Please see Forms Of Business Organisation Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes provided below. These revision notes have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books for Class 11 Business Studies issues by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should revise these notes for Chapter 2 Forms Of Business Organisation daily and also prior to examinations for understanding all topics and to get better marks in exams. We have provided Class 11 Business Studies Notes for all chapters on our website.
Chapter 2 Forms Of Business Organisation Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes
Life is a unique, complex organization of molecules, expressing through chemical reactions which lead to growth, development, responsiveness, adaptation & reproduction.
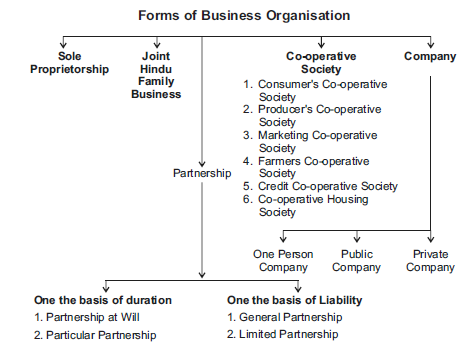

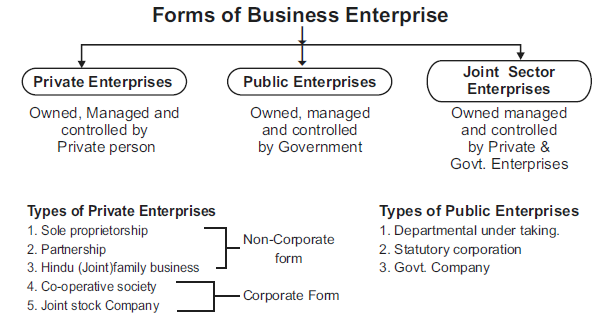
Meaning :- A business enterprises is an institutional arrangement to form any business activity. On the basis of ownership business enterprises can be divided into following 3 categories.
Sole Proprietorship :-

Sole proprietor means a form organization in which there is only owner of business. He himself manages and is the only receipt of all profits and losses (risks).
Features of Sole-Proprietorship :-
1) Single ownership :- He is sole owner of all the assets and resources of business.
2) No separate Legal Entity :- The Business has no separate existance or entity that of the business. All the assets and liabilities of the business are that of the business man.
3) No Legal Formalities :- No Legal Formalities are required to start, manage and dissolv2e such business organization.
4) Control and management :- Sole proprietor has full power to control and manage such organizations.
5) Unlimited liability :- The liability of owner is unlimited. In case, the assets of business are not sufficient to meet its debts, the personal property of owner can be used for paying debts.
6) Undivided Risk :- Means the owner bears all the losses and enjoys all the gains.
7) Suitable for some special form of business :- It is suitable in areas of personalized services and small scale activities like agriculture, the job of stitching, bakery, beauty parlour etc.

8) Secrecy :- All the important informations concerning the business rests only with the owner so that no outside party can take any under advantage of it.
Merits :-
1) Easy Formation :- It can be easily started and closed as there is no need to observe any legal formalities.
2) Quick Decision :- A Sole trader takes the decision quickly as he is not required to consult anybody about his decisions.
3) Secrecy :- All the secrets are confined with the owner. They are not shared with any body.
4) Direct motivation :- Direct relationship between efforts and reward provide incentive to the sole trader to work hard.
5) Personal touch :- The side trader can maintain personal contacts with his customers and employees. In this way, good work is possible at less cost and time.
Limitations :-
1) Limited financial resources :- Funds are limited to the owner’s personal savings (i.e. his capital) and his borrowing capacity.
2) Limited managerial ability :- Sole trader can’t be good in all aspects of business and he can’t afford to employ experts also.
3) Unlimited liability :- As the sole trader has to face the entire risk of business, so he compels him to avoid risky and bold decisions.
4) Uncertainty :- Death, insolvency, lunacy or illness of a proprietor may leads to its closure.
5) Limited scape for expansion :- Due to limited capital and managerial skills, it can’t expand to a large scale.
SUITABILITY :
Sole Trader-ship is suitable.
- Where the personal attention to customer is required as in tailoring beauty parlour.
- Where goods are unstandardized like artistic jewelery.
- Where modest capital & limited managerial skills are required as in case or retail store.
- Business where risk is not extensive i.e., lesser fluctuation in price and demand i.e. stationary shop.
Joint Hindu Family Business
It is owned by the members of undivided joint Hindu Family and managed by the eldest member or manager of teh family known as KARTA. It is governed by the provisions of Hindu Law. The basis of membership is birth in a particular family. The common properties include
a) There should be at least two member in a family.
b) Ancestral property to be inherited by them.
There are two systems which govern membership:-

Features:-
1) Formation :- There should be at best two members in a family and some ancestral property to be inherited by them to form this type of Business.
2) Membership :- Membership automatically starts by birth in the family.
3) Control :- In this, Business is managed wholly by Karta only.The others members can suggest him only.
4) Liability :- Liability of Karta is unlimited but of all other members in limited to the extent of their share in property.
5) Permanent Existence :- The existence is permanent like the existence of the company. There is no effect of the death, insolvency or luncy of the members on the business.
6) Minor Members :- A minor can also become full-fledged member of the family business.
7) Registration :- There is no need of any registration.
Merits
1) Effective Control :- The Karta can prompty take decisions as he has the absolute decision making power.
2) Continued business Existance :- The death, Lunacy of Karta will not affect the business as next eldest member will then take up the position.
3) Limited Liability :- The ilabilty of all members except Karta is limited. It gives them a relief.
4) Secrecy :- Complete secrecy regarding business decisions can be maintained by Karta.
5) Loyalty and Co-operation :- It helps in securing better cooperation and greater loyalty from all the members who run the business.
LIMITATION
1) Limited capital :- There is shortage of capital as it is limited to ht ancestral property.
2) Limited Managerial Skill :- In this, all the decision have to be taken by the Karta but he is not intelligent in all fields of business. Therefore, sometimes the decisions taken are not
fevourbale to the business.
3) Unlimited Liabilities :- In this, the responsibility of the Karta is unlimited so, he hesitates in taking new and risky decisions.
4) Unbalances decision :- As Karta is overburdened, with work, he may take hart and unbalances decisions.
Note :- The joint Hindu Family business is an decline because of the diminishing number of joint Hindu families in the country.
Q. Abdul is the sole owner of a shoe manufacturing factory, It expands and grows, but now it faces the problem of limited financial and managerial resources.
i) Name the form of organization on which is being carried out by Abdul.
ii) Give two alternatives to solve the problem.
[Hint : (i) Employ a paid assistant (ii) Admit one or more partners
PARTNERSHIP
Q.1 What is the maximum number of partners in a partnership firm with :-
i) Banking Business
ii) Non-Banking Business
Definition :- According to Indian Partnership Act 1932. “Partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share profits of a business carried on by all or any of them acting for all.”
Characteristic of Partnership :-
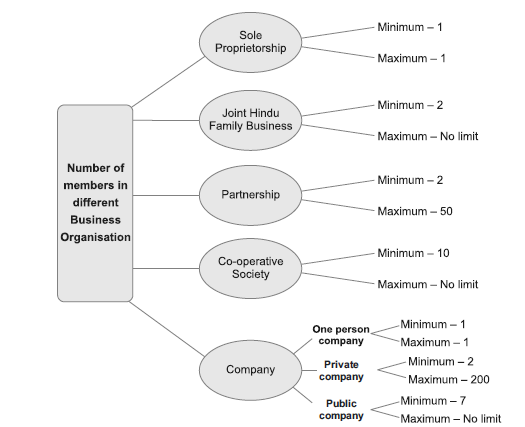
i) More than one person :- Partnership needs a minimum number of two persons and maximum 20.
ii) Agreement :- It is an outcome of an ord or written agreement.
iii) Profit motive and sharing of profit :- Main characteristic of partnership into earn profit in business and divide it among the partners.
iv) Decision making and control :- Every partner has a right to participate in management and decision making.
v) Unlimited Liability :- Partners have unlimited liability.
vi) Lock of continuity :- Firms existance comes to end by the death, Lunacy and insolvency of any of its partner.
vii) Principal Agent Relationship :- Every partner plays double role of an owner and an agent.
Merits of Partnership :-
i) Ease of Formation and closure :- It can be easily formed and closed without any legal formalities.
ii) Large financial Resources :- There are more funds as capital in contributed by number of partners.
iii) Balanced Decisions :- As all important decisions are taken jointly by partners, they are good and balanced.
iv) Sharing of Risks :- Risks get distributes among partners.Which reduces burden and stress on individual partner.
v) Secrecy :- The accounts of partnership firms are not presented before public and are not required to publish. So, business affairs are kept secret.
Limitations :-
i) Limited Resources :- As there is a restriction on the number of partners so capital contributed by them is also limited.
ii) Unlimited liability :- The liability of all partners is unlimited.
iii) Lock of continuity :- Partnership comes to an end with the death, retirement, insolvency or lunacy on any of its partner.
iv) Lack of public confidence :- Partnership firms are not required to publish their reports and accounts. Thus, they lack public confidence.
v) Lack of Harmony :- Because of more people, there can be difference of opinions which leads to discard and lack of coordination.
Note : When the business happens to be of medium size and te partners have mutual understanding and goodwill, then partnership form of business organisation is the best eg. C.A. firms, hotels and factories of middle level etc.
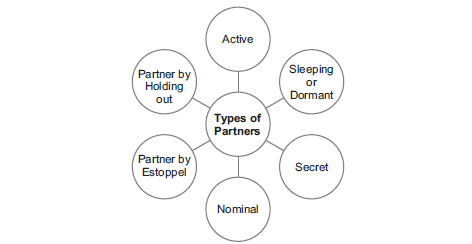
Types of Partners
i) Classification on the Basis of Duration

ii) Classification on the basis of Liability :-

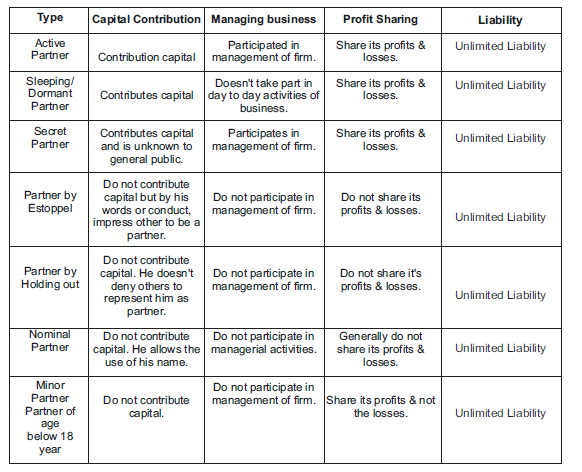
Partnership Deed :- The Written agreement on a stamped paper which specifies the terms and conditions of partnership is called the Partnership Deed.
It generally includes the following aspects :–
1) Name and address of the firm.
2) Names and Address of Partners.
3) Duration of Partnership.
4) Scope of Business.
5) Contribution of Capital by Partners.
6) Profit and loss Ratio.
7) Terms relating or salaries, drawing interest on capital and interest on drawing of partners.
8) Duties & obligations of partners.
9) Terms governing admission, retirement & expulsion of a power.
10) Method for solving disputes.
11) Valuation of goodwill.
Registration of Partnership :- Registration is not compulsory but it is always beneficial to get the firm registered. The consequences of nonregistration of a firm are as follows :-
i) A partner of an unregistered firm can’t file suit against the firm or the partner.
ii) The firm can’t file a suit against third party.
iii) The firm can’t file a case against it’s partner.
‘Co-operative’ means working together and with others for a common purpose. A Co-operative society means a voluntary organization which is established by some persons on the basis of co-operative and equality to safeguard their common economic interests.
Features :-
1) Voluntary Membership :- Every one having a common interest is free to join a co-operative society.
2) Legal Status :- Its registration is compulsory and it gives it a separate legal identify.
3) Limited Liability :- The liability of the members is limited to the extent of their capital contribution in the society.
4) Control :- Management and control lies with the managing committee elected by the members by giving vote.
5) Service motive :- The main aim is to serve it’s members and not to maximize the profit.
6) Cash trading :- They give preference to cash trading.
7) Government control :- They have to sent their annual report and accounts to the register so that the government exercise it’s control from time to time by checking their accounts.
8) Arrangement of Finance :- They arrange finance from sale of shares to members, loans obtained from the government etc.
Merits of Co-operative Societies :-
1) Ease of Formation :- Any ten adults having common objective can establish co-opetative society by getting registered with register.
2) Stable existance :- Due to registration it is a separate legal entity and is not affected by the death, lunacy or in solvency of any of its member.
3) Limited liability :- The liability of members is limited to the extent of their capital contribution.
4) Supply of Goods ay Cheaper Role :- These societies benefit their members by supplying them goods at cheaper rates than the market.
5) Government Support :- Govt. provides support by giving loans at lower interest rates, subsidies and by charging less taxes.
Limitations :-
1) Shortage of Capital :- It suffers from shortage of capital as it is usually formed by people with limited means.
2) Inefficient Management :- These are managed by elected members who may not be competent and experienced. Due to lack of managerial knowledge. They can’t run the society
effectively.
3) Lack of Secrecy :- These have to send their annual reports and accounts to the registrar of co-oprative societies. In this way, the secrets of business become public.
4) Excessive Govt. Control :- It suffers from excessive rules and regulations of Good.
5) Conflict among members :- The members are from different sections of society with different view point. Sometime as when some members become rigid the result is conflict.
6) Lack of motivation :- Members are not in dined to put their best efforts as there is no direct link between efforts and rewards.
TYPES OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETIES
1. Consumers co-operative Society :- It seeks to eliminate middleman by establishing a direct link with the producers. It purchases goods of daily consumption directly from manufacturer or wholesalers and sells them to the members at reasonable prices.
2. Producer s Co-operative Society :- The main aim is to help small producers who cannot easily collect various items of production and face some problem in marketing. These societies purchase raw materials, tools, equipments and other items in large quantity and provide these things to their members at reasonable price.
3. Marketing Co-operative Society :- It performs various marketing function such as transportation, warehousing,packing, grading, marketing research etc. for the benefit of its members. The production of different members is pooled together and sold by society at good price.
4. Farmer’s Co-operative Society :- In such societies, small farmers join together and pool their resources for cultivating their land collectively. Such societies provide better quality seeds,fertilizers, machinery and other modern techniques for use in the cultivation of crops. It provides them opportunity of cultivation on large scale.
5. Credit co-opearative Society :- Such societies protect the members from exploitation by money lenders. They provide loans to their members at easy terms and reasonably low rate of interest.
6. Co-operative Housing Society :- The main aim is to provide houses to people with limited means/income at reasonable price.
JOINT STOCK COMPANY
Meaning – Joint stock company is a voluntary association of persons having a separate legal existence, perpetual succession and common seal. Its capital is divided into transferable shares.
FEATURES
1. Incorporated association :- The company must be incorporated or registered tender the companies Act 1956.without registration no companies Act. 1956. Without registration no company can come into existence.
2. Seperate Legal Existence :- It is created by law and it is a distinct legal entity independent of its members. It can own property, enter into contracts, can file suits in its own name.
3. Perpetual Existence :- Death, insolvency and insanity or change of members as no effect on the life of a company It can
come to an end only through the prescribed legal procedure.
4. Limited Liability :- The liability of every member is limited to the nominal value of the shares bought by him or to the amt. guaranteed by him.
5. Transferability of shares :- Shares of public Co. are easily transferable. But there are certain restrictions on transfer of share of private Co.
6. Common Seal :- It is the official signature of the company and it is affixed on all important documents of company.
7. Separation of ownership and control :- Management of company is in the hands of elected representatives of shareholders known individually as c.,•rector and collectively as board of directors.
MERITS
1. Limited Liability :- Limited liability of shareholder reduces the degree of risk borne by him.
2. Transfer of Interest :- Easy transferability of shares increases the attractiveness of shares for investment.
3. Perpetual Existence :- Existence of a company is not affected by the death, insanity. Insolvency of member or change of membership. Company can be liquidated only as per the provisions of companies Act.
4. Scope for expansion :- A company can collect huge amount of capital from unlimited no. of members who are ready to invest because of limited liability, easy transferability and chances of high return.
5. Professional management :- A company can afford to employ highly qualified experts in different areas of business management.
LIMITATIONS
1. Legal formalities :- The procedure of formation of Co. is very long, time consuming, expensive and requires lot of legal formalities to be fulfilled.
2. Lack of secrecy :- It is very difficult to maintain secrecy in case of public company, as company is required to publish and file its annual accounts and reports.
3. Lack of Motivation :- Divorce between ownership and control and absence of a direct link between efforts and reward lead to lack of personal interest and incentive.
4. Delay in decision making :- Red papism and bureaucracy do not permit quick decisions and prompt actions. There is little scope for personal initiative.
5. Oligarchic management :- Co. is said to be democratically managed but actually managed by few people i.e. board of directors. Sometimes they take decisions keeping in mind their personal interests and benefit, ignoring the interests of shareholders and Co.
Types of Companies :-
On the basis of ownership, companies can be divided into two categories :-
i) Private Company ii) Public Company
Private Company :
Acc to Sec 2(68) of Companies Act, 2013, a Private Company means a company which :
1. Restricts the right of members to transfer shares.
2. Restricts the no. of its members between 2 to 200 excluding present and previous employees of Co. who are members also.
3. Puts a ban on inviting the public to subscribe to its shares.
4 Puts a ban on inviting the public to subscribe to its public deposits.
5 Must have a min. paid up share capital of 1 lakh rupees.
Public Company :
Acc to Sec 2 (71) of Companies At, 2013 a Public Company means a company which is not a private company. A public Company is one which :
1. has no restriction on the transfer of its shares.
2. has no max limits of its members
3. has no restriction on inviting the public to subscribe to its shares and debentures
4. has no restriction on inviting public to subscribe to its Public deposits.
5. has a min. paid up capital of 5 lakh rupees.
Difference between A Private and A Public Company.

One Person Company :
One Person Company refers to a company which has only one peron as a member and which works on the principle of an ordinary company.
Causes of the Formation of OPC
1. Making the unorganised sector as organised – Sole traders have got a good opportunity to move from the unorganised sector and enter the organised sector without getting other people to join him and have all benefits of on organised sector.
2. Perpetual Succession.
Formation of A Company
Formation of a company means bringing a company into existence and starting Its business. The steps involved in the formation of a company are :-
(I) Promotion
(ii) Incorporation
(iii) Capital subscription
(iv) Commencement of business.
A private company has to under go only first two steps but a public company has to undergo all the four stages.
I. Promotion :-
Promotion means conceiving a business opportunity and taking an initiative to from a company.
1. Identification of Business Opportunity :- The First and foremost function of a promoter is to identify a business idea e.g. production of a new product Or service.
2. Feasibility Studies :- After identifying a business opportunity the promoters undertake detailed studies of technical, Financial, Economic feasibility of a business.
3. Name Approval :- After selecting the name of company the promoters submit an application to the Registrar of companies for its approval.
4. Fixing up signatories to the Memorandum of Association :- Promoters have to decide about the director who will be signing the memorandum of Association.
5. Appointment of professional :- Promoters appoint merchant bankers, auditors etc.
6. Preparation of necessary documents :- The promoters prepare certain legal documents such as memorandum of Association, Articles of Association which have to be submitted to the Registrar of the companies.
II. Incorporation
Incorporation means registration of the company as body corporate under the companies Act 1956 and receiving certificate of Incorporation.
Steps for Incorporation
1. Application for incorporation :- Promoters make an application for the incorporation of the company to the Registrar of companies.
2. Filing of necessary documents :- Promoters files the following documents
(i) Memorandum of Association.
(ii) Articles of Association.
(iii) Statement of Authorised Capital
(iv) Consent of proposed director
(v) Agreement with proposed managing director.
(vi) Statutory declaration.
3. Payment of fees :- Along with filing of above documents,registration fees has to be deposited which depends on amount of the authorised capital.
4. Registration :- The Registrar verifies all the document submitted. If he is satisfied then he enters the name of the company in his Register.
5. Certificate of Incorporation :- After entering the name of the company in the register. The Registrar issues a Certificate of Incorporation. This is called the birth certificate of the company.
III. Capital Subscription:-
A public company can raise funds from the public by issuing shares and Debentures. For this it has to issue prospectus and undergo various other formalities:-
Step required for raising funds from public :-
1. SEBI Approval :- SEBI regulates the capital market of India. A public company is required to take approval from SEBI.
2. Filing of Prospectus :- Prospectus means any documents which invites offers from the public to purchase share and Debenture of the company.
3. Appointment of bankers, brokers, underwriters :- Banker of the company receive the application money. Brokers encourage the public to apply for the hares, underwriters are the person who undertake to buy the shares if these are not subscribed by the public. They receive a commission for underwriting.
4. Minimum subscription :- According to the SEBI guide lines minimum subscription is 90% of the issue amount. If minimum subscription is not received then the allotment cannot be made and the application money must be returned to the applicants within 30 days.
5. Application to Stock Exchange :- It is necessary for a public company to list their shares in the stock exchange therefore the promoters apply in a stock exchange to list company shares.
6. Allotment of Shares :- Allotment of shares means acceptance of share applied. Allotment letters are issued to the shareholders.The name and address of the shareholders submitted to the Registrar.
IV. COMMENCEMENT OF BUSINESS :-
To commence business a public company has to obtain a certificate of com-mencement of Business. For this the following documents have to be filled with the registrar of companies.
1. A declaration that 90% of the issued amount has been subscribed.
2. A declaration that all directors have paid in cash in respect of allotment of shares made to them.
3. A statutory declaration that the above requirements have been completed and must be signed by the director of company.
Important documents used in the formation of company:-
1. Memorandum of Association – It is the principal document of a company. No company can be registered without a memorandum of association and that is why it is sometimes called a life giving document.
Contents of Memorandum of Association :-
1. Name clause – This clause contains the name of the company.The proposed name should not be identicator similar to the name of another exiting company.
2. Situation clause – This clause contains the name of the state in which the registered office of the company is to be situated.
3. Object clause – This clause defines the objective with which the company is formed. A company is not legally entitled to do any business other than that specified in the object clause
4. Liability Clauses – This clause limits the liability of the members to the amount unpaid on the shares held by them.
5. Capital clause – This clause specifies the maximum capital which the company will be authorized to ranise tough the issue of shares called authorised capital.
2. Articles of Association :-
The articles of Association are the rules for the internal management of th( affaires of a company the articles defines the duties,rights and powers of the officers and the board of directors.
Contents of the Article:-
1 . The amount of share capital and different classes of shares.
2. Rights of each class of shareholders.
3. Procedure for making allotment of shares.
4. Procedure for issuing share certificates.
5. Procedure for forfeiture and reissue of forfeited shares.
6. Rules regarding casting of votes and proxy voting
7. Procedure for selection and removal of directors
8. Dividend declaration and payment related rules
9. Procedure for capital readjustment
10. Procedure regarding winding up of the company.
I. Prospectus:
Prospectus means any document which invites deposits form the public to purchase share or debentures of a company.
Main contents of the Prospectus:-
1. Company’s name and the address of its registered office.
2. The main object of the company
3. The number and classes of shares.
4. Qualification shares of the directors
5. The name and addresses of the directors, managing director or manager.
6. The minimum subscription which is 90% fo the size of the issue.
7. The time of opening and closing of the subscription list.
8. The amt. payable on the application and allotment of each class of share.
9. Underwriters to the issue.
10. Merchant bankers to the issue.
4. Statement is Lieu of Prospectus:
A public company having a share capital may sometimes decide not to funds form the public because it may be confident of obtaining the required capital privately. In such case it will have to submit a statement in lieu of prospectus with the Registrar of companies.
It Contains information much similar to that of a prospectus.
Q. 1 Name the documents :-
i) Which document defines the objectives of joint stock company ?
ii) In which document are the rules for attaining the internal objectives mentioned in the Memorandum of Association.
Difference between Memorandum and Articles of Association

Choice of Forms of Business Organization :- The following factors are important for taking decision about form of organization.
i) Cost and ease in setting up the Organization :- Sole proprietorship is least expensive and can be formed without any legal formalities to be fulfilled. Formation of a company is expensive with lot of legal formalities. So, sole proprietorship is better.
ii) Liability :- The liability of the owners in sole proprietor business and partnership business is unlimited but the responsibility of the share holders in a company is limited. So, Company organization should be selected.
iii) Continuity :- In sole proprietorship and partnership firms death,lunacy or insolvency of any of its member, business ends but in Joint Hindu Family Business & Co-oprative Societies company business is not affected by there above picture. So, company cooperative society are much better to be chosen.
iv) Managerial Needs :- In sole proprietorship & Joint Hindu Family Business, experts opinion is not affordable but companies can afford exports for management. so keeping in view, the nature of work and managerial needs company is liked.
v) Capital Considerations :- Business activities requiring huge financial resources prefer company form while for small & medium size business, partnership or sole proprietorship is better.
vi) Control :- For direct control & direct decision. Sole proprietor is liked while where the control has to be shared, they prefer company.
vii) Nature of Business :- If the work requires personal attention, it is generally set up as a sole proprietorship Units engaged in large seals manufacturing are more likely to be organized in company form or partnership form.
Points to be remembered
1. There are different forms of organisation —
– Sole Proprietorship
– Partnership
– Joint Hindu Family Business
– Co-operative Society
– Company
2. There is unlimited liability in sole proprietorship, Joint Hindu Family Business and Partnership.
3. There is limited liability in co-operative society and company.
4. Registration is not required in sole proprietorship, Joint Hindu Family Business and Partnership. While it is required in cooperative society and company.
5. Co-operative society and company are separate legal entity.
6. Schools of Hindu Law —
(I)Mitakshara – It is applicable in all India except Assam, West Bengal and some parts of Orissa.
(ii) Dayabhag – It is applicable in Assam, West Bengal and some parts of Orissa only.
7. Stages of formation of company —
(I) Promotion
(ii) Incorporation of registration
(iii) Commencement of Business
8. Main documents of a company —
(i) Memorandum of association
(ii) Articles of association
(iii) Prospectus
9. Clauses of memorandum of Association
(i) Name clause (ii) Situation clause
(iii) Objects clause (iv) Liability clause
(v) Capital clause (vi) Subscription clause
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which forms of business organisation has not the feature of unlimited liability?
(a) Sole Proprietorship
(b) Partnership
(c) Joint Hindu Family Business
(d) Company
2. Registration is compulsory in —
(a) Sole proprietorship
(b) Co-operative Society
(c) Partnership
(d) Joint Hindu Family Business
3. What are the maximum number of members in a Public Company?
(a) 50
(b) 10
(c) Unlimited
(d) 200
4. What are the main documents required to form a company?
(a) Memorandum of association
(b) Article of association
(c) Prospectus
(d) All of the above
5. Which of the following in a public company —
(a) Samsung
(b) PARLE
(c) BHEL
(d) Airtel
6. Which of the following has a separate legal entity?
(a) Co-operative society
(b) Partnership
(c) Joint Hindu Family Business
(d) All of the above
7. Which of the following statement is true?
(a) Partnership is registered under Partnership Act 1986
(b) A minor can’t be partner
(c) Written agreement among partners is called partnership deed.
(d) There should be minimum 3 directors in one person company.
8. Partnership is registered under —
(i) Partnership Act 1932
(ii) Partnership Act 1948




23. Shiv, Anandi & John were partners John died in a car accident Both Shiv & Anandi decided to admit his son Ryan who was 16 years old as partner. Can they do so ? Justify.
[Hint : Minor as a partner]
24. Mr. Singh is in ‘lighting’ business for the post 15 years. To help his friend, Mr Yadav, a beginner he projected himself as a partner before Mohd. Abdul, a whole sale dealer of fancy lights. Mohd.Abdul gave Mr. Yadav the stock without asking for payment and gave him credit limit of one month. Will Mr. Singh be liable to Md. Abdul if Mr. Yadav does not pay him on time ? Classify Mr. Singh’s role here along with an explanation.
[Hint : Partner by Estoppel]
25. Akriti, Sonam & Supreeti were friends who started a partnership business. They did not get their firm registered as it was optional.Soon, Sonam & Supreeti started having conflicts. Sonam wanted to approach a lawyer. If you were a lawyer than how would you guide her ?
26. Mangal, Sazia & Suqhbeer Singh wish to start a business in partnership. They want to make a partnership deed, Suggest what aspects of the deed should be included in it ?
27. Explain any four limitations of Joint Stock Company.
28. A, B & C were partners in a financing firm. B&C had gone for a meeting in America for analysing business prospects in that country. In the mean while, A invested a huge amount of money in buying shares of a new company by borrowing money from Mr. X. This turned out to be a bad deal as the share prices soon fell. When B&C came back they said they were not liable to pay to Mr. X as they did not take the money. Were B&C right in doing so ? Under which aspect of partnership are they bound ?
29. Rohan has a shop of stationary products. He takes assistance from his brother to handle it and pays him a fixed salary. He also employed a 11 year old boy for his shop. Both the brothers regularly abuse him and cut his wages as and when desired.
i) Which form of organization is referred here ?
ii) Write any one feature associated with it.
30. Ravina is a Science teacher in a coaching institute. She is not satisfied with the salary being received here. So she decides to start her own coaching institute. But students generally take coaching for Science as well as maths. What do you recommand Ravina to do ?
[Hint : Go for partnership with a maths expert.]
31. The business assets of a firm are worth $70,000 but debt remain unpair at worth $1,00,000. What course of action can creditors take in following cases !
i) The organization is a sole proprietorship firm.
ii) The organization is a partnership with 2 partners A and B sharing profits and losses equally.
32. Sita and Zoya are two friends belonging to Hindu and Muslim religion. They start a business of handicrafts together. They decide to open the factory in rural area and give employment opportunities to local residents.
i) Which form of business organization have they opted ?
ii) Write any one feature of the form ?
iii) Mention the values involved in this question.
33. Continous exploitation of milkman of charm wood village by the intermediaries compel them to form a voluntary association to protects their interest gain access to markets there by ensuring maximum returns for their efforts and welfare of the members.
i) Name the form of business organization adopted by the milkman.
ii) Give an example of organization identifies in (i) above
iii) Which principle governs such organization and how government support them ?
34. All the members of a company are killed in an earthquake. While holding a general meeting. Will the company wind up ? Why ?
35. Rohit and Mohit are partners dealing in shares. Mohit uses firm’s money to buy shares on his name. He didn’t disclose this information with his friend Rohit.
a) Does Rohit have any share in the profit earned from sale of these shares?
36. Rohan, Sohan and Mohan are partners of a business of publishing books. They have adopted three villages which are educationally backward. Every year they distribute books to
schools established in these villages for free to promote education. Write any one feature of partnership. Identify three values followed by the partnership firm.
37. Star Ltd. has received applications for 48 crores (issue size was 50 crores). Discuss the documents filled with the register of companies. [Hint]:
i) A declaration that 90% of the issued amount has been subscribed.
ii) A declaration that all the directors have paid in cash in respect of allotment of shares made to them.
iii) A statutory declaration that the above requirements have been completed and must be signed by the director of company.
38. Aditya is promoting a company. Before the company is formed,he enters into a contract with DLF for purchase of land and also agreed to pay 10 crores within a period of 2 moths. The company was formed within 1 month. On the basis of the facts, answer the following :-
i) Which type of contract is entered by Aditya ?
ii) Is the contract legally binding on the company ?
iii) Can DLF Ltd. hold Aditya liable for the payment money?
iv) What can the company do to prevent Aditya from such a situation?
5-6 Marks Questions :-
39. Differentiate between private & public company.
40. Mr. Amit Kumar is interested in the floatation of a company.Briefly discuss the steps he should take.
41. Discuss the reasons of superiority of joint stock company over sole proprietorship and partnership.
42. Which form of business is suitable for following types of business and why ?
(a) Beauty Parlour
(b) Coaching Centre for science students
(c) Hotel
(d) Shopping mall
(e) Restaurant
(f) Small retail business.
43. Dhirubhai Chaurasiya operates a textile business. His family is joint and has a lot of ancestral property. All the 15 family members are a part of this business. He is the eldest male
member in the family so he heads the business. He is liable to all the creditors of the business as he is the decision maker.Dhirubhai’s grandson has just born a few days ago and he is also the member of the business.
(a) Which form of business is being undertaken by Dhirubhai Chaurasiya ?
(b) Identify the features of this form of business based on the information given.
(c) Textile business is part of which type of industry according to you ?
44. Every day Amul collects milk from 2.12 million farmers (many illiterate) & converts the milk into branded packaged products & delivers goods all over the country. The story of Amul started in Dec, 1946 with a group of farmers been to free themselves from intermediaries, gain access to the market & there by ensure maximum returns for their efforts”
(a) From the above information, identify the form of business organisation used by Amul.
(b) Also quote the line which suggest its features ?
(c) According to you. Amul is part of which type of industry ?
45. Mohan, Sohan and Ramesh are brothers living in a village Mohan is a farmer. He grows sugar cane in his field sohan is manufacturer of sugar who is doing the business with his friends Rohan Singh and Jitender. Ramesh is a transporter. He sells the sugar in the city using his truck. This year the sugar got spoiled due to heavy rain. Sohan his friends reduced the wages of his workers to cut down their losses.
1. Classify the business activity undertaken by Mohan & Ramesh.
2. What form of business is Sohan doing with his friends. write any two features of the form ?
3. What type of business risk is faced by them ? Explain
46. Rahul and Sanchali felt that there was an opportunity of business in providing a service of online grocery stores for working people.They analysed the idea in terms of technical, financial and economic liability. Once they found all the aspects satisfactory they decided to start a company called ‘convenience @ home’
private Ltd. They got the name registered with the registrar.
(a) Which steps of formation of company are being referred to here ?
(b) Also write the next 3 steps associated with it.
[Hint : steps in promotion of a company]
47. Lakhvinder Singh is confused as to which form of business he should follow for his garment business. You are his friend. Help him by rationally discussing the different factors so that he can take a sound business decision.
48. Comment on the following :-
i) Meeting of X Ltd. was going on in which all the members of the company were present suddenly a natural calamityoccurred and all the members of the company X Ltd. died.
What would happen to the existence of the company ‘X’ Ltd. Why?
ii) The company being an artificial person acts through its Board of Directors. All teh agreements on behalf of the company are entered by the Board of Directors. When is an agreement entered by the Board of directors not legally binding on the company.
49. Sachin’s father Mahesh was running a small shop selling accessories such as artificial jewellay, hair caps etc. Over the past couple of month he has been facing problem in managing it due to increase demand of the items. Although Sachin also helps his father but they both fail to attend all the customers due to
space constraint. Non-availability of required finance acts as a hindrance in expanding their business. Sachin asks his father to join hands with Raja (his father’s friend) to solve the problem. His father agreed and entered in to agreement with Raja in writing containing various terms and conditions.
i) Which form of business organization does Mahesh form with Raja ?
ii) Which documents contains the written agreement specifying the terms and conditions between Mahesh and Raja ?
iii) In which form of business organization Sachin help his father to attend customers.
50. Sonu, a tailor by profession was working in a famous boutique in Kamla Nagar. He was a skilled worker with many years of experience at and saving worth rupees 5 lakh. He finally decided that he would start his own boutique. He rented a shop in Rohini.He was not sure about his venture as now he would not have any security of income. But soon he started getting lot of work due to his efficiency & his profits increased.
(a) Which type of economic activity was Sonu undertaking when he was working in a boutique?
(b) Which form of business organization did he opt for later?
(c) Identify any 2 merits & 2 demerits you can recognize of the form of business opted by him.
51. Aarti is a sole proprietor. Over the part 15 years, her business has grown from operating a neighbourhood shop selling Kurtis,bags, cosmetics etc. to a retail chain with four branches in the branches, she is thinking to form a company to manage the business better. She also wants to grow further.
a) Explain two merits of Aarti remaining a sole proprietor.
b) Explain two advantages of her converting to a joint stock co.
c) If she wishes to grow further then which of the two options is better?
52. Identify the type of partner highlighted in the following statements:
i) This partner doesn’t take part in the day to day activities of the business.
ii) He gives an impression of his being partners to others by his words or conduct.
iii) He allows reuse of his goodwill to benefit the firm and can be represented as a partner.
iv) He is represented as a partner and in spite of knowing this, he does not deny such impression.
v) His association with the firm is not disclosed to the general public.
vi) This takes active part in carrying out business of the firm.
53. Which form of business organization is suitable in the following cases :-
i) A business organization having stability and continuity.
ii) There should be minimum expenses in starting the business.
iii) The business organization should be suitable from the point of view of investors.
iv) The ancestral property is to be used for doing the business.
v) More funds and professional services are required.

