Please see Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science Revision Notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books for Class 10 Social Science issues by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should revise these notes for Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries daily and also prior to examinations for understanding all topics and to get better marks in exams. We have provided Class 10 Social Science Notes for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science Revision Notes
1. Manufacturing is production of goods in large quantities after processing raw materials to more valuable products.
2. Classification of Industries is done on the basis of their Main Role, Capital Investment, Ownership, source of Raw Materials and the bulk and weight of raw material and Finished Goods.
3. Large Scale Industries employ a large number of labourers.
4. Small Scale Industries employ a small number of labourers.
5. Heavy Industries use heavy and bulky raw materials.
6. Light Industries use light raw materials.
7. Manufacturing is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular.
8. The NMCC (National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council) was set up when it was felt that, with appropriate policy interventions by the government and renewed efforts by the industry to improve productivity, manufacturing can achieve its target over the next decade.
9. Industrial locations are influenced by availability of raw materials, labour, capital, power and market. It is rarely possible to find all these factors available at one place.
10. Agro-based industries: – Industries based on agricultural raw materials. For example, Cotton Textiles, Jute Textiles, Woollen Textiles, Silk Textiles, Synthetic Textiles, Sugar Industry.
11. Cotton textiles: – It occupies a unique position in Indian economy, contributes 14% of industrial production. Provides employment to 35 million persons directly. Earlier the Cotton textile industries were located in Maharashtra and Gujarat. Today, they are spread over 80 towns and cities of India. Scarcity of good-quality Cotton, obsolete machinery, erratic power supply, low productivity of labour and stiff competition are some of the problems faced by the Cotton textiles industry.
12. Jute textiles: – There are about 70 Jute mills in India and most of the Jute is produced in West Bengal Mainly in the Hugli basin produced in Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Assam and Tripura.
13. Sugar: – There are 460 Sugar mills in the country. 50% of them are found in Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra. Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat are also important producers of Sugar in the country.
14. Mineral-based Industries: – Industries using minerals as their raw materials — Iron and Steel, Cement, Chemical Industries, Aluminium Smelting, Copper Smelting, Fertiliser Industry, etc.
Iron and Steel Industry :-
(i) The Iron works of Kulti, Burnpur started local production in 1870.
(ii) The first modern Steel plant was set up at Jamshedpur in 1907.
(iii) Today there are 10 primary integrated iron and Steel plants and around 200 mini Steel plants in the country.
(iv) Raw materials used in this industry are Iron Ore, Coal, Limestone and Manganese Ore.
(v) The location of this industry is decided by the availability of raw materials. All the important Iron and Steel plants are located in the North-Eastern and Southern parts of the Indian Peninsula.
(vi) Only Visakhapatnam has a coastal location.
(vii) These plants are managed by the Steel Authority of India Ltd. (SAIL)
(viii) India produces about 32.8 million tonne of Steel and ranks ninth among the world crude Steel producers.
Aluminium Smelting: –
(i) Aluminium is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
(ii) It is used as a substitute of Steel, Copper, Zinc and Lead.
(iii) In the production of one tonne of Aluminium, 6 tonnes of Bauxite and 18,600 kWh of electricity is required.
(iv) The availability of electricity and Bauxite decides the location of this industry.
(v) The 8 Aluminium plants in the country are located in Orissa, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
(vi) India produces over 600 million tonnes of aluminium per annum.
Chemical Industry:-
(i) Heavy inorganic chemicals include Sulphuric Acid, Nitric Acid, Alkalis, Caustic Soda and Soda ash. They are widely spread around the country. Sulphuric Acid is used in the manufacture of Fertilisers, Synthetic Fibres, Plastics, Paints and Dyes. Soda ash is used in the manufacture of Glass, Paper, Soap and Detergents.
(ii) Heavy organic chemicals include Petrochemicals which are used in the manufacture of Synthetic Fibres, Synthetic Rubber, Plastics, Dyestuffs, Drugs and Pharmaceuticals. These chemical plants are located near Oil refineries and Petrochemical plants.
(iii) The chemical industries contribute 14% of the production of entire manufacturing sector.
Fertiliser Industry:-
(i) The first plant was set up at Ranipet in Tamil Nadu.
(ii) With the setting up of a plant at Sindri by the Fertiliser Corporation of India (FCI) in 1951, the production of fertilisers increased.
(iii) With the onset of the Green Revolution, this industry was set up in Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab and Kerala.
(iv) Other important producers are Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, Rajasthan, Bihar, Maharashtra, Assam, West Bengal, Goa, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
(v) There are 57 fertiliser units manufacturing Nitrogenous Fertilisers, 29 for Urea and 9 for Ammonium Sulphate as a byproduct, 68 other small units produce single super phosphate.
Cement Industry: –
(i) Cement is used for the construction of buildings, houses, factories, roads and dams.
(ii) The raw materials used are Limestone, Silica, Alumina and Gypsum, Coal and Electric power are also used.
(iii) The first Cement plant was set up at Chennai in 1904. At present, there are 119 large and over 300 mini Cement plants in India.
(iv) Indian Cement is in great demand in South and East Asia, Middle East and Africa because of its superior quality.
15. Automobiles: – Commercial vehicles like trucks, passenger buses, cars, motor cycles, scooters, etc., are manufactured in large numbers. India is the second largest producer of three wheelers. The industries producing bicycles, scooters and bicycles are distributed around Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Indore, Hyderabad, Jamshedpur and Bengaluru.
16. Electronic Industry: – Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India. Other major electronicgoods producing centres are Hyderabad, Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kanpur, Pune, Lucknow andCoimbatore. Many Software Technology Parks have also developed.
17. Industries create four types of pollution, namely air, water, land and noise.
18. Air pollution is caused due to the presence of Carbon Monoxide and Sulphur Dioxide. Dust, fume, mistspray and smoke contain both types of particles.
19. Water pollution:- Coal, Dyes, Soaps, Pesticides, Fertilisers, Plastics and Rubber are some commonpollutants. The principal industries which create water pollution are Paper,Pulp, Textiles, Chemical,Petroleum, Refinery, Tannery and Electroplating.
20. Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot-water from factories and thermal plants is drained into riversand ponds before cooling.
21. Noise pollution means unwanted, extra, noise created due to industrial machineries etc.
22. Measures to Control Environmental Degradation: –
(1) Proper fuel selection and utilisation.
(2) Useof oil instead of coal in the industries.
(3) Treatment of liquids in three phases: –
(i) Primary treatment bymechanical process.
(ii) Secondary treatment by biological process.
(iii) Tertiary treatment by biological,chemical and physical processes.
(4) Pollution of land and soil can be controlled by three activities: –
(i)Collection of wastes from different places.
(ii) Dumping and disposing the wastes by land-filling.
(iii) Recycling of wastes for further use.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name two most important sugar producing states of India.
Answer : Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Question. Why is iron and steel industry called a basic industry?
Answer : Iron and steel industry is called the basic industry because:
(i) It is the industry which lays the foundation of rapid development of other industries such as heavy Engineering, defence equipment, automobiles, aeroplanes etc.
(ii) It is also helpful in providing employment.
(iii) It also helps in the development of agriculture.
Question. Write any two human inputs that control location of industries.
Answer : Human inputs that control location of industries are:
1. Labour
2. Market
Question. How would you classify industries on the bases of their main role?
Answer : Industries can be classified under the following categories on the basis of their main role:
1. Basic and Key Industries: Basic and key industries which supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other products. Example: Iron and steel industry, copper smelting and aluminum smelting.
2. Consumer Industries: Consumer Industries that produce goods for direct use by consumers.
Example: Sugar, Toothpaste, paper, sewing machines and fans etc.
Question. What are various types of industrial pollution.
Answer : 1. Air pollution.
2. River water pollution.
3. Underground water pollution.
4. Noise pollution.
5. Soil pollution
Question. Write any two physical factors that affect location of industries.
Answer : The factors are
a. Availability of raw materials.
b. Power resources
Question. Highlights the features of National jute policy of India.
Answer : 1. National Jute Policy of India was formed in the year 2005 by the central Government of India.
2. Government made a policy to mandatory use of Jute packaging.
Question. Cotton textile industry has close links with agriculture. Explain.
Answer : The industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton bull pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing.
Question. Read the data in the table given below and answer the questions that follow:
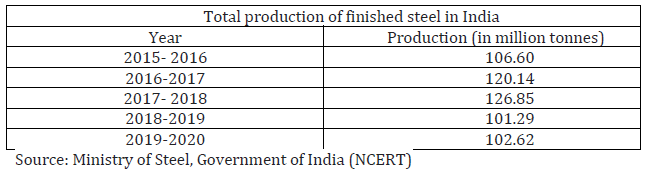
(i) Why is production and consumption of steel considered as an index of a country’s development?
Answer : (i) The steel products are used as a raw material in different industries.
(ii) It is required for export.
(ii) Compare the 2015-2016 and 2019-2020 data and give any one reason for the reduction of production of steel in 2019-2020.
Answer.
(i) High costs
(ii) Limited availability of coking coal
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Classify industries on the basis of source of raw material. How are they different from each other?
Answer : A. Agro based industries
B. Mineral based industries
These industries are different from each other on following basis-
A. Agro based industries –
1) Draws their raw materials from agricultural products
2) Eg: Textiles – Cotton, Jute, Silk and Woolen.
Rubber, Sugar, Coffee, Tea and Edible Oil etc.
B. Mineral based industries –
1) Draws their raw materials from Minerals
2) Eg:- Iron and Steel , Cement , Machine tools , Petro chemicals etc
Question. Analyse the role of the manufacturing sector in the economic development of India.
Answer : i. Manufacturing industries not only help in modernizing agriculture but also reduces the heavy dependence of people on agriculture income.
ii. Eradication of Unemployment and poverty.
iii. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
iv. Countries that transform their raw material into a wide variety of furnished goods of higher value are prosperous.
Question. Describe the importance of manufacturing industries as a backbone of economic development of the country.
Answer : 1. Help in modernising agriculture
2. Eradication of unemployment and poverty
3. Expands trade and commerce
4. Brings foreign exchange
5. Transform their raw materials also a wide variety of finished goods.
6. Increase standard of living and PCI
7. Self Sufficiency
Question. Suggest any three steps to minimize the environmental degradation caused by the industrial development in India.
Answer : Every liter of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of fresh water.
1) Minimizing use of water for processing by Reusing and Recycling it in two or more successive stages.
2) Harvesting of rain water to meet water requirements.
3) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
4) Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators.
5) Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
6) Machinery and equipments can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers.
7) Almost all machineries can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
Question. Why has the ‘Chhotanagpur Plateau Region’ the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries? Analyze the reasons.
Answer : 1) Low cost of iron ore is available.
2) High grade raw material is in proximity.
3) Cheap labour.
4) Vast growth potential in the home market.
Question. Describe the role of industries in the development of agriculture.
Answer : 1. Provides Agricultural tools & machines
2. Increase agricultural & industrial production
3. Mechanisation of agriculture
4. Eradication of unemployment
5. Self Sufficiency is occurred
Question. Consequences of environmental degradation do not respect national or state boundaries. Justify the statement.
Answer : 1. The increase in pollution of land water, air, noise and resulting in degradation of environment cannot be overlooked.
2. Pollution of river waters effects all as most of the rivers passes through different states.
3. Air pollution caused by the presence of high proportion of undesirable gases adversely affects human health and atmosphere as a whole.
4. Thermal pollution of river water effect the aquatic life irrespective of state and national boundaries.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Describe the significance of Textile Industry in India with specific reference to Cotton industry.
Answer : a. The Textile Industry occupies unique position in the Indian economy, because it contributes significantly to industrial production (14 per cent), employment generation (35 million persons directly – the second largest after agriculture) and foreign exchange earnings (about 24.6 percent).
b. It contributes 4 per cent towards GDP. It is the only industry in the country, which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain i.e., from raw material to the highest value-added products.
c. In the early years, the Cotton Textile Industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport including accessible port facilities, labour, moist climate, etc. contributed towards its localisation.
d. This industry has close links with agriculture and provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing.
e. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as, chemicals and dyes, mill stores, packaging materials and engineering works.
Question. Why does the textile industry occupy an important position in the Indian economy? Explain.
Answer : i. It contributes significantly to industrial production (14 percent).
ii. It generates employment in India (35 million persons).
iii. It earns foreign exchange (about 24.6 percent).
iv. It contributes 4 percent towards GDP.
v. It is the only industry in the country which is self-reliant.
vi. It is the only industry which is complete in the value chain i.e., from raw material to thehighest value-added products.
Question. Explain any five factors that are responsible for the location of the ‘jute mills’ mainlyalong the banks of the ‘Hugli River’.
Answer : 1. Proximity of Jute producing areas.
2. Inexpensive water transport supported by a good network.
3. Water transport is supported by good network railways and roadways.
4. Abundant water for processing raw jute.
5. Availability of cheap labour.
6. Kolkata port facility is available.
7. Insurance, banking facilities are also available.
Question. Why is the economic strength of a country measured by the development ofmanufacturing industries? Explain with examples. OR, Explain the importance of manufacturing sector in the economic development of a country.
Answer : i.Manufacturing industries help in modernizing agriculture whichforms the backbone of our economy.
ii. They reduce the heavy dependence of people on agriculturalincome by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
iii. Industrial development is pre-condition for eradication ofunemployment and poverty from our country.
iv. Manufacturing goods expand trade and commerce
v. Export brings in much needed foreign exchange.
vi. Manufacturing is the process of value addition.
vii. It also brings down regional disparities by establishing industriesin tribal and backward areas.
viii. It increases the GDP/ National Income of the country.
Question. How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced? Explain various ways.
Answer : (i) Minimizing the use of water for processing by reusing.
(ii) Harvesting of rain water to meet water requirement.
(iii)Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
(iv) Regulation of use of ground water by industries.
(v) Installing water treatment plants at the industrial sites for recycling.
Question. Why was the cotton textile industry concentrated in the cotton growing belt in the early years? Explain.
Answer : 1) Availability of raw cotton-eg belt of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
2) Nearness to market.
3) Transport
4) Port facilities
5) Cheap labour
6) Moist climate
Question. How are industries responsible for environmental degradation in India? Explain with examples.
Answer : 1. Pollution of land, water and air from industries caused environmental degradation.
2. Burning of fossil fuels in big and small factories emit smoke in the air.
3. Organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents are discharged into rivers.
4. Dumping of wastes from industries renders the soil useless.
5. Rain water carrying pollutants from wastes dumped by industries percolates and contaminated the ground water.
Question. Explain with examples any five factors that are responsible for industrial location.
Answer : 1. Availability of raw material at low cost.
2. Government policies.
3. Availability of specialized labour.
4. Availability of markets and services facilities like Banking, Transport etc.
5. Availability of power.
Question. ‘‘Sugar industry in India is facing challenges.’’ Analyse the statement with suitable arguments.
Answer : Challenges faced by Sugar Industry:
i. Seasonal nature of industry.
ii. Old machinery.
iii. Inefficient method of production.
iv. Transport delay.
v. The need to maximize the use of baggase.
Question. Explain any five features of sugar industry in India
Answer : i. India stands second as a world producer for sugar.
ii. The raw material of this industry is bulky.
iii. In haulage its sucrose content reduces.
iv. This industry is seasonal in nature.
v. It occupies the first place in the production of gur and Khandsari.
vi. In recent years there is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states.
vii. It is ideally suited to the Cooperative Sector.
Question. Explain any five factors that are responsible for concentration of ‘iron andsteelindustries mainly in ‘Chhotanagpur Plateau Region’.
Answer : 1. High grade raw material in proximity.
2. Availability of labour.
3. Raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky containing heavy transport cost.
4. Roads and railways transport facilities are available.
5. Vast growth potential in the home market.
6. Low cost iron ore.
Case Based Questions
Question. Read the text given below and answer the following questions.
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavydependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is aprecondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industriesand joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backwardareas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreignexchange. Countries that transformtheir raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifyingitsmanufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive ofeach other. They move hand in hand. Forinstance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
1. Manufacturing provides job opportunities to reduce dependence on agriculture. Identify which sector the following jobs belong to
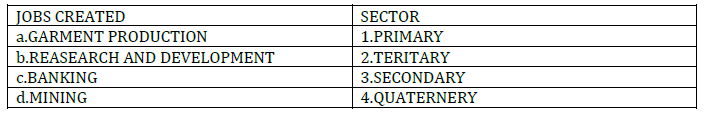
Choose the correct option –
A. a-1, b-2, c-3, d-4
B. a-3, b-4, c-2, d-1
C. a-2, b-3, c-1, d-2
D. a-4, b-1, c-4, d-3
Answer : B. a-3, b-4, c-2, d-1
2. Which of the following options does not help in modernising agriculture?
A. Manufacturing farm equipment
B. Providing unskilled labour force
C. Supplying fertilizers and pesticides
D. Producing tube well pumps and sprinklers
Answer : B. Providing unskilled labour force
3. In order to attract foreign manufacturing firms, a country needs to develop –
A. Agrarian facilities
B. Cultivable lands
C. Media facilities
D. Infrastructure facilities
Answer : D. Infrastructure facilities
4. Manufacturing industries fall in _________ and agriculture in ___________ .
A. Primary, Secondary Sector
B. Secondary, Tertiary Sector
C. Primary, Tertiary Sector
D. Secondary, Primary Sector
Answer : D. Secondary, Primary Sector
Question. Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follows:
Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes eight times the quantity of freshwater.
How can the industrial pollution of fresh water be reduced? Some suggestions are-
(i) minimising use water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages
(ii) harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements
(iii) treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases
(a) Primary treatment by mechanical means. This involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
(b) Secondary treatment by biological process of Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of wastewater.
Overdrawing of groundwater reserves by industry where there is a threat togroundwaterresources also needs to be regulated legally. Particulate matterin the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostaticprecipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery and equipmentcan be used andgenerators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise. Noise absorbing material may be used apart from personal use of earplugs and earphones.
The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
1. How could particulate matter in the air be reduced?
a. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacksto schools withelectrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers andinertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using water or gas instead of coal in factories.
b. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacksto factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers andinertial separators. Smoke can bereduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
c. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacksto factories withhydrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers andinertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using petrol or gas instead of coal in factories.
d. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks tohouses with hydrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in schools.
Answer : b. Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacksto factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers andinertial separators. Smoke can bereduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
2. What could be done to reduce pollution of machinery and equipment?
a. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with knifes. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to decrease energy efficiency and reduce noise.
b. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to decrease energy efficiency and increase noise.
c. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with noisier. Almost allmachinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
d. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
Answer : d. Machinery and equipment can be used and generators should be fitted with silencers. Almost all machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
3. How many treatments are there for industrial effluents? Name them.
a. There are three treatments: industry treatment, garbage treatment,and chemical treatment.
b. There are three treatments: house treatment, school treatment, and road treatment.
c. There are three treatments: primary treatment, secondary treatment, and tertiary treatment.
d. There are three treatments: private treatment, public treatment, and joint treatment.
Answer : c. There are three treatments: primary treatment, secondary treatment, and tertiary treatment.

