VBQs Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry with Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. The following Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids VBQs Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Benzaldehyde is obtained from Rosenmund’s reduction of
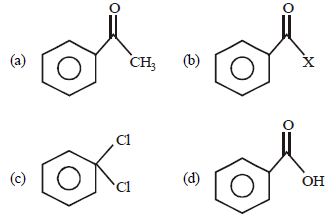
Answer
B
Question. The IUPAC name of CH3COCH(CH3)2 is
(a) 2-methyl-3-butanone
(b) 4-methylisopropyl ketone
(c) 3-methyl-2-butanone
(d) Isopropylmethyl ketone
Answer
C
Question. Acetaldehyde reacts with
(a) Electrophiles only
(b) Nucleophiles only
(c) Free radicals only
(d) Both electrophiles and nucleophiles
Answer
B
Question. IUPAC name of ethyl isopropyl ketone is
(a) 4-methyl pent-3-one
(b) 2-methyl pent-3-one
(c) 4-methyl pent-2-one
(d) 2-methyl pent-2-one
Answer
B
Question. The reaction

(a) Rosenmund’s reaction
(b) Stephen’s reaction
(c) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(d) Gatterman-Koch reaction
Answer
D
Question. Acetone reacts with iodine (I2) to form iodoform in the presence of
(a) CaCO3
(b) NaOH
(c) KOH
(d) MgCO3
Answer
B
Question. Aldehydes and ketones are generally reduced by :
(a) Clemmensen reduction
(b) H2S
(c) H2 / Ni
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. In which reaction, > C = O can be reduced to > CH2?
(a) Wolf-Kishner reaction
(b) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is correct for carbonyl compounds?
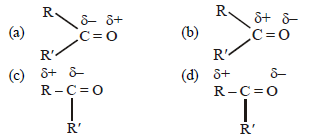
Answer
B
Question. Cross aldol condensation occurs between
(a) two same aldehydes
(b) two same ketones
(c) two different aldehydes and ketones
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which gives lactic acid on hydrolysis after reacting with HCN ?
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3CHO
(c) C6H5CHO
(d) CH3COCH3
Answer
B
Question. Primary and secondary alcohols on action of reduced copper give
(a) Aldehydes and ketones respectively
(b) Ketones and aldehydes respectively
(c) Only aldehydes
(d) Only ketones
Answer
A
Question. Which alkene on ozonolysis gives CH3CH2CHO and
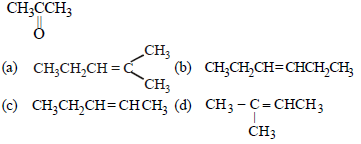
Answer
A
Question. When acetaldehyde is heated with Fehling’s solution it gives a precipitate of
(a) Cu
(b) CuO
(c) Cu2O
(d) Cu(OH)2
Answer
C
Question. Benzaldehyde can be prepared by oxidation of toluene by
(a) Acidic KMnO4
(b) K2Cr2O7 / H+
(c) CrO2Cl2
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Which is highly soluble in water?
(a) Methanal
(b) Propanal
(c) Propanone
(d) Butanone
Answer
A
Question. Cannizzaro reaction occurs with
(a) CH3 — CH2OH
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3 — CO — CH3
Answer
B
Question. An aldehyde group can be present
(a) in between carbon chain
(b) at any position in carbon atom
(c) only at the end of carbon chain
(d) at the second carbon atom of the carbon chain
Answer
C
Question. IUPAC name of following will be
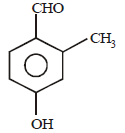
(a) 4-formyl 3-methyl 1-hydroxy benzene
(b) 4-formyl 3-methyl phenol
(c) 4-hydroxy 2-methyl benzaldehyde
(d) 4-hydroxy 2-methyl carbaldehyde
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not used in the preparation of ketone?
(a) Oxidation of secondary alcohols
(b) Dehydrogenation of 2° alcohol
(c) Pyrolysis of calcium acetate
(d) Acid hydrolysis of alkyl cyanide
Answer
D
Question. In > C = O group sigma bond is formed by
(a) sp2-p-overlapping
(b) sp3-p-overlapping
(c) sp-p-overlapping
(d) s-p-overlapping
Answer
A
Question. Find out B in the given reactions
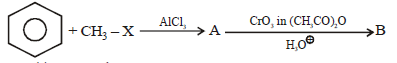
(a) acetophenone
(b) benzaldehyde
(c) cyclohexyl carbaldehyde
(d) benzoic acid
Answer
A
Question. When acetaldehyde reacts with alcohol then produce
(a) Acetal
(b) Ketal
(c) Acetone
(d) None
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compound will show positive silver mirror test ?
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3(CHOH)3CHO
(c) CH3CO(CHOH)CH3
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Which aldehyde cannot be obtained by Rosenmund’s reaction?
(a) CH3CHO
(b) HCHO
(c) CH3CH2CHO
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. The π-bond in carbonyl group is formed by
(a) s-s-overlapping
(b) p-p-overlapping
(c) s-p-overlapping
(d) p-d-overlapping
Answer
B
Question. The conversion PhCN → PhCOCH3 , can be achieved most conveniently by reaction with
(a) CH3MgBr followed by hydrolysis
(b) I2 – NaOH, CH3I
(c) Dil. H2SO4 followed by reaction with CH2N2
(d) LiAlH4 followed by reaction with CH3I
Answer
A
Question.Which of the following forces explain the boiling point of aldehydes and ketones?
(a) Hydrogen bonding
(b) van der Waal’s forces
(c) Dipole-dipole attraction
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Aldehydes can be oxidised by :
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Fehling solution
(c) Benedict solution
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. (CH3)3C–CHO does not undergo aldol condensation due to
(a) three electron donating methyl groups
(b) cleavage taking place between —C— CHO bond
(c) absence of alpha hydrogen atom in the molecule
(d) bulky (CH3)3C—group
Answer
C
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Which of the following is an example of nucleophilic addition ?

Answer
C
Question. A new carbon – carbon bond is formed in
(i) Aldol condensation
(ii) Kolbe’s reaction
(iii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(iv) Wurtz Fittig reaction
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iiv)
(d) All the four
Answer
D
Question. Which is the most suitable reagent for the following conversion?

(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Benzoyl peroxide
(c) I2 and NaOH solution
(d) Sn and NaOH solution
Answer
C
Question. In the given reaction,

Identify the product(s) formed in the given reaction.
I II
(a) 2 molecules of benzoic acid 2 molecules of ethanoic acid
(b) 2 molecules of benzoic acid 1 molecules of benzoic acid and 1 molecule of ethanoic acid
(c) 1 molecule of ethanoic acid 1 molecule of benzoic acid
(d) 1 molecule of benzoic acid 1 molecule of butanoic acid
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following undergoes haloform reaction ?
(i) CH3CH2COCH2Cl
(ii) C6H5COCH3
(iii) C6H5COCHCl2
(iv) CH3CH2COCCl3
(a) Only (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) All the four
Answer
D
Question. Primary alcohols can be readily oxidised to carboxylic acids by.
(i) KMnO4 in neutral medium.
(ii) KMnO4 in acidic or alkaline medium.
(iii) K2Cr2O7 in alkaline medium.
(iv) K2Cr2O7 in acidic medium.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. When benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde undergoes reaction with the 2, 4–DNP ?
(a) Benzaldehyde reacts slowly than acetaldehyde
(b) Acetaldehyde reacts slowly than benzaldehyde
(c) Both reacts equally
(d) Both do not react with 2, 4-DNP
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is an example of aldol condensation?
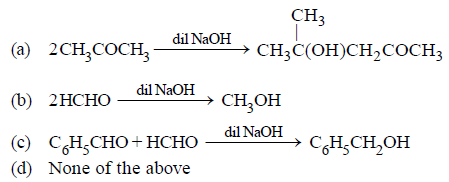
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of increasing acid strength of the compounds
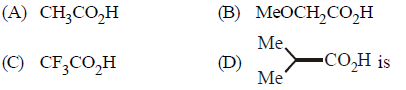
(a) D < A < B < C
(b) A < D < B < C
(c) B < D < A < C
(d) D < A < C < B
Answer
A
Question. Structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 3-ethyl- 2-hydroxy-4-methylhex-3-en-5-ynoic acid is :
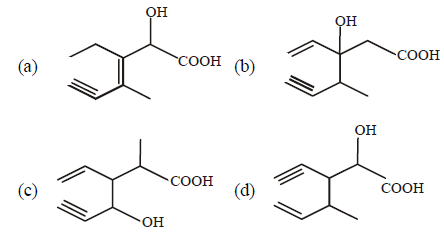
Answer
A
Question. RCOOH can be reduced to RCH2OH by
(i) NaBH4 (ii) LiAlH4
(iii) Na/C2H5OH
(iv) H2/Catalyst
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following acts as a nucleophile in the Cannizzaro reaction involving benzaldehyde ?
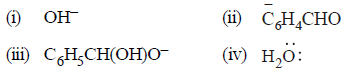
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) Only (i)
Answer
C
Question. Acetal formation is a reversible reaction
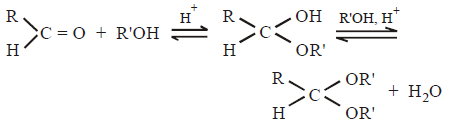
Under what conditions, the reaction can be forced to proceed only in right (forward) direction ?
(a) Using excess of alcohol
(b) Using high temperature
(c) Using dilute acid and excess of alcohol
(d) Using dry acid and excess of alcohol
Answer
D
Question. Nitration of the compound is carried out, this compound gives red–orange ppt. with 2,4–DNP, this compound undergoes Cannizzaro reaction but not aldol, than possible product due to nitration is
(a) 3–nitroacetophenone
(b) (2–nitro)–2–phenylethanal
(c) (2–nitro)–1–phenylpropan–2–one
(d) 3–nitrobezaldehyde
Answer
D
Question. Kolbe’s electrolytic method can be applied on

(iii) C6H5COOK (iv) CH3COOK
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Identify X,

(a) CH3OH
(b) Ethyl alcohol
(c) Methyl cyanide
(d) tert-Butyl alcohol
Answer
D
Question. Benzaldehyde is less reactive than propanal because
(i) the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of benzaldehyde is less electrophilic as in propanal.
(ii) the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of benzaldehyde is more electrophilic as in propanal.
(iii) carbonyl group in benzaldehyde is more polar due to resonance
(iv) carbonyl group in benzaldehyde is less polar due to resonance
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer
B
Question. Addition of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones takes place in presence of dry HCl gas because it
(i) Protonates the oxygen of the carbonyl compounds
(ii) Increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon
(iii) Removes the excess moisture from the reaction
(iv) Helps the reaction to move in the forward direction
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) ,(iii), and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Through which of the following reactions number of carbon atoms can be increased in the chain?
(i) Grignard reaction
(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(iii) Aldol condensation
(iv) HVZ reaction
Choose the correct option.
(a) Only (iii) and (i)
(b) Only (iii) and (ii)
(c) Only (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following conversions can be carried out by Clemmensen Reduction ?
(i) Benzaldehyde into benzyl alcohol
(ii) Cyclohexanone into cyclohexane
(iii) Benzoyl chloride into benzaldehyde
(iv) Benzophenone into diphenyl methane
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones occurs in presence of a base.The role of base is to
(i) catalyse the reaction
(ii) generate CN– ion
(iii) slow down the reaction
(iv) to stabilize the cyanohydrins
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Benzophenone can be obtained by_____________.
(i) Benzoyl chloride + Benzene + AlCl3
(ii) Benzoyl chloride + Diphenyl cadmium
(iii) Benzoyl chloride + Phenyl magnesium chloride
(iv) Benzene + Carbon monoxide + ZnCl2
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
A
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (1-MARK)
Question. Why do carboxylic acids not give the characteristic reactions of a carbonyl group?
Answer. Due to resonance, It does not have free carbonyl.
Question. Aromatic acids are solid while most of aliphatic acids are liquids. Why?
Answer. Aromatic acids have higher molecular weight and strong Van der Waals force of attraction as compared to aliphatic acids so they are solids.
Question. Why is the boiling point of an acid anhydride higher than the acid from which it is derived?
Answer. Acid anhydrides are bigger in size than corresponding acid. These have more surface area so have strong van der Waals Force of attractions. Hence they have higher boiling point.
Question. The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than that of the corresponding acids. Why?
Answer. This is due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acids.
Question. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3
Answer. CH3CH2CH3< CH3OCH3< CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH
Question. Why carboxylic acid have higher boiling point than alcohols as both have intermolecular hydrogen bonding?
Answer. Carboxylic acid forms a dimer due to double H-bonding. So it has higher boiling point than alcohols.
Question. What happens when ethanoyl chloride is subjected to rosenmund reduction?
Answer. Ethanoyl chloride is converted in to Ethanal. OR
CH3COCl + H2 Pd-BaSO4/S CH3CHO + HCl
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of acidic character : HCOOH, CH2ClCOOH ,CF3COOH , CCl3COOH
Answer. HCOOH < CH2ClCOOH < CCl3COOH < CF3COOH
Question. Why PCC cannot oxidize methanol to methanoic acid while KMnO4 can?
Answer. This is because PCC is a mild oxidizing agent and can oxidize methanol to methanal only.while KMnO4 is strong oxidizing agent which oxidizes it to methanoic acid.
Question. Why does solubility decrease with increasing molecular mass in carboxylic acid?
Answer. Because with increase of molecular mass size of hydrophobic carbon chain length increases.