Please refer to Business Services Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Business Studies based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions Business Services
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. State the five I’s of services?
Answer : Nature of services are Intangibility, Inconsistency, Inseparability, Inventory and Involvement
Question. It is the prime responsibility of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize loss/damage to the insured property. Name the principle of insurance
Answer : Mitigation principle of Insurance says as the owner of an insurance policy, you have an obligation to take necessary steps to minimize the loss of your insured property. The law doesn’t allow you to be negligent or irresponsible just because you know you’re insured.
Question. Rahul’s father wants to save Rs. 100,000 so that he can gift the money to Rahul on his graduation day. Which type of deposit should he open with bank?
Answer : Fixed Deposit should be opened with bank. Fixed accounts are time deposits with higher rate of interest as compared to the savings accounts.
Question. A company insures its stock against fire for Rs. 15 Lakh. A fire broke down and the total stock was lost. At the time of fire there was stock worth Rs. 25 Lakh. What is the value of compensation company would be entitled to?
Answer : The contract of fire insurance is a contract of strict indemnity. The insured can, in the event of loss, recover the actual amount of loss from the insurer. This is subject to the maximum amount for which the subject matter is insured. So, maximum amount of Rs, 15 lakh is the value of compensation.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Mr. Satish gets his house insured against fire of Rs. 20 Lakh with insurer A and for Rs. 10 Lakh with insurer B. A loss of Rs. 3 Lakh occurred.
(1) How much compensation can be claimed from A and B separately and Why?
(2) Name the principle of Insurance in the above case.
Answer :
1. According to this principle, the insured can claim the compensation only to the extent of actual loss either from all insurers or from any one insurer. If one insurer pays full compensation then that insurer can claim proportionate claim from the other insurers
A=20Lakh*3Lakh/30Lakh
A=2 Lakh
B=10Lakh*3Lakh/30Lakh
B=1Lakh
2. Principle of Contribution is followed. It applies to all contracts of indemnity, if the insured has taken out more than one policy on the same subject matter.
The right of contribution arises when:
(a) There are different policies which related to the same subject matters;
(b) The policies cover the same period which caused the loss;
(c) All the policies are in force at the time of loss; and
(d) One of the insurer has paid to the insured more than his share of loss.
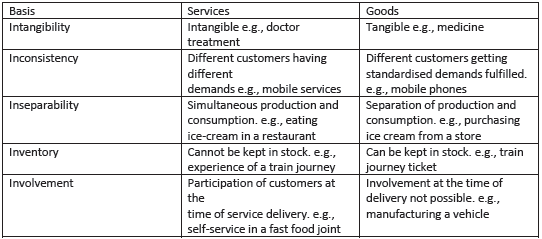
Question. Explain the Difference between Goods and services based on its nature
Answer :
Question. Explain the types of Life Insurance Policies?
Answer : Types of Life Insurance Policies:
♦ Whole Life Policy: In this kind of policy, the amount payable to the insured will not be paid before the death of the assured. The sum then becomes payable only to the beneficiaries
or heir of the deceased.
♦ Endowment Life Assurance Policy: The insurer undertakes to pay a specified sum when the insured attains a particular age or on his death whichever is earlier. The sum is payable to his legal heir/s or nominee named therein in case of death of the assured.
Otherwise, the sum will be paid to the assured after a fixed period
♦ Joint Life Policy: This policy is taken up by two or more persons. The premium is paid jointly or by either of them in instalments or lump sum assured sum or policy money is payable upon the death of any one person to the other survivor or survivors
♦ Annuity Policy: The assured sum or policy money is payable after the assured attains a certain age in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual instalments
♦ Children’s Endowment Policy: This policy is taken by a person for his/ her children to meet the expenses of their education or marriage. The agreement states that a certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age
Question. Explain the Functions of Warehousing?
Answer : Functions of Warehousing
1. Consolidation:
The warehouse receives and consolidates, materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment.
2. Break the bulk:
The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities. These smaller quantities are then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business.
3. Stock piling:
The next function of warehousing is the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses. Goods or raw materials, which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing, are stored in warehouses.
They are made available to business depending on customers’ demand
4. Value added services:
Certain value added services are also provided by the warehouses, such as in transit mixing, packaging and labelling. Goods sometimes need to be opened and repackaged and labelled again at the time of inspection by prospective buyers
5. Price stablisation:
By adjusting the supply of goods with the demand situation, warehousing performs the function of stabilizing prices. Thus, prices are controlled when supply is increasing and demand is slack and vice versa
6. Financing:
Warehouse owners advance money to the owners on security of goods and further supply goods on credit terms to customers
Long Answer Type Questions
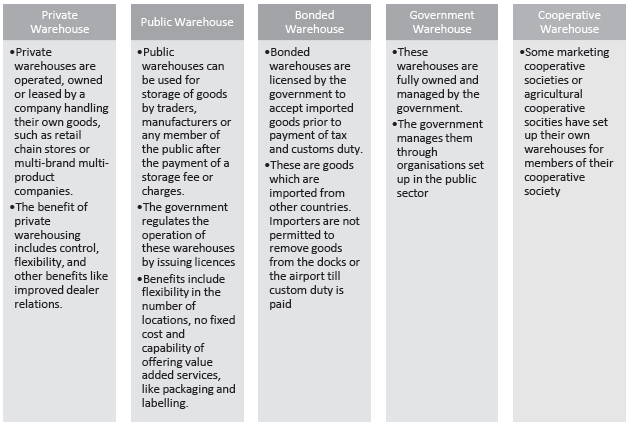
Question. Describe briefly Types of warehouses?
Answer :
Question. Write notes on RTGS system and NEFT. Also state the difference between them.
Answer : NEFT refers to National Electronic Funds Transfer. It is an online system for transferring funds from one financial institution to another within India (usually banks). The system was launched in November 2005, and was set to inherit every bank that was assigned to the SEFT clearing system. It was made mandatory by the RBI for all banks on the SEFT system to migrate to NEFT by mid December 2005. As such, SEFT was discontinued as of January 2006. The RBI welcomed banks that were full members of the RTGS to join the NEFT system.
RTGS is an acronym that stands for Real Time Gross Settlement. RTGS is a funds transfer system where
money is moved from one bank to another in ‘real-time’, and on gross basis. When using the banking
method, RTGS is the fastest possible way to transfer money. ‘Real-time’ means that the payment transaction isn’t subject to any waiting period. The transaction will be completed as soon as the
processing is done, and gross settlement means that the money transfer is completed on a one to one
basis without clustering with another transaction. The transaction is treated as final and irrevocable as
the money transfer occurs in the books of the RBI (Reserve Bank of India). This system is maintained by
the RBI, and is available during working days for a given number of hours. Banks using RTGS need to
have Core banking to be able to initiate RTGS transactions.
Difference between RTGS and NEFT:
1. RTGS is Real Time Gross Settlement, while NEFT is National Electronic Funds Transfer.
2. RTGS completes transactions in real-time, and is therefore faster than NEFT, which completes
transactions in cycles.
3. RTGS is gross settlement, where a transfer is completed on a one-to-one basis, while NEFT is on a
Deferred Net Basis, where transfers are bundled and deferred for a specific time.
4. RTGS is a high value transfer system, handling funds worth Rs 100,000 and above, while NEFT
transfers smaller amounts below Rs 100,000.
Question. Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by Indian Postal Department and different types of telecom services offered?
Answer : Indian post and telegraph department provides various postal services across India. Through their regional and divisional level arrangements the various facilities provided by postal department are
broadly categorised into:
o Financial facilities: These facilities are provided through the post office’s savings schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra, and National Saving Certificate
o Mail facilities: Mail services consist of parcel facilities that is transmission of articles from one place to another; registration facility to provide security f the transmitted articles and insurance facility to provide insurance cover for all risks in the course of transmission by post
o Allied Facilities: Greeting post, media post, International money transfer, speed post, passport facilities, e-bill
Different types of Telecom services are as follows:
♦ Cellular mobile services: These are all types of mobile telecom services including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area.
♦ Fixed line services: These are all types of fixed services including voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkages for long distance traffic. These utilise any type of network equipment primarily connected through fiber optic cables
♦ Cable services: These are linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services, which are essentially one-way entertainment related services.
♦ VSAT services: VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal) is a satellite-based communications service. It offers businesses and government agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
♦ DTH services: DTH (Direct to Home) is again a satellite-based media services provided by cellular companies. One can receive media services directly through a satellite with the help of a small dish antenna and a set top box.
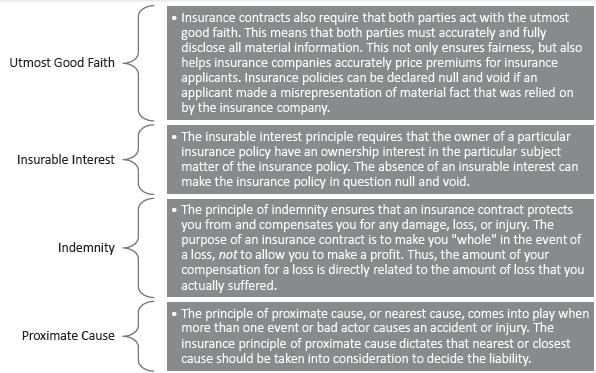
Question. Explain in detail the principles of Insurance?
Answer :