Please refer to Transport in Plants Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Transport in Plants
Objective Questions
Question. In a fully turgid cell
(a) ψs will be negative and ψp will be positive.
(b) ψp will be negative and ψs will be positive.
(c) Both ψp and ψs will be positive.
(d) Both ψs and ψp will be negative.
Answer
A
Question. The process in which water moves out of the cell and the cell membrane of a plant cell shrinks away from its cell wall is known as
(a) diffusion
(b) osmosis
(c) plasmolysis
(d) bulk flow
Answer
C
Question. When a cell is plasmolysed, it becomes
(a) flaccid and its TP becomes zero.
(b) turgid and its TP becomes zero.
(c) turgid and TP becomes equal to OP.
(d) flaccid and DPD becomes zero.
Answer
A
Question. The process by which water is absorbed by solids like colloids causing them to increase in volume is called _______.
(a) osmosis
(b) plasmolysis
(c) imbibition
(d) diffusion
Answer
C
Question. Bulk flow of substances over the longer distances through the vascular tissue is called
(a) simple diffusion
(b) facilitated diffusion
(c) active transport
(d) translocation
Answer
D
Question. Casparian strip is made up of
(a) lignin
(b) pectin
(c) suberin
(d) cellulose
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following organism helps in the absorption of water and mineral ions from the soil?
(a) Nostoc
(b) Anabaena
(c) Mycorrhiza
(d) Spirullina
Answer
C
Question. Guttation is loss of impure water which is the result of
(a) osmosis
(b) diffusion
(c) root pressure
(d) transpiration
Answer
C
Question. The force responsible for upward conduction of water against gravity comes from _______.
(a) transpiration
(b) translocation
(c) respiration
(d) photosynthesis
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following wall of guard cells is thick?
(a) Side wall
(b) Middle wall
(c) Inner
(d) Outer
Answer
C
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following the statements regarding mycorrhizae is incorrect?
(a) Mycorrhizal fungi form a network around the young root and they penetrate the root cells.
(b) Mycorrhizae helps the plant to absorb water and minerals.
(c) Root provides sugar and nitrogenous organic compounds to the mycorrhizae.
(d) Pinus seed can germinate and establish without mycorrhizae.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Unlike water, all minerals cannot be passively absorbed by roots.
(b) Most of the minerals enter the root by active transport.
(c) Ions are absorbed from soil by both passive and active transport.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) The apoplastic movement of water occurs exclusively through the cell wall without crossing any
membranes.
(ii) The apoplastic movement occurs from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata.
(iii) Endodermis is impervious to water because of a band of suberised matrix.
(iv) Symplastic movement may be aided by cytoplasmic streaming which occurs in Hydrilla leaf and
chloroplast.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements, (i -v) regarding transpiration is/are correct?
(i) It creates transpiration pull for absorption and transport of plants.
(ii) It supplies water for photosynthesis.
(iii) It transports minerals from the soil to all parts of the plants.
(iv) It heats leaf surfaces, sometimes 10 to 15 degrees.
(v) It maintains the shape and structure of the plants by keeping cells turgid.
(a) Only (ii)
(b) Only (iii)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii) and (v)
(d) All
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match column-I with column-II and find out the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Isotonic | I. External solution is more concentrated |
| B. Hypotonic | II. Shrinkage of protoplasm |
| C. Hypertonic | III. Solution is more dilute than the cytoplasm |
| D. Plasmolysis | IV. Two solutions have the same osmolarity |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(b) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(c) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
B
Question. Match the name of the activities given under column-I with the description of activity given under column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Transpiration | I. Anaerobic respiration in yeast |
| B. Guttation | II. Active absorption of water |
| C. Exudation | III. Loss of water vapour from plant parts |
| D. Fermentation | IV. Loss of liquid water from leaves |
| V. Loss of water from injured plant parts |
(a) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – V
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – III; B – IV; C – V; D – I
(d) A – IV; B – V; C – II; D – III
Answer
C
Diagram Type Questions
Question. In the given figure, chamber A and B are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Study the given figure and choose the right option.
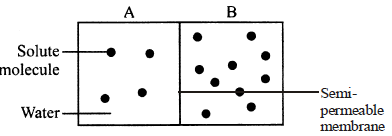
(a) Chamber A has higher water potential and water will move from A to B.
(b) Chamber B has lower solute potential and water will move from A to B.
(c) Chamber A has higher solute potential and water will move from B to A.
(d) Chamber B has lower water potential and water will move from B to A.
Answer
A
Question. Choose the option which shows the correct labelling of the parts marked as A, B, C, D and E in the given figure of water movement in the leaf.
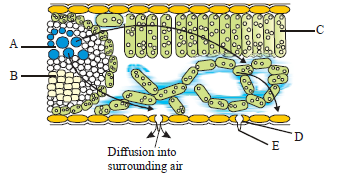
(a) A – Tracheids, B – Phloem, C – Mesophyll, D – Stomatal pore, E – Guard cell
(b) A – Phloem, B – Xylem, C – Palisade, D – Guard Cell, E – Water pore
(c) A – Xylem, B – Phloem, C – Palisade, D – Guard cell, E – Stomatal pore
(d) A – Phloem, B – Xylem, C – Mesophyll cell, D – guard cell, E – Water pore
Answer
C
Question. The given figure represents symplastic and apoplastic pathways of water & ion absorption & movement in roots.
Few parts are marked as A, B, C & D. At the endodermis, water movement through the apoplast pathway is obstructed by which part (marked as A, B, C & D)?
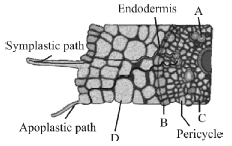
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Seeds when soaked in water, they imbibe because of
(a) OP inside the seed is low.
(b) OP of water is high.
(c) DPD of seed is very much low.
(d) water potential gradient between the seed coat and water.
Answer
D
Question. Dry wooden stakes, if driven into a small crack in a rock and then soaked, can develop enough pressure to split the rock. Such a pressure is built up through the phenomenon of
(a) imbibition
(b) transpiration
(c) turgor pressure
(d) plasmolysis
Answer
A
Question. The movement of water from one cell of the cortex to the adjacent one in roots is due to
(a) water potential gradient.
(b) chemical potential gradient.
(c) turgor pressure.
(d) mass flow.
Answer
A
Question. The path of water from soil upto secondary xylem is
(a) Soil → Root hair cell wall → Cortex → Endodermis → Pericycle → Protoxylem → Metaxylem
(b) Metaxylem → Protoxylem → Cortex → Soil → Root hair
(c) Cortex → Root hair → Endodermis → Pericycle → Protoxylem → Metaxylem
(d) Pericycle → Soil → Root hair → Cortex → Endodermis → Protoxylem → Metaxylem
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is correct regarding guttation?
(a) It occurs through stomata.
(b) It occurs through hydathodes.
(c) It occurs mostly during night and early morning.
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following compound is used to study water loss from a leaf and turns colour on absorbing water?
(a) Calcium chloride
(b) Magnesium chloride
(c) Cobalt chloride
(d) Sodium chloride
Answer
C
Question. Stomata closes because
(a) guard cells lose turgidityand becomes flaccid
(b) of increased turgidity of the guard cells brought about by exposure to light.
(c) O.P. of the guard cell increases
(d) of the movement of water from neighbouring cells into guard cells.
Answer
A
Question. If a stem is girdled,
(a) root dies first.
(b) shoot dies first.
(c) both die together.
(d) none of the above.
Answer
A
Question. Transpiration facilitates
(a) electrolyte balance
(b) absorption of water by roots
(c) opening of stomata
(d) excretion of minerals.
Answer
B
Question. In part A of a plant, sugars are actively transported into the phloem tissue. In part B, sugars are actively transported out of the phloem. Which way will the phloem sap move under these conditions?
(a) From A to B.
(b) From B to A.
(c) First from A to B; then, once the pressure builds up, from B to A.
(d) First from B to A; then, once the pressure builds up, from A to B.
Answer
A

