Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Chapter 4 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Chemical Kinetics Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation :
A(g) + 2B(g) → 2C(g)
Concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ were changed keeping the concentration of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as function of initial concentration. Following results were obtained.Choose the correct option for this reaction
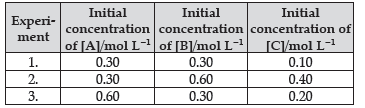
(A) Rate = k [A]2[B]
(b) Rate = k [A][B]2
(C) Rate = k [A][B]
(d) Rate = k [A]2[B]0
Answer
B
Question. A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion ?
(A) 1.26 × 1015 s
(B) 2.52 × 1014 s
(C) 2.52 × 1028 s
(D) Infinite
Answer
D
Question. Consider the reaction

The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
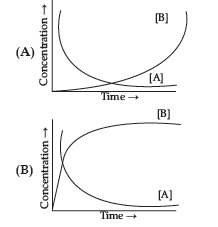
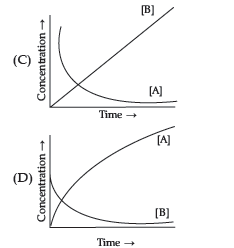
Answer
B
Question. The half-life period for a zero order reaction is equal to:

(where [R]0 is initial concentration of reactant and k is rate constant).
Answer
D
Question. A graph of volume of hydrogen released vs. time for the reaction between zinc and dilute HCl is given in figure. On the basis of the graph, mark the correct option.
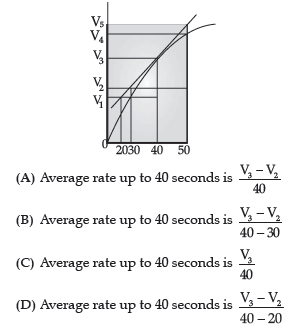
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) The rate of a reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants decreases.
(B) The rate of a reaction is same at any time during the reaction.
(C) The rate of a reaction is independent of temperature change.
(D) The rate of a reaction decreases with increase
in concentration of reactant(s).
Answer
A
Question. The slope in the plot of ln[R] vs. time gives:

(where [R] is the final concentration of reactant.)
Answer
C
Question. Rate law can be determined from balanced chemical equation if
(A) reverse reaction is involved.
(B) it is an elementary reaction.
(C) it is a sequence of elementary reactions.
(D) any of the reactants is in excess.
Answer
B
Question. The value of rate constant of a pseudo-firstorder reaction:
(A) depends on the concentration of reactants present in small amount.
(B) depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess.
(C) is independent of the concentration of reactants.
(D) depends only on temperature.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following expressions is correct for the rate of reaction given below?
5Br− (aq) + BrO3– (aq) + 6H+ (aq) → 3Br2 (aq) +3H2O (l)
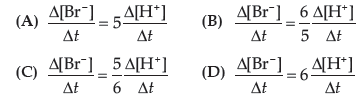
Answer
C
Question. The unit of rate constant depends upon the
(A) molecularity of the reaction
(B) activation energy of the reaction
(C) order of the reaction
(D) temperature of the reaction
Answer
C
Question. In a chemical reaction X → Y, it is found that the rate of reaction doubles when the concentration of X is increased four times. The order of the reaction with respect to X is:
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) 2
(D) 1/2
Answer
D
Question. In the presence of a catalyst, heat evolved or absorbed during reaction
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) remains unchanged
(D) may increase or decrease
Answer
C
Question. Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below: reaction given below:
A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was ‘pi’. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt’. The rate constant k for the reaction is given as:

Answer
B
Question. For the reaction A → B, the rate of reaction becomes three times when the concentration of A is increased by nine times. What is the order of reaction ?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 1/2
(D) 0
Answer
C
Question. For a zero order reaction, the slope in the plot of [R] vs. time is:
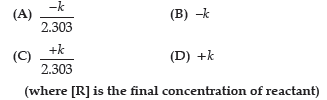
Answer
B
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): Elementary reactions have same value of order and molecularity.
Reason (R): Molecularity is the number of molecules that participate in the reaction, while order is an experimental quantity.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Order of the reaction can be zero or fractional.
Reason (R): We cannot determine order from balanced chemical equation.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Dust particles suspended in the air inside grain elevators (unheated) can sometimes react explosively.
Reason (R): The dust particles have large surface area for the reaction.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): For a first order reaction, half-life period is independent of initial concentration of the reacting species.
Reason (R): The half-life of a reaction is the time in which the reactant concentration is reduced to one half of its initial concentration.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): The rate of reaction increases with the increase in temperature.
Reason (R): The reactant molecules collide less frequently on increasing temperature.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Hydrolysis of an ester follows first order kinetics.
Reason (R): Concentration of water remains nearly constant during the course of the reaction.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Rate of reaction doubles when concentration of reactant is doubled if it is a first order reaction.
Reason (R): Rate constant also doubles with twice increase in the concentration of reactant.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): For complex reactions molecularity and order are not same.
Reason (R): Order of reaction may be zero.
Answer
B
A statement of assertion is followed by a statement of a reason. Mark the correct choice from the options given below:
a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
d) Assertion is false and reason is true.
Question. Assertion: Rate constant of a zero-order reaction has same units as the rate of reaction.
Reason: : Rate constant of a zero order reaction does not depend upon the concentration.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: With increase in temperature the rate of reaction decreases.
Reason: For every 10 0C rise in temperature , the rate of the reaction doubles for most of the reaction.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion: In a zero order reaction , if concentration of the reactant is doubled, half life period is also doubled.
Reason: The total time taken for a zero order reaction to complete is double of the half life period.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Order of reaction with respect to any reactant or product can be zero, positive ,negative and fractional.
Reason: Rate of a reaction cannot decrease with increase in concentration of a reactant or product.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: 50% of a reaction is completed in 50 sec, 75% of the reaction will be completed in 75 sec.
Reason: The rate constant of a zero-order reaction depends upon time.
Answer
C
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is – dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm of Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1. The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the bth power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via.,
rate = k CAα CAβ
the overall order of the reaction is simply
n = α + β
Such a reaction is said to be of the ath order with respect to the substance A, the bth order with respect to B.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: For a chemical reaction, P + 2Q → Products, Rate = k [P]1/2[Q]1 so the order of reaction is 1.5
Reason: Order of reaction is the sum of stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: Rate of reaction is a measure of change in concentration of reactant with respect to time.
Reason: Rate of reaction is a measure of change in concentration of product with respect to time.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: Reactions can occur at different speeds.
Reason: Rate of reaction is also called speed of reaction.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: The unit of k is independent of order of reaction.
Reason: For zero order reaction, the unit of k is mol L–1s–1.
Answer
D
II. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Question. The rate law equation is:
(A) Rate = k [C2H6]
(B) Rate = k [C2H4]2
(C) Rate = k [C2H4]
(D) Rate = k [C2H4]2
Answer
C
Question. The rate constant of the reaction after 5 minutes is
(A) 0.4290 min–1
(B) 0.1297 min–1
(C) 0.2197 min–1
(D) 0.6591 min–1
Answer
C
Question. Find the order of reaction.
(A) Zero order
(B) First order
(C) Second order
(D) Fractional order
Answer
B
Question. The half-life for the reaction is
(A) 2.772 × 10–24 s
(B) 2.772 × 10–24 s
(C) 1.386 × 10–24 s
(D) 1.386 × 10–24 s
Answer
A
III. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Question. Under which condition a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order reaction?
(A) When two reactants are involved.
(B) When one of the reactants is in excess.
(C) When one of the reactants does not involve in reaction.
(D) None of these
Answer
B
Question. When the rate constant has same units as the rate of reaction, the order of the reaction is:
(A) Zero order
(B) First order
(C) Second order
(D) Fractional order
Answer
A
Question. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g?
(A) 222.189 s
(B) 444.379 s
(C) 111.095 s
(D) 888.789 s
Answer
B
Question. For a reaction, A + H2O → B
Rate ∝ [A]
The order of the reaction is:
(A) Zero order
(B) Fractional order
(C) Pseudo first order
(D) Second order
Answer
C
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Consider the following statements with respect of zero order reaction
(i) The rate of the reaction is independent of reactant concentration
(ii) The rate of the reaction is independent of temperature
(iii) The rate constant of the reaction is independent of temperature
(iv) The rate constant of the reaction is independent of reactant concentration
Choose the correct statement(s).
(A) (i) only
(B) (i) and (ii) only
(C) (iii) and (iv) only
(D) (i) and (iv)only
Answer
D
Question. Study the following graphs and choose the correct option
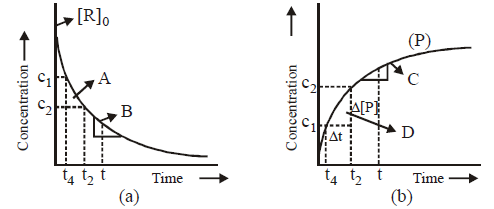
(i) in fig. a, A represents average rate and B represents instantaneous rate
(ii) in fig. b, D represents average rate and C represents instantaneous rate
(iii) fig. a, A represents instantaneous rate and B represents average rate
(iv) fig. b, C represents average rate and D represents instantaneous rate
(A) (i) and (ii) are correct
(B) (ii) and (iv) are correct
(C) (i) and (iv) are correct
(D) (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer
A
Question. Consider the following statements
(i) Rate constant for every physical and chemical change gets doubled with 10°C rise in temperature
(ii) On taking log both side Arrhenius equation will become

(iii) The energy required to form activated complex is known as activation energy
Which of the following is the correct code for statements above?
(A) TTT
(B) FTT
(C) FTF
(D) TFT
Answer
B
Question. Read the following statements
(i) Order of reaction can be fractional or zero.
(ii) Molecularity of a reaction can be fractional but cannot be zero.
(iii) Slowest step in the complex reaction is considered as a rate determining step.
(iv) Units of rate constant for second order reaction are mol L s–1.
(v) Order is applicable to elementary as well as complex reactions whereas molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions.
Which of the following is the correct code for the statements above ?
(A) TTFFT
(B) TFTFT
(C) FFFTT
(D) FTTFF
Answer
B
Question. Consider the following reaction :
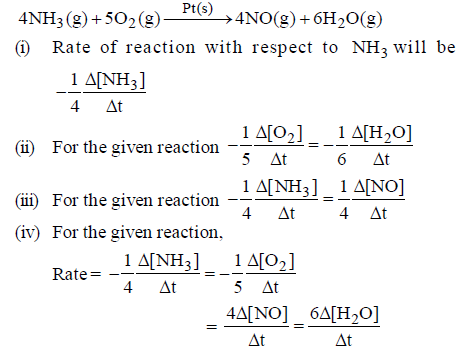
Which of the following is the correct code for the statements above.
(A) TTTT
(B) TFTF
(C) FTFT
(D) TFFT
Answer
B
Question. The following statement(s) is (are) correct :
(i) A plot of log kp versus 1/T is linear
(ii) A plot of log [X] versus time is linear for a first order reaction, X → P
(iii) A plot of log p versus 1/T is linear at constant volume
(iv) A plot of p versus 1/V is linear at constant temperature
(A) (i) only
(B) (ii) only
(C) (i) and (iv)
(D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ?
(i) For a zero order reaction concentration [R] vs time (t) gives a straight line plot
(ii) For a first order reaction log [R]0/[R] does not vary linearly with time.
(iii) Inversion of cane sugar is a pseudo first order reaction.
(A) (i) and (iii)
(B) (i) only
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (iii) only
Answer
A
Question. Read the following statements.
(i) e-Ea /RT corresponds to the fraction of molecules that have kinetic energy greater than Ea.
(ii) Ea can be calculated as follows
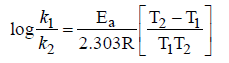
(iii) Catalyst can alter a reaction both ways means it can either decrease on increase rate of reaction
(iv) A catalyst always decreases the activation energy of the reaction but does not alter Gibb’s energy.
(v) A catalyst does not alter equilibrium constant rather, it helps in attaining the equilibrium faster.
Which of the following is the correct codes for above statements ?
(A) TTTFF
(B) TFFTT
(C) TFFTF
(D) FTFTT
Answer
B
Question. At high pressure the following reaction is of zero order.
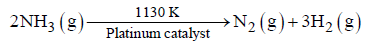
Which of the following statements are correct for above reaction?
(i) Rate of reaction = Rate constant
(ii) Rate of reaction depends on concentration of ammonia.
(iii) Rate of decomposition of ammonia will remain constant until ammonia disappears completely.
(iv) Further increase in pressure will change the rate of reaction.
(A) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(B) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iv)
(D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. According to collision theory, not all collisions between molecules lead to reaction. Which of the following statements provide reasons for the same ?
(i) The total energy of the two colliding molecules is less than some minimum amount of energy.
(ii) Molecules cannot react with each other unless a catalyst is present.
(iii) Molecules that are improperly oriented during collision will not react.
(iv) Molecules in different states of matter cannot react with each other.
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Consider the following statements:
(i) Increase in concentration of reactant increases the rate of a zero order reaction.
(ii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0.
(iii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = ∞.
(iv) lnk vs T is a straight line.
(v) lnk vs 1/T is a straight line.
Correct statements are
(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (ii) and (v)
(C) (iii) and (iv)
(D) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(i) Rate of reaction decreases with passage of time as the concentration of reactants decrease.
(ii) For a reaction
pP + qQ → rR + sS
Rate = k[P]x[Q]y where x = p and y = q
(iii) Rate law is the expression in which reaction rate is given in terms of molar concentration of reactants with each term raised to some power, which may or may not be same as the stichiometric coefficient of the reacting species in a balanced chemical equation.
(A) (i) and (iii)
(B) (i) and (ii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i) only
Answer
A
Question. Choose correct option based on following statements. Here T stands for true statement and F for false statement.
(i) Molecularity is defined as the number of reacting species taking part in a complex reaction,
(ii) Molecularity helps in understanding the mechanism of reaction.
(iii) Reactions with the molecularity three are very rare and slow to proceed.
(iv) Complex reactions involving more than three molecules take place in more than one step.
(A) TTTF
(B) TFTF
(C) FTTF
(D) FTTT
Answer
D
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Define order of reaction. Predict the order of reaction in the given graphs:
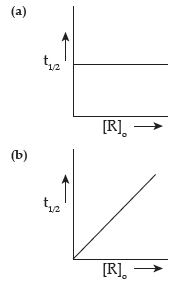
Where [R]0 is the initial concentration of reactant and t1/2 is half life.
Answer. Order of reaction is defined as the sum of powers to which the concentration terms are raised in the rate law equation.
(a) First order (b) zero order
Question. For a reaction the rate law expression is represented as follows:
Rate = k [A][B]1/2
(i) Interpret whether the reaction is elementary or complex. Give reason to support your answer.
(ii) Write the unit of rate constant for this reaction if concentration of A and B is expressed in moles/L.
Answer. (i) This is a complex reaction.
Order of reaction is a fraction value. i.e., 1.5.Molecularity cannot be a fraction. The reaction occurs in steps, so it is a complex reaction where order and molecularity has different values.
(ii) Rate = k[A][B][½]
Unit of Rate constant (k)

Question. For a reaction,

The proposed mechanism is given below:
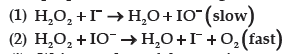
(i) Write rate law of the reaction.
(ii) Write overall order of reaction.
(iii) Out of step (1) and (2), which one is rate determining step?
Answer.(i) The rate law for the reaction is

(ii) This reaction is first order with respect to both H2O2 and I–.
1. The overall order of the reaction is bimolecular.
2. The order of the reaction is determined from the slowest step of the reaction mechanism.
(iii) The first reaction is slow, so this is the rate determining step.
Question. (i) Explain why H2 and O2 do not react at room temperature.
(ii) Write the rate equation for the reaction
A2 + 3B2 → 2C, if the overall order of the reaction is zero.
Answer. (i) Due to high activation energy of the reaction between O2 and H2.
(ii) Rate = k [A2]0[B2]0
Question. For a reaction:
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
Answer. (i) Zero order reaction, Molecularity is 2 / bimolecular reaction.
(ii) mol L–1 s–1.
Question. For a reaction: 2NH3 (g) pt→ N2(g) + 3H2(g);
Rate = k ;
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k.
Answer. (i) Zero order, bimolecular / unimolecular.
(ii) mol L–1 s–1.
Question. (i) What is the order of the reaction whose rate constant has same units as the rate of reaction ?
(ii) For a reaction A + H2O → B; Rate ∝ [A].
What is the order of this reaction ?
Answer. (i) Zero order
(ii) Pseudo-first order
Question. Explain the following terms:
(i) Rate constant (k)
(ii) Half-life period of reaction (t1/2).
Answer. (i) Rate constant (k): Rate constant is rate of the reaction when the concentration of reactants is unity.
(ii) Half-life period of a reaction (t1/2): Half-life of a reaction is the time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to half of its original value.
Question. Write units of rate constants for zero order and for the second order reactions if the concentration is expressed in mol L–1 and time in second.
Answer. Zero order: mol L–1s–1
Second order: L mol–1s–1
Question. For the reaction
2N2O5 (g) → 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g),
the rate of formation of NO2 (g) is 2.8 × 10–3 M s–1. Calculate the rate of disappearance of N2O5 (g).
Answer.


Question. For a chemical reaction R → P, variation in ln [R] vs time (t) plot is given below:
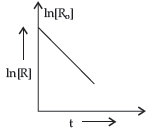
For this reaction:
(i) Predict the order of reaction.
(ii) What is the unit of rate constant (k)?
Answer. (i) First order.
(ii) s-1/time-1
Question. For a chemical reaction R → P, variation in log [Ro]/[R] vs time plot is given below:
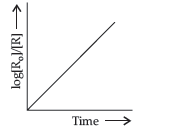
For this reaction:
(i) Predict the order of reaction
(ii) What is the unit of rate constant (k)?
Answer. (i) First order.]
(ii) s-1/time-1
Question. For a certain chemical reaction variation in concentration [A] vs. time (s) plot is given below:
(i) Predict the order of the given reaction?
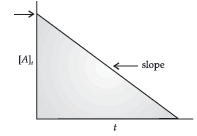
(ii) What does the slope of the line and intercept indicate?
(iii) What is the unit of rate constant k?
Answer. (i) Zero order reaction
(ii) Slope represents –k ; Intercept represents [A]0
(iii) mol L–1 s–1
Question. (i) For which reaction, the rate of reaction does not decrease with time?
(ii) What is the order of photochemical reaction?
Answer. (i) For zero order reaction the rate of reaction does not decrease with time because it does not depend on concentration of reactants.
(ii) Zero Order reaction.
Question. State a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order reaction.
Answer. Let us take a bimolecular reaction :
A + B → Product
Rate = k [A] [B]
When concentration of [B] is taken in excess then rate law will become:
Rate = k [A]
where, k = constant
The rate depends only on one of the reactant as there is negligible change in its concentration so it is bimolecular but is of first order.
Question. The following results have been obtained during the kinetic studies for the reaction:
P + 2Q → R + 2S
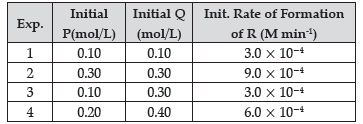
Determine the rate law expression for the reaction.
Answer. Let the rate law expression be Rate = k [P]x [Q]y from the table we know that
Rate 1 = 3.0 × 10–4 = k (0.10)x (0. 10)y
Rate 2 = 9.0 × 10–4 = k (0.30)x (0.30)y
Rate 3 = 3.0 × 10–4 = k (0.10)x (0.30)y
Rate 1/ Rate 3 = (1/3)y or 1 = (1/3)y
So, y = 0
Rate 2/ Rate 3 = (3)x or 3 = (3)y
So, x = 1
Rate = k [P]
Question. The C-14 content of an ancient piece of wood was found to have three tenths of that in living trees.
How old is that piece of wood? (log 3= 0.4771,log 7 = 0.8540 , Half-life of C-14 = 5730 years)
Answer.
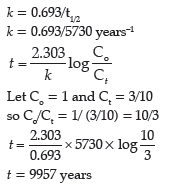
Question. (i) If the rate equation is given below:
Rate = k[A]2[B] then what will be the unit of its rate and rate constant?
(ii) Write the slope value obtained in the plot of log [R0] / [R] vs. time for a first order reaction.
Answer.


Question. (i) What is the order of the reaction whose rate constant has same units as the rate of reaction ?
(ii) For a reaction A + H2O → B; Rate ∝ [A]. What is the order of this reaction?
Answer. (i) Zero order
(ii) Pseudo-first order
Question. A first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10−3 s−1. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g ?
Answer. Initial amount = 5 g
Final concentration = 3 g
Rate constant = 1.15 × 10–3 s–1
We know that for a First order reaction,
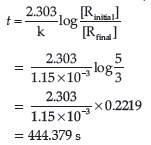
Question. (i) Why the molecularity of a reaction can not be zero?
(ii) Write the formula for expressing rate of the reaction.
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
Answer. (i) The molecularity of a reaction is the number of total molecules taking part in elementary step of reaction. So, minimum one molecule is required for a reaction to occur. Hence, the value of molecularity is never zero.
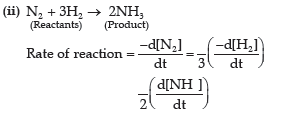
Question. (i) The rate of reaction decreases with the progress of reaction. Why?
(ii) Reactions having molecularity more than three occur rarely. Why?
Answer. (i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of reactants. Since, the concentration of reactants decreases with time, so rate of reaction also decreases.
(ii) It is because of the fact that collision of more than three molecules is not possible at a time.
Question. Derive integrated rate equation for rate constant of a first order reaction.
Answer.

Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. For the reaction
2A + B → A2B
Rate = k[A] [B]2, k = 2.0 × 10–6 mol–2L2s–1
Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when
[A] = 0.1 mol L–1 and [B] = 0.2 mol L–1 . Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L–1.
Answer. 2A + B → A2B
Initial rate = k[A] [B]2
= 2.0 × 10−6 × 0.1 × (0.2)2
= 8.0 × 10−9 mol L–1
When concentration of [A] is reduced from
0.10 mol L–1 to 0.06 mol L–1 i.e., 0.04 mol L–1,concentration of A has been used in the reaction.
Therefore, the concentration of B

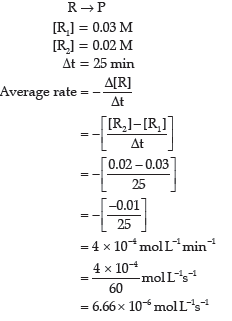
Question. For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 to 0.02 M in 25 minutes.Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
Answer.
Question. The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is a zero order reaction. What will be rate of production of N2 and H2 when the value of k is 2.5 × 10−9 mol L–1 s–1?
Answer.

Question. Following data are obtained for the reaction:
N2O5 → 2NO2 + ½O2
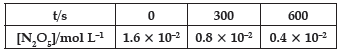
(a) Show that it follows first order reaction.
(b) Calculate the half-life.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
Answer.

Question. The following data were obtained for the reaction:
A + 2B → C
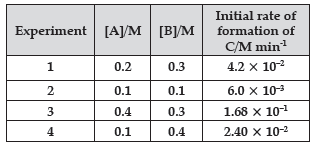
(a) Find the order of reaction with respect to A and B.
(b) Write the rate law and overall order of reaction.
(c) Calculate the rate constant (k).
Answer.
Let the order of reaction with respect to A be x and with respect to B be y.
∴ Rate of reaction = k[A]x[B]y
According to details given ,
4.2 × 10–2 = k[0.2]x [0.3]y …(i)
6.0 × 10–3 = k[0.1]x [0.1]y …(ii)
1.68 × 10–1 = k[0.4]x [0.3]y …(iii)
2.40 × 10–2 = k[0.1]x [0.4]y …(iv)
Dividing equation (iv) by (ii), we get

(i) So the rate of reaction with respect to A is 2 and with respect to B is 1.
(ii) Rate law = k[A]2[B]
Overall order of reaction is 3.
Question. For the first order thermal decomposition reaction, the following data were obtained:
C2H5Cl(g) → C2H4(g) + HCl(g)
Time / sec Total pressure / atm
0 0.30
300 0.50
Calculate the rate constant
(Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Answer.

Question. A first order reaction takes 20 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate the time when 75% of the reaction will be completed.
(Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Answer.
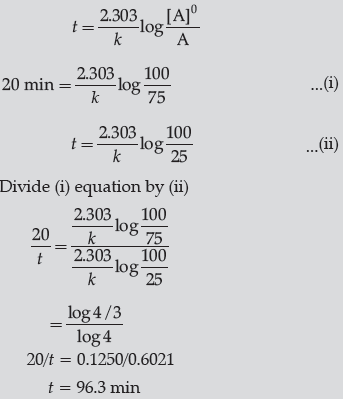
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (i) A first order reaction is 75% completed in 40 minutes. Calculate its t1/2.
(ii) Predict the order of the reaction in the given plots:
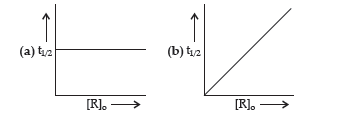
where [R]0 is the initial concentration of reactant.
(Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
Answer.

(ii) (a) First order reaction
(b) Zero order reaction
Question. (a) A first order reaction is 25% complete in 40 minutes.
Calculate the value of rate constant. In what time will the reaction be 80% completed?
(b) Define order of reaction. Write the condition under which a bimolecular reaction follows first order kinetics.
Answer.

(b) Order of reaction: The sum of the coefficients of the reacting species that are involved in the rate equation for the reaction, is called order of reaction. The condition under which a bimolecular reaction follows first order kinetics is when one of the reactants is taken in large excess that its concentration hardly changes.
Question. (i) For a reaction A + B → P, the rate is given by
Rate = k[A] [B]2
(a) How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled ?
(b) What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess ?
(ii) A first order reaction takes 30 minutes for 50% completion. Calculate the time required for 90% completion of this reaction. (log 2 = 0.3010) U[Question for Green board]
Answer. (i) A + B → P
Rate = k[A] [B]2
(a) When concentration of B is doubled it means concentration of B becomes 2 times.
Thus, Rate = k[A]1 [2B]2
= k[A] [4B2]
So, the rate becomes 4 times.
(b) Order of reaction is the number of molecules whose concentration alters after the reaction. If A is present in excess i.e., its concentration is unaffected.
So, rate depends only on the concentration of B. as k = [B]2
Thus, the reaction is of second order.
(ii) STEP 1: For the 1st order reaction:


Question. (i) Write the rate law for a first order reaction.Justify the statement that half life for a first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
(ii) For a first order reaction, show that the time required for 99% completion of a first order reaction is twice the time required for the completion of 90%.
Answer.


Question. For a given chemical reaction determine the order of reaction with respect to HgCl2, with respect to C2O4 2– and overall reaction.
HgCl2(aq) + C2O42–(aq) → 2 Cl–(aq) + 2CO2(g) + Hg2Cl2(s)

Answer. From the reaction, rate law will be expressed as follows, Rate = k[HgCl2]m[C2O42–]n
Compare the rates in experiments 1 and 2 (or 3 and 4) to find the order in oxalate ion:

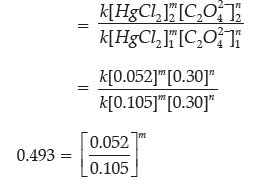
0.493 = 0.495m
m = 1
Therefore, the reaction is first order with respect to mercury (II) chloride and second order with respect to oxalate. The overall order = m + n = 2 + 1 = 3, third order.
Question. The following data were obtained for the reaction:
2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2
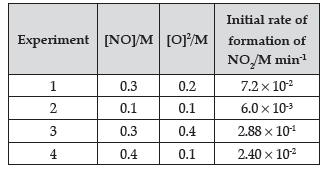
(i) Find the order of reaction with respect to NO and O2.
(ii) Write the rate law and overall order of reaction.
(iii) Calculate the rate constant (k).
Answer. (i) Rate = k[NO]x[O2]y
7.2 × 10-2 = k[0.3]x[0.2]y Eqn (1)
6.0 × 10-3 = k[0.1]x[0.1]y Eqn (2)
2.88 × 10-1 = k[0.3]x[0.4]y Eqn (3)
2.40 × 10-2 = k[0.4]x[0.1]y Eqn (4)

Question. A reaction is of first order with respect to A and second order with respect to B
(i) Write differential rate equation.
(ii) How is the rate effected when the concentration of B is tripled?
(iii) How is the rate affected when the concentration of both A and B is doubled?
Answer.(i) Differential rate equation
dx/dt= k[A][B]2
(ii) Let [A] = a, [B] = b
If [B] increases three times
[B] = 3b
∴ Rate = k[A][B]2
Rate1 = k × a × b2 …(i)
Rate2 = k × a × (3b)2 …(ii)
From eq (i) and (ii)
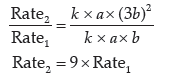
∴ The rate becomes nine times when the concentration of B is tripled.
(iii) If [A] and [B] is doubled then [A] = 2a [B] = 2b
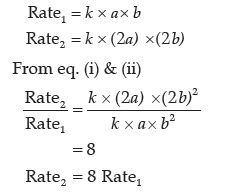
∴ The rate becomes eight times when the concentration of both A and B is doubled.
Question. (a) Reaction 2A + B + C → D + 2E shows first order with respect to A, second order with respect to B and zero order with respect to C. Determine:
(i) Rate law of reaction
(ii) What will be the rate of reaction on doubling of concentration of A, B and C?
(b) For the reaction,
N2 O5 → 2NO2 +1/2 O2
The rate of dissociation of N2O5 is 5.65 × 10–5 mol L–1 s–1. Determine:
(i) Rate of reaction
(ii) Rate of formation of NO2
(iii) Rate of formation of O2
Answer. (a) (i) 2A + B + C → D + 2E
Rate Law
Rate (r) = k[A]1 [B]2[C]0
(ii) If concentration of A, B & C is doubled


Question. Calculate overall order of reaction which has the rate rxpression r = k [A]3/2 [B] -1
Answer. Order = 3/2+(-1) =1/2
Question. A reaction is first order in A. How is the rate affected if the concentration of A is reduced to half?
Answer. r = k [A]1 now r1 = k [1/2 A] =1/2 r
Question. What is the unit of rate constant for a pseudo first order reaction ?
Answer. Sec -1
Question. What is the order of reaction whose rate constant has the same unit as the rate of reaction?
Answer. Zero order
Question. A reaction is 50% complete in 4 hrs and 75% completes in 8 hrs . What is the order of reaction ?
Answer. Since half life remains constant so it is a first order reaction.
Question. For the reaction R —> P , the concentration of a reactant changes fron .05M to .02M in 30 sec. Calculate average rate of reaction .
Answer.
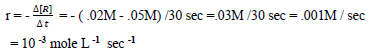
Question. The rate constant for first order reaction is 60/s. How much time will it take to reduce the concentration of the reaction to 1/10 of its initial value.
Answer.
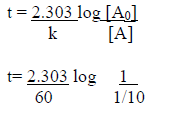

Question. A first order reaction is found to have a rate constant k =5.5 x 10 -12 sec -1 .
Find the half life of the reaction.
Answer. Half life for a first order reaction is t ½ = 0.693/𝑘 = 0.693 / 5.5 x 10 -12 sec -1
= 1.26 x 10 +11 sec
Question. A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 x10 -3 sec -1.How long will 5 gm of this reactant take to reduce to 3 gm ?
Answer. t =( 2.303/k) log( a/a-x) = (2.303/ 1.15 x10 -3) log (5/3) =2000 log 1.667
=2000 x 0.2219 = 443.8 sec


