Please refer to Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Chemistry based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Thermodynamics
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Define enthalpy of formation.
Answer : The enthalpy change accompanying the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements is called enthalpy of formation.
Question. State the second law of thermodynamics.
Answer : Whenever a spontaneous process takes place, it is always accompanied by an increase in total entropy of the universe.
ΔSuniv = ΔSsys + ΔSsurr > 0
Question. When is bond energy equal to bond dissociation energy?
Answer : When bond energy is measured in isolated gaseous state, it becomes equal to bond dissociation energy.
Question. State two ways by which the internal energy of a system may be changed.
Answer : (i) If the work is done by or on the system.
(ii) Heat is absorbed by the system or heat is evolved from the system.
Question. State first law of thermodynamics.
Answer : According to first law of thermodynamics, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed although it may be changed from one form to another.
Question. What will be the sign of ΔS for the following reaction?
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Answer : The sign of ΔS for the reaction,
CaCOO3(s) → CaO(s)+ COO2(g), is +ve as the solid changes into gaseous state
Question. Give an example of a spontaneous process which is endothermic.
Answer : N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g)
It is endothermic as well as spontaneous.
Question. State the difference between adiabatic and isothermal processes.
Answer : In adiabatic process no heat can flow from the system to the surroundings or vice versa, whereas, in isothermal process temperature remains constant throughout the process.
Question. Give one point of difference : Extensive and intensive properties.
Answer : Extensive properties: Properties that depend on the quantity of matter contained in the system, e.g., mass, volume, etc.
Intensive properties: Properties which depend on the nature of the substance and not on the amount of substance, e.g., viscosity, etc.
Question. Under what conditions will a reaction be spontaneous if both ΔH and ΔS are negative?
Answer : ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Given, ΔH = –ve and ΔS = –ve
For a reaction to be spontaneous, DG should be negative, reaction takes place spontaneously only at lower temperature.
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Justify the following statements :
(a) Many thermodynamically feasible reactions do not occur under ordinary conditions.
(b) At low temperature, enthalpy change dominates the value of ΔG and at high temperature it is the entropy which dominates the value of ΔG.
Answer : (a) Under ordinary conditions, the average energy of the reactants may be less than the threshold energy. They require some activation energy to initiate the reaction.
(b) ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
At lower temperature, if value of ΔH is negative ΔG will be –ve and if ΔH is positive, ΔG will be positive. While at higher temperature –TΔS will be high, thus, sign of ΔS will decide whether ΔG will be positive or negative.
Question. Benzene burns in O2 according to the equation:
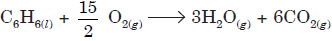
If enthalpy of formation of C6H6(l), H2O(g) and CO2(g) are 11.7, – 68.3, and –94 k cal respectively, calculate the amount of heat liberated by burning 1 kg benzene.
Answer :
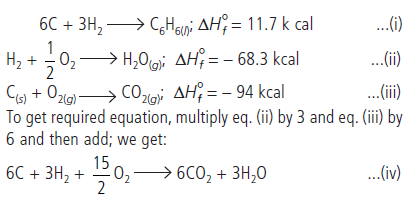
Question. Calculate the free energy change when 1 mole of NaCl is dissolved in water at 298 K.
Given:
(a) Lattice energy of NaCl = 778 kJ mol–1
(b) Hydration energy of NaCl = –774.3 kJ mol–1
(c) Entropy change at 298 K = 43 J mol–1
Answer :

Question. 10 g of argon gas is compressed isothermally and reversibly at a temperature of 27 °C from 10 litre to 5 litre. Calculates q, w and ∆U for this process.
(R = 2.0 cal K–1 mol–1, atomic weight of Argon = 40)
Answer :
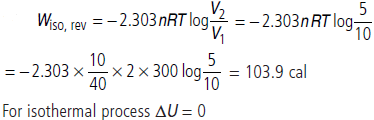

Question. In a process, 701 J of heat is absorbed by a system and 394 J of work is done by the system. What is the change in internal energy for the process?
Answer : Heat absorbed by the system (q) = 701 J
Work done by the system (w) = –394 J
According to first law of thermodynamics,
ΔU = q + w = 701 + (–394) = 701 – 394 = 307 J
Question. Derive the relationship, ΔH = ΔU + ΔngRT.
Answer : The enthalpy H can be written as :
H = U + pV …(i)
For finite changes at constant pressure, we can write equation
(i) as
ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV)
Since p is constant, we can write
ΔH = ΔU + pΔV …(ii)
Let us consider a reaction involving gases. If VA is the total volume of the gaseous reactants, VB is the total volume of the gaseous products, nA is the number of moles of gaseous reactants and nB is the number of moles of gaseous products, all at constant pressure and temperature, then using the ideal
gas law, we write,
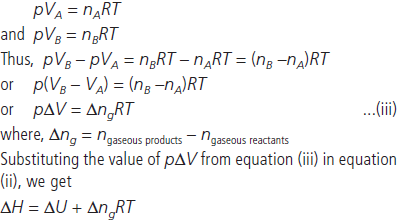
Question. The enthalpy of reaction for the reaction :
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2O(l) is Δr H° = –572 kJ mol–1.
What will be standard enthalpy of formation of H2O(l) ?
Answer : 2H2 + O2 2H2O; Δr H° = 572 kJ mol–1
Δf H° will be half of the enthalpy of the given equation as enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change of the reaction when 1 mole of the compound is formed from its elements.

Question. Although heat is a path function but heat absorbed by the system under certain specific conditions is independent of path. What are those conditions? Explain.
Answer :
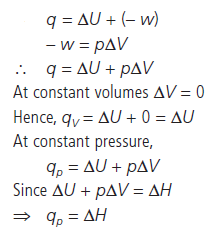
Hence, at constant volume and at constant pressure heat change is a state function because it is equal to ΔU and ΔH respectively which are state functions.
Question. 18.0 g of water completely vapourises at 100°C and 1 bar pressure and the enthalpy change in the process is 40.79 kJ mol–1. What will be the enthalpy change for vapourising two moles of water under the same conditions?
What is the standard enthalpy of vaporisation for water?
Answer : Enthalpy of a reaction is the energy change per mole for the process.
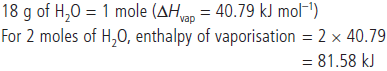
Question. A heated copper block at 130 °C loses 340 J of heat to the surroundings which are at room temperature of 32 °C. Calculate
(i) the entropy change of the system (copper block)
(ii) the entropy change in the surroundings
(iii) the total entropy change in the universe due to this process.
Assume that the temperature of the block and the surroundings remains constant.
Answer :

Question. (i) Explain why the enthalpy changes for the given reactions are not enthalpies of formation of CaCO3 and HBr.

Answer : (i) (a) Given enthalpy change is not enthalpy of formation of CaCO3 because it is not being formed from constituting elements.
(b) Given enthalpy change is not enthalpy of formation of HBr because 2 moles of HBr are being formed.
Question. If the combustion of 1 g of graphite produces 20.7 kJ of heat, what will be molar enthalpy change? Give the significance of sign also.
Answer : Molar enthalpy change for graphite (ΔH)
= enthalpy change for 1 g × molar mass of C
= – 20.7 × 12
= – 2.48 × 102 kJ mol–1
Since the sign of ΔH = –ve, it is an exothermic reaction.
Question. Diborane is a potential rocket fuel which undergoes combustion according to the reaction
B2H6(g) + 3O2(g) B2O3(s) + 3H2O(g)
From the following data, calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion of diborane.
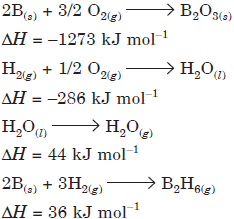
Answer : The given reaction can be obtained as follows:

Question. Assume ∆H° and ∆S° to be independent of temperature, at what temperature will the reaction given below become spontaneous?
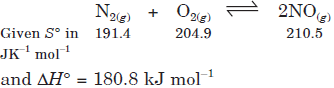
Answer :

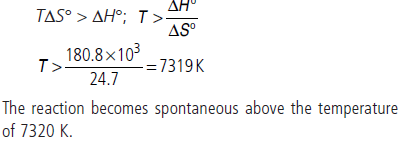
Question. A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process of expansion and compression as shown in figure. What will be the value of ΔH for the cycle as a whole?

Answer : For a cyclic process ΔH = 0
Question. (i) Classify the following processes as reversible or irreversible :
(a) Dissolution of sodium chloride.
(b) Evaporation of water at 373 K and 1 atm pressure.
(c) Mixing of two gases by diffusion.
(d) Melting of ice without rise in temperature.
(ii) When an ideal gas expands in vacuum, there is neither absorption nor evolution of heat. Why?
Answer : (i) (a) Reversible
(b) Reversible
(c) Irreversible
(d) Reversible.
(ii) In an ideal gas, there are no intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, no energy is required to overcome these forces. Moreover, when a gas expands against vacuum, work done is zero as Pext = 0. Hence, internal energy of the system does not change i.e., there is no absorption or evolution of heat.
Question. (a) What is a thermochemical equation?
(b) Write one application of Hess’s law.
Answer : (a) The balanced chemical equation which includes the amount of heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction is called a thermochemical equation.
(b) Hess’s law is found very useful in calculating the enthalpy change for the reaction for which experimental determination is not possible.
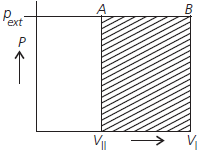
Question. What will be the work done on an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder, when it is compressed by a constant external pressure, pext in a single step as shown in Figure. Explain graphically.

Answer : Work done is equal to the shaded area ABVIVII
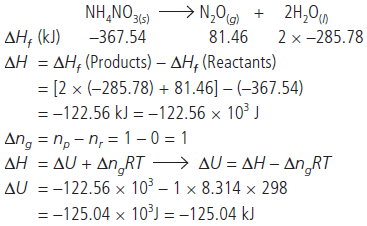
Question. The molar heat of formation of NH4NO3(s) is – 367.54 kJ and those of N2O(g) and H2O(l) are +81.46 kJ and –285.78 kJ respectively at 25 °C and 1.0 atmospheric pressure. Calculate ∆H and ∆U for the reaction,
NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2H2O(l)
Answer :
Question. The enthalpy change involved in the oxidation of glucose is –2880 kJ/mol. Twenty five percent of this energy is available for muscular work. If 100 kJ of muscular work is needed to walk one kilometer, what is the maximum distance that a person will be able to walk after consuming 125 g of glucose?
Answer : Energy available for muscular work from

Question. The heat of solution of anhydrous CuSO4 is –15.9 kcal and that of CuSO4. 5H2O is 2.8 kcal. Calculate the heat of hydration of CuSO4.
Answer : Given:

Question. The following data is known about ZnSO4 :
∆H = 7.25 kJ mol–1 and ∆S = 7.0 JK–1 mol–1.
Calculate its melting point.
Answer :

Question. 10 g of argon gas is compressed isothermally and reversibly at a temperature of 27°C from 10 L to 5 L. Calculate the value of q, w, ∆U and ∆H.
(R = 2.0 cal K–1 mol–1, at. wt. of Ar = 40)
Answer :
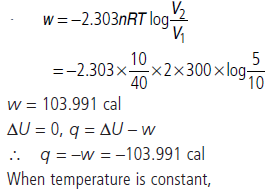
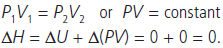
Question. Calculate the entropy change in surrounding when 1.00 mol of H2O(l) is formed under standard conditions.
ΔfH° = – 286 kJ mol–1.
Answer :

Question. Comment on the spontaneity of a reaction at constant temperature and pressure in the following cases :
(i) ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0
(ii) ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
(iii) ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
Answer : (i) Both energy factor and randomness factor favour the process. Hence, reaction will always be spontaneous.
(ii) Both factor opposes the process. Hence, reaction would always be non-spontaneous.
(iii) Energy factor opposes but randomness factor favours. For spontaneity, TΔS > ΔH. Hence, reaction is spontaneous at high temperature and non-spontaneous at low temperature.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. Whenever an acid is neutralised by a base, the net reaction is
H+(aq) + OH–(aq) H2O(l); ∆H = –57.1 kJ
Calculate the heat evolved for the following experiments:
(i) 0.50 mole of HCl solution is neutralised by 0.50 mole of NaOH solution.
(ii) 0.50 mole of HNO3 solution is mixed with 0.30 mole of KOH solution.
(iii) 100 mL of 0.2 M HCl is mixed with 100 mL of 0.3 M NaOH solution.
(iv) 400 mL of 0.2 M H2SO4 is mixed with 600 mL of 0.1 M KOH solution.
Answer : According to reaction :


Question. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy change for the combustion of a-D glucose at 298 K
C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
Given that standard enthalpies of formation

Answer :
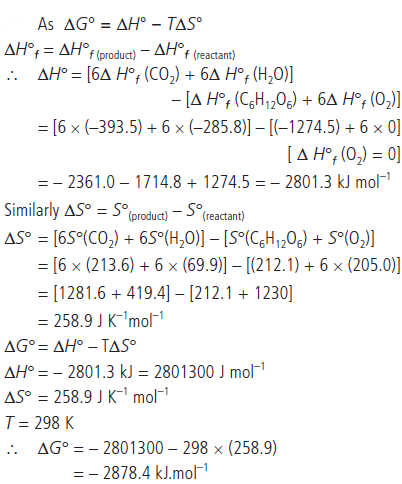
Question. (a) The melting point of ice is 273 K. At this temperature the enthalpy of fusion of ice is 6.025 kJ mol–1. Calculate the entropy change for melting of 1 mole of ice. State giving reason whether the entropy change for vaporization of one mole of water will be more or less than entropy change per mole for fusion of ice.
(b) Calculate the entropy change involved in the conversion of one mole of liquid water at 373 K to vapour at the same temperature (Latent heat of vaporization, ∆Hvap = 2.257 kJ/g).
Answer :
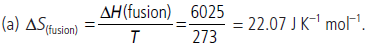
The entropy change for the conversion of 1 mole of liquid water to steam at the boiling point will be more as compared to the value at the freezing point, because in the vaporisation randomness increases (due to the conversion of liquid into vapour) much more than in fusion.
(b) Latent heat of vaporisation per mole
= 2.257 × 103 × 18 = 40,626 J mol–1
Question. A gas absorbs 120 J of heat and expands against the external pressure of 1.10 atm from a volume of 0.5 L to 2.0 L. What is the change in internal energy? (1 L atm = 101.3 J)
Answer : Work of expansion,

Question. Answer the following :
(i) Why does entropy of a solid increases on fusion?
(ii) State the thermodynamic conditions of spontaneous occurrence of a process.
(iii) Why a non-spontaneous reaction becomes spontaneous when coupled with a suitable spontaneous reaction?
(iv) For an isolated system, ∆U = 0, what will be ∆S?
Answer : (i) In a solid, the constituent particles are fixed. On melting, they fall apart and are free to move, i.e., their randomness increases.
(ii) For spontaneous occurrence, DG of the process must be < 0, i.e., –ve. This can be so under the following conditions :
(a) ∆H is negative and ∆S is positive (at any temperature).
(b) If ∆H and ∆S both are positive, then T should be so high that T∆S < ∆H.
(c) If both ∆H and ∆S are negative, then T should be so low that T∆S < ∆H.
(iii) The overall free energy change of the coupled reaction is negative.
(iv) When energy factor has no role to play, for the process to be spontaneous ∆S must be +ve i.e., ∆S > 0.


