See below CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Set C with solutions. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern issued by CBSE for the current academic year. All sample papers provided by our Class 12 Chemistry teachers are with answers. You can see the sample paper given below and use them for more practice for Class 12 Chemistry examination.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry Set C
Topic-1
Carbohydrates, their Classification and Importance
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of a-Dglucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.Structure of glycogen is similar to __________.
(a) Amylose
(b) Amylopectin
(c) Cellulose
(d) Glucose
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following polymer is stored in the liver of animals?
(a) Amylose
(b) Cellulose
(c) Amylopectin
(d) Glycogen
Answer
D
Question. Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide. One molecule of sucrose on hydrolysis gives _________.
(a) 2 molecules of glucose
(b) 2 molecules of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(c) 1 molecule of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(d) 2 molecules of fructose
Answer
C
Question. Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.

(a) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘a’ carbon of fructose.
(b) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and e’ carbon of fructose.
(c) ‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘b’ carbon of fructose.
(d) ‘f’ carbon of glucose and ‘f’ carbon of fructose.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(a) It is an aldohexose.
(b) On heating with HI it forms n-hexane.
(c) It is present in furanose form.
(d) It does not give 2,4-DNP test.
Answer
C
B. Answer the following:
Question. Name the components of starch.
Answer. There are two components of starch, i.e., amylose and amylopectin.
Question. Which of the two components of starch are water soluble ?
Answer. Amylose.
Question. Which component of starch is branched polymer of a glucose and insoluble in water ?
Answer. Amylopectin.
Question. Write the products of hydrolysis of maltose ?
Answer. 2 molecules of Glucose.
Question. What are the products of hydrolysis of sucrose ?
Answer. Fructose and Glucose are the products of hydrolysis of sucrose.
Question. What are the products of hydrolysis of lactose ?
Answer. It gives β-D galactose and β-D glucose.
Question. Write a reaction which shows that all the carbon atoms in glucose are linked in a straight chain.
Answer.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Write any two reactions of glucose which cannot be explained by the open chain structure of glucose molecule.
Answer. Reactions of glucose that cannot be explained by open chain structure :
(i) Glucose gives the characteristic reaction of alcohols and carbonyl group (aldehydes and ketones).
However, it does not form addition compound with ammonia and sodium bisulphite and does not respond to 2, 4-DNP test and Schiff ’s test.
(ii) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free– CHO group
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Glycosidic linkage
(ii) Invert sugar
(iii) Oligosaccharides.
Answer. (i) Glycosidic linkage : The two monosaccharides units are joined together through an oxide linkage formed by loss of a molecule of H2O.
(ii) Invert sugar : Hydrolysis of sucrose brings about a change in sign of rotation from dextro (+) to laevo (–) and the product is known as invert sugar.
(iii) Carbohydrates that yield two to ten monosaccharides units on hydrolysis are called polysaccharides.
Examples are starch, cellulose, glycogen etc.
Question. Give three reactions of glucose which cannot be explained by its chain structure.
Answer. (i) Glucose does not give 2,4- DNP test.
(ii) Glucose does not give Schiff’s test.
(iii) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(iv) Glucose does not form the hydrogensulphite addition product with NaHSO3.
Question. How will you distinguish 1° and 2° hydroxyl groups present in glucose? Explain with reaction.
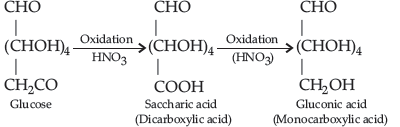
Answer. Glucose on treatment with acetic anhydride in presence of pyridine or a few drops of conc. H2SO4. It forms penta-acetyl derivative indicating the presence of 5-OH groups. Out of which, one –OH group is primary (1o) alcoholic and four (C2, C3, C4 and C5) – OH groups are secondary (2o) alcoholic groups.

Glucose (or gluconic acid) on oxidation with HNO3 gives saccharic acid (a dicarboxylic acid) indicating that one of the primary (1o) alcoholic group is oxidized to –COOH group but secondary (2o) hydroxyl groups undergo oxidation only in drastic conditions.
Long Answer Type Questions-II
Question. On the basis of which evidences D-glucose was assigned the following structure?

Answer. This structure was assigned on the basis of the following evidences :
(i) Molecular formula : C6H12O6 is molecular formula of glucose.
(ii) Straight chain structure :
(a) When aqueous solution of glucose is treated with sodium amalgam (Na/Hg) or sodium borohydride,it is reduced to sorbitol (or glucitol) a hexahydric alcohol.

(b) Prolonged heating with hydriodic acid and red phosphorous at 100°C gives a mixture of n-hexane and 2-iodohexane.
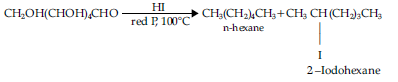
The formation of n-hexane suggests that all the six carbon atoms in glucose are arranged in a straight chain structure.
(c) Presence of five –OH groups : On acetylation with acetic anhydride, glucose gives a pentaacetate. This confirms that glucose contains five –OH groups. We
know that the presence of two or more –OH groups on the same carbon atom makes the molecules unstable.
Since glucose is a stable compound, therefore, the five –OH groups must be present on different carbon atoms.
(d) Presence of one primary alcoholic group : On oxidation with conc. HNO3, both glucose and gluconic acid give the same dicarboxylic acid and saccharic acid. The primary alcoholic group (–CH2OH) is always present at the end of the carbon chain.
(e) Presence of an aldehyde (–CHO) group : Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine, NH2OH to form oxime.
This suggest that glucose contains a carbonyl (>C=O) group.
On the basis of above observations, the following open CH2OH chain structure for glucose can be written as follows :
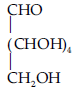
Topic-2
Proteins, Hormones, Vitamins and Nucleic Acids
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures, viz. a-helix and b-pleated sheet structure. g-helix structure of protein is stabilised by
(a) Peptide bonds
(b) van der Waals forces
(c) Hydrogen bonds
(d) Dipole-dipole interactions
Answer
C
Question. Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be
(a) primary structure of proteins.
(b) secondary structure of proteins.
(c) tertiary structure of proteins.
(d) quaternary structure of proteins
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following acids is a vitamin?
(a) Aspartic acid
(b) Ascorbic acid
(c) Adipic acid
(d) Saccharic acid
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following B group vitamins can be stored in our body?
(a) Vitamin B1
(b) Vitamin B2
(c) Vitamin B6
(d) Vitamin B12
Answer
D
Question. Nucleic acids are the polymers of
(a) Nucleosides
(b) Nucleotides
(c) Bases
(d) Sugars
Answer
B
Question. Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage.Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
(a) 5’ and 3’
(b) 1’ and 5’
(c) 5’ and 5’
(d) 3’ and 3’
Answer
A
Question. DNA and RNA contain four bases each. Which of the following bases is not present in RNA?
(a) Adenine
(b) Uracil
(c) Thymine
(d) Cytosine
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following bases is not present in DNA?
(a) Adenine
(b) Thymine
(c) Cytosine
(d) Uracil
Answer
D
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.
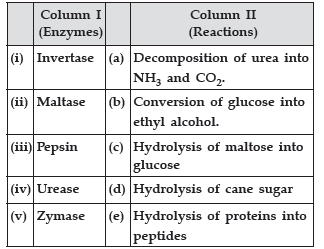
Answer. (i) → (d), (ii) → (c), (iii) → (e), (iv) → (a), (v) → (b)
C. Answer the following:
Question. Write the linkage joining amino acids ?
Answer. Peptide bond.
Question. What are the different types of RNA molecules which perform different functions ?
Answer. (i) Messenger RNA (m–RNA)
(ii) Transfer RNA (t–RNA)
(iii) Ribosomal RNA (r–RNA)
Question. What type of bonding help in stabilising the a-helix structure of proteins ?
Answer. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding present between —NH group of each amino acid residue and the >C=O of an adjacent turn of the helix mainly helps in stabilising the a-helix structure of proteins.
Short Answer Type Questions (2 marks each)
Question. What is meant by :
(i) Peptide linkage,
(ii) Biocatalysts.
Answer. (i) Peptide linkage : Proteins are complex nitrogenous polymeric substances present in all forms of living matter. These are obtained by the condensation polymerisation of α-amino acids through the formation of peptide bonds.
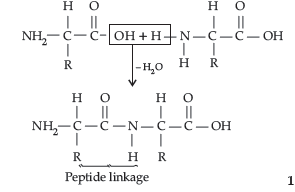
(ii) Biocatalyst : Enzymes are complex nitrogenous substances (proteins) having molecular weight of 10,000 or even more. Enzymes increase the rate of biochemical reactions by providing alternative path of lower activation energy.
Therefore, enzymes are termed as biochemical catalyst and phenomenon is known as biochemical catalysis.
Question. Write the main structural difference between DNA and RNA. Of the two bases, thymine and uracil, which one is present in DNA ?
Answer. Structural differences between DNA and RNA
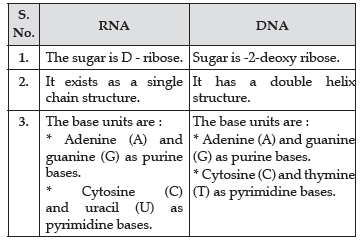
Thymine is present in DNA.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Define the following as related to proteins :
(i) Peptide linkage, (ii) Primary structure,
(iii) Denaturation
Answer. (i) Peptide linkage : Proteins are complex nitrogenous polymeric substances present in all forms of living matter. These are obtained by the condensation polymerisation of α-amino acids through the formation of peptide bonds.
(ii) Primary structure – each polypeptide in a protein molecule having amino acids which are linked with each other in a specific sequence.
(iii) Denaturation – When a protein is subjected to physical change like change in temperature or chemical change like change in pH, protein loses its biological activity.
Question. Define the following with an example of each :
(a) Polysaccharides
(b) Denatured protein
(c) Essential amino acids
OR
(a) Write the product when D-glucose reacts with conc. HNO3.
(b) Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why ?
(c) Write one difference between a-helix and b-pleated structures of proteins.
Answer. (i) (a)Carbohydrates that give large number of monosaccharide units on hydrolysis / large number of monosaccharides units joined together by glycosidic linkage
Starch/ glycogen/ cellulose (or any other)
(b) Proteins that lose their biological activity / proteins in which secondary and tertiary structures are destroyed Curdling of milk (or any other)
(c) Amino acids which cannot be synthesised in the body.
Valine / Leucine (or any other)
OR
(a) Saccharic acid / COOH-(CHOH)4-COOH
(b) Due to the presence of carboxyl and amino group
in the same molecule / due to formation of zwitter
ion or dipolar ion.
(c) a-helix has intramolecular hydrogen bonding while b pleated has intermolecular hydrogen bonding / a-helix results due to regular coiling of polypeptide chains while in b pleated all polypeptide chains are stretched and arranged side by side.
Question. (i) Write the name of two monosaccharides obtained on hydrolysis of lactose sugar.
(ii) Why vitamin C cannot be stored in our body ?
(iii) What is the difference between a nucleoside and nucleotide ?
Answer. (i) b-D-Glucose and b–D–Galactose.
(ii) It is water soluble, hence it is excreted through urine.
(iii) Nucleoside : It is formed when pentose sugar combines with nitrogen base.
Nucleotide : When nucleoside bonds with phosphate group.
Question. (i) Write the structural difference between starch and cellulose.
(ii) What type of linkage is present in Nucleic acids ?
(iii) Give one example each for fibrous protein and globular protein.
Answer. (i) In starch, the glucose monomers are in alpha configuration while in cellulose the glucose
monomers are in beta configuration. Starch is a polymer consisting of amylose and amylopectin while cellulose is a long chain composed only of b—D— glucose units.
(ii) Phosphodiester linkage between the 5’ and 3’ atoms is present in nucleic acids.
(iii) Example of fibrous protein—Collagen, keratin, myosin. (Any one)
Example of globular protein—Insulin,haemoglobin, egg albumin. (Any one)
Question. How are vitamins classified ? Name the vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood.
Answer. Vitamins are classified into :
(i) Water soluble vitamins : Vitamins which are soluble in water but insoluble in fat and oils. e.g.,vitamin B and C.
(ii) Fat soluble vitamins : Vitamins are soluble in fat and oils but insoluble in water. e.g., vitamin A, D, E and K.Vitamin K is responsible for coagulation of blood.
Question. (i) Which one of the following is a polysaccharide : starch, maltose, fructose, glucose
(ii) Write one difference between a-helix and b-pleated sheet structures of protein.
(iii) Write the name of the disease caused by the deficiency of vitamin B12.
Answer. (i) Starch.
(ii) a- Helix polypeptide chains are stabilized by intramolecular H-bonding whereas b-pleated sheet is stabilized by intermolecular H-bonding. (or any other difference)
(iii) Pernicious anaemia.
Question. (i) Deficiency of which vitamin causes night blindness ?
(ii) Name the base that is found in nucleotide of RNA only.
(iii) Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose ?
Answer. (i) Vitamin A
(ii) Uracil
(iii) It suggests that six carbon atoms are in straight chain/CHO—(CHOH)4—CH2OH
Question. (i) Deficiency of which vitamin causes scurvy ?
(ii) What type of linkage is responsible for the formation of proteins ?
(iii) Write the product formed when glucose is treated with HI.
Answer. (i) Vitamin C.
(ii) Peptide linkage.
(iii) n-hexane or its structure.
Question. (i) A non reducing disaccharide ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute acid gives an equimolar mixture of D–(+)–glucose and D-(-)-Fructose.
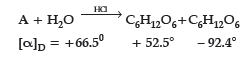
Identify A. What is the mixture of D–(+)–glucose and D-(-)-Fructose known as ? Name the linkage that holds the two units in the disaccharide.
(ii) a-amino acids have relatively higher melting points than the corresponding halo acids.
Answer. (i) A–Sucrose (C12H22O11)
The mixture of D-(+)- glucose and D-(-)-Fructose is known as invert sugar.
The linkage which holds the two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
(ii) The amino acids exits as dipolar Zwitter ion. Due to their dipolar salt like character they have strong dipole-dipole attractions. Thus, their melting points are higher than the corresponding halo acids which do not exist as Zwitter ions.
Question. (i) Which one of the following is a disaccharide :
Starch, Maltose, Fructose, Glucose ?
(ii) What is the difference between fibrous protein and globular protein ?
(iii) Write the name of vitamin whose deficiency causes bone deformities in children.
Answer. (i) Maltose
(ii) Fibrous proteins : parallel polypeptide chain, insoluble in water, Globular proteins: spherical shape, soluble in water, (or any 1 suitable difference)
(iii) Vitamin D
Question. (i) Why water soluble vitamins must be supplied regularly in the diet? Give one example of it.
(ii) Differentiate between the follwing:
(a) Essential and non-essential amino acids.
(b) Fibrous and globular proteins.
Answer. (i) Because they are excreted in urine and cannot
be stored in body; Vitamin C/B1/ B6
(ii) (a) Essential amino acids are those which cannot be synthesized in the body and are supplied through diet whereas non-essential amino acid can be synthesized in the body
(b) In fibrous proteins, the polypeptide chains run parallel and are held together by hydrogen or disulphide bonds while in globular, polypeptide chains coil around to give a spherical shape
Question. (i) What type of linkage is present in disaccharides?
(ii) Write one source and deficiency disease of vitamin B12.
(iii) Write the difference between DNA and RNA.
Answer. (i) Glycosidic linkage.
(ii) Source: Meat, fish, egg, curd (any one); Pernicious anemia
(iii) DNA is a double strand while RNA is a single strand molecule (or any other correct difference)
Question. (i) What type of linkage is present in proteins?
(ii) Give one example each of water soluble and fat soluble vitamins.
(iii) Draw pyranose structure of glucose.
Answer. (i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Water soluble – Vit B/C, Fat soluble – Vit A/D/E/K/ B12
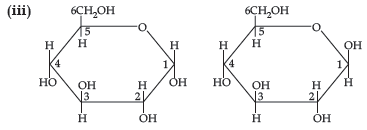
Question. (i) Which vitamin deficiency causes rickets?
(ii) Name the base that is found in nucleotide of RNA only.
(iii) Glucose on reaction with acetic acid gives glucose penta acetate. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Answer. (i) Vitamin D
(ii) Uracil
(iii) 5 OH groups are present
Question. (a) Name the branched chain component of starch.
(b) Ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA differ in the structure around which carbon atom?
(c) How many peptide linkages are present in a tripeptide?
Answer. (a) Amylopectin.
(b) C- 2
(c) Two peptide linkages.
Question. Explain the following :
(i) Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids.
(ii) The two strands of DNA are complementary to each other.
(iii) Reaction of glucose that indicates that the carbonyl group is present as an aldehydic group in the open structure of glucose.
Answer. (i) Due to the formation of zwitter ion.
(ii) The two strands are complementary to each other because the hydrogen bonds are formed between specific pairs of bases.
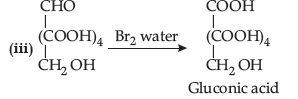
Or glucose gets oxidised to gluconic acid on reaction with mild oxidising agent like Bromine water.
Long Answer Type Questions-II
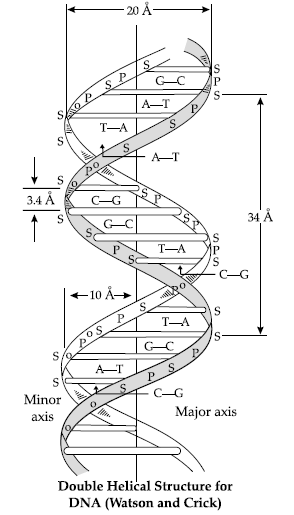
Question. Write the structures of fragments produced on complete hydrolysis of DNA. How are they linked in DNA molecule? Draw a diagram to show pairing of nucleotide bases in double helix of DNA.
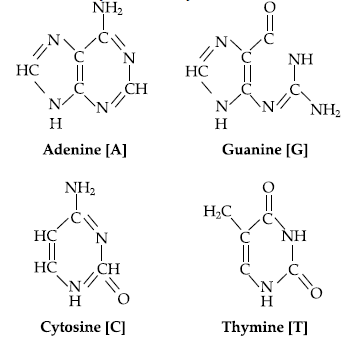
Answer. Complete hydrolysis of DNA yields a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds called bases.
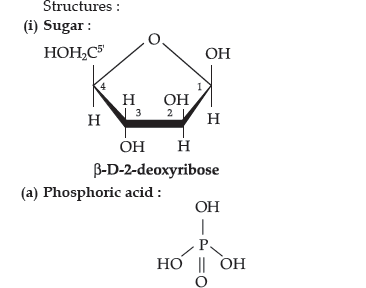
(b) Nitrogen base : DNA contains four bases : Adenine,Guanine, Thymine and Cytosine.
A unit formed by the attachment of a base to 1’-position of sugar is called nucleoside.
When nucleoside links to phosphoric acid at 5’-position of sugar moiety, a nucleotide is formed. Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’- and 3’- carbon atoms of the pentose sugar
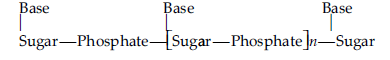
In DNA, two chains of nucleic acid coil around each other and held together by H-bonds between bases of two chains.