Please refer to Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with solutions. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Question. Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid which is :
(a) 15 – 20%
(b) 20 –25%
(c) 6 – 8%
(d) 2 – 4%
Answer
C
Question. The correct order of increasing acidic strength is__________
(a) Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
(b) Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
(c) Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
(d) Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol < Ethanol
Answer
C
Question. Methyl cyanide can be converted into acetic acid by one of the following reactions.
(a) Reduction
(b) Hydrolysis
(c) Electrolysis
(d) Decarboxylation
Answer
B
Question. The product obtained by the reaction of an aldehyde and hydroxylamine is
(a) hydrazone
(b) aldoxime
(c) primary amine
(d) alcohol
Answer
B
Question. Which one gives positive iodoform test ?
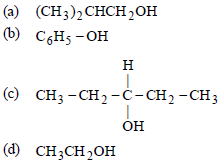
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following esters is obtained by the esterification of propan-2-ol with ethanoic acid ?
(a) (CH3)2CHCOOCH3
(b) CH3COOCH2CH3
(c) CH3COOCH(CH3)2
(d) (CH3)2CHCOOCH2CH3
Answer
C
Question. Schiff’s reagent gives pink colour with
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) acetone
(c) acetic acid
(d) methyl acetate
Answer
A
Question. The yield of ester in esterification can be increased by
CH3CH2OH + CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COOCH2CH3 + H 2O
(a) removing water
(b) taking ethanol in excess
(c) taking acetic acid in excess
(d) all the above factors
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following has the maximum acidic strength ?
(a) o- nitrobenzoic acid
(b) m-nitrobenzoic acid
(c) p-nitrobenzoic acid
(d) p-nitrophenol
Answer
A
Question. In the reaction of NaHSO3 with carbonyl compounds to form bisulphite product, the nucleophile is
(a) HSO3–
(b) SO3Na
(c) SO3– –
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Tollen’s reagent is
(a) ammonical CuSO4
(b) ammonical AgNO3
(c) alkaline solution containing complex of copper nitrate
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the correct decreasing order of acidic strength of
(i) Methanoic acid (ii) Ethanoic acid
(iii) Propanoic acid (iv) Butanoic acid
(a) (i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv)
(b) (ii) > (iii) > (iv) > (i)
(c) (i) > (iv) > (iii) > (ii)
(d) (iv) > (i) > (iii) > (ii)
Answer
A
Question. The reaction
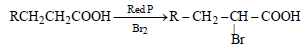
is called as
(a) Reimer- Tiemann reaction
(b) Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction
(c) Cannizzaro reaction
(d) Sandmeyer reaction
Answer
B
Question. Among the following the strongest acid is
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH2ClCH2COOH
(c) CH2ClCOOH
(d) CH3CH2COOH
Answer
C
Question. Compound of general formula
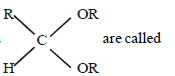
(a) diester
(b ) acid anhydride
(c) hemiacetal
(d) acetal
Answer
D
Question. In the following reaction
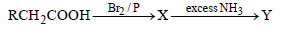
The major compounds X and Y are
(a) RCHBrCONH2 ; RCH(NH2)COOH
(b) RCHBrCOOH ; RCH(NH2)COOH
(c) RCH2COBr ; RCH2COONH4
(d) RCHBrCOOH ; RCH2CONH2
Answer
B
Question. Benzoic acid may be converted to ethyl benzoate by reaction with
(a) sodium ethoxide
(b) ethyl chloride
(c) dry HCl—C2H5OH
(d) ethanol
Answer
C
Question. The difference between aldol condensation and Cannizzaro’s reaction is that:
(a) the former takes place in the presence of α-H-atom.
(b) the former takes place in the absence of α-H-atom.
(c) the former takes place in the presence of β-H-atom.
(d) none of the above
Answer
A
Question. The product obtained when acetic acid is treated with phosphorus trichloride is
(a) CH3COOPCl3
(b) ClCH2COCl
(c) CH3COCl
(d) ClCH2COOH
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following pairs of compounds will undergo aldol and Cannizzaro reaction respectively ?
(i) acetone; benzaldehyde
(ii) acetaldehyde; butan–2–one
(iii) propanone; formaldehyde.
(iv) cyclopentanone, benzaldehyde
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. The compound that neither forms semicarbazone nor oxime is
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3COCH2Cl
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3CONHCH3
Answer
D
Question. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
(a) Sodium hydrogensulphite
(b) Phenyl hydrazine
(c) Fehling’s solution
(d) Grignard reagent
Answer
C
Question. A and B in the following reactions are
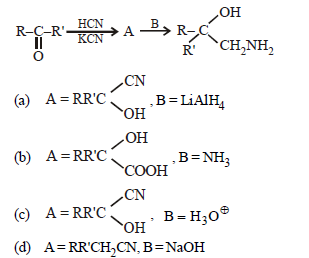
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following does not represent the natural source of the corresponding acids ?
(a) Formic acid : Red ant
(b) Acetic acid : Vinegar
(c) Butyric acid : Rancid butter
(d) Isobutyric acid : Automobile exhausts
Answer
D
Question. Arrange the following carboxylic acid in their decreasing acidity.
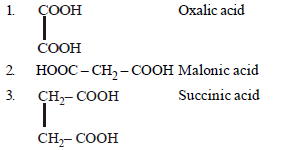
(a) 3 > 2 > 1
(b) 1 > 2 > 3
(c) 2 > 3 > 1
(d) 2 > 1 > 3
Answer
B
Question. Which reagent can convert acetic acid into ethanol ?
(a) Na + alcohol
(b) LiAIH4 + ether
(c) H2 + Pt
(d) Sn + HCl
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following does the best represent the structure of the carboxylate ion ?
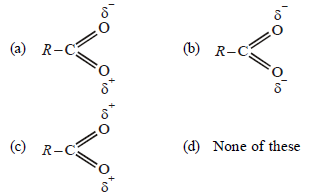
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following products is formed when benzaldehyde is treated with CH3MgBr and the addition product so obtained is subjected to acid hydrolysis ?
(a) A secondary alcohol
(b) A primary alcohol
(c) Phenol
(d) tert-Butyl alcohol
Answer
A
Question. Benzophenone can be converted into benzene by using
(a) fused alkali
(b) anhydrous AlCl3
(c) sodium amalgam in water
(d) acidified dichromate
Answer
A
Question. In the given reaction
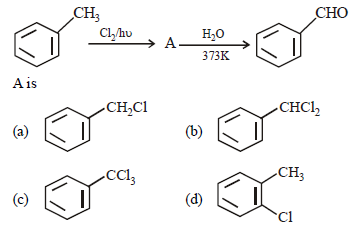
Answer
B
Question. Imine derivatives of aldehyde and ketone is called as
(a) Schiff’s reagent
(b) Fehling’s reagent
(c) Schiff’s base
(d) Schiff’s acid
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
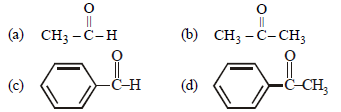
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following can not be oxidised to give carboxylic acid?

Answer
D
Question.
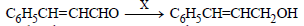
In the above sequence X can be :
(a) H2 /Ni
(b) NaBH4
(c) K2Cr2O7/H+
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(Reactions) (Reagents)
(A) Benzophenone → (p) LiAlH4
Diphenylmethane
(B) Benzaldehyde → (q) DIBAL–H
1-Phenylethanol
(C) Cyclohexanone → (r) Zn(Hg)/Conc HCl
Cyclohexanol
(D) Phenyl benzoate → (s) CH3MgBr
Benzaldehyde
(a) A – (p), B – (s), C – (r), D – (q)
(b) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(c) A – (s), B – (r), C – (q), D – (p)
(d) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
Answer
D
Question.Match the columns
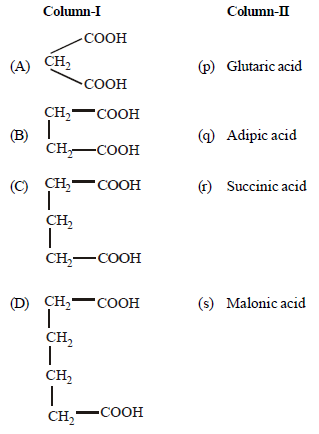
(a) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (s), D – (q)
(c) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
(d) A – (r), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns
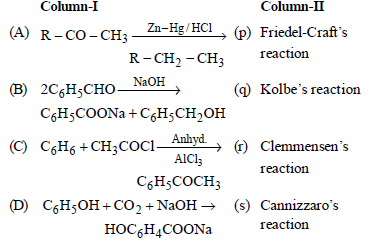
(a) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(b) A – (q), B – (p), C – (r), D – (s)
(c) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
(d) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Etard reaction (p) Alcoholic KOH
(B) Hydroxylation (q) Anhydrous AlCl3
(C) Dehydrohalogenation (r) Chromyl chloride
(D) Friedel-Crafts reaction (s) Dilute alkaline KMnO4
(a) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (q)
(b) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
(c) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
(d) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(Common names) (IUPAC names)
(A) Cinnamaldehyde (p) Pentanal
(B) Acetophenone (q) Prop-2-enal
(C) Valeraldehyde (r) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
(D) Acrolein (s) 3-Phenylprop-2-enal
(E) Mesityl oxide (t) 1-Phenylethanone
(a) A – (s), B – (t), C – (p), D – (q), E – (r)
(b) A – (p), B – (q), C – (s), D – (t), E – (r)
(c) A – (t), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r), E – (q)
(d) A – (q), B – (t), C – (r), D – (s), E – (p)
Answer
A
Question. Match the acids given in Column-I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column-II.
Column-I Column-II
(Acids) (IUPAC names)
(A) Phthalic acid (p) Hexane-1, 6-dioic acid
(B) Oxalic acid (q) Benzene-1, 2-dicarboxylic acid
(C) Succinic acid (r) Pentane-1, 5-dioic acid
(D) Adipic acid (s) Butane-1, 4-dioic acid
(E) Glutaric acid (t) Ethane-1, 2-dioic acid
(a) A – (t), B – (q), C – (r), D – (p), E – (s)
(b) A – (p), B – (s), C – (t), D – (q), E – (r)
(c) A – (q), B – (t), C – (s), D – (p), E – (r)
(d) A – (r), B – (t), C – (p), D – (s), E – (q)
Answer
C
Question Match the columns
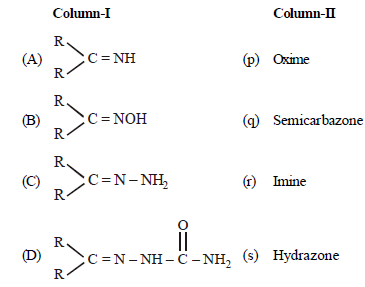
(a) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C– (s), D– (q)
(c) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D– (q)
(d) A – (s), B – (r), C – (q), D– (p)
Answer
B
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason : It contains sp2 hybridised carbon atom.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses.
Reason : There is a weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of the dipole-dipole interactions.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The molecular mass of acetic acid in benzene is 120 instead of 60.
Reason : The carboxylic acids exist as cyclic dimers in which the two molecules of the acid are held together by two strong hydrogen bonds.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Compounds containing –CHO group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason : Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4.
Answer
B
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 MARK)
Question. Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
CH3CHO, CH3CH2CHO ,CH3COCH3,CH3COCH2CH3.
Answer. CH3COCH2CH3< CH3COCH3< CH3CH2CHO < CH3CHO
Question. Name the reagent which is used to convert allyl alcohol to propanol.
Answer. PCC (Pyridinium Chlorochromate)
Question. Name the aldehyde which does not give Fehling solution test.
Answer. Benzaldehyde.
Question. Write IUPAC name of the compound CH2 = CHCOCH2COOH
Answer. 3‐Oxopent‐4‐ enoic acid
Question. Complete the reaction:

Answer.
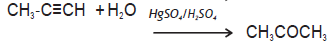
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Arrange the following.
(i) C6H5COOH, FCH2COOH, NO2CH2COOH( decreasing order of their acidic character)
(ii) Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone reaction (increasing order of their nucleophilic addition reaction)
Answer. (i) NO2‐CH2‐COOH> F‐CH2‐COOH >C6H5‐COOH
(ii) Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal
Question. Give a chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs:‐
(i) Phenol and benzoic acid
(ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Answer. (i) Benzoic acid reacts with NaHCO3 giving CO2 gas with effervescence where as phenol does not.

(ii) Acetophenone on reacting with hot NaOH / I2 gives yellow ppt of CHI3 while
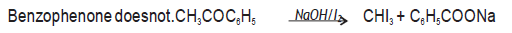
Question. Write chemical equation to illustrate following name reactions:‐
(a) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(b) Hell‐Volhard‐ Zelinsky reaction
Answer. (a) Cannizzaro’s reaction
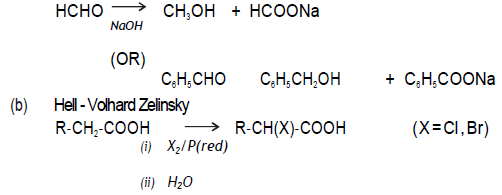
Question. An organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C8H8O gives positive DNP and iododorm test. It does not reduce Tollens’ or Fehling’s reagent and does not decolourise bromine water also . On oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid ‘B’ with molecular formula C7H6O2. Deduce the structures A and B.
Answer. Since A does not give Fehling’s or Tollen‘s test but gives iodoform test and 2,4‐ DNP test so it has CH3 CO‐ group. Hence:
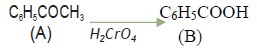
Question. Account for the following :‐
(i) Chloroacetic acid Cl‐CH2COOH is a stronger acid than acetic acid CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give the reaction of carbonyl group.
Answer. (i) The –I effect of Cl atom in ClCH2 COOH stabiles the ClCH COO ion while +I e ffect of CH ‐ group in CH3 COOH destabilizes the CH3COO .
(ii) In the resonating structures of carboxylic acid and carbonyls, the carbonyl carbon of carboxylic acid is less electro‐positive (less electrophile) than carbonyl carbon in aldehydes and ketones. Therefore carboxylic acids do not give the reaction of carbonyl group
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question.1. Explain the following name reaction by giving one suitable example of each:‐
(i) Wolff‐kishner reduction (ii) Aldol condensation (iii) Clemensen’s reduction
Answer. (i) Wolff‐kishner reduction
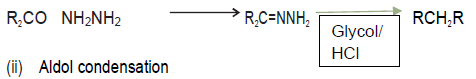
Carbonyl compounds with α‐ hydrogen in basic medium undergo condensation to give Hydroxy aldehydes and ketones.

(iii) Clemensen’s reduction

Question. Explain : (i) Ethanal is more reactive than acetophenone towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
(ii)(CH3)3C‐CHO does not undergo aldol condensation.
(iii)Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than alcohols.
Answer. (i) The presence of two alkyl groups in ketones hinder the approach of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon,and reduce the positive charge on carbonyl carbon more effectively in ketones than in aldehydes.
(i) Due to unavailability of α‐hydrogen in the given compound it does not undergo aldol condensation.
(ii) Due to extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding,(exist as dimer)
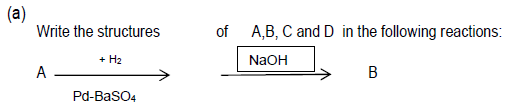
Question.
Write the products in the following reactions:
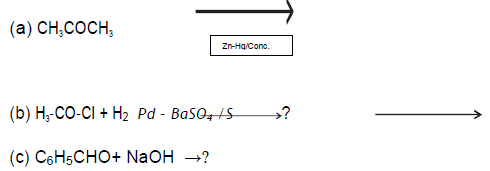
Answer.
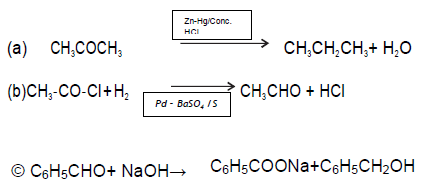
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question.
Answer. A- Benzoyl chloride B- Benzaldehyde
C – Benzylalcohol
D – Sodium benzoate
(b) Distinguish between: (i) Acetone and Acetaldehyde (ii) Benzaldehyde and Benzophenone
Answer. (iii) Bezaldehyde gives Tollens’ test, while benzophenonedoes not.
C6H5CHO + 2[Ag(NH3)2] → C6H5COONH4 +2Ag + 3NH3 +H2O
Question. (a) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
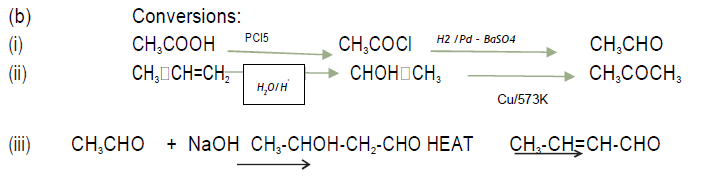
(b) How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Acetic acid to Acetaldehyde
(ii) Propylene to Acetone
(iii) Ethanal to but‐2‐enal
Answer. (a) (i) resonating structures of carboxylate ion are more stable than phenoxide ion.
(ii) Negative charge is dispersing on two electronegative oxygen in carboxylate ion whereas in phenoxide ion it is on one oxygen.