Please refer to Market Equilibrium Class 12 Economics Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 12 Economics based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 12 Economics for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 12.
Class 12 Economics Important Questions Market Equilibrium
MCQs
Question. When a firm’s TR>>TC, it cannot cover its normal profit
a) False
b) Can’t say
c) TRUE
d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. A firm maximizes its profits only when MR=MC
a) False
b) None of these
c) True
d) Cannot say
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is price taker firm?
Answer : Price taker firm is one who has no option but to accept the price determined by the industry.
Question. An individual firm under perfect competition cannot influence the market price, then who can and how?
Answer : Under perfect competition, the industry can influence market price by raising or lowering output.
Question. What are advertisement costs?
Answer : Advertisement cost are the expenditure incurred by a firm for the promotion of its sales such as publicity through TV, Radio, Newspaper, Magazine etc.
Question. What do you mean by abnormal profits?
Answer : It is a situation for the firm when TR > TC.
Question. What are selling cost?
Answer : Cost incurred by a firm for the promotion of sale is known as selling cost.
Question. What do you mean by patent rights?
Answer : Patent rights is an exclusive right or license granted to a company to produce a particular output under a specific technology.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain two features of monopoly market.
Answer : The important two features of monopoly market is as follows:
1. There is only one single seller in the market so that the seller can influence the market price on its own.
2. There are entry barriers of new firms, this enables seller to get abnormal profits which is much more above normal profits.
Question. Explain the implicaions of large buyer in a perfectly competitive market?
Answer : Large numbe r of buyers are assumed to be so large that an individual buyer’s share in total purchases is so negligible that he cannot influence the market price on its own by purchasing more or less. The outcome is that price remains unchanged.
Question. Explain briefly why a firm under perfect competition is a price taker not a price maker?
Answer : A firm under perfect competition is a price taker not a price maker because the price is determined by the market forces of demand of supply. This price is known as equilibrium price. All the firms in the industry have to sell their outputs at this equilibrium price. The reason is that, number of firms under perfect competition is so large. So no firm can influence the price by its supply. All firms produce homogeneous product.
Long Answer Type Questions
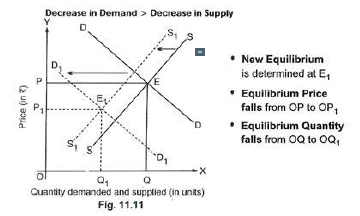
Question. Market for a good is in an equilibrium. There is simultaneous decrease both in demand and supply, but there is no change in the market price. Explain with the help of diagram, how it is possible.
Answer : When there is decrease in demand is more than decrease in supply, then there is no change in the market price. When decrease in demand is proportionately more than decrease in supply, then leftward shift in demand curve from DD to D1D1 is proportionately more than leftward shift in supply curve from SS to S1S1. The new equilibrium is determined at E1, equilibrium price falls from OP to OP1 and equilibrium quantity falls from OQ to OQ1.
Question. How a fall in the price of tea will affects an equilibrium price of coffee? Explain the chain effects.
Answer : With a fall in price of tea, the demand of coffee that is substitute of tea decreases. As a result, demand curve of coffee shifts to the left. Accordingly, an equilibrium price would tend to decrease and also an equilibrium quantity tends to decrease.
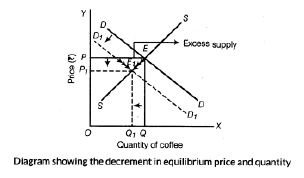
The figure shows a situation of decrease in demand. The demand curve shifts to left side. Consequently, equilibrium price and quantity, both are decreasing from OP to OP1 and OQ to OQ1.


