Please see below Case Study MCQ Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science. These MCQ Questions with Answers for Case study have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines of Class 10 Science. Cased Study Based MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science are expected to come in the upcoming exams. We have provided a lot of case studies for all chapters in standard 10 science. Please solve the MCQ Questions and compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Case Study MCQ Questions
Elements can be classified as metals or non-metals on the basis of their properties. The easiest way to start grouping substances is by comparing their physical properties. Metals, in their pure state, have a shining surface. This property is called metallic luster. metals are generally hard. The hardness varies from metal to metal. some metals are used for making cooking vessels.
Question. Metal present in chloroplast is
(a) Iron
(b) Copper
(c) Magnesium
(d) Cobalt
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following metal(s) catch fire on reaction with water?
(a) Sodium
(b) Potassium
(c) Magnesium
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Metals generally are
(a) reducing agents
(b) oxidising agent
(c) both oxidising and reducing agents
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The metal that reacts with cold water is –
(a) mercury
(b) sodium
(c) zinc
(d) tungsten
Answer
B
Question. The most abundant metal in the earth’s crust is –
(a) iron
(b) copper
(c) aluminium
(d) mercury
Answer
C
The huge annual loss due to corrosion is a national waste and should be minimized. Following are some methods which are helpful to prevent corrosion
(i) Coating the iron surface with paint or oil or grease prevents moist oxygen from coming in contact with the metal and thus effectively prevents rusting of iron.
(ii) Galvanisation : Iron is blasted with fine sand to make the surface rough dipped in molten zinc and then cooled. A thin layer of zinc forms on the iron surface. Since zinc is more reactive than iron, it acts as a sacrificial metal and is preferentially oxidised thus preventing oxidation of iron.
(iii) Electroplating with tin, nickel or chromium also prevents rusting.
(iv) Alloying (mixing iron in its molten state with other metals) prevents rusting. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron with Cr or Ni.
Question. The best way to prevent rusting of iron is :
(a) making it cathode
(b) putting in saline water
(c) both of these
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question. The most durable metal plating on iron to protect against corrosion is :
(a) nickel plating
(b) copper plating
(c) tin plating
(d) zinc plating
Answer
D
Question. The most convenient method to protect the bottom of ship made of iron is :
(a) coating it with red lead oxide.
(b) white tin plating.
(c) connecting it with Mg block.
(d) connecting it with Pb block.
Answer
C
On the basis of reactivity of different metals with oxygen, water and acids as well as displacement reactions, the metals have been arranged in the decreasing order of their reactivities. This arrangement is known as activity series or reactivity series of metals. The basis of reactivity is the tendency of metals to lose electrons. If a metal can lose electrons easily to form positive ions, it will react readily with other substances. Therefore, it will be a reactive metal. On the other hand, if a metal loses electrons less rapidly to form a positive ion, it will react slowly with other substances. Therefore, such a metal will be less reactive.
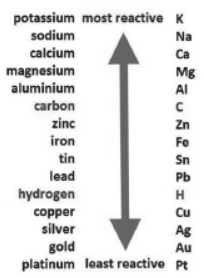
Question. Which of the following metals is more reactive than hydrogen?
(a) Mercury
(b) Platinum
(c) Iron
(d) Gold
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following represents the correct order of reactivity for the given metals?
(a) Na > Mg > Al > Cu
(b) Mg > Na > Al > Cu
(c) Na > Mg > Cu > Al
(d) Mg > Al > Na > Cu
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following metals is less reactive than hydrogen?
(a) Copper
(b) Zinc
(c) Magnesium
(d) Lead
Answer
A
Question. Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the H2 produced to water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, NO2). But ____________ and ____________ react with very dilute HNO3 to evolve H2 gas.
(a) Pb, Cu
(b) Na, K
(c) Mg, Mn
(d) Al, Zn
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following metals reacts vigorously with oxygen?
(a) Zinc
(b) Magnesium
(c) Sodium
(d) Copper
Answer
C
Non-metals are highly electronegative in nature. They have a tendency to gain electrons in their valence shell to achieve nearest noble gas configuration. Thus they form anions and act as good oxidising agents.
X + ne– → Xn–
(non-metal atom) (anion)
They react with air or oxygen on heating to form oxides which react with water to form acids. Thus non-metal oxides are acidic in nature. Non-metals do not react with dilute acids at all. This is because they are electronegative and therefore, cannot hydrogen form acids but they form covalent hydrides when heated with hydrogen.
Question. Non-metals generally act as
(a) oxidising agents
(b) reducing agents
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following elements produces basic oxide on reacting with oxygen?
(a) Chlorine
(b) Sulphur
(c) Phosphorus
(d) Magnesium
Answer
D
Question. The acid formed when sulphur trioxide reacts with water is
(a) sulphurous acid
(b) sulphuric acid
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a covalent hydride?
(a) CH4
(b) NH3
(c) H2S
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. An element ‘X’ forms an oxide XO2, which is a very useful gas used in the process of photosynthesis. The element ‘X’ is
(a) sulphur
(b) nitrogen
(c) carbon
(d) phosphorus
Answer
C
Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Nonmetals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc.
Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling and are poor conductors of electricity.
Question. Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
(a) Carbon
(b) Bromine
(c) Iodine
(d) Sulphur
Answer
B
Question. Generally, non-metals are bad conductors of electricity but ‘X’ which is a form of carbon is a good conductor of electricity and is an exceptional non-metal. ‘X’ is
(a) Diamond
(b) Graphite
(c) Coal
(d) Coke
Answer
B
Question. __________ is a non-metal but is lustrous.
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Sulphur
(c) Bromine
(d) Iodine
Answer
D
Question. Hydrogen is used
(a) for the synthesis of ammonia.
(b) for the synthesis of methyl alcohol.
(c) in welding torches.
(d) all of these.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is known as ‘King of chemicals’?
(a) Urea
(b) Ammonia
(c) Sulphuric acid
(d) Nitric acid
Answer
C
Metallic Character. The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ion (cation) is known as electropositivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size. Non-Metallic Character. The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electronegativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
Question. Which of the following has highest electronegativity?
(a) F
(b) Cl
(c) Br
(d) I
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following Reason correctly justifies that “Fluorine (72 pm) has smaller atomic radius than Lithium (152 pm)”?
(a) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size increases down the group.
(b) F and Li are in the same period. Atomic size increases across the period due to increase in number of shells.
(c) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size decreases down the group.
(d) F and Li are in the same period and across the period atomic size/radius decreases from left to right.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following correctly represents the decreasing order of metallic character of Alkali metals plotted in the graph?
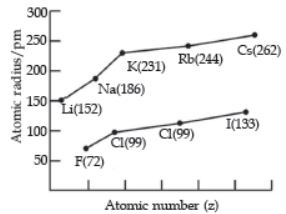
(a) Cs > Rb > Li > Na > K
(b) K > Rb > Li > Na > Cs
(c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li
(d) Cs > K > Rb > Na > Li
Answer
C
Question. Identify the Reason for the gradual change in electronegativity in halogens down the group.
(a) Electronegativity increases down the group due to decrease in atomic size.
(b) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to decrease in tendency to lose lectrons
(c) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/tendency to gain electron decreases.
(d) Electronegativity increases down the group due to increase in forces of attractions between nucleus & valence electrons.
Answer
C
Question. Hydrogen is placed along with Alkali metals in the modern periodic table though it shows non-metallic character.
(a) as Hydrogen has one electron & readily loses electron to form negative ion.
(b) as Hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion.
(c) as Hydrogen can gain one electron easily like Halogens to form negative ion.
(d) as Hydrogen shows the properties of nonmetals.
Answer
B
Some metals are chemically very reactive, whereas others are less reactive or unreactive. On the basis of vigourness of reactions of various metals with oxygen, water and acids, as well as displacement reactions, the metals have been arranged in a group or series according to their chemical reactivity. The arrangement of metals in a vertical column in the order of decreasing reactivities is called reactivity series of metals (or activity series of metals). In reactivity series, the most reactive metal is placed at the top whereas the least reactive metal is placed at the bottom. As we come down in the series, the chemical reactivity of metals decreases. Since the metals placed at the bottom of the reactivity series (like silver and gold) are less reactive, so they are usually found in free state (native state) in nature.
Question. When metal Z is added to dilute HCl solution, there is no evolution of gas. Metal is :
(a) K
(b) Na
(c) Ag
(d) Zn
Answer
C
Question. Metal always found in free state is :
(a) gold
(b) silver
(c) copper
(d) sodium
Answer
A
Question. Copper sulphate solution can be safely kept in a container made of :
(a) aluminium
(b) lead
(c) silver
(d) zinc
Answer
C
Metals are electropositive elements. They can easily lose electrons to form ions. Metals show distinguished physical as well as chemical properties. Generally most of the metals are ductile and malleable with exception such as mercury. These properties make them valuable for commercial as well as domestic uses. Reaction of a metal with water is one of important chemical property. Metals like sodium and potassium reacts with cold water while magnesium reacts with hot water. Metals like aluminium, zinc do not react with hot/cold water but they easily react with steam. When a metal react with hot/ cold water the products are metal hydroxide and hydrogen, and when it react with steam, the product are metal oxide and hydrogen. Some metals like sodium, potassium react violently with water.
Question. During the reaction of calcium with water, pieces of metal start floating due to the formation of:
(a) Ca(OH)2
(b) CO2
(c) H2
(d) none of these
Answer
C
Question. Metals can be converted into thin sheet by hammering. This property is known as:
(a) Ductility
(b) Sonorous
(c) Malleability
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. When zinc reacts with steam it produces:
(a) Zn(OH)2
(b) ZnO
(c) O2
(d) ZnO2
Answer
B
Question. Most ductile metal among the following is:
(a) Au
(b) Ag
(c) Cu
(d) Al
Answer
A
Question. Consider the reactions:
Na(s) + H2O (l) → NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) ……….(i)
Ca(s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) ………(ii)
(a) Reaction (i) is endothermic reaction.
(b) Reaction (ii) is endothermic reaction.
(c) Reaction (ii) is more exothermic than reaction (i).
(d) Reaction (i) is more exothermic than reaction (ii).
Answer
D



