Please refer to Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 12 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 12 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 12.
Class 12 Biology Important Questions Biotechnology Principles and Processes
Objective Questions
Question. Which one of the following techniques made it possible to genetically engineer living organisms?
(a) Recombinant DNA techniques
(b) X-ray diffraction
(c) Heavier isotope labelling
(d) Hybridisation
Answer
A
Question. Following statements describe the characteristics of the enzyme restriction endonuclease. Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) The enzyme recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
(b) The enzyme cuts DNA molecule at identified position within the DNA.
(c) The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands.
(d) The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand.
Answer
C
Question. Given below are four statements pertaining to separation of DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis. Identify the incorrect statements.
(i) DNA is negatively charged molecule and so it is loaded on gel towards the anode terminal.
(ii) DNA fragments travel along the surface of the gel whose concentration does not affect movement of DNA.
(iii) Smaller the size of DNA fragment larger is the distance it travels through it.
(iv) Pure DNA can be visualized directly by exposing UV radiation.
Choose the answer from the options given below.
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. What is the criterion for DNA fragments movement on agarose gel during gel electrophoresis ?
(a) The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
(b) Positively charged fragments move to farther end.
(c) Negatively charged fragments do not move.
(d) The larger the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a restriction endonuclease?
(a) DNaseI
(b) RNase
(c) HindII
(d) Protease
Answer
C
Question. The procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium is called
(a) Cloning
(b) Transformation
(c) PCR
(d) Clonal selection
Answer
B
Question. One of the key factors, which makes the plasmid the vector in geretic engineering in that-
(a) It is resistant to antibiotics
(b) It is resistant to restriction enzymes
(c) Its ability to carry a foreign gene
(d) Its ability to cause infection in the host
Answer
C
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
(a) EcoRI cuts the DNA between bases G and A.
(b) Each EcoRI restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific palindromic nucleotide sequences in DNA.
(c) When cut by same restriction enzyme, the resultant DNA fragments do not have the same kind of stickyends.
(d) Making multiple identical copies of any template DNA is called cloning.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not correct about pBR 322 vector ?
(a) It was constructed by using DNA derived from naturally occurring plasmids of E coli.
(b) It has two drug resistance genes-tetR and ampR.
(c) It was developed by Bolivar and Rodriguez.
(d) Selectable markers present in it can differentiate recombinants from non-recombinants on the basis of their inability to produce colour in the presence of chromogenic substrate.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
(a) T-DNA transform normal plant cell into a tumor.
(b) Retroviruses in animals have the ability to transform normal cell into cancerous cells.
(c) T plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is modified into cloning vector which is more pathogenic to plants.
(d) Retrovirus have also been disarmed and are now used to deliver desirable genes into animal cells.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is a correct statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR ?
(a) It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cell.
(b) It serves as a selectable marker.
(c) It is isolated from a virus.
(d) It remains active at high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements (i-iv) are correct.
(i) In elution, the separated bands of DNA are cut out from agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece.
(ii) E. coli cloning vector pBR 322 shows several restriction, Ori antibiotic resistance genes and rop.
(iii) The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.
(iv) Competent bacterial cell cannot take up the plasmid.
(a) All of the above
(b) None of the above
(c) (i), (ii), and (iii)
(d) Only (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the given statements (i-iv) are correct about bioreactor?
(i) Bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for obtaining the desired product.
(ii) Raw materials are biological which are converted into specific products.
(iii) Stirred-tank reactor is horizontal in shape.
(iv) Large volume of culture cannot be processed.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Assertion/Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : In recombinant DNA technology, human genes are often transferred into bacteria (prokaryotes) or yeast (eukaryote).
Reason : Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge population to express the desired gene.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Restriction endonucleases have been designated as molecular scissors.
Reason : Fragments produced by restriction endonucleases upon mixing join due to their sticky ends.
Answer
D
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Plasmid | I. Selectable marker |
| B. amp | II. Extrachromosomal DNA |
| C. Ti-plasmid | III. Enzyme |
| D. Chitinase | IV. Agrobacterium tumefaciens |
(a) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – III; D – II
(d) A – I; B – IV; C – II; D – III
Answer
B
Question. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. EcoRI | I. Bacilius amyloliquefaciens |
| B. Bam HI | II. Haemophilus influenza |
| C. Hind III | III. Escherichia coli |
| D. pBR 322 | IV. Artificial plasmid |
(a) A – III; B – I; C – II; D – IV
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – III; D – II
(d) A – I; B – IV; C – II; D – III
Answer
A
Question. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct combination from the option given below.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Competent | I. Thermus aquaticus |
| B. Taq DNA polymerase | II. Antibiotic |
| C. Ampicillin | III. Micro-injection |
| D. Ethidium bromide | IV. DNA staining |
(a) A – III; B – I; C – II; D – IV
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – III; D – II
(d) A – I; B – IV; C – II; D – III
Answer
A
Question. Match Column I with Column II and identify the correct option.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Primers | I. PCR |
| B. Separation and purification of products | II. C2H5OH |
| C. Precipitation of DNA | III. Uptake of foreign DNA by bacterium |
| D. Transformation | IV. Down stream processing |
(a) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – III; D – II
(d) A – I; B – IV; C – II; D – III
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Questions
Question. Biotechnologists refer to Agrobacterium tumifaciens as a natural genetic engineer of plants.Give reasons to support the statement.
Ans. This is because A. tumifaciens can transfer genes naturally by delivering a piece of T-DNA to plant cells. It has a tumour inducing plasmid.
Question. Name the compound used for staining the isolated DNA in the gel electrophoresis.
Ans. Ethidium bromide.
Question. Give any two microbes that are useful in biotechnology.
Ans. E. coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question. Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
Ans. Other advantages of stirred tank bioreactors over shake flasks are that these facilitate temperature control system, pH control system, foam control system and sampling ports from where small volume of the cultures can be obtained and tested time to time.
Question. Why does DNA move towards the anode in gel electrophoresis?
Ans. The DNA fragments are negatively charged so they move towards the positively charged anode.
Question. How is repetitive/satellite DNA separated from bulk genomic DNA for various genetic experiments?
Ans. By density gradient centrifugation.
Question. Suggest a technique to a researcher who needs to separate fragments of DNA.
Ans. Gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments.
Question. How can bacterial DNA be released from the bacterial cell for biotechnology experiments?
Ans. The bacterial cell wall is digested by the enzyme lysozyme to release DNA from the cell.
Short Answer Questions
Question. Write any four ways used to introduce a desired DNA segment into a bacterial cell in recombinant technology experiments.
Ans. (i) The desired DNA segment is inserted into a cloning vector and the bacterial cell can be made to take it up after making them competent by treating them with specific concentration of divalent cations such as calcium.
(ii) Microinjection
(iii) Biolistics
(iv) Disarmed pathogen vector
Question. Explain with the help of an example the relationship between restriction endonuclease and a palindromic nucleotide sequence.
Ans. Restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
Restriction endonuclease cuts the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of palindromic nucleotide sequence but between the same two bases on the opposite strands, leaving single stranded portions at the end called sticky ends.
Question. Write the use of the following in biotechnology.
(a) Chilled ethanol (b) Microinjection
(c) Bioreactor (d) Plasmid
Ans. (a) It is added to precipitate the purified DNA to isolate it.
(b) It is used to inject the foreign gene into a host cell, directly.
(c) It is the set up to culture large volumes of transgenic bacteria to get large quantities of the product protein.
(d) It is the vector to transform a foreign gene.
Question. How can DNA segments, separated by gel electrophoresis, be visualised and isolated?
Ans. The separated DNA molecules are visualised only after staining DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation. They appear as bright orange coloured bands. The separated bands of DNA (on the gel) are cut from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece. This process is called elution.
Question. Why is Agrobacterium tumifaciens a good cloning vector? Explain.
Ans. Agrobacterium tumifaciens is a soil bacterium which causes disease in many dicot plants. It is able to deliver a piece of DNA known as T-DNA, to transform the normal cells into tumour cells and direct these tumour cells to produce the chemicals required by the pathogen. The tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens has now been modified into a cloning vector which is no more pathogenic to the plants but still deliver genes of interest into a variety of plants.
Question. Explain the process of gel-electrophoresis technique.
Ans. Separation and Isolation of DNA Fragments (Gel Electrophoresis)
• Gel electrophoresis is a technique for separating DNA fragments based on their size.
• Firstly, the sample DNA is cut into fragments by restriction endonucleases.
The separated DNA fragments are visualised after staining the DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation.
• The DNA fragments are seen as orange coloured bands.
• The separated bands of DNA are cut out and extracted from the gel piece. This step is called elution.
Question. Why does the ‘insertional inactivation’ method to detect recombinant DNA is preferred to ‘antibiotic resistance’ procedure?
Ans. In insertional inactivation method, the presence of a chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured colonies in absence of an insert. Presence of an insert in the enzyme site does not produce colour. This is because insertional inactivation of the b-galactosidase has taken place due to the insert.
Antibiotic resistance method requires duplicate plating. It is a cumbersome procedure to perform.
Question. Is there any difference between recombinant DNA and recombinant protein? Support your answer.
Ans. rDNA is the plasmid vector containing the foreign DNA whereas recombinant protein is the product of transgenic gene in the host body or cell.
Question. How is insertional inactivation of an enzyme used as a selectable marker to differentiate recombinants from non-recombinants?
Ans. When a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme b-galactosidase, it results into inactivation of the enzyme. The bacterial colonies having recombinant plasmid,show no colouration while those without recombinant plasmid show blue colour.
Question. A wine maker and a molecular biologist who has developed a recombinant vaccine, both claim themselves to be biotechnologist. Who in your opinion is right?
Ans. Both are right because biotechnology is a very wide area which deals with techniques of using a ‘natural’ organism (or its parts) as well as genetically modified organism to produce products and processes useful for mankind. A wine maker employs a strain of yeast to produce wine by fermentation (a natural phenomenon), while the molecular biologist has cloned gene for the antigen (that is used as vaccine) in an organism which allows the production of the antigen in large amount.
Question. For producing a recombinant protein (for therapeutic purpose) in large scale, which vector would you choose—a low copy number or high-copy number?
Ans. High-copy number, because higher the copy number of vector plasmid, higher the copy number of gene and consequently, protein coded by the gene is produced in high amount.
Question. DNA being hydrophilic cannot pass through the cell membrane of a host cell. Explain how does recombinant DNA get introduced into the host cell to transform the latter.
Ans. Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA)
• DNA being a hydrophilic molecule, cannot pass through cell membranes.
• Therefore, the bacteria should be made competent to accept the DNA molecules.
• Competency is the ability of a cell to take up foreign DNA.
• The cell is made competent by the following methods:
(i) Chemical method (ii) Physical method
Question. Rearrange the following in the correct sequence to accomplish an important biotechnological reaction:
(a) In vitro synthesis of copies of DNA of interest
(b) Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides
(c) Enzyme DNA-polymerase
(d) Complementary region of DNA
(e) Genomic DNA template
(f) Nucleotides provided
(g) Primers
(h) Thermostable DNA-polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(i) Denaturation of dsDNA
Ans. Correct sequence is
i e b/g g/b c/b h/c f d a
Question. Restriction enzymes present in the cloning site of a vector should not have more than one recognition site. Comment.
Ans. If the restriction enzymes have more than one recognition site in a vector, then the vector itself will get fragmented on treatment with the restriction enzyme.
Question. (a) How has the development of bioreactor helped in biotechnology ?
(b) Name the most commonly used bioreactor and describe its working.
Answer : (a) Larger biomass / large volume of culture can be processed leading to higher yields of desired specific products (protein / enzymes), under controlled condition ½ + ½
(b) Stirred-type ½
• Mixing of reactor contents evenly (with agitator system or a stirrer). ½
• Facilitates oxygen availability. ½
• Temperature / pH / foam control under optimum conditions.
Question. Explain the role(s) of the following in Biotechnology :
(i) Restriction endonuclease
(ii) Gel – electrophoresis
(iii) Selectable markers in pBR322.
Answer : (i) Cuts at specific position within the DNA / cuts DNA at specific nucleotide / cuts at palindromic nucleotide sequence.
(ii) Separation of DNA fragments (under the influence of electric field).
(iii) Helps in identifying and eliminating nontransformants from transformants / selection of transformants.
Question. Name and explain the technique that helps in the separation of DNA fragments for DNA recombinant technology experiments.
How can these separated DNA fragments be visualised ?
Answer : Gel electrophoresis, Since DNA fragments are negatively charged, they move towards anode (under an electric field) through a medium / matrix / agarose gel. The fragments separate (resolve) according to their sizes through sieving effect provided by agarose gel. The separated DNA fragments can be visualised after staining the DNA with ethidium bromide, followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Question. What is an “origin of replication” (ori) in a chromosome ? State its function.
Answer : This is the point on DNA where replication originates / starts.
It controls the copy number of linked DNA.
Question. Draw a diagram of a typical agarose gel electrophoresis showing migration of undigested and digested sets of DNA fragments. Label (a) the digested and
undigested DNA fragments, (b) Anode and cathode ends of the plate. Mention the role of electrophoresis in biotechnology.
Answer :

The cutting of DNA by restriction endonuclease results in fragments of DNA. These fragments can then be separated by (Gel) electrophoresis.
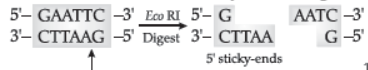
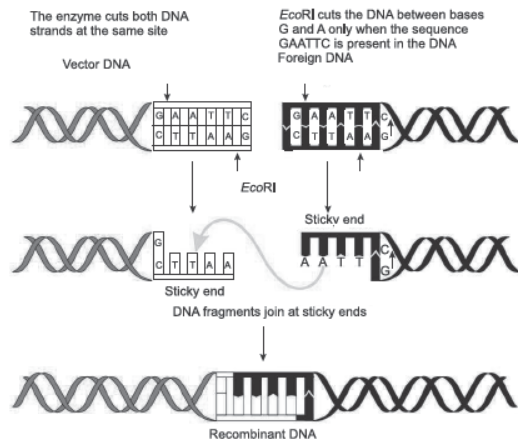
Question. How does EcoRI specifically act on DNA molecule? Explain.
Answer : EcoRI cuts the DNA between bases G and A only when the sequence GAATTC is present in the DNA.
This leaves single-stranded overhanging stretches at the ends. These are called sticky ends. This stickiness facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. Mention the role of (i) selectable marker, (ii) Ori and (iii) rop in E. coli cloning vector pBR322.
Answer : (i) Selectable marker : Eliminating non transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants.
(ii) Refer Q. 4
(iii) Codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid.
Question. “Cotton bollworms enjoy feeding on cotton plants, but get killed when feed on Bt cotton plant”. Justify the statement.
Answer : Bt-cotton plant is a transgenic plant that produces an insecticide for bollworm. Bacillus thuringiensis is the bacterium that has a Bt gene or Cry gene which is incorporated in the cotton plant through biotechnological methods and thus, it produces a crystalline product Bt. The product acts as a toxin when ingested by the pests as it gets activated after reaching the alkaline gut of pests and creates pores in the intestine and kills the pests. The gene protects the GMO against budworm, bollworm, beetle, borer, etc.
Question. (i) Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322. Mention the role they play.
(ii) Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme β-galactosidase is preferred as a selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above ?
Answer : (i) ampR / ampicillin resistance genes, tetR/ tetracycline resistance gene.
They help in identifying and eliminating nontransformants / non- recombinants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants /recombinants.
Long Answer Questions
Question. List the steps involved in rDNA technology.
Ans. Steps in rDNA technology:
(i) Isolation of DNA.
(ii) Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonucleases.
(iii) Isolation of the desired DNA fragments.
(iv) Amplification of the gene of interest.
(v) Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector using DNA ligase.
(vi) Transfer of recombinant DNA into the host organism.
(vii) Culturing the host cell on a suitable medium on a large scale.
(viii) Extraction of the desired product.
(ix) Downstream processing of the products as finished products are ready for marketing.
Question. Write the steps you would suggest to be undertaken to obtain a foreign-gene-product.
Ans. Recombinant DNA technology involves the following steps:
(i) Isolation of DNA
(ii) Fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonucleases
(iii) Isolation of a desired DNA fragment
(iv) Amplification of the gene of interest
(v) Ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector
(vi) Insertio n of recombinant DNA into the host
(vii) Culturing the host cells on a suitable medium at a large scale
(viii) Extraction of the desired gene product
(ix) Downstream processing of the products as finished product
Question. (i) Describe the characteristics that a cloning vector must possess.
(ii) Why DNA cannot pass through the cell membrane? Explain. How is a bacterial cell made ‘competent’ to take up recombinant DNA from the medium?
Ans. (i) A cloning vector must have the following characteristics:
(a) ori or origin of replication which can make large number of copies
(b) Selectable marker i.e., genes encoding for an antibiotic resistance or genes encoding for α-galactosidase.
(c) Recognition site for the restriction enzyme to recognise.
(ii) DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, therefore it cannot pass through the cell membrane.
The bacterial cells can be made competent by treating them with a specific concentration of a divalent ion like calcium. The cells are then incubated on ice followed by a heat shock by placing them briefly at 42°C and then putting back on ice.
Question. (a) Explain the significance of ‘palindromic nucleotide sequence’ in the formation of recombinant DNA.
(b) Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
Ans. (a) Palindromic nucleotide sequence is the recognition (specific) sequence present both on the vector and on a desired or alien DNA for the action of the same (specific) restriction endonuclease to act upon.
(b) (i) Every endonuclease inspects the entire DNA sequence for the palindromic recognition sequence.
(ii) On finding the palindrome, the endonuclease binds to the DNA.
(iii) It cuts the opposite strands of DNA in the sugar–phosphate backbone; a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites but between the same bases on both strands.
(iv) This results in the formation of single stranded overhanging stretches at the end of each strand called sticky ends.
(v) The sticky ends facilitate the action of the enzyme DNA ligase by readily forming hydrogen bonds with complementary strands.
Question. Explain three basic steps to be followed during genetic modification of an organism.
Ans. The three basic steps are:
(i) Identification of DNA with desirable genes.
(ii) Introduction of the identified DNA into the host.
(iii) Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host and transfer of the DNA to its progeny.
Question. Prepare a flow chart in formation of recombinant DNA by the action of restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoRI.
Ans.
Question. Draw a schematic sketch of pBR322 plasmid and label the following in it:
(a) Any two restriction sites.
(b) ori and rop genes.
(c) An antibiotic resistant gene.
Ans.

Question. Name and describe the technique that helps in separating the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonuclease.
Ans. Gel electrophoresis helps in separating DNA fragments.
DNA fragments are negatively charged then they are forced to move towards anode under an electric field through agarose gel matrix. The fragments separate according to their size through sieving effect. Hence the smaller fragments move faster and further than the larger ones.
• Gel electrophoresis is a technique for separating DNA fragments based on their size.
• Firstly, the sample DNA is cut into fragments by restriction endonucleases.
• The DNA fragments being negatively charged can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix.
• Commonly used matrix is agarose, which is a natural linear polymer of D-galactose and 3, 6-anhydro- L-galactose which is extracted from sea weeds.
• The DNA fragments separate-out (resolve) according to their size because of the sieving property of agarose gel. Hence, smaller the fragment size, the farther it will move.
Question. (a) What is EcoRI? What does ‘R’ represent in this?
(b) Explain its action.
Ans. (a) EcoRI is a restriction endonuclease, obtained from an E. coli bacterium.R represents the name of the strain.
(b) It cuts the DNA between bases G and A on both the strands only when the sequence GAATTC is present in DNA.
Question. (a) Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322? Mention the role they play.
(b) Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme b-galactosidase is a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above?
Ans. (a) Selectable markers are ampR/ampicillin resistance genes and tetR/tetracycline resistance gene. They help in identifying and eliminating non-transformants/non-recombinants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants/recombinants.
(b) This is because it is simpler and less cumbersome. In the presence of chromogenic substrate recombinants form colourless colonies and non-recombinants form blue in colonies.
Question. (a) Why are engineered vectors preferred by biotechnologists for transferring the desired genes into another organism?
(b) Explain how do “ori”, “selectable markers” and “cloning sites” facilitate cloning into a vector.
Ans. (a) Engineered vectors are preferred by biotechnologists because they help in easy linking of foreign DNA and selection of recombinants from non-recombinants.
(b) Origin of replication (ori)
• This is a DNA sequence that is responsible for initiating replication. Any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can replicate within the host cells.
• ori also controls the copy numbers of the linked DNA. For many copies of target DNA, it should be cloned in a vector whose origin supports high copy number.
Selectable marker
• It helps to select the host cells which contain the vector (transformants) and eliminate the nontransformants.
• Transformation is defined as the procedure by which a piece of DNA is introduced into a bacterial cell.


