Please refer to the Yoga Revision Notes given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 11th Physical Education book. We have provided chapter wise Notes for Class 11 Physical Education as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 4 Yoga
Students of Class 11 Physical Education will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 11 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Meaning and Importance of Yoga:
Meaning: The term ‘yoga’ is derived from a Sanskrit word ‘Yuj’ which means join or union.
In fact, joining the individual self with the divine or universal spirit is called yoga.
Patanjali: ‘Checking the impulses of mind is Yoga.’
Mahrishi Ved Vyas: ‘Yoga is attaining trance.’
In Bhagwat Gita, Lord Krishna says, “Skill in actions or efficiency alone is yoga.”

Yoga as on Indian Heritage: History of yoga is as old as the history of Indian culture.
Although, there is no written proof in this regard. Yoga is known as the heritage of India only should go through the related periods of history.

Elements of yoga: Around 147 BC, Patanjali developed a system of yoga that contains Eight steps also known as ‘Astanga Yoga.
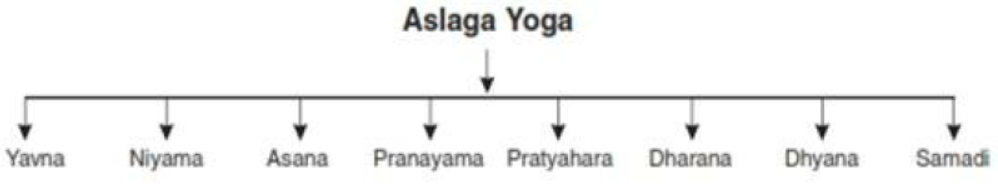
Introduction to Asanas, Pranayama, Mediation and yogic Kriyas :
Asanas: Asana is ‘to be seated in a position that is firm and relaxed’ for extended periods.
Pranayama: Pranayam means extension of the breath of extension of the life force. ‘Prana’ means life force and ‘Ayama’ means control. There are three parts of Pranayama:
1. Purka – Means inhalation
2. Rechaka – Means exhalation
3. Kumbhaka – Means retaining the breath
Types of Pranayam: Suryabhedi, Ujjayi, Sheetkari, Sheetle, Bhastrika, Bhramari, Plavini, Moorchha etc.
Meditation: Meditation: means concentration of mind, resulting in Samadhi.
Yogic Kriya: Yogic Kriya are cleansing techniques that cleanses various internal as well as external organs of the body. There are six yogic kriyas also known as ‘Khsatkarm Kriyas’.
1. Neti
2. Dhayti Kriya
3. Basti Kriya
4. Kapalabhati Kriya
5.Trataka Kriya
6. Nauli Kriya
Body related benefits of Asana and Pranayam: Improves concentration power, correct body posture, Rehabilitation of injuries, Increases flexibility, Improves breathing system, Improves function of heart, Improves digestive system, Improve overall health, Improves coordination of function between neurology and muscles.
Prevention and Management of common Lifestyle diseases: obesity, Diabetes,
Obesity: Obesity is a medical condition when the body of a person contains 20% or more fat as compared to ideal weight.
Weight in Kg.
According to WHO, the BMI =————————————
(Height in Mtv)2
| Classification | BMI |
| Underweight | <18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 – 24.9 |
| Over Weight | 25.0 – 29.9 |
| Class I Obesity | 30.0 – 34.9 |
| Class II Obesity | 35.0 – 39.9 |
| Class III Obesity | ≥ 40.0 |
Diabetes: Diabetes is a metabolism disorder in which the person has high blood glucose may be either due to inadequate production of insulin or the body cells do not respond properly to the insulin produced by the pancreas. There are two types of diabetes.
1. Type I diabetes: In this type of diabetes, the body does not produce insulin.
2. Type II diabetes: In this stage of diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin for proper functioning of the cells in the body and do not react to insulin.
Hypertension: High blood pressure or hypertension means high pressure in arteries. It is measured in mm/Hg.

Back pain: Back pain is a pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine. Main causes of back pain are lack of physical activities, lack of flexibility, smoking, excessive pressure on back etc.



