VBQs Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry with Electrochemistry has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Electrochemistry. The following Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Electrochemistry VBQs Class 12 Chemistry
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION (MCQ)
Question. The cell constant of a conductivity cell _____________.
a. changes with change of electrolyte.
b. changes with change of concentration of electrolyte.
c. changes with temperature of electrolyte.
d. remains constant for a cell.
Answer
D
Question. An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell when ____________.
a. Ecell = 0
b. Ecell > Eext
c. Eext > Ecell
d. Ecell = Eext
Answer
C
Question. The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu indicates that ____________.
a. this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple.
b. this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2.
c. Cu can displace H2 from acid.
d. Cu cannot displace H2 from acid.
Answer
D
Question. What will happen during the electrolysis of aqueous solution of CuSO4 in the presence of Cu electrodes?
a. Copper will deposit at cathode.
b. Copper will dissolve at anode.
c. Oxygen will be released at anode.
d. Copper will deposit at anode.
Answer
A,B
Question. The quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from Al2O3 is ___________.
a. 1F
b. 6F
c. 3F
d. 2F
Answer
C
Question. The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ___________.
a. Cell potential
b. Cell emf
c. Potential difference
d. Cell voltage
Answer
C
Question. While charging the lead storage battery ______________.
a. PbSO4 anode is reduced to Pb.
b. PbSO4 cathode is reduced to Pb.
c. PbSO4 cathode is oxidised to Pb.
d. PbSO4 anode is oxidised to PbO2.
Answer
A
Question. For the given cell, Mg|Mg 2+|| Cu 2+|Cu
a. Mg is cathode
b. Cu is cathode
c. The cell reaction is Mg + Cu 2+ → Mg 2+ + Cu
d. Cu is the oxidising agent
Answer
B,C
Question. Conductivity of an electrolytic solution depends on ____________.
a. nature of electrolyte.
b. concentration of electrolyte.
c. power of AC source.
d. distance between the electrodes.
Answer
A,B
Question. Which of the following statement is not correct about an insert electrode in a cell?
a. It does not participate in the cell reaction.
b. It provides surface either for oxidation or for reduction reaction.
c. It provides surface for conduction of electrons.
d. It provides surface for redox reaction.
Answer
D
Question. Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on ___________.
a. temperature.
b. distance between electrodes.
c. concentration of electrolytes in solution.
d. surface area of electrodes.
Answer
A,C
Question. What will happen during the electrolysis of aqueous solution of CuSO4 by using platinum electrodes?
a. Copper will deposit at cathode.
b. Copper will deposit at anode.
c. Oxygen will be released at anode.
d. Copper will dissolve at anode.
Answer
A,C
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 76-90, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : At the end of electrolysis using platinum electrodes, an aqueous solution of copper sulphate turns colourless.
Reason : Copper in CuSO4 is converted to Cu(OH)2 during the electrolysis.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : If λoNa+ and λo Cl− are molar limiting conductivities of the sodium and chloride ions respectively, then the limiting molar conductivity for sodium chloride is given by the equation, NaCl Λ0 NaCl− = λoNa+ λo Cl− .
Reason : This is according to Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Specific conductance decreases with dilution whereas equivalent conductance increases.
Reason : On dilution, number of ions per millilitre decreases but total number of ions increases considerably.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The conductivity of solution is greater than pure solvent.
Reason : Conductivity depends upon number of the ions present in solution.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The electrical resistance of any object decreases with increase in its length.
Reason : The electrical resistance of any object decreases with increase in its area of crosssection.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : If standard reduction potential for the reaction,
Ag+ + e– → Ag is 0.80 volt, then for the reaction,
2Ag+ + 2e– → 2Ag, it will be 1.60 volt.
Reason : If concentration of Ag+ ions is doubled, the standard electrode potential remains same.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution cannot be determined experimentally.
Reason : Kohlrausch law helps to find the molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Kohlrausch law helps to find the molar conductivity of weak electrolyte at infinite dilution.
Reason : Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution cannot be determined experimentally.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The observed conductance depends upon the nature of the electrolyte and the concentration of the solution.
Reason : The cell constant of a cell depends upon the nature of the material of the electrodes.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The conductivity depends on the charge and size of the ions in which they dissociate, the concentration of ions or ease with which the ions move under potential gradient.
Reason : The conductivity of solutions of different electrolytes in the same solvent and at a given temperature is same.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The molar conductivity of strong electrolyte decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason : At high concentration, migration of ions is slow.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Substances like glass, ceramics,etc. having very low conductivity are known as insulators.
Reason : They do not allow the passage of electric current through them.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Equivalent conductance of all electrolytes decreases with increasing concentration.
Reason : More number of ions are available per gram equivalent at higher concentration.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The ratio of specific conductivity to the observed conductance does not depend upon the concentration of the solution taken in the conductivity cell.
Reason : Specific conductivity decreases with dilution whereas observed conductance increases with dilution.
Answer
B
A statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice from the options given below:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Question. Assertion : A standard hydrogen electrode is also called reversible electrode.
Reason : It can act on both as anode as well as cathode in an electrochemical cell.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Fluorine is the best oxidising agent.
Reason : Fluorine has highest reduction potential.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Kohlrausch law helps to find the molar conductivity of weak electrolyte at infinite dilution.
Reason : Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte at infinite dilution cannot be determined experimentally.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Current stops flowing when Ecell = 0.
Reason : Equilibrium of the cell reaction is attained.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : When a copper wire is dipped in silver nitrate solution, there is no change in the colour of the solution.
Reason : Copper cannot displace silver from its salt solution.
Answer
D
1 Mark Questions.
Question. What is the effect of dilution of concentration on specific conductance ?
Answer. Specific conductance decrease with dilution because it is the conduction power of ion present in unit volume of solution and number of ion in unit volume decreases on dilution. Specific conductance increases with concentration.
Question. Why mercury cell gives constant voltage throughout its life?
Answer. As the overall reaction does not involve any ion in solution whose conc. can change during its life.
Question. What is meant by limiting molar conductivity ?
Answer. The molar conductivity of a solution at infinite dilution is called limiting molar conductivity
Question. What is meant by limiting molar conductivity?
Answer. Molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution.
Question. What is the unit of molar conductivity?
Answer. . ohm–1cm2mol–1
Question. What type of metals can be used in cathodic protection of iron against rusting?
Answer. A metal which is more electropositive than iron i.e. having lower reduction potential. Example- Zn, Mg etc.
Question. Give the relationship between molar conductivity and specific conductivity ?
Answer. ᴧm = k (1000\M)
Question. Name the solid substance produced, during the discharge of lead- storage battery.
Answer. Lead sulphate
Question. How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required to produce 100g of Ca from molten CaCl2 ?
Answer. 5F
Question. What is electrode potential?
Answer.Tendency to lose and gain electron.
Question. Under what condition is ECell = 0 or ΔrG= 0?
Answer.When the cell reaction reaches equilibrium.
Question. Give an example of antirust solution.
Answer. Alkaline chromate solution
2 marks Questions
Question. Represent the galvanic cell in which the following reactions take place
Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
i.) Which one of the electrodes is negatively charged ?
ii.) Write the reaction taking place at each of t he electrodes.
iii.) Name the carrier of current within the cell.
Answer. .The cell is represented as
Zn(s) │Zn2+(aq) ││Ag+(aq) │Ag(s) │
i) Zn electrode is negatively charged
ii) At anode
Zn(s) → Zn2+ + 2e–
At cathode
Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s)
iii) Ions are the carrier of current within the cell.
Question.How many moles of mercury will be produced by electrolysing 1.0 M Hg (NO3)2 solution with a current of 2.00 A for three hours ?
Molar mass of Hg(NO3)2= 200.6 g/mol
Answer. . Current = 2A
Time = 3h = 3(60)(60)s
w = ZIt
Z for Hg in compound =200.6/2F
w= 200.6x2x (3)(60)(60)/2(96500)
w= 22.45g
number of moles = 22.45\200.6 = 0.112 mol
Question. What is fuel cell ? Write two chemicals which can be used as fuel.
Answer. . The cell which converts combustion energy of fuel into electricity .
Methane and hydrogen can be used as fuel 2H2(g) + 4OH–(aq) → 4H2O(l) + 4e–O2 + 2H2O (l) + 4e– →4OH–(aq)
Question. State Faraday’s laws. How much charge is required for the reduction of 1 mole of Cu2+ to Cu?
Answer. Statements Cu2++2e → Cu
Charge required for the reduction of 1 mole Cu2+ = 2F
=2(96500 C)
= 193000C
Question. What type of battery is the lead storage battery? Write the anode and the cathode reaction and the overall reaction occurring when current is drawn from it ( reaction during discharge of it )
Answer. Lead storage battery is the secondary cell. So it can be recharged by passing direct current through it .
Discharge reaction –
At anode : Pb(s) + SO4 2–(aq) → PbSO4 (s) +2e–
At cathode: PbO2(s) + SO42–(aq) + 4H+(aq) + 2e– → 2PbSO4 (aq) +2H2O(l) Overall solution :
Pb + PbO2+ 4H+ + SO42–(aq) → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
3 marks Questions
Question. Calculate the standard electrode potential of Ni 2+// Ni electrode if emf of the Ni 2+/Ni(0.01) // Cu 2+(0.1) / Cu (s) electrochemical cell is 0.059V. Given E0 = 0.34 V
Answer. Ecell = 0.059V
E0 Cu = 0.34 V [Cu+2 ] = 0.1 M
Ecell = E0cell‐ 0.0591/n log [Ni 2+ (aq)] / [Cu2+(aq)] 0.059 = E0cell – 0.059/2 log ( 0.01/0.1)
0.059 = E0cell – 0.0295 log 1/10
0.059 = E0cell ‐0.0295 ( log 1 – log 10 )
= E0cell – 0.0295(‐1) 0.059 = E0cell + 0.0295
E0cell = 0.05g – 0.0295= 0.0295V
E0cell = E0cathode‐ E0anode
0.0295 = 0.34 ‐ E0anode
E0anode = 0.34 – 0.0295 = 0.3105V
Question. The resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohm, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution . Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 m–1
Answer. i) Cell constant G = conductivity ( resistance )
= 1.29 S m–1 (100Ω) 129 m–1 or 1.29 cm–1
ii) conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution
(k) = cell constant /resistance = 1.29 cm–1/520Ω
2.48 x 10–3 S cm–1
iii) molar conductivity = k x 1000\M = 2.48 x 10–3 x 1000/0.02
= 124S cm2 mol–1
Question. Determine the value of equilibrium constant and Δ G0 for the following reaction :
Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq)→ Ni2+ (aq) + 2 Ag(S) (E0 = 1.05V)
Answer. n=2 Δ G0 = ‐nF E0
Δ G0 = ‐2 ( 96500) C (1.05) V
Δ G0 = ‐202650 Jmol-1 = – 202.65 kJ mol-1
‐nFE0 = ‐2.303 RT logKc
logKc =nE0/0.0591
=2(1.05/0.0591) = 35.532 g
Kc = antilog 35.532
Kc = 3.411× 1035
Question. Give an example of a fuel cell and write the cathode and anode reaction for it .
Answer. Galavanic cell that are designed to convert the energy of combustion of fuel like hydrogen , methane,
methanol directly into electrical energy are called fuel cell.
Cathode reaction: O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– → 4OH–(aq) Anode reaction : 2H2(g) + 4OH–(aq) → 4H2O(l) + 4e– Overall
reaction : 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
5 marks questions
Question. a. Write the formulation for galvanic cell in which the reaction
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
takes place , identify the cathode and the anode reaction in it.
ii) Write Nernst equation. Calculate the emf of the following cell:
Sn(s) / Sn2+(0.04M) // H+ (0.02M) / H2(g),Pt(s) (given E0 Sn2+/Sn = 0.14V )
Answer.
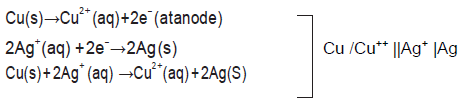

Question. i)Define the molar conductivity of a solution and explain how molar conductivity changes with change in concentration of solution for a weak and strong electrolyte
ii.)The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001M KCl solution at 298K is 1500Ω.
What is the cell constant, if the conductivity of 0.01M KCl solution at 298 K is
0.146X ( 10–3) S cm–1 ?
Answer. i) Molar conductivity – it is defined as the conductance of the solution which contain one mole of electrolyte such that entire solution is in between two electrodes kept one centimeter apart sharing unit area of cross section
b. Given conductivity K = 0.146x (10–3) S cm–1
Cell constant G = k(R)
= 0.146 x 10–3 x 1500= 0.219 cm–1