Please refer to the Atoms And Molecules Revision Notes given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 9th Science book. We have provided chapter wise Notes for Class 9 Science as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 3 Atoms And Molecules
Students of Class 9 Science will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 9 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Laws of Chemical Combination
A solution of sodium chloride and silver nitrate are taken separately in the two limbs of an ‘H’ shaped tube. The tube is sealed and weighed precisely. The two reactants are made to react by inverting the tube. The following reaction takes place. 3 (aq) AgNO3(aq) + NaCl (aq) • AgCl (s) + NaNO
The whole tube is kept undisturbed for sometime so that the reaction is complete.
When the tube is weighed again it is observed that:
Weight before the reaction = Weight after the reaction
Limitation of “Law of definite proportion”
This law does not hold good when the compound is obtained by using different isotopes of the combining elements .
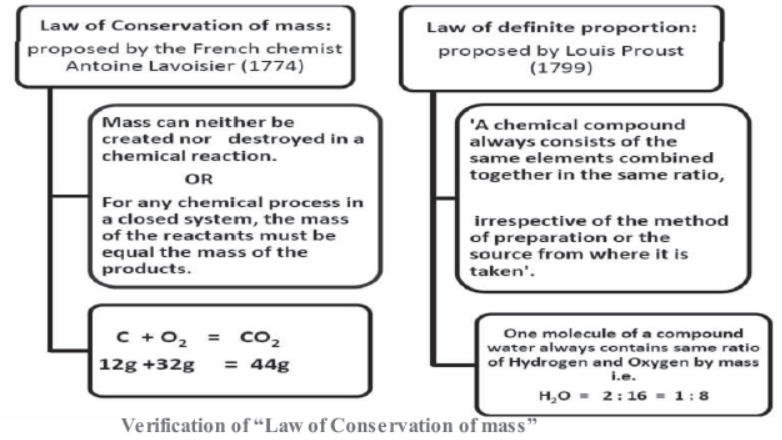
Law of Conservation of mass:
proposed by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier (1774)
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
For any chemical process in a closed system, the mass of the reactants must be equal the mass of the products.
C + O2 = CO212g +32g = 44g
John Daltons Atomic The ory
Using his theory, Dalton rationalized the various laws of chemical combination which were in existence at that time. However, he assumed that the simplest compound of two elements
a) Each element is made up of extremely small particles called atoms.
b) Atoms of a given element are identical in chemical properties but have different
physical properties.
c) Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed.
d) Compounds are formed by the chemical union of atoms of two or more elements in fixed proportion.
Atoms ,Mole cule s , Ions Chemical Formula

• Molecules of element : The molecules of an element are constituted by the same type of atoms.
• Molecules of compound: Atoms of different elements join together in definite proportions to form molecules of compounds.(hetero atomic molecules)
• Atomicity : The number of atoms contained in a molecule of a substance (element or compound) is called its atomicity.

• Based upon atomicity molecules can be classified as follows.
Monoatomic molecules: Noble gases helium, neon and argon exist as He Ne and Ar respectively.
Diatomic molecules: H2 , O2, N2,Cl2, CO , HCl .
Triatomic molecules: O3 ,CO2 , NO2.
• SYMBOLS</p>
• The abbreviation used to represent an element is generally the first letter in capital of the English name of element.
capital of the English name of element.
Oxygen • O Nitrogen • N
• When the names of two or more elements begin with the same initial letter, the initial letter followed by the letter appearing later in the name is used to symbolize the element Barium
• Ba Bismuth • Bi
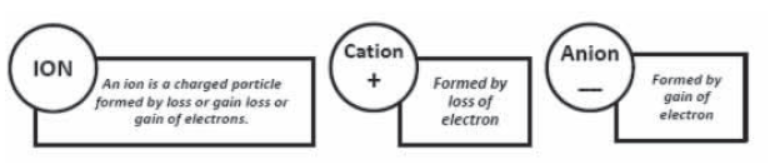
Polyatomic Ion : A group of atoms carrying a charge is as polyatomic ion.
eg: NH4+ – Ammonium Ion ; CO32- Carbonate ion
Valency :The number of electrons which an atom can lose , gain or share to form a bond.
It is the combining capacity of an atom of the element.
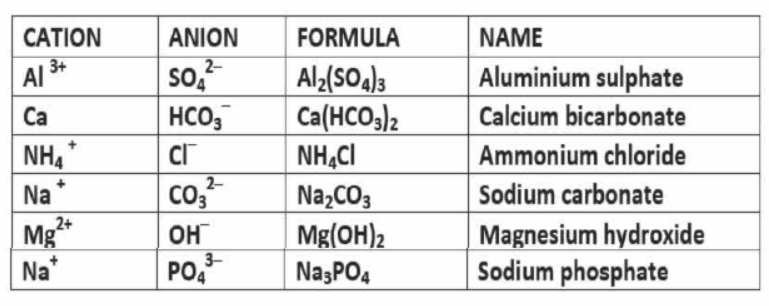
• Chemical Formula: A chemical formula is a short method of representing chemical elements and compounds.
Writing a Chemical Formula -CRISS-CROSS rule

RULE 4 > When there are multiple numbers of an individual polyatomic ion , parentheses must be used to separate the polyatomic ion from the subscirpt.
Ex. Ammonium Sulphate- – NH4 1+ SO42-……. (NH4)2 SO4
EXAMPLES
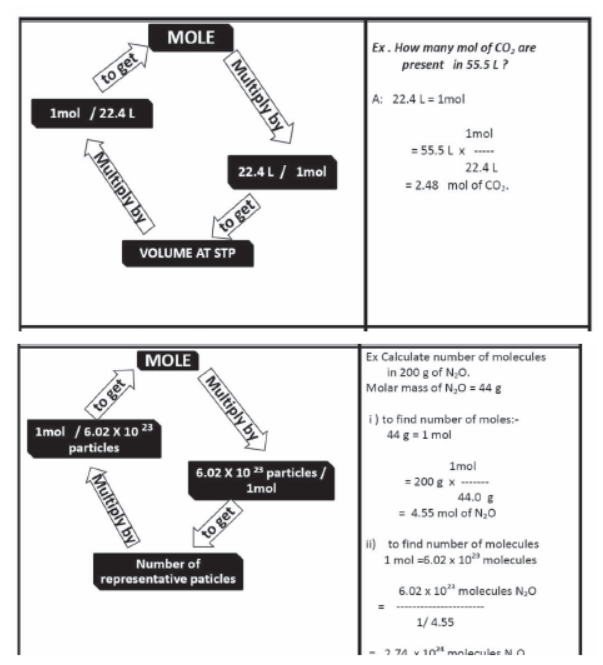
Mole Concept
The mole (mol) is the amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 12.00 grams of 12C
The Avogadro constant is named after the early nineteenth century Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro.
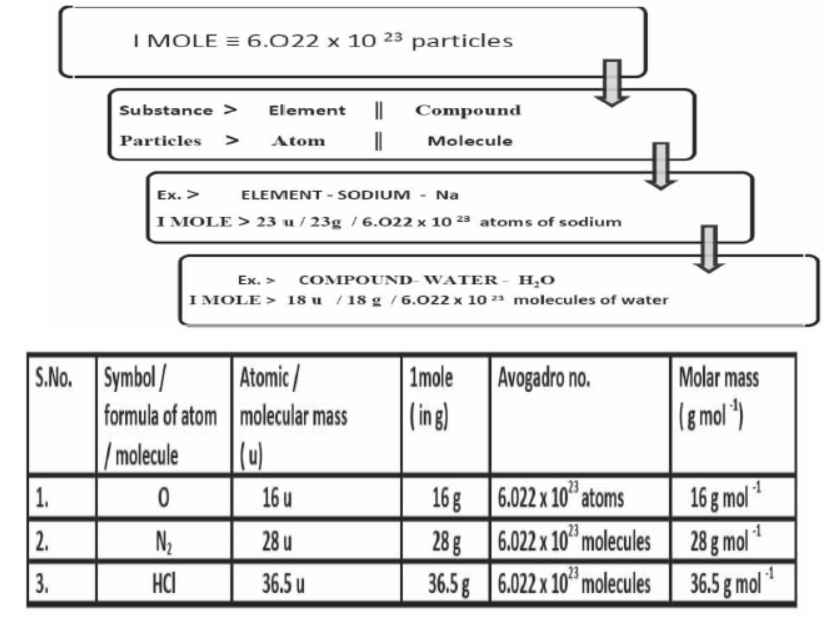
Gram Molecular mass
Gram molecular mass is the mass in grams of one mole of a molecular substance. Ex: The molecular mass of N2 is so the gram molecular mass of N2 is 28 g.
Atomic mass unit
An atomic mass unit or amu is one twelfth of the mass of an unbound atom of carbon-12. It is a unit of mass used to express atomic masses and molecular masses.
Also Known As: Unified Atomic Mass Unit
Molecular Mass : A number equal to the sum of the atomic masses of the atoms in a molecule.
The molecular mass gives the mass of a molecule relative to that of the 12C atom, which is taken to have a mass of 12.
Examples: The molecular mass of C2H6 is approximately 30 or [(2 x 12) + (6 x 1)] . Therefore the molecule is about 2.5
times as heavy as the 12C atom or about the same mass as the NO atom with a molecular mass of 30 or (14+16) .
Molar Mass & Avogadro Constant