Please see The Living World Class 11 Biology Revision Notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books for Class 11 Biology issues by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should revise these notes for Chapter 1 The Living World daily and also prior to examinations for understanding all topics and to get better marks in exams. We have provided Class 11 Biology Notes for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 1 The Living World Class 11 Biology Revision Notes
Life is a unique, complex organization of molecules, expressing through chemical reactions which lead to growth, development, responsiveness, adaptation & reproduction.
A living organism is self-replicating, evolving and self-regulating interactive system capable of responding to external stimuli
PROPERTIES OF LIVING ORGANISMS
1. Growth
♦ It is the increase in number & mass of cells by cell division.
♦ In plants, growth continues throughout their lifespan.
♦ In animals, growth is only up to a certain age. However, cell division occurs to replace lost cells.
♦ Basically, growth is the increase in mass & size. Thus nonliving objects also grow (surface accumulation of material) . So growth is not a defining property of living organisms.
♦ In living organisms, growth is from inside.
2. Reproduction
♦ It is the production of progeny having features similar to those of parents.
♦ Organisms reproduce asexually and sexually.
♦ In unicellular organisms, growth & reproduction are same because they reproduce by cell division.
♦ Many organisms do not reproduce (e.g. mules, worker bees, infertile human couples, etc). Hence, reproduction is not a perfect defining property of living organisms.
3. Metabolism
♦ It is the sum total of all biochemical reactions taking place inside a living system.
♦ It is the defining feature of living organisms.
♦ Metabolic reactions can be demonstrated outside the body in cell-free systems. Isolated metabolic reactions in vitro are not living things but are living reactions.
4. Cellular organization
♦ Organisms are made up of one or more cells.
♦ It is the defining feature of living organisms.
5. Consciousness
♦ It is the ability of organisms to sense their environment and respond to environmental stimuli (like light, water , temperature, other organisms, chemicals, pollutants, etc).
♦ All organisms are ‘aware’ of their surroundings. So, it is the defining property of living organisms.
♦ Human is the only organism having self-consciousness
DIVERSITY IN THE LIVING WORLD
♦ The number and types of organisms present on earth refer to biodiversity.
♦ Number of species described is 1.7-1.8 million.
♦ Taxonomy is the study of identification, classification & nomenclature of organisms.
Systematics (Latin ‘systema’ = systematic arrangement) deals with evolutionary relationships among organisms.
♦ Systema Naturae is the book written by Linnaeus.
Basic processes of taxonomy
♦ Characterization: It is the understanding of characters of organisms such as external and internal structure, structure of cell, development process, ecological information etc.
♦ Identification: It is the correct description of the organism so that the naming is possible.
♦ Classification: It is the grouping of organisms into convenient categories (taxa) based on characters.
♦ Nomenclature (naming): It is the standardization of names of the organisms such that an organism is known by the same name all over the world.
The system of naming with two components is called Binomial nomenclature. It is proposed by Linnaeus. Botanical names are based on the rules in International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN).
Zoological names are based on International Code for Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN).
Universal rules of Binomial nomenclature
♦ Scientific names are in Latin or Latinised and written in italics. When handwritten, they are underlined separately.
♦ The first word is genus name (Generic name) and second word is the species name (specific epithet).
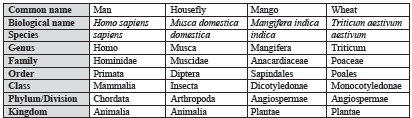
E.g. Homo sapiens- Homo represents the genus name and sapiens represents the species name.
♦ The Genus name starts with capital letter and the species name starts with small letter.
♦ Name of the author (in abbreviated form) appears at the end of the biological name.
E.g., Mangifera indica Linn. It indicates that this species was first described by Linnaeus.
TAXONOMIC CATEGORIES
♦ Classification involves hierarchy of steps in which each step represents a taxonomic category (rank).
♦ All categories together constitute a taxonomic hierarchy.
♦ A group of organisms occupying a particular category is called a taxon (pl. taxa). E.g. Class Mammalia.
♦ Each category or taxon represents a unit of classification.
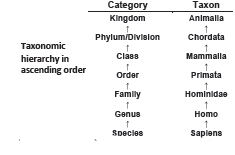
Species: It is a group of closely related organisms capable of interbreeding to produce fertile offspring.
It is the lowest category. E.g.

Genus: It is the aggregates of closely related species. E.g.
Potato, tomato & brinjal are species of genus Solanum. Lion, leopard & tiger are species of genus Panthera. This genus differs from genus Felis (genus of cats).
Family: It is a group of closely related genera. E.g.
Family Solanaceae includes Genus Solanum, Genus Petunia and Genus Datura.
Family Felidae includes Genus Panthera and Genus Felis.
Order: It is the assemblage of related families. E.g.
Order Polymoniales includes Family Convolvulaceae and Family Solanaceae.
Order Carnivora includes Family Felidae & Family Canidae.
Class: It is the assemblage of related orders. E.g.
Order Primata, Carnivora etc. is placed in class Mammalia.
Phylum (Division in case of plants): It is the assemblage of related classes.
E.g. Classes Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia etc. come under phylum Chordata.
Kingdom: The assemblage of related phyla. It is the highest category.
E.g. Kingdom Plantae, Kingdom Animalia etc.
Organisms with their taxonomic categories
TAXONOMICAL AIDS
a. Herbarium
♦ It is a store house (repository) of plant specimens that are dried, pressed and preserved on sheets and are arranged according to universally accepted classification.
♦ Herbarium sheets are labelled with information about date and place of collection, English, local and botanical names, family, collector’s name etc.
b. Botanical gardens
♦ These are specialized gardens having collections of living plants for reference and identification.
♦ Each plant is labelled with its botanical name and family.
♦ Famous botanical gardens:
a. Royal Botanical Garden at Kew (England).
b. Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah (India).
c. At National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow (India).
c. Biological Museum
♦ It is a collection of preserved plants and animals for study and reference.
♦ A museum contains
a. Specimens preserved in preservative solutions in containers or jars.
b. Preserved dry specimens of plants and animals.
c. Insects preserved in insect boxes after collecting, killing and pinning.
d. Stuffed larger animals like birds and mammals.
e. Collections of animal skeletons.
d. Zoological Parks (Zoos)
♦ These are the places where live wild animals are kept in protected environments under human care.
♦ It helps to learn about their food habits and behaviour.
e. Key
♦ It is an analytical method of identification of organisms based on similarities and dissimilarities.
♦ It is based on the contrasting characters generally in a pair called couplet.
♦ Each couplet has two opposite options. Of these, only relevant option is accepted and other is rejected.
♦ Each statement in the key is called a lead. Flora, manuals, monographs & catalogues
♦ Flora: Actual account of habitat and distribution of plant species of a given area.
♦ Manuals: The record that contains information for identification of names of species found in an area.
♦ Monographs: The records that contain information on any one taxon.
♦ Catalogue: Alphabetical list of species.



