Please refer to Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Chemistry based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Chemistry Important Questions Equilibrium
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Calculate the pH of a solution formed by mixing equal volumes of two solutions A and B of a strong acid having pH = 6 and pH = 4 respectively.
Answer : pH of solution A = 6
[H+] = 10–6 mol L–1
pH of solution B = 4
[H+] = 10–4 mol L–1
On mixing one litre of each solution
Total volume = 1 L + 1 L = 2 L
Total amount of H+ in 2 L solution formed by mixing solutions A and B = 10–6 + 10–4 mol
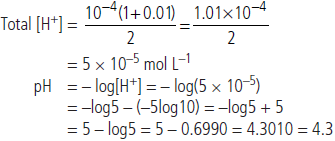
Question. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant Kc for the following equilibrium :
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) ⇌ Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Answer :

Question. Classify the following species into Lewis acids and Lewis bases and show how these act as Lewis acid/base :
(a) OH– (b) F– (c) H+ (d) BCl3.
Answer : (a) : OH– : OH– is a Lewis base because it can donate lone pair of electrons.
(b) F– : F– is a Lewis base because it can donate lone pair of electrons.
(c) H+ : H+ is a Lewis acid because it can accept lone pair of electrons.
(d) BCl3 : BCl3 is a Lewis acid because it is electron deficient and can accept a lone pair of electrons.
Question. For the system 3A + 2B ⇌ C,the expression for equilibrium constant K is?
Answer :
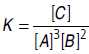
Question. Explain why pure liquids and solids can be ignored while writing the equilibrium constant expression.
Answer : For the concentration of pure solid or pure liquid,

Since density of pure solid or liquid is constant at constant temperature and molar mass is also constant therefore, their molar concentrations are constant and are included in the equilibrium constant.
Question. Give two important characteristics of chemical equilibrium.
Answer : Characteristics of chemical equilibrium are as follows :
(i) Chemical equilibrium is dynamic in nature.
(ii) A catalyst does not alter the state of equilibrium.
Question. A mixture of 1.57 mol of N2, 1.92 mol of H2 and 8.13 mol of NH3 is introduced into a 20 L reaction vessel at 500 K. At this temperature, the equilibrium constant, Kc for the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) is 1.7 × 102. Is the reaction mixture at equilibrium? If not, what is the direction of the net reaction?
Answer : The reaction is :

As Qc ≠ Kc, the reaction mixture is not in equilibrium.
As Qc > Kc, the net reaction will be in the backward direction.
Question. The pH of a sample of vinegar is 3.76. Calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions in it.
Answer : We know that pH = – log[H+]
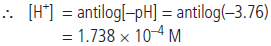
Question. Give relation between [A] and [B] for the stage of half completion of the reaction A ⇌ B.
Answer : A ⇌ B
At the stage of half completion of reaction [A] = [B].
Question. Equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. What will be the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction?
Answer :

Question. Conjugate acid of a weak base is always stronger. What will be the decreasing order of basic strength of the following conjugate bases?
OH–, RO–, CH3COO–, Cl–
Answer : Conjugate acids of given bases are H2O, ROH, CH3COOH, HCl.
Their acidic strength is in the order
HCl > CH3COOH > H2O > ROH
Hence, basic strength is in the order
RO–, OH–, CH3COO–, Cl–
Question. What is the equilibrium concentration of each of the substances in the equilibrium when the initial concentration of ICl was 0.78 M?
2ICl(g) ⇌ I2(g) + Cl2(g); Kc = 0.14
Answer :
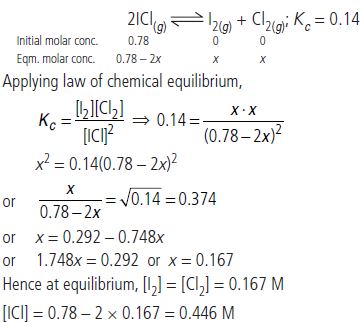
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Equal volumes of 0.002 M solutions of sodium iodate and copper chlorate are mixed together.
Will it lead to precipitation of copper iodate? (For copper iodate, Ksp = 7.4 × 10–8)
Answer : When equal volumes of sodium iodate and copper chlorate are mixed, the molar concentrations of both the solutes would be reduce to half i.e., 0.001 M.
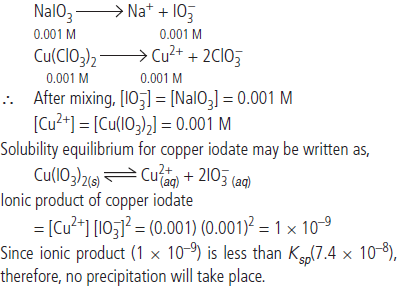
Question. On increasing the pressure, in which direction will the gas phase reaction proceed to re-establish equilibrium, is predicted by applying the Le Chatelier’s principle. Consider the reaction.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
What will be the effect on K. if the total pressure at which the equilibrium is established, is increased without changing the temperature?
Answer : N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, at constant temperature, the equilibrium composition will change but K will remain same.
Question. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium giving examples.
Answer : Equilibrium is said to be homogeneous if reactants and products are in same phase, e.g.,
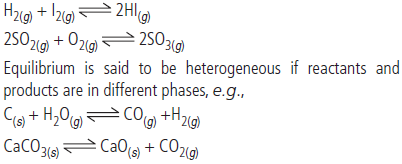
Question. We know that the relationship between Kc and Kp is
Kp = Kc(RT)Δn
What would be the value of Dn for the reaction
NH4Cl(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
Answer : Δn = np – nr = 2 – 0 = 2
Question. What is the pH of 0.001 M aniline solution? The ionisation constant of aniline is 4.27 × 10–10. Calculate the degree of ionisation of aniline in the solution. Also calculate the ionisation constant of the conjugate acid of aniline.
Answer :

Question. The ionization constant of HF, HCOOH and HCN at 298 K are 6.8 × 10–4, 1.8 × 10–4 and 4.8 × 10–9 respectively. Calculate the ionization constants of the corresponding conjugate base.
Answer :

Question. Calculate (a) ΔG° and (b) the equilibrium constant for the formation of NO2 from NO and O2 at 298 K.
NO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) ⇌ NO(g)
where ΔfG° (NO2) = 52.0 kJ mol–1,
ΔfG° (NO) = 87.0 kJ mol–1,
ΔfG° (O2) = 0 kJ mol–1
Answer :
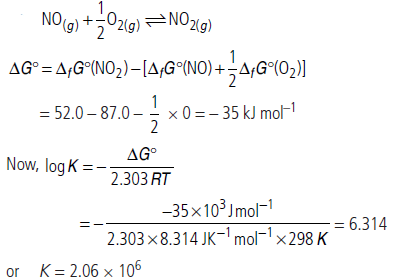
Question. Define Le-Chatelier’s Principle. What is the effect of :
(i) addition of H2
(ii) removal of CO
on the equilibrium :
2H2(g) + CO(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) ?
Answer : When an equilibrium is subjected to any kind of stress (change in concentration, temperature or pressure) it shifts in a direction so as to undo the effect of stress.
(i) When H2 is added, the rate of forward reaction will increase.
(ii) Addition of CH3OH will lead to increase in rate of backward reaction
Question. What will be the correct order of vapour pressure of water, acetone and ether at 30°C? Given that among these compounds, water has maximum boiling point and ether has minimum boiling point?
Answer : Higher the boiling point, lesser the vapour pressure hence the order of V.P. is
water < acetone < ether
Question. Write expressions for Kp and Kc for the decomposition reaction of calcium carbonate.
Answer :
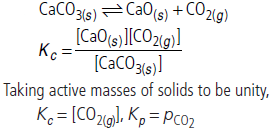
Question. Equilibrium constant, Kc for the reaction,
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) at 500 K is 0.061.
At a particular time, the analysis shows that composition of the reaction mixture is 3.0 mol L–1 N2, 2.0 mol L–1 H2 and 0.5 mol L–1 NH3. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not in which direction does the reaction tend to proceed to reach equilibrium?
Answer :

Question. In 1 L saturated solution of AgCl
[Ksp = 1.6 × 1010], 0.1 mol of CuCl
[Ksp = 1.0 × 10–6] is added. Find out the resultant concentration of Ag+ in the solution.
Answer : Let the concentration of AgCl be x mol/litre and that of CuCl be y mol/litre
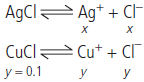

Question. What is the effect of increase of temperature on the pH of a buffer solution?
Answer : pH of a buffer changes with temperature because concentration of H+ ions increases, thus pH decreases with increase of temperature.
Question. What will be the conjugate bases for the Bronsted acids: HF, H2SO4 and HCO–3 ?
Answer :

Question. Reaction between N2 and O2 takes place as follows :
2N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2N2O(g)
If a mixture of 0.482 mol of N2 and 0.933 mol of O2 is placed in a 10 L reaction vessel and allowed to form N2O at a temperature for which Kc = 2.0 × 10–37, determine the composition of equilibrium mixture.
Answer :
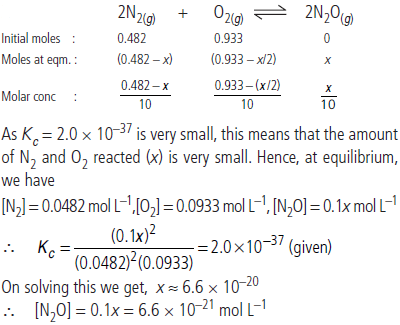
Question. The solubility product of AgCl is 1.5 × 10–10. Predict whether there will be any precipitation by mixing 50 mL of 0.01 M NaCl and 50 mL of 0.01 M AgNO3 solution.
Answer : On mixing 50 mL of 0.01 M NaCl and 50 mL of 0.01 M AgNO3 the total volume becomes 100 mL.
Therefore,

Since, ionic product is greater than its solubility product, precipitation will occur.
Question. (i) Define Lewis acids and bases with example.
(ii) The value of Ksp of two sparingly soluble salts Ni(OH)2 and AgCN are 2 × 10–15 and 6 × 10–17. Which salt is more soluble and why?
Answer : (i) Lewis acids are those which can accept a pair of electrons or negatively charged ions e.g., BCl3. Lewis bases can donate a pair of electrons or negatively charged ions e.g., NH3.
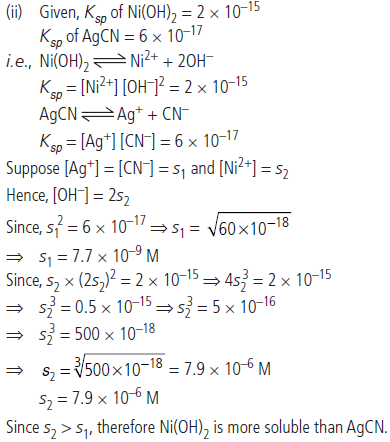
Question. Write the relation between Qc and Kc for reverse reaction.
Answer : Qc > Kc , for reverse reaction.
Question. For the reaction,
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g); ΔHr° = –92 kJ/mol
predict the direction of the reaction when
(i) pressure is doubled
(ii) temperature is doubled.
Answer : CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g); ΔHr ° = – 92 kJ/mol
(i) When pressure is doubled, equilibrium will shift in the direction where pressure decreases i.e., forward direction.
(ii) As this is an exothermic reaction, so the equilibrium will shift in backward direction when the temperature is doubled.
Question. Which of the following combinations would result in the formation of a buffer solution?
(i) NH4Cl + NH3
(ii) CH3COOH + HCl
(iii) CH3COONa + CH3COOH
(iv) NH3 + HCl in the molar ratio of 2 : 1
(v) HCl + NaOH
Answer : (i), (iii), (iv) would result in the formation of a buffer solution.
Question. A sparingly soluble salt having general formula Axp+Byq– and molar solubility S is in equilibrium with its saturated solution. Derive a relationship between the solubility and solubility product for such salt.
Answer :

Question. The value of ΔG° for the phosphorylation of glucose in glycolysis is 13.8 kJ/mol. Find the value of Kc at 298 K.
Answer :
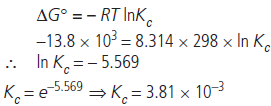
Question. Ka1, Ka2 and Ka3 are the respective ionisation constants for the following reactions.
H2S ⇌ H+ + HS–
HS– ⇌ H+ + S2–
H2S ⇌ 2H+ + S2–
The correct relationship between Ka1, Ka2 and Ka3 is
Answer :

Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. At 473 K, equilibrium constant, Kc for decomposition of PCl5 is 8.3 × 10–3. If decomposition is depicted as :
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g); ΔrH° = 124.0 kJ mol–1
(a) Write an expression for Kc for the reaction.
(b) What is the value of Kc for the reverse reaction at same temperature?
(c) What would be the effect on Kc if
(i) the pressure is increased
(ii) the temperature is increased?
Answer :

Question. One mole of N2 and 3 moles of PCl5 are placed in a 100 litre vessel heated to 227°C. The equilibrium pressure is 2.05 atm. Assuming ideal behaviour, calculate the degree of dissociation for PCl5 and Kp for the reaction
PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
Answer :

Question. (i) Point out the differences between ionic product and solubility product.
(ii) The solubility of AgCl in water at 298 K is 1.06 × 10–5 mole per litre. Calculate its solubility product at this temperature .
Answer : (i) The term ionic product has a broad meaning since it is applicable to all types of solution, may be unsaturated or saturated. On the other hand, the solubility product has restricted meaning since it applies only to a saturated solution in which there exists a dynamic equilibrium between the undissolved salt and the ions present in solution. Thus, the solubility product is, in fact the ionic product for a saturated solution.
The solubility product of a salt is constant at constant temperature whereas ionic product depends upon the
concentrations of ions in the solution.
(ii) The solubility equilibrium in the saturated solution is
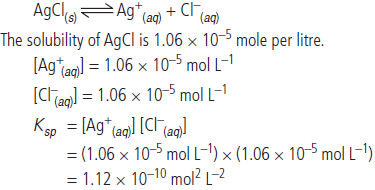
Question. (i) Derive the relationship between pKw, pH and pOH starting from ionisation constant of water, Kw. What is the numerical value of pKw at 298 K?
(ii) If 0.561 g of KOH is dissolved in water to give 200 mL of solution at 298 K. Calculate the concentrations of K+ and OH–. What is its pH?
(Give atomic masses K = 39, O = 16, H = 1)
Answer : (i) Sorensen (1909) defined pH of a solution as negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration of the solution.

Question. (i) What is common ion effect?
(ii) Write the Ksp expressions for Ag2CrO4 and zirconium phosphate.
(iii) Calculate the pH of 0.005 M HCl solution.
Answer : (i) Common ion effect can be defined as the suppression of the degree of ionisation of a weak electrolyte by the addition of a strong electrolyte having an ion common with the weak electrolyte.



