Please refer to Assignments Class 10 Social Science Agriculture Chapter 4 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 10 Social Science Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 4 Agriculture Class 10 Social Science have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Agriculture Assignments Class 10 Social Science
ONE MARK QUESTIONS
Question. Which state is the largest producer of ragi?
Ans : Karnataka.
Question. In which type of soil does maize grow well?
Ans : Old alluvial.
Question. In which system of agriculture, a single crop is grown on a large area?
Ans : Plantation agriculture.
Question. Name some plantation crops.
Ans : Tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane and banana.
Question. By which other name is ‘slash and burn’ agriculture known?
Ans : Primitive subsistence farming/jhumming
Question. In which country the ‘slash and burn’ agriculture is known as ‘Roca’ ?
Ans : Brazil.
Question. Which type of farming is intensive subsistence farming?
Ans : Labour intensive farming.
Question. Which crop is known as golden fibre?
Ans : Jute.
Question. Which two areas of India produce oranges mainly?
Ans : Nagpur in Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
Question. Which crop is used both as food and fodder?
Ans : Maize.
Question. A short season between the rabi and kharif season is known as:
(a) Aus
(b) Boro
(c) Zaid
(d) None of the above
Ans. (c) Zaid
Question. Kharif crops are grown:
(a) with the onset of monsoon and harvested in September-October
(b) with the onset of winter and harvested in summer
(c) with onset of Autumn and harvested in summer
(d) None of the above
Ans. (a) with the onset of monsoon and harvested in September-October
Question. Name two major tea-producing states of India.
Ans. Assam and West Bengal.
Question. What are the two important beverage crops of India?
Ans. coffee and tea
Question. Punjab is major producer of the maize in India. True or False
Ans. False
Question. …………….. is the largest producer as well as the consumer of pulses in the world.
Ans. India
Question. Choose the correct match-
(a) Kharif crop …………………… paddy and maize
(b) Rabi crop ……………………… muskmelon and cucumber
(c) Zaid crop ………………………. gram and mustard
Ans. (a) Kharif crop …………………… paddy and maize
Question. In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).Mark your answer as per the codes provided below :
(A) Tea cultivation is a labour – intensive industry.
(R) Cultivation can be done throughout the year. Tea bushes require warm and moist frost free climate.
Options:
(1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(3) A is true but R is False.
(4) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (2) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
THREE MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. Which are the two main cropping seasons in India? Mention their growing and harvesting periods.
Ans : The two main cropping seasons are Rabi and Kharif:
a. Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June.
b. Kharif crops are sown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and harvested in September-October.
Question. Give an account of oilseeds in India. State the importance of groundnut and name the states where it is grown.
or
Describe the uses of oilseeds? Which state is the largest producer of groundnut?
Ans : Importance:
a. Are edible and used as cooking medium.
b. Used as raw material in production of soap, cosmetics and ointment.
c. India-largest producer.
Groundnut:
a. Kharif crop.
b. Accounts half of the total oilseed production.
c. State: Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Question. Describe the institutional and technical changes introduced in the field of agriculture in India in the recent years.
or
What were the attributes of the comprehensive land development programme initiated in India in the decade 1980 and 1990.
or
Describe any three technological and institutional reforms made in the field of agriculture in India.
Ans : a. Land reforms: collectivization, . consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari.
b. Agricultural reforms: Green revolution and White revolution.
c. Land development programmes : Provision for crop in surance against drought, flood, cyclone etc., establishment of Grameen banks, Cooperative societies and banks for providing loans.
d. Issuing of Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme, etc.
e. Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers on radio and TV.
Question. Describe the impact of globlisation on indian agriculture.
Ans. (1) The Indian farmers might have to force much unstable prices for these products fluctuated largely on year-to-year basis.
(2) The impact of trade liberalization on the prices of agricultural products at international level and domestic level depend on what policies other countries follow .
(3) Export of major agriculture commodities have been liberalised.
(4) Major transformation took place with the introduction of high-yielding varieties of crops .
(5) This innovation , coupled with investments in infrastructure, expansion of credit marketing and processing facilities led to a significant increase in the use of modern inputs.
Question. What are the Geographical conditions required for rice growth. Name the major areas of its production.
Ans. (a) Climate: Paddy is a tropical crop and grows well in the wet monsoon.
(b) Temperature: Above 25°C, coupled with heavy humidity.
(c) Rainfall: above 100 cm. It requires heavy rainfall in summer and irrigation in areas of less rainfall.
(d) Areas of Cultivation: plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic region. Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan. With the help of irrigation.
Question. What is the importance of agriculture in Indian economy?
Ans. (a) India is an agricultural country.
(b) Nearly two-thirds of its population depends directly on agriculture for its livelihood.
(c) Agriculture is the main stay of India’s economy.
(d) It accounts for 26% of the gross domestic product.
(e) It ensures food security for the country and produces several raw materials for industries.
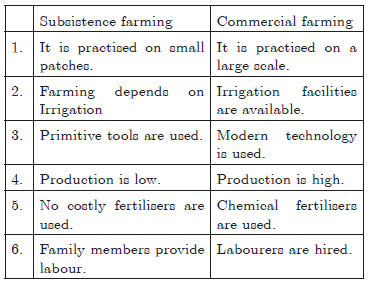
Question. Distinguish between intensive subsistence farming and commercial farming.
Ans.

Question. Name three features of Indian agriculture.
Ans. (a) Farmers own small piece of land and grow crops primarily for their own consumption,
(b) Animals play a significant role in the various kinds of agricultural activities.
(c) Farmers depend mainly upon monsoon rains.
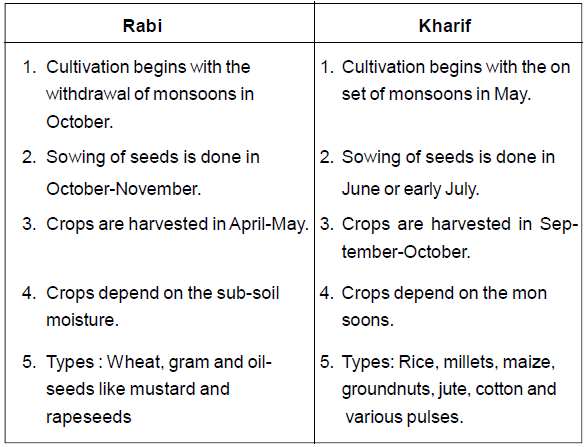
Question. Distinguish between: Rabi and Kharif Crops.
Ans.
Question. Describe the four negative impacts of green revolution on Indian Agriculture.
Ans. (a) Land degradation due to overuse of chemicals
(b) Lowering the ground water level due to over irrigation
(c) Vanishing Bio-diversity
(d) Difference between rich and poor farmers is increasing
FIVE MARKS QUESTIONS
Question. What are millets? Give brief description of the climatic conditions and producing states of the millets grown in India.
Ans : Millets are coarse grains but have high nutritional value e.g., ragi-rich in iron, calcium.
a. Jowar-Rain fed crops mostly grown in moist area. States producing-Maharashtra, Karnataka and MP.
b. Bajra-grown well on sandy soils and shallow black soil. States producing- Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Haryana and UP and loamy soils. States producing-Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim.
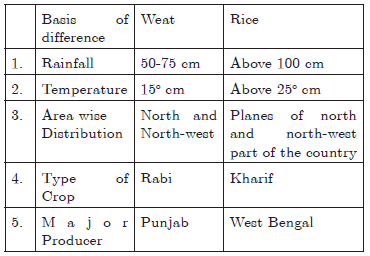
Question. “Wheat and rice farming in India are fairly different from each other”. Support the statement with five suitable examples.
or
Wheat and rice farming in India are fairly different from each other. Explain.
Ans :
Question. Describe four geographical conditions required for the growth of sugarcane. Name two major sugarcane producing states of North India.
or
What geographical conditions are required for the cultivation of sugarcane? Name two largest producing states of sugarcane.
Ans : Geographical conditions required for the growth of sugarcane in India:
a. It is a tropical as well as sub-tropical crop
so it requires a hot and humid climate with a temperature of 24°C to 27°C.
b. It requires an annual rainfall between 75 to 100 cm.
c. It can be grown on a variety of soils.
d. Major sugarcane producing states of North
e. India are : Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Question. Explain any four features of primitive subsistence agriculture in India.
Ans : Features of primitive subsistence agriculture in India are:
a. It is practised on small patches of land with the help of primitive tools.
b. Tools which are used are basically traditional tools such as hoe, dao and digging stick.
c. This type of agriculture totally depends upon monsoon.
d. When the soil fertility decreases, the farmers shift to another plot of land.
Question. Name any four oilseeds produced in India. Explain the importance of oilseeds in our day-to-day life.
Ans : (i) Groundnut
(ii) Mustard
(iii) Coconut
(iv) Sesamun
(v) Soyabean, sunflower; etc.
Importance of oilseeds:
Most of these are edible in the form of oil. Used as raw material for manufacturing paints, varnishes, soaps, perfumes etc, oil cake is used as cattle feed. Oil cake is also used as a fertiliser.
Question. Mention any two geographical conditions required for the growth of maize crop in India. Describe any three factors which have contributed to increase in maize production.
Ans : Geographical conditions required for the growth of maize crop in India:
a. It is a kharif crop which requires temperature between 21°C to 27°C.
b. It grows well in alluvial soil. Use of modern inputs such as HYV seeds, fertilisers and irrigation have contributed to the increasing production of maize.
Question. What is intensive subsistence farming? Write three features of intensive farming.
Ans : Intensive subsistence farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land. In this type of farming, the agricultural production is increased by using high doses of biochemical inputs and better agricultural inputs.
Features of intensive farming:
a. High yielding variety (HYV) seeds and modem chemical inputs and irrigation are used to increase the production.
b. The per hectare yield is very high.
c. More than one crop is cultivated during a year.
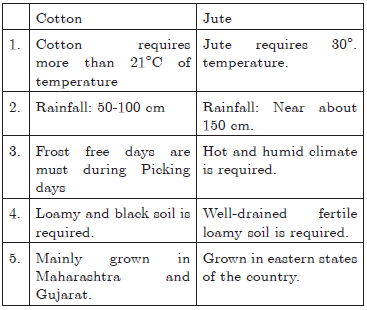
Question. Compare the geographical conditions required for the production of cotton and jute.
Ans :
Question. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and commercial farming by stating five points of distinction.
Ans :
Question. Describe any four geographical conditions required for the growth of tea. Mention the two major tea producing states of South India.
or
Name the important beverage crop introduced by the British in India. Explain the geographical conditions needed for its cultivation. Write any two important states where it is grown.
or
In which agricultural production, India is the leading producer as well as exporter in world? Describe the geographical requirements for its growth and development.
or
What are the soil type, climatic conditions and rainfall conditions required for the cultivation of tea? Write two states of India where tea grows.
Ans : a. Tea: Grows well in tropical and sub¬tropical climates.
b. Soil type: Deep and fertile, well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matters.
c. Climate: Warm and moist, frost-free climate throughout the year.
d. Rainfall: Frequent showers throughout the year.
e. Two states: Assam, West Bengal, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Andhra Pradesh, Meghalaya and Tripura.
Question. Suggest any five measures to enhance the agricultural production in India.
or
Explain any five institutional and technical reforms brought by the government to improve the condition of Indian Agriculture.
or
Describe any five steps taken by the government of India to increase the productivity of agriculture in India.
Ans : 1. Land reforms: Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari.
2. Agricultural reforms: Green revolution and White revolution.
3. Land development programmes: Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, etc, establishment of Grameen banks, Cooperative societies and banks for providing loans.
4. Issuing of Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme, etc.
5. Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes for farmers on radio and TV.
6. Government announces Minimum Support Price (MSP) and remunerative and procurement prices to check exploitation.
7. The government provides HYV seeds and fertilisers.
8. Government provides technical assistance and training for farmers.
9. Soil testing facilities, cold storage and transportation facilities are provided by government for farmers.
SOURCE BASED QUESTIONS
Question. Read the following passage and answer the questions at the end.
Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September-October. Important crops grown during this season are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean. Some of the most important rice-growing regions are Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradeshjelangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra, particularly the (Konkan coast) along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Recently,paddy has also become an important crop of Punjab and Haryana. In states like Assam, West Bengal and Odisha, three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are Aus, Aman and Boro.
(a) When is the Kharif crop sown?
Ans. Kharif crop with the onset of monsoon
(b) What are the main kharif crops?
Ans. Kharif crop paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad etc.
(c) In which Indian states, three crops of paddy are sown in a year?
Ans. Assam, West Bengal and Odisha
(d) Which are the major rice producing regions in India?
Ans. West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh , Andhra Pradesh, Biharjelangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra

