deep blue coloured complex is formed. The complex is
(a) tetrahedral and paramagnetic
(b) tetrahedral and diamagnetic
(c) square planar and diamagnetic
(d) square planar and paramagnetic.
Answer
D