Please see Sources of Energy Class 10 Science Revision Notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books for Class 10 Science issues by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should revise these notes for Chapter 14 Sources of Energy daily and also prior to examinations for understanding all topics and to get better marks in exams. We have provided Class 10 Science Notes for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Class 10 Science Revision Notes
Good Source of Energy
We are familiar with the term energy. Everyday, we hear about the scarcity of energy and a looming crisis caused by the rapid depletion of energy reserves. Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. Hence, it should be conserved.
Energy is the ability or the capacity of a physical system to do work.
Are there different forms of energy? Can each form of energy be changed into another form?
Yes, energy exists in various forms such as kinetic energy, heat energy, chemical energy, etc. We can change energy from one form to another. For example, when a candle is burned, it produces heat and light. Here, we can see that the chemical energy in the candle is converted to light and heat energy.

Thus, we can say that a candle is a source of both light and heat. On the other hand, burning of coal produces heat. Does it also produce light?
What makes some forms of energy good while others bad?
Let us answer the question using light and coal as examples. Which of the two will you use as a source of heat energy to cook food?
You will use coal as a source of heat energy to cook food. But, why coal and not candle?
After all, both sources of energy produce heat.
This is because the heat from the candle is not sufficient to cook.
This implies that specific sources of energy are used for specific purposes, which we refer to as good sources of energy for that particular task.
Good sources of energy exhibit some special characteristics that are listed below.
- It should possess a high calorific value, i.e., the amount of energy obtained by burning one kilogram of the fuel should be high.
- It should not leave residue after burning, i.e., it should burn completely
- It should burn without producing too many pollutants
- It should be easily available and accessible
- It should be economical
- It should be easy to store and transport
- Coming back to our earlier discussion,
- When we compare coal and candle as sources of heat energy, we find that both are easily available, economical, and easy to store. However, coal is more efficient than candle, i.e., coal has a higher calorific value. One kilogram of coal will provide more energy as compared to one kilogram of candle-wax. Therefore, we prefer coal to candle when we require heat energy.
- Let us further understand some characteristics of a good fuel.
- In addition to a high calorific value, a good fuel must also have a fairly low ignition temperature. What will happen if the ignition temperature of a substance is lower than the normal room temperature?
- The fuel will be very difficult to store and transport. Any thermal contact with the atmosphere will ignite the fuel and it may result in an explosion.
- Calorific value is defined as the amount of heat energy obtained by burning one gram of a substance. The unit of calorific value is kJ/g.
- The ignition temperature of a substance is defined as the temperature at which the substance starts burning. It is measured in °C, °F, or K.
- Calorific values and ignition temperatures of some common fuels are listed in the following table.
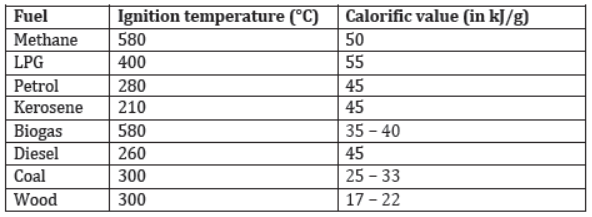
- Now, can you distinguish a good fuel from a bad fuel?
- You can see that methane has the highest calorific value but it has a very high ignition temperature. Petrol has high calorific value as well as low ignition temperature. Hence, petrol is the best fuel among those listed in the above table.
Now you know why most cars use petrol as a source of energy (fuel).
Renewable and Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
Natural resources are the materials that occur in nature and are useful to humans. These resources may be either living or non living.
Living resources includes living organisms like forests and wildlife or the products derived form these living organisms like leather, wood etc. It also includes the fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, natural gas etc.
that are derived from remains of dead and decayed living organisms over a long period of time.
Non living resources include the land, water, soil, air and mineral ores.
Based on whether a source of energy can be replenished, it can be classified as a
- Renewable source of energy
- Non-renewable source of energy
Renewable sources of energy are those that are replenished at a rate faster than that at which they are consumed. About 13 percent of the primary energy comes from renewable resources. Renewable resources of energy are known as inexhaustible sources of energy as they can be easily regenerated at a constant rate.
Examples of renewable sources of energy include sunlight, wind, tides, and geothermal energy.
Non-renewable sources of energy are those that are consumed at a rate faster than that at which they are replenished. Non-renewable resources of energy are known an exhaustible sources of energy as they can be easily exhausted.
Examples of non-renewable resources of energy are fossil fuels, which include coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These resources are widely used. In addition to being an exhaustible source of energy, fossil fuels also release polluting emissions on burning.
Coal: It is a non-renewable source of energy made up of complex compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen along with some free carbon and compounds of nitrogen and sulphur. It is found in mines under the Earth’s surface. In India, coal is found in abundance in Jharkhand, West Bengal, Orissa and Chattishgarh. It is a most common source of energy for us.
Petroleum: It is a dark coloured viscous liquid also known as crude oil or black gold. It is a complex mixture of many hydrocarbons with water, salt, earth particles and other compounds of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur. We obtain petroleum by drilling oil wells into earth’s crust at its reservoirs. Assam and Mumbai are the two petroleum reservoirs of India. The petroleum extracted from wells has to be purified to obtain different useful components.
The process of separating useful components from the crude oil is called refining and this process is done by fractional distillation in big refineries. The petroleum gas obtained as a by-product from the fractional distillation of petroleum majorly contains butane and a small quantity of propane and ethane. These gases generate a lot of heat on burning and can be liquefied easily under pressure. This petroleum gas liquefied under pressure is known as LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) which we use it in domestic gas stoves as fuel. Gas cylinders are used to store LPG and a strong smelling substance called ethyl mercaptan C2H5SH is added in this gas to detect any leakage.
Natural Gas: Same as petroleum, natural gas is also found deep under the Earth’s crust either alone or above the petroleum reservoirs. The main constituents of natural gas are methane (upto to 95%), ethane and propane. It easily burns to produce heat. In India, there are number of reservoirs of natural gas such as in Tripura, Jaisalmer, offshore area of Mumbai and Krishna-Godavari delta.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are the most commonly used sources of energy. Essentially, fossil fuels are hydrocarbons found within the top layer of the Earth’s crust. These include liquid petroleum, coal, natural gas, etc. The development of civilization has increased the requirement and demand for energy.
Fossil fuels are formed by biogenic processes from the fossils of dead plants and animals in the Earth’s crust. These fuels take over millions of years to form. The dead plants on the surface of the Earth were deposited under sediments of sand and clay in low lying swamp areas. In the course of time, as the thickness of this sediment increased, it compressed the dead plants under conditions of high pressure and temperature. This led to the formation of coal.
Petroleum, on the other hand, is formed from dead organisms found deep at the bottom of oceans. These organisms were covered by a layer of sediment, which, over the course of time, increased in thickness, thereby causing the dead organisms to compress. This compression of dead organisms under high pressure and temperature, in the absence of oxygen, converted these ancient sea organisms into petroleum.
Fossils Fuels
The fuels that have formed from the remains of plants and animals that got buried inside the earth millions of years ago are called fossil fuels.
Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are main fossil fuels.
Fossils fuels are present in limited quantities on earth. It is feared that their reserves will soon get exhausted. Hence, they are called non-renewable sources of energy. Therefore, we must avoid their wastage.
Coal

Most of us have seen coal being used in some way or the other. The neighbourhood presswallah (the person who irons your clothes) uses it. It is also used in traditional fireplaces. In earlier times, coal was used to run rail engines. It is a hard, stone-like blackish substance that releases heat and smoke on burning.
Coal was formed by decomposition of dead remains of plants when they got buried in the land owing to the high temperature and pressure conditions present there.
Coal is mainly carbon. Therefore, this process of change of dead vegetation to coal is called carbonisation. Coal is also called a fossil fuel because it was formed from the remains of plants and vegetation. Based on the content of carbon present, normally three types of coal deposits exist and these are as follows.
- Anthracite with carbon content of about 80%.
- Lignite with 50-60% of carbon content.
- Bituminous coal with less than 40% carbon.
Characteristic features of coal
- It is black in colour.
- It is as hard as stone.
- On burning, it releases heat and polluting smoke.
- It is formed from dead vegetation. It therefore contains the remains of vegetation.
- It takes millions of years to form. Thus, we cannot make coal under laboratory conditions.
Uses of coal
- As a fuel for cooking
- For heating of bricks
- As an industrial fuel
- In railway engines to produce steam
- In thermal power plants to generate electricity
Products obtained after processing coal
- Coke
- Coal tar
- Coal gas
Petroleum
- Petroleum (Crude oil) is formed from the remains of living organisms, which got buried in water millions of years ago.
- Petroleum is a mixture of solid, liquid, and gaseous hydrocarbons. It is mostly found in sedimentary rocks and is obtained on digging these rocks.
- On distillation of petroleum, several useful compounds are obtained such as petrol, diesel, kerosene, lubricating oil, wax, naptha etc.
Natural Gas
- Natural gas was formed along with petroleum.
- It has 95% of methane and 5% of other gases such as ethane, propane, and ethylene.
- Low content of sulphur present in the natural gas makes it a least polluting source of fuel.
The industrial revolution led to a rapid increase in the consumption and demand for energy. Petroleum and coal are two important sources of energy used by industries that are engaged in the manufacturing of various goods. They are also known as fossil fuels,as these fuels have been formed from fossils present deep inside the Earth’s crust. Specifically, coal and petroleum are formed by the decomposition of biomass. It takes millions of years for biomass to decompose and form petroleum.
Petroleum and coal are exhaustible sources of energy. It is estimated that if we continue to consume fossil fuels at the current rate, then all the petroleum reserves will get exhausted in the next 40 years, and the coal reserves will be completely consumed over the next two hundred years. Therefore, it is very important that adequate measures are taken to conserve these valuable natural resources.
Some facts that emphasise the need to conserve these sources of energy are listed below.
- They are the main sources of energy
- Fossil fuels are an exhaustible source of energy
- They release many pollutants on burning. Their use, therefore, should be limited
- They are formed from biomass and the process takes millions of years
- The current petroleum reserves will last only for about forty to fifty years
- The coal reserves will last for about two hundred years at the current rate of consumption
Consequences of using coal and petroleum
- Fossil fuels are an exhaustible source of energy. Therefore, a continuous use of these fuels will eventually lead to a depletion of all existing reserves.
- Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that is released when fossil fuels are burnt. It is the primary cause of global warming.
- Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur are also released when fossil fuels are burnt. These are poisonous and harmful to health.
- Carbon monoxide is a harmful gas that is released when fossil fuels are burnt under conditions of limited supply of oxygen. It is a very poisonous gas and can be fatal if inhaled.
Hydel and Thermal Power Plants

Power plants generate power. You may have seen smoke coming out of the chimneys of power stations. These power stations use coal or petroleum as fuel to produce steam by heating water. The steam is then used to rotate a turbine, which drives a generator. Electric energy thus generated is known as thermal power, and such power stations are known as thermal power plants.
Steam is passed through the turbine and is allowed to condense in a condenser. Since a thermal power plants uses coal or petroleum as fuel, it releases huge amounts of smoke from its chimneys.
Make your own power station

You can make your own, miniature thermal power plant at home using a bicycle dynamo, pressure cooker, turbine, and bulb as illustrated in the figure.
Heat is used to make steam from water in the pressure cooker. Steam spins the turbine, which in turn spins the dynamo. The dynamo generates electricity and this lights the bulb.
Since it is more convenient to transport electricity rather than fossil fuels such as coal, many thermal power plants are set up near coal or oil fields.
Hydro power plants
Instead of using steam to spin a turbine, hydro power plants use the potential energy of water accumulated at a height to spin a turbine.
Hydropower plants have various components, such as water reservoir, turbine and generator, all of which work together to generate electicity. This process is summarised in the following flow chart:
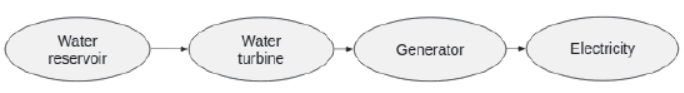
In India, most of the hydropower plants are associated with dams. This is because the natural flow of water in our water bodies is not such that it can spin a turbine. Construction
of dams over rivers helps to accumulate water and increase its force. A quarter of our energy requirement is met by hydroelectricity.
Major hydropower plants in India


Advantages of hydropower plants
- Clean and cheap
- Do not produce pollutants
- No waste by-products are produced
- They do not require transportation of fuels
- Hydro power is a renewable source of energy
Disadvantages of hydropower plants
- Limited geographic potential
- Causes a change in the course of rivers
- Sediment accumulates in a dam and eventually reduces its water storage potential
- Lot of land is submerged under water
- Fish and wildlife are affected drastically
- Large dams release methane, which is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming
Biomass Energy and Biogas Plant
Biomass refers to those living and non living organic materials that can be used as sources of energy in the form of fuel. Some examples of biomass fuels are wood, crops, and organic garbage. The chemical energy in biomass is released as heat on burning.
Biomass can also be converted to other usable forms of energy such as methane gas or transportation fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel. It is a renewable source of energy.
Wood as biomass
The most common form of biomass is wood. For thousands of years people have burned wood for heating and cooking. Until the mid-1800s, wood was the main source of energy in the world. It still continues to be a major source of energy in most of the developing countries. Many manufacturing plants in the wood and paper products industry use wood waste to produce their own steam and electricity.

Municipal solid waste as biomass
Garbage is another source of biomass. This is also called municipal solid waste (MSW).
MSW includes food scraps, lawn clippings, leaves, etc. These are also called biomass trash.

Biogas
Gas made from the anaerobic digestion of agricultural and animal waste is called biogas. When this biomass (agriculture and animal waste) is decomposed in the absence of oxygen, it releases biogas.
In India, biogas is commonly known as “gobar gas”. Biogas is a mixture of methane (75%) and CO2. It is used for cooking, lighting of lamps, generating electricity, etc. In “landfills”, biomass rots and releases methane gas through the process of biodegradation.
Biodegradation is the process of biological degradation of organic matter by bacteria and fungi.
Biogas production
Biogas technology provides an alternate source of energy in rural India. It is a more efficient and developed form of fuel.
It uses a thick mixture of cattle waste and kitchen garbage. This is fed into an inlet chamber. The micro organisms present in the digester tank are mainly methanogens.
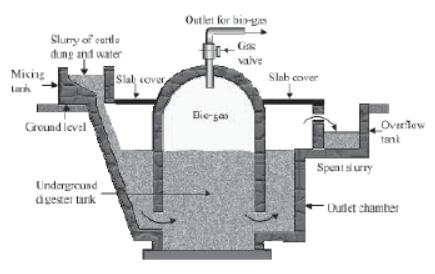
These methanogens decompose the organic waste (slurry) anaerobically to produce methane and some carbon dioxide. This process is called biodegradation.
Biofuels
Biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, are fuels that are made from biomass materials. These are used in transport vehicles. These fuels are usually blended with petroleum fuels such as gasoline and diesel.
Biodiesel
Biodiesel is a domestic renewable fuel for diesel engines derived from natural oils such as soybean oil. It is typically produced by the reaction of a vegetable oil, or animal fat with an alcohol such as methanol or ethanol in the presence of a catalyst to yield mono-alkyl esters and glycerine. Glycerine is removed from the biodiesel.
Biodiesel fuel can be used in diesel engines without making any modifications to the engine. It is a safe, renewable, and biodegradable fuel that produces fewer polluting emissions.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is the energy harnessed from wind. The kinetic energy of wind is converted into mechanical energy. If this energy is used directly by a machine (such as a grinding stone or a water pump), it is called a windmill. If the mechanical energy is first converted into electricity, then the machine is called a wind turbine.

How does wind energy work?
- The wind blows on the blades and rotates them.
- The blades turn a shaft inside the nacelle (the box at the top of the turbine)
- The shaft goes into a gear box and starts producing electrical energy
- The national grid transmits the power around the country
- Wind turbines operate at wind speeds of about 10 miles an hour. They reach a maximum power output at about 33 miles per hour. When a number of windmills are erected over a large area, in the same location, it is known as a wind farm. One such farm in India is near Muppandal, Tamil Nadu.
- Windmills are pollution free. The energy harnessed by windmills can be used in pumps to lift water from wells or for grinding grains. Most of these windmills can be found at high altitudes where there is a continuous wind speed of over 10 mph.
The advantages and limitations of wind energy are listed in the following table.

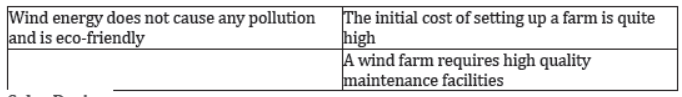
The advantages and limitations of wind energy are listed in the following table.
Solar Devices
We have studied about photosynthesis, a process in which plants absorb solar energy and convert it into chemical energy. Scientists too have developed technologies that enable us
to trap solar energy to produce heat energy or electricity.
Solar Energy
Let us understand the uses of solar energy through an animation.
the following devices help in production of solar energy:
1. Photovoltaic cells or solar cells. Such cells are made up of semiconductors that convert solar energy directly into electricity.
2. Solar cooker
3. Solar heater
How does a photovoltaic solar cell work?
Photovoltaic (PV) cells are made of special materials called semiconductors, such as silicon. When light strikes the solar cell, a certain portion of it is absorbed by the semiconductor material. This means that the energy of the absorbed light is transferred to the semiconductor.
This energy loosens the electrons from the atoms in the semiconductor material and allows them to flow freely. This produces direct current (DC) or electricity.

Working of a solar cooker:
This device is used for cooking food by harnessing solar energy. This device consists of a box made up of heat resistant material. The box is painted black on the inside for efficient absorption of solar radiations. It is covered with a lid of plane glass to allow retention of heat energy. A mirror is attached on the inner surface of the box.
When it is kept in the direction of sun’s rays, they fall on the mirror. The mirror reflects the sun rays inside the box which increases the temperature of the box, thereby cooking food placed inside the box.
Working of a solar water heater:
It consists of a copper pipe painted black on the outer surface and is curled in the form of a coil. The copper coil is fitted in a box. coiled copper pipe increases the surface area for
absorption of solar energy. A tank storing cold water is placed above the heater and another tank is connected to the heater for storage and supply of hot water.
The working of solar water heater is similar to that of solar cooker.
The advantages and disadvantages of solar energy are listed in the following table.

Current applications
Current applications
Solar energy is currently being used in the following ways:
- Some water heaters use solar panels.
- Calculators and many toys are powered by solar cells.
- Traffic signals in most cities are powered by solar energy.
- In some remote areas, the electricity requirements of households are fulfilled by generating electricity using solar energy.
Tidal Energy
Sea water is a highly potential resource of energy. Some forms of energy that can be obtained from sea water are tidal energy, wave energy, and ocean thermal energy.
Tidal Energy

Tides are the daily rise and fall of ocean levels relative to coastlines. They are a result of the gravitational forces of the moon and the sun on Earth, and also the revolution of the Earth.
A large amount of energy is stored in tides. They can be used as renewable sources of energy to generate electricity.
Tidal electricity generation involves the construction of a barrage across deltas, estuaries,beaches, or other places that witness increased tidal action.
How does it work?
The barrage (dam) allows incoming tidal water during high tides, but does not allow it to flow out. This causes water to accumulate at a higher level in the coastal basin. When the tide flows out, the level of water in the sea decreases, and the water which was blocked using the dam is released. The head of this water is then used to spin the turbine of the electric generator.

The barrage is equipped with sluices and turbines (similar to hydropower plants). Turbines generate electricity as the water flows out.
The vast potential energy of the seas and oceans can make a significant contribution toward meeting the increasing energy needs. Commercially viable technologies to harness
tidal power, wave power, and ocean thermal energy are therefore being developed.
The advantages and disadvantages of tidal energy are listed below.
Advantages
- It does not need any fuel
- Waves are predictable
- It is available free of cost
- It is relatively cheap and easy to maintain
- It produces no greenhouse gases or other polluting wastes
Disadvantages
- There are only limited sites that are suitable for constructing tidal barrages
- Shipping facility is affected due to the construction of barrages
- Construction of barrages causes changes in the level of tides, thereby resulting in floods
- Building a barrage across an estuary is a very expensive affair. It also affects a very wide area. This results in the loss of biodiversity in the particular area. Many birds rely on the uncovering of mud flats by tides for feeding
Wave energy
Ocean waves are caused by winds as they blow across the sea. Waves are a powerful source of energy. Electricity can also be produced from wave energy.
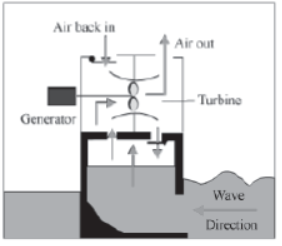
How is electricity produced from wave energy?
At a wave power station, waves cause the water in the chamber to rise and fall, which means that air is forced in and out of the hole located at the top of the chamber. A turbine placed in this hole is turned by the movement of air rushing in and out. The turbine turns a generator to produce electricity.
Advantages
- The energy is free – no fuel is needed, no waste is produced
- It is not expensive to operate and maintain
- A wave power station can produce a lot of energy
Disadvantages
- It needs a suitable site where waves are consistently strong
- It is less viable for commercial exploitation in comparison to other traditional forms of energy
- We are able to harness only a minuscule part of a potentially huge energy resource
Ocean thermal energy
Sunlight falls on oceans and seas. This causes the temperature of water on the surface to rise, while the temperature at the bottom remains comparatively cooler. Ocean thermal energy conversion plants use the warm surface-water to boil volatile liquids such as ammonia. Ammonia gas, thus produced, creates pressure and runs the turbine of the generator. This produces electricity. Cold water is pumped up to liquefy the gas. This creates a cycle for generating electricity.
Limitations
- Power plants can be operated only if there is a temperature difference of 20°C between the surface sea water and the sea water at a depth of up to 2 km
- Commercial exploitation is difficult
Geothermal Energy

Geothermal energy is the heat energy in the Earth’s interiors. The temperature at the centre of the Earth is about 6000°C. In some areas, molten rock (magma) is found very close to the surface of the Earth. This hot rock meets underground water and heats it up. This produces steam. Such a place is known as a hot spot. Sometimes, this heated underground water finds an outlet through which it comes out on the surface of the Earth. Such outlets are known as hot springs.
Holes are drilled down to the regions through which steam comes up. This flow of steam is used to drive the turbines of generators to produce electricity. One important use of geothermal energy is to heat buildings.
The advantages and disadvantages of geothermal energy are listed below.
Advantages
No fuel is needed
Once a geothermal power station is built, the energy is almost free
It does not produce any polluting emissions and does not contribute to the greenhouse effect
Since geothermal power stations are not very large, they have a minimal impact on the environment
Disadvantages
Geothermal energy is not commercially viable
Sometimes, a geothermal site may undergo depletion and may lose its heat. These geothermal sites then have to be left alone to help them recover their lost heat
Hot spots or regions that can generate this energy are limited
Hazardous gases and minerals may emerge, which may be difficult to dispose off Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy
In order to understand nuclear energy we should first understand nuclear fission reaction.
What is nuclear fission?
Do you know that the difference in mass (Δm) between the original nucleus and the product nuclei is converted into energy, E? The amount of energy produced is governed by Einstein’s equation,
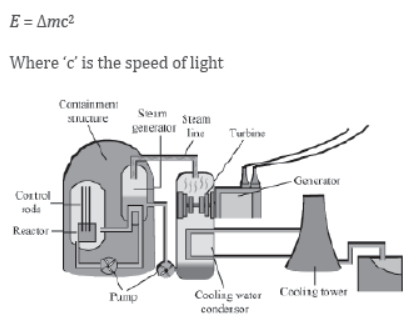
How is electricity produced in nuclear power plants?
Nuclear power plants consist of nuclear reactors. These reactors use uranium rods as fuel and heat is generated by the process of nuclear fission.
Neutrons smash into the nucleus of the uranium atoms, which roughly split into half and release energy in the form of heat.
Carbon dioxide gas is pumped through the reactor to take the heat away. The hot gas then heats water to form steam. This steam drives the turbines of generators to produce electricity.
Disadvantages of nuclear energy
- Construction of nuclear power plants needs huge investments
- Radioactive wastes such as used uranium are a dangerous hazard to the environment
- Nuclear energy can be used for negative purposes. Therefore, there is always a fear of misuse
- There is always a danger of leakage of radioactive material and radiations from nuclear power plants
Did you know that during World War II nuclear bombs were dropped on the twin cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan by America?
Handling and Disposal of Nuclear Wastes:
Radioactive materials pose a serious threat to mankind and hence their safe disposal is a necessity. The radiations emitted from radioactive materials can lead to mutation which result in alteration of DNA sequences. Exposure to such radiations can lead to certain types of cancer and various hereditary disorders.
Disposal of nuclear wastes requires special procedure. The radioactive material is impregnated into glass slabs, packed in strong steel containers and burried deep under the sea. It is burried deep under the sea so that radiations do not reach the level of biosphere.


