Please see Private Public and Global Enterprises Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books for Class 11 Business Studies issues by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should revise these notes for Chapter 3 Private Public and Global Enterprises daily and also prior to examinations for understanding all topics and to get better marks in exams. We have provided Class 11 Business Studies Notes for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 3 Private Public and Global Enterprises Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes
Life is a unique, complex organization of molecules, expressing through chemical reactions which lead to growth, development, responsiveness, adaptation & reproduction.
Private, Public and Global Enterprises
Since the Indian economy consists of both privately owned and government owned business enterprises, it is known as a mixed economy.

Private sector Enterprises
It consist of business owned by individuals or a group of individuals whose main objective is to earn profit and growth of business. For example Reliance Industries limited, ITC limited, HDFC Bank limited etc.
Public sector Enterprises
It consists of various organization owned, managed and controlled by central or state of by both government. For example- Indian Railway, Indian Post, Doordarshan, Bharat Heavy electricals Limited (BHEL) etc. Its main objective is public welfare or service.
FORMS OF PUBLIC ENTERPRISES
1. Department Undertaking
These are established as departments of the ministry and are financed, managed and controlled by either central govt. or state govt. or jointly by both. For examples-Indian Railways, Post & Telegraph, Doordarshan, Prasar Bharti.
Features
1) It is establish as department of concerned ministry under central of State Govt.
2) No Separate Entity :- It has no Separate legal entity.
3) Finance :- It is financed by annual budget allocation of the govt. and all its earnings go to govt. treasury.
4) Accounting & audit :- The Govt. rules relating to audit & accounting are applicable to it.
5) Staffing :- Its employees are govt. employees & are recruited & appointed as per govt. rules.
6) Accountability :- These are accountable to the concerned ministry.
Merits
1) It is more effective in achieving the objective laid down by govt. as it is under the direct control of govt.
2) It is a source of govt. income as its revenue goes to govt. treasury.
3) It is accountable to parliament for all its actions which ensures proper utilization of funds.
4) Due to budgetary, Accounting and audit controls, risk of misuse of public funds is less
5) It is suitable for activities where secrecy and strict control is require like defence production.
Demerits
1) It Lacks flexibility which is essential for smooth operation of business.
2) It suffers from political interference in their day to day working.
3) It suffers from red tapism in day to day work and any required action is taken after completion of proper process.
4) These organization are usually insensitive to consumer needs due to absence of competition and monopoly.
5) Such organization are managed by civil servants and govt. officials who may not have the necessary expertise and experience in management.
Suitability :-
1) Where full Govt. control is needed.
2) Where secrecy is very important such as defence Industry.
Box -1

Statutory Corporations
It is established under a special Act Passed in parliament or state legislative assembly. Its objectives, powers and functions are clearly defined in teh special Act.
Examples :- Unit Trust of India. Life Insurance Corporation, GAIL, SCI, FCI
Features
1. It is established under a special act which defines its objects, powers and functions.
2. It has a separate legal entity.
3. Its management is vested in a Board of directors appointed or nominated by government. There is no govt. interference in day to day functioning.
4. It has its own staff, recruited and appointed as per the provisions of act.
5. Its initial capital is provided by the govt.This type of enterprise is usually independently financed. It obtains funds by borrowing from govt. or form public or through earnings.
6. It is not subject to same accounting & audit rules which are applicable to govt. department.
Merits
1. Internal Autonomy :- It enjoys a good deal of autonomy in its day to day operations and if free from political interference.
2. Quick decision :- It can take prompt decisions and quick actions as it is tree from the prohibitory rules or govt.
3. Parliaments control :- Their performance is subject to discussion in parliament which ensures proper use of public money.
4. Efficient Management :- These are Independent in recruitment and selection of their employees and Professionals. Experience and specialists are appointed on important posts.
Demerits
1. In reality, there is not much operational flexibility. It suffers form lot of political interference from minister, Govt. officials and political parties.
2. Usually they enjoy monopoly in their field and do not have profit motive due to which their working times out to be inefficient.
3. Where there is dealing with public, rampant occupation exists.
Thus public corp. is suitable for undertaking requiring monopoly powers e.g. public utilizes.
Suitability : Public enterprise is suitable when :–
i) The enterprise requires special powers under on Act.
ii) The enterprise requires a huge amount of capital investment.
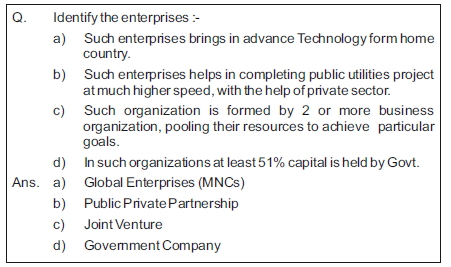
Government Company
A Government company is a company in which not less than 51% of the paid up share capital is held by teh central govt. or state Govt. or jointly by both. It is registered as per company act, 1956.
Examples :- State Trading Corp. of India, Hindustan Machines Tools.
Features
1. It is registered of Incorporated under companies Act, 1956
2. It has a separate legal entity.
3. Govt. has minimum 51% of paid up capital.
4. It is managed by board of director selected by Govt. and other shareholders.
5. Employees are recruited and appointed as per the rules and regulations contained in its Memorandum and Articles or Association.
6. The Govt. Co. obtains funds from govt. shareholdings and other private shareholdings. It can also funds form capital market.
Merits
1. It can be easily formed as per the prevision of companies Act.There is no need to pass special act in the parliament.
2. It enjoys full autonomy in management decisions and flexibility in day to day working.
3. It can appoint professional managers on high salaries.
Limitations
1. It suffers from interference from Govt. Official, ministers and politicians.
2. It evades constitutional responsibility which a company financed by the govt. should have, as it is not directly answerable to parliament.
3. The board usually consists of the politicians and civil servants who are interested more in pleasing their political bosses than in efficient operation of the company.
SUITABILITY :
i) Where the Govt. want to work along with private sector.
ii) Where projects need govt. planing and funds.
Box 2

Changing role of Public Sector
Public sector in India was created to achieve two types of objective-
(1) to speed up the economic growth of the country and
(2) to achieve a more equitable distribution of income and wealth among different sections of society.
The role and importance of public sector in the society has been changing with time. Its role in the development of the country over a period of time can be summarized as following :-
1. Development of Infrastructure :- At the time of Independence, India suffered from acute shortage of heavy industries such as transport, communication, Electricity,Generation, iron and Steel, oil refineries, heavy engineering etc. Because of huge investment requirement and long gestation period, private sector was not willing to enter these areas. The duty of development of basic infrastructure was assigned to public sector which it discharged quite efficiently.
2. Regional Balance :- Earlier private sector was hesitant to establish industries in backward or remote areas due to lack of infrastructure. To provide employment to the people and to accurate the economic development of backward areas, many new industries were set up by Govt. in these areas.
3. Economies of scale :- In certain industries (like Eclectic power plants. natural gas, petroleum etc.) huge capital and large base are required to function economically. Such areas were taken up by public sector.
4. Restricting Economics Concentration :- Only few industrial houses in private sector had invested at large scale, resulting in concentration of capital in few hands. As a result, monopoly increased and leads to inequality of income. To stop such practices, industries were established in public sector so that large scale division of income and money among workers and labour is done.
5. Import Substitution :- Firstly Public Enterprises were established in production of capital equipments which were earlier imported from other countries. And several enterprises were also established to promote export of goods. It increase the foreign currency reserves a lot. Very important role was assigned to public sector but is performance was far from satisfactory which forced govt. to do rethinking on public enterprises.
Public Sector Reforms
In the industrial policy 1991, the govt, of India introduced four major reforms in public sector.
i) Reduction in No. of Business reserved for public Sector from 17 to 8 and to 3 only in 2001. These three industries are atomic energy, arms and rail transport.
ii) Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) :- Under this public sector was provided with greater autonomy govt. lays down performance target for the management and gives
greater autonomy these units to hold the management accountable for the results.
iii) Disinvestment :- Equity Shares of some public sector enterprises were sold to private sector and the public. It was expected that this would lead to improved managerial performance and better financial discipline.
iv) Re- structural and Revival :- All public sector sick units were referred to Board of Industrial and financial REConstruction (BIFR). Units which were potentially viable were restructured and which could not be reviewed were closed down by the board.
Multinational Companies/Global Enterprises
Multinational company may be defined of a company that has business operation in several countries by having its factories,branches or office in those countries. But it has its headquarter in that country where it is incorporated. Examples :- Coca Cola, Sony, Reebok etc.
Features
1. Huge capital Resources :- MNCs posses huge capital resources and they are able to raise lot of funds from various sources.
2. International Operations :- MNS do business in several countries. For this it has business, factories and offices in several countries.
3. Centralized control:- MNCs have headquarters in their home countries from where they exercise control over all branches and subsidiaries. and there is no interference their day to day operations.
4. Foreign Collaboration:- Usually they enter- into agreements relating to sale of technology, production of goods, use of brand name etc. with local firms in the host country.
5. Advanced technology :- These organisations possess advanced and superior technology which enable them to provide world class products & services.
6. Product Innovations:- MNCs have highly sophisticated research and development departments. These are engaged in developing new products and superior design of existing products.
7. Marketing Strategic – MNCs use aggressive marketing strategies. Their brands are well known and spend huge amounts on advertising and sale promotion.
JOINT VENTURES
Meaning :- When two or more independent firms together establish a new enterprise by pooling their capital, technology and expertise, it is known as a joint venture.
Example :- Hero Cycle of India and Honda Motors Co. of Japan jointly established Hero Honda. Similarly Suzuki Motors of Japan and Maruti of Govt. of India come together to form Maruti Udyog.
FEATURES
1. Capital is provided jointly by the Government and Private Sector Entrepreneurs.
2. Management may be entrusted to the private entrepreneurs.
3. It combines both social and profit objectives.
4. It is responsible to the Government and the private investors.
BENEFITS
1. Greater resources and Capacity :- In a joint venture the resources and capacity of two or more firms are combined which enables it to grow quickly and efficiently.
2. Access to advanced technology :- It provides access to advanced techniques of production which increases efficiency and then helps in reduction in cost and improvement in quality of product.
3. Access to New Markets and distribution network :- A foreign co. gain access to the vast Indian market by entering into a joint venture with Indian Co. It can also take advantage of the well established distribution system of local firms.
4. Innovation :- Foreign partners in joint ventures have the idea and technology to develop innovative products and service. As a result, new products and their new uses come in the market.
5. Low cost of production :- Raw material and labour are comparatively cheap in developing countries so if one partner is form developing country they can be benefitted by the low cost of production.
6. Well known Brand Names :- When one party has well established brands & goodwill, the other party gets its benefits. New products of such brands names can be easily launched in the market.
7. Division of Risk :- Inherent risk of new project get divided among partners of joint venture and it also increases the competitive powers of small firms.
Public Private Partnership (PPP)
It means an enterprise in which a project or service is finance and operated through a partnership of public and private enterprise.PPP is a long term partnership between public and private sector. PPP model is being used in following areas :-
1) Transport – Rad, Railway and Toll Bridge
2) Health – Hospital
3) Water – Collecting, Cleaning and Distributing
4) Education – School and University
Features of PPP
1. Facilities partnership between public sector and private sector.
2. Pertaining high priority project.
3. Suitable for big project (Capital intensive and heavy industries.)
4. Useful in public welfare projects example Delhi Metro Railway Corporation.
5. Sharing revenue – Revenue is shared between public and private enterprises in the agreed Ratio.
Box 3
Points to be remembered
1. Private Sector’s Business are owned by private individuals or groups — Reliance Industries, Airtel, LG, Samsung.
2. Public Sector Business are owned by the State.
3. When two or more companies agree to run a business for specific purpose, it is called joint venture.
4. Departmental undertakings are run as a part of govt. dept under the direction of the minister concerned.
5. Public corporation is created by a Special Act of Parliament or State Legislature.
6. Govt. Company is a Public Enterprises which has a minimum 51% of the paid up capital in the name of the Central Govt. or State Govt.
7. MNC’s are those companies which run in more than one Country.
8. PPP — Public Private Partnership — refers to the investment of private sector in the govt. projects aimed at Public Benefit.
MCQ’s
1. LIC is the example of —
(I) Departmental undertaking
(ii) Statutory corporation
(iii) Govt. Company
(iv) Private company
2. Which of the following is govt. company —
(I) Hindustan Steel Ltd.
(ii) Tata Steel Ltd.
(iii) Jindal Steel Ltd.
(iv) All the above
3. Which of the following is related to a specific ministry?
(I) Indian Railway
(ii) FCI
(iii) Coal India
(iv) BHEL
4. Which of the following is not a MNC?
(I) Ranbaxy
(ii) Infosys
(iii) Brook Bond
(iv) Asian Paint
5. Who works to uplift the sick industries of Public Sector?
(i) MOFA
(ii) MOU
(iii) BIFR
(iv) NRF
6. Govt. holds minimum __________ paid up Capital of a govt. company.
(i) 49%
(ii) 50%
(iii) 51%
(iv) 26%
7. When two business enterprises work together for a particular purpose that is called —
(I) Partnership
(ii) Joint venture
(iii) Company
(iv) Joint Hindu Family Business
8. Which of the following is created by Special Act of Parliament or State Legislature?
(i) Departmental Undertaking
(ii) Statutory Corporation
(iii) Govt. company
(iv) Private company
9. Which has not seperate Legal Entity?
(i) Departmental Undertaking
(ii) Statutory Corporation
(iii) Govt. company
(iv) Private company
10. How many industries are reserved for public sector?
(i) 3
(ii) 4
(iii) 8
(iv) 17
Answer the following in one or two words :-
1. Write the name of a govt. company?
2. ‘Toyota Motors’ is a company of which country?
3. When private sector involves in public sector for public benefit then it is called?
4. What is main objective of a private company?
5. Write the name of a bank of public sector.
6. What percentage of capital held by govt. in govt. company?
7. Write the name of two MNC’s.
8. FCI is an example of ________ form of public enterprises
9. Write one drawback of govt. company.
10. Who is the owner of public sector enterprises?
Very Short Answer Question (1 Mark)
1. Name the type of business enterprise which operates in more than one country.
2. Which type of organization is most suitable if it is concerned with National Security and public interest.
3. Atomic Energy is one of the three sectors that are reserved for public sector in spite of its huge potential for electricity production. Give one reason.
4. Which type of business enterprise would emerge when two business firms agree to join together to achieve a common purpose and mutual benefit.
5. Mention any two objective of public sector enterprises.
Short Answer Questions (3/4 Marks)
1. Explain any three features of Public Private Partnership.
2. How does the govt. maintain regional balance in the country.
3. Identify the form of public sector enterprise in the following cases:-
(a) This is the oldest and traditional form of public enterprise.
(b) Special act of the parliament brings this public enterprise into existence.
(c) Minimum 51% of the paid up capital is held by Government.
4. Explain three differences between Departmental undertakings and Government Company.
Long Answer Questions (5/6 Marks)
1. Define Joint Venture and explain its major benefits.
2. It is a public enterprise established under Indian Companies Act and conducts business in competition with companies in private sector.
(a) Identify the type of public enterprise.
(b) What is the minimum investment Govt. has to make in such companies.
(c) In whose name shares of this type of company are purchased.
(d) Explain any two advantages and limitations of such companies.
3. Explain three merits and three limitations of Departmental undertaking.
4. Multinational companies establish themselves in developing countries to enjoy huge profits by selling consumer goods or luxury items. They start business by offering wide variety of good at prices cheaper than local retailers offer. But once they are established they increase prices.
a) State the values the government of a developing country ignores while allowing MNC’s to establish in their country.
b) Which values do the MNC’s Violate ?
5. After 1991, government wanted to speed up the infrastructure development that required huge investment & expertise. In the coming years, govt. devised a new way for it in which
public sector enterprises, through clear agreements. Like Terminal 3 of Indira Gandhi International Airport.
i) What such agreement/arrangements are called ?
ii) Write any 3 advantages of such arrangements.
[Hints : Public Private Partnership]
6. It is are enterprises which is organized, financed and controlled wholly by the centre 4 state Govt. and it is under the control of its head Mrs. Jeevan Raj (IAS). He is not taking any interest in its functioning of providing cheap clean water to a large section of the society as he is busy in the preparation of his son’s marriage coming after 3 months. As a result, important decisions are getting delayed resulting in the suffering of revenue and well being of public, as it required the consent of its head.
a) Which type of organization has been described in the above para ?
b) What social values are achieved by govt, through such organization.
c) What are the limitations of such organization in this case.
[Hints : Departmental Undertaking]
7. It is a public sector enterprises in which Govt. of India held 80% of paid up share capital and it is registered as per company Act,1956. It deals in manufacturing of Engineering goods and compete with private sector enterprises in order to achieve higher profits.
i) Which type of public sector enterprise is discusses above.
ii) Do the employees of such organization considered as Civil Employees ?
iii) Write any two characteristics of such organization.
iv) Write any two limitations of such organization.
[Hints : Government Company ]
8. Food Corporation of India (FCI) was established through special Act. passed in Parliament in 1964 with the objective to create buffer stocks of foods like wheat, rice etc. for emergency situations like drought, flood famine etc.
i) Which type of public sector enterprise is discussed above ?
ii) Does such enterprises have separate legal entity ?
iii) Who provided initial capital to such enterprises ?
iv) Write any 2 demerits of such organization.
[Hints : Stationary Corporation]



