Please refer to Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production HOTs Class 12 Biology provided below with solutions. All HOTs for Class 12 Biology with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Biology should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Biology provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Class 12 Biology HOTs
Single Cell Protein
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is economic value of Spirulina?
Answer.Spirulina is a microorganism (blue green algae), which is used as human food rich in protein,minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins.
Question. Write an alternate source of protein for animal and human nutrition.
Answer. The alternate source of protein for animal and human nutrition is single cell protein (SCP).
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is single cell protein? How is it produced?
Discuss its importance. In what ways is it useful to humans?
Answer. The microorganisms such as bacteria, yeasts, filamentous algae, are treated in various ways to be used as food and are called single cell protein (SCP). The term SCP does not indicate its actual meaning because the biomass is not only obtained from unicellular microorganisms but also from multicellular microorganisms. Microbes like Spirulina can be grown on waste water from potato processing plants (containing starch), straw, molasses, animal manure and even sewage, to produce food rich in proteins, minerals, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins. Commercial production of SCP is mostly based on yeasts and some other fungi.
Advantages of SCP are as follows:
(i) It provides a protein rich supplement in human diet.
(ii) It reduces the pressure on agricultural production systems for the supply of the required proteins.
(iii) SCP production is based on industrial efluents so it helps to minimise environmental pollution.
Tissue Culture
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why is the enzyme cellulase used for isolating genetic material from plant cells but not for animal cells?
Answer.Cellulase enzyme digests cellulose present in cell wall of plant cells. As animal cell does not possess cell wall hence cellulase enzyme is not used in case of animal cell.
Question. Identify the two correct statements from the following :
(a) Apiculture means apical meristem culture.
(b) Spinach is iron-enriched.
(c) Green revolution has resulted in improved pulse-yields.
(d) Aphids cannot infest rapeseed mustard.
Answer.Statement (b) and (d) are correct.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How can healthy potato plants be obtained from a desired potato variety which is virus infected? Explain.
Answer. Healthy potato plants can be obtained from the desired potato variety which is virus infected by meristem culture. Cultivation of axillary or apical shoot meristems is called meristem culture. The apical and axillary meristems of the infected plant is virus free because rate of division of meristematic cells is higher than the rate at which virus multiplies hence virus cannot invade newly formed meristematic cell. Meristem is removed and grown in vitro to obtain healthy virus-free potato plants.
Question. What is haploidy? How are haploid plants raised? How are they helpful in plant breeding?
Answer.Individuals or cells that contain one set of chromosomes as in gametes, are called haploids and this condition is called haploidy.
Haploid plants are of great significance as they are used in plant breeding for the production of homozygous plants. Formation of haploids is called haploid production. Haploid individuals arise from the gametes and are sterile hence of no direct value. The chromosome number of these haploids is doubled by using colchicine to obtain homozygous plants.
Question. Name the technology used in micropropagation of plants. Write the genetic significance of the plants raised through this technique. Give two examples where this technology is commercially exploited.
Answer. The method of producing thousand of plants through tissue culture is called micropropagation. Each of these plants will be genetically identical to the original plant from which they are grown, i.e., they are somaclones. Many important food plants like tomato, banana, apple, etc., have been produced on commercial scale using this method.
Question. (a) Why are the plants raised through micropropagation termed as somaclones?
(b) Mention two advantages of this technique.
Answer.
(a) Micropropagation is the tissue culture technique used for rapid vegetative multiplication of ornamental plants and fruit trees by using small explants. This method of tissue culture produces several plants. Each of these plants is genetically identical to the original plant from which they were grown. Hence, plants obtained by micropropagation constitute a somaclone.
(b) Advantages of micropropagation are : (i) A large number of plantlets are obtained within a short period and in a small space. (ii) The rare plants and endangered species are multiplied by this method and such plants are saved.
Question. Why are plants obtained through micropropagation termed somaclones? Name three food plants produced on commercial scale through this method.
Answer. Micropropagation is the tissue culture technique used for rapid vegetative multiplication of ornamental plants and fruit trees by using small explants. This method of tissue culture produces several plants. Each of these plants is genetically identical to the original plant from which they were grown. Hence, plants obtained by micropropagation constitute a somaclone.
The method of producing thousand of plants through tissue culture is called micropropagation. Each of these plants will be genetically identical to the original plant from which they are grown, i.e., they are somaclones. Many important food plants like tomato, banana, apple, etc., have been produced on commercial scale using this method.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Write the two limitations of traditional breeding technique that led to promotion of micropropagation.
(b) Mention two advantages of micropropagation.
(c) Give two examples where it is commercially adopted.
Answer.(a) Two limitations of traditional breeding techniques that led to promotion of micropropagation are :
(i) They have limited production therefore it failed to keep pace with the demand.
(ii) They were unable to provide suffciently fast and effcient system for crop improvement.
(b) Two advantages of micropropagation are :
(i) It helps in producing thousands of plants from a single plant in very short duration.
(ii) It is useful in the recovery of healthy plant from a virus infected plant.
(c) Commercial production of ornamental plants like lily, orchids, eucalyptus and fruits like tomato, apple, banana etc. is commenced through micropropagation. Sterile plants or plants which cannot maintain their characters by sexual reproduction can be multiplied by this method.
Question. (a) Mention the property that enables the explants to regenerate into a new plant.
(b) A banana herb is virus-infected. Describe the method that will help in obtaining healthy banana plants from this diseased plant.
Answer. (a) Totipotency is the property by which whole plant is regenerated from any cell or explant in in vitro condition.
(b) In case of asexually reproducing crops like banana, virus infections spread rapidly. This is because the vegetative propagules from virus-infected plants contain virus particles. But the shoot apical meristems and some young tissues surrounding them are often free from viruses. Meristem culture, therefore, is often useful in recovering virus-free plants from virus-infected plants or clones. The explants commonly used in meristem culture are shoot tips and nodal segments. These explants are cultured on a medium containing a cytokinin (generally BAP). The plantlets thus obtained are subjected to hardening and, ultimately, established in the field.
Question. A sugarcane has been affected by virus. How can a virus free cane be developed from it? Explain the procedure.
Answer. A virus-free sugarcane can be obtained from infected sugarcane plant by meristem culture. Although, the plant is infected with a virus, yet the meristem is free of virus. It is because meristem is a localised group of actively dividing cells, hence virus cannot invade them. Meristem culture involves the use of explants like shoot tips and nodal segments. The explant or shoot tip is grown in a test tube under sterile conditions on a medium containing a cytokinin (generally BAP). The plantlets of sugarcane thus obtained are subjected to hardening and ultimately established in the field. Thus, cane plants obtained are free of virus.
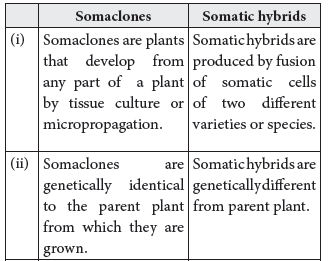
Question. Differentiate between somaclones and somatic hybrids. Give one example of each.
Answer. Differences between somaclones and somatic hybrids are as follows :

Question. Scientists have succeeded in recovering healthy sugarcane plants from a diseased one.
(a) Name the part of the plant used as explant by the scientists.
(b) Describe the procedure the scientists followed to recover the healthy plants.
(c) Name this technology used for crop improvement.
Answer.(a) Explant used by scientists in this case could be any meristematic cell or tissue viz. shoot tip or nodal segment.
(b) Procedure followed by scientists to recover healthy plants is :
– Preparation of suitable nutrient medium as per objective of culture.
– Selection of explants such as shoot tip.
– Sterilisation of explants with disinfectants.
– Inoculation of the explant into nutrient medium under sterile condition.
– Incubating the culture under appropriate physical conditions i.e., artificial light (16 hours of photoperiod), temperature (–26°C) and relative humidity (50-60%):
– Regeneration of plants from cultured plant tissues.
– Hardening of plantlets
– Transfor of regenerated plantlets to the greenhouse or field conditions.
(c) Plant tissue culture (micropropagation)
Question. Mention the property of plant cells that has helped them to grow into a new plant in invitro conditions. Explain the advantages of micropropagation.
Answer. Totipotency is the property by which whole plant is regenerated from any cell or explant in in vitro condition.
Advantages of micropropagation are : (i) A large number of plantlets are obtained within a short period and in a small space. (ii) The rare plants and endangered species are multiplied by this method and such plants are saved.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is somatic hybridisation ? Explain the various steps involved in the process. Mention any two uses of somatic hybridisation.
Answer. Somatic hybridisation is the process of fusing protoplasts of somatic cells derived from different varieties or species of plants, on a suitable nutrient/ culture medium, to produce a somatic hybrid. Pomato is a somatic hybrid between tomato and potato.
Steps involved in somatic hybridisation are :
– Removal of cell wall of the fusing cells by digestion with a combination of pectinase and cellulase; which results in the formation of protoplasts.
– Fusion between protoplasts of selected parents induced by the use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) or a very brief high voltage electric current.
– These are cultured on a suitable medium, regenerate cell walls and begin to divide to produce plantlets which are the somatic hybrids. Process of somatic hybridisation can be illustrated by the following figure.

Uses of somatic hybridisaton are :
– Species of plants which cannot be sexually hybridised (by breeding) can be hybridised and allopolyploids can be raised by this method.
– Somaclonal variations can be created.
Question. (a) Name the technology that has helped scientists to propagate on a large scale the desired crops in a short duration. List the steps carried out to propagate the crops by the said technique.
(b) How are somatic hybrids obtained?
Answer.
(a) The technique that has helped scientists to propagate the desired crops in short duration is called tissue culture or micropropagation. Plant tissue culture can be defined as the technique of maintaining and growing of plant cells, tissues and organs on a suitable culture medium in vitro under controlled environmental conditions.
The basic technique of plant tissue culture involves the following steps :
(i) Preparation of suitable nutrient medium and storage into suitable containers.
(ii) Selection of explants such as shoot tip and sterilisation by disinfectants.
(iii) Inoculation (transfer) of the explants into the suitable nutrient medium under sterile conditions.
(iv) Growing the culture in the growth chamber or plant tissue culture room, having the appropriate physical conditions i.e., artificial light (16 hours of photoperiod), temperature (–26°C) and relative humidity (50- 60%).
(v) Regeneration of plants from cultured plant tissues and hardening.
(vi) Transfer of plantlets to the greenhouse or field conditions following acclimatisation of regenerated plants.
(b) Isolated naked protoplasts from two different varieties of plants each having a desirable character can be fused to get hybrid protoplasts, which can be further grown to form new plant. These hybrids obtained are called somatic hybrids.