Please see below Case Study MCQ Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes Class 10 Science. These MCQ Questions with Answers for Case study have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines of Class 10 Science. Cased Study Based MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science are expected to come in the upcoming exams. We have provided a lot of case studies for all chapters in standard 10 science. Please solve the MCQ Questions and compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
Chapter 6 Life Processes Class 10 Science Case Study MCQ Questions
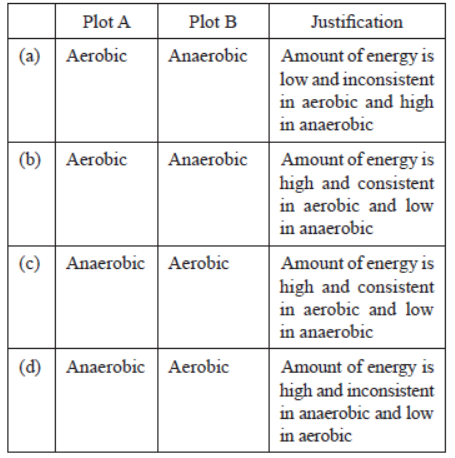
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
Question. Study the graph below that represents the amount of energy supplied with respect to the time while an athlete is running at full speed.
Choose the correct combination of plots and justification provided in the following table.
Answer
B
Question. The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration are:
(i) presence of oxygen
(ii) release of carbon dioxide
(iii) release of energy
(iv) release of lactic acid
(a) (i), (ii) only
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) only
(c) (ii), iii), iv) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer
C
Question. Study the table below and select the row that has the incorrect information.
Aerobic Anaerobic
(a) Location Cytoplasm Mitochondria
(b) End Porduct CO2 and H2O Ethanol and CO2
(c) Amount of ATP High Low
(d) Oxygen Needed Not needed
Answer
B
Question. Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by
(a) Breathing
(b) Tissue respiration
(c) Organ respiration
(d) Digestion of food
Answer
B
Question. The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a peak at point D. Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race.
Respiration in athletics. The blood of an athlete was tested before, during and after a 400m race:

Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event?
Which of the following processes explains this event?
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(c) Fermentation
(d) Breathing
Answer
B
The force exerted by the blood against the wall of a vessel is called blood pressure. This pressure is much greater in arteries than in veins. The pressure of blood inside the artery during ventricular systole (contraction) is called systolic pressure and pressure in the artery during ventricular diastole (relaxation) is called diastolic pressure.
Question. Choose the correct combination to depict the given figure:

(a) x. Systolic pressure, y. Systolic pressure
(b) x. Systolic pressure, y. Diastolic pressure
(c) x. Diastolic pressure, y. Systolic pressure
(d) x. Diastolic pressure, y. Diastolic pressure
Answer
B
Question. In the case (iv), the health care provider used an instrument to check the blood pressure of the patient. Name the instrument used by the health care provider.

(a) Stethoscope
(b) Pulse oximeter
(c) Sphygmomanometer
(d) Otoscope
Answer
C
Question. Study the table given below and select the row that has incorrect information:

Answer
D
Question. A person travelling through a public transport suddenly fainted. Upon check-up by a health care provider, it was found that his blood pressure was 152-95. Name the medical condition that the person is going through.
(a) Low blood pressure
(b) High blood pressure
(c) Low sugar level
(d) High sugar level
Answer
B
Question. The characteristics observed in hypertension are:
(i) Constriction of arterioles
(ii) Results in rupture of an artery
(iii) Causes internal bleeding
(iv) Increased blood flow
Choose the correct option based on the statements.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) Only 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Answer
D
During inhalation, the diaphragm is contracted which increases the volume of the lung cavity. During exhalation, the diaphragm is relaxed which decreases the volume of the lung cavity. The given graph is related to the changes in the volume of lungs of a person at a rest over a period of 20 seconds.
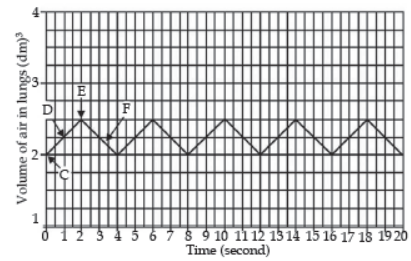
Question. Which two points in the graph (C, D, E or F), shows inspiration and expiration?
(a) D, E
(b) D, F
(c) C, D
(d) E, F
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following muscles help during inhalation?
(a) External intercostal muscles
(b) Internal intercostal muscles
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. How many breaths per minute is the person taking when at rest?
(a) 110
(b) 15
(c) 17
(d) 20
Answer
B
Question. Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils → larynx → pharynx → trachea → lungs
(b) Nasal passage → trachea → pharynx → larynx → alveoli
(c) Larynx → nostrils → pharynx → lungs
(d) Nostrils → pharynx → larynx → trachea → alveoli
Answer
D
Question. During vigorous exercise, the rate of breathing of normal man is
(a) 20 to 25 times per minute
(b) 50 to 90 times per minute
(c) 100 to 150 times per minute
(d) 40 to 70 times per minute
Answer
A
In human being, the holozoic nutrition takes place in five steps:
1. Ingestion. The process of taking food inside the body is called ingestion.
2. Digestion. In digestion, the ingested food is converted into simple form with the help of digestive enzymes.
3. Absorption. In this stage the food digested in second step is absorbed into the cells of body.
4. Assimilation. Assimilation is the process of utilising the food absorbed in third step by various cells of the body.
5. Egestion. Egestion is the final step of holozoic nutrition in which the undigested food is removed from the body.
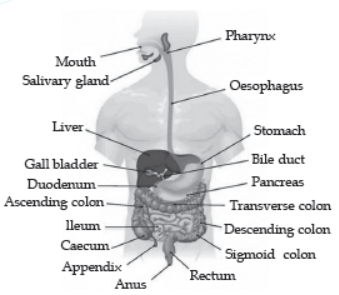
Question. The inner lining of stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid, choose the correct one:
(a) Pepsin
(b) Mucus
(c) Salivary amylase
(d) Bile
Answer
B
Question. Which is the correct sequence of parts in human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth → Stomach → Small intestine → Oesophagus → Large intestine
(b) Mouth → Oesophagus → Stomach → Large intestine → Small intestine
(c) Mouth → Stomach → Oesophagus → Small intestine → Large intestine
(d) Mouth → Oesophagus → Stomach → Small intestine → Large intestine
Answer
D
Question. Which part of alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
Answer
B
Question. Choose the function of the pancreatic juice from the following.
(a) Trypsin digests proteins and lipase carbohydrates
(b) Trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase proteins
(c) Trypsin and lipase digest fats.
(d) Trypsin digests proteins and lipase digests emulsified fats droplets
Answer
D
Question. If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which event in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(a) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(b) Starch breaking down into sugars
(c) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(d) Absorption of vitamins
Answer
B
Each capillary cluster in the kidney is associated with the cup-shaped end of a tube that collects the filtered urine (see adjoining figure). Each kidney has large numbers of these filtration units called nephrons packed close together. Some substances in the initial filtrate, such as glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water, are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. The amount of water reabsorbed depends on how much excess water there is in the body, and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted. The urine forming in each kidney eventually enters a long tube, the ureter, which connects the kidneys with the urinary bladder. Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until the pressure of the expanded bladder leads to the urge to pass it out through the urethra. The bladder is muscular, so it is under nervous control, as we have discussed elsewhere. As a result, we can usually control the urge to urinate.
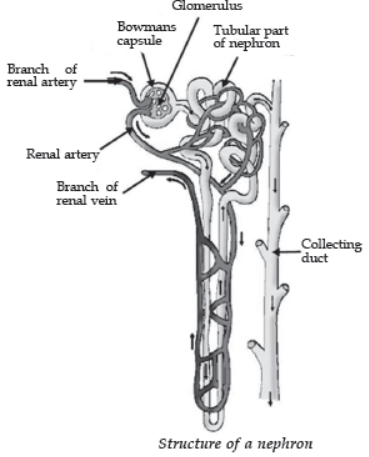
Question. The substance which is not reabsorbed into the blood capillaries surrounding the tubule of a nephron is mainly:
(a) glucose
(b) amino acid
(c) urea
(d) water
Answer
C
Question. The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(a) nutrition
(b) respiration
(c) excretion
(d) transportation
Answer
C
Question. The procedure of cleaning the blood of a person by using a kidney machine is known as:
(a) ketolysis
(b) hydrolysis
(c) dialysis
(d) photolysis
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the correct path taken by urine in our body?
(a) kidney → ureter → urethra → bladder
(b) kidney → bladder → urethra → ureter
(c) kidney → ureter → bladder → urethra
(d) bladder → kidney → ureter → urethra
Answer
C
Question. The excretory unit in the human excretory system is called:
(a) nephron
(b) neuron
(c) nephridia
(d) kidney
Answer
A
The human heart is a muscular organ made up of cardiac muscles. It is a four-chambered organ to prevent intermixing of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood. A thick wall muscle called septum that separates the two sides left and right of the heart. Look at the picture.

Question. The de-oxygenated blood from the body organs first enters:
(a) into right atrium of the heart through vena cava.
(b) into left atrium of the heart through vena cava.
(c) into right ventricle of the heart through vena cava.
(d) into right atrium of the heart through aorta.
Answer
A
Question. Pulmonary vein brings:
(a) oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
(b) de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
(c) oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
(d) de-oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Answer
A
Question. Tricuspid valve is found between:
(a) right auricle and right ventricle
(b) left auricle and left ventricle
(c) right auricle and left ventricle
(d) left auricle and right ventricle
Answer
A
Question. The upper two chambers and lower two chambers are called:
(a) Ventricles and auricles respectively
(b) Auricles and ventricles respectively
(c) Ventricles and valves respectively
(d) Arteries and veins respectively
Answer
B
Question. The artery which carries de-oxygenated blood from the heart into lungs is called __________.
(a) Pulmonary artery
(b) Hepatic artery
(c) Renal artery
(d) All arteries
Answer
A
There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the waist. A waste product Q formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in the liver is brought into organ P through blood by an artery R. The numerous tiny filters S present in organ P clean the dirty blood by removing the waste product Q. The clean blood goes into circulation through a vein T. The waste substance Q, other waste salts, and excess water form a yellowish liquid U which goes from organ P into a bag-like structure V through two tubes W. This liquid is then thrown out of the body through a tube X.
Question. Name (i) liquid U (ii) structure V (iii) tubes W, and (iv) tube X.
Answer
(i) Urine (ii) Bladder (iii) Ureters (iv) Urethra
Question. What is (i) organ P, and (ii) waste substance Q?
Answer
(i) Kidneys (ii) Urea
Question. Name (i) artery R, and (ii) vein T.
Answer
(i) Renal artery (ii) Renal vein
Question. What are tiny filters S known as?
Answer
Nephrons