Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Chapter 2 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Biology Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Assignments Class 12 Biology
Question. Polar nuclei are situated in the central cell
(a) Below the egg apparatus
(b) Above the egg apparatus
(c) Below the antipodals
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. The synergids have special cellular thickening at the micropylar tip, called
(a) Antipodals
(b) Filiform apparatus
(c) Obturators
(d) Vascular tissue
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following part of the flower serves as a landing platform for pollen grain ?
(a) Stigma
(b) Ovary
(c) Style
(d) Ovule
Answer
A
Question. Embryo develops at which end of embryosac?
(a) Micropylar end
(b) Chalazal end
(c) Funiculus
(d) Outside the ovary
Answer
A
Question. The microsporangia develop further and become pollen sacs. In anther these pollen sacs extends
(a) Transverslly
(b) Longitudinally
(c)Obliquely
(d) Sometimes transversaly and some times longitudinally
Answer
B
Question. Enclosed within the integuments is a mass of cells called
(a) Micropyle
(b) Nucellus
(c) Chalaza
(d) Embryosac
Answer
B
Question. An example of insect pollinated flower, in which flower provides safe place to lay eggs for insect is
(a) Vallisneria
(b) Salvia
(c) Amorphophallus
(d) Maize
Answer
C
Question. Endosperm development precedes embryo development, because
(a) Embryo provides nutrition to developing endosperm
(b) Endosperm provides nutrition to developing embryo
(c) Endosperm development starts after embryo development
(d) All of the above
Answer
B
Question. The portion of embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is called
(a) Hypocotyl
(b) Epicotyl
(c) Tigellum
(d) Scutellum
Answer
B
Question. The portion of embryonal axis below the level of cotyledons is called
(a) Hypocotyl
(b) Epicotyl
(c) Tigellum
(d) Scutellum
Answer
A
Question. During embryo sac formation how many nuclei out of eight nucleus go through cytokinesis or wall formation?
(a) All eight
(b) Two
(c) Six
(d) Four
Answer
C
Question. Geitonogamy is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of another flower of the same plant is :-
(a) Functionally cross pollination
(b) Genetically self pollination
(c) Ecologically cross pollination
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. Genetically geitonogamy is
(a) Allogamy
(b) Xenogamy
(c) Autogamy
(d) Cleistogamy
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following pollen structure exhibits a fascinating array of patterns and designs
(Sculpturing pattern)?
(a) Germpores
(b) Exine
(c) Intine
(d) Tapetum
Answer
B
Question. Regarding to formation of pollen grain from microspore which of the following statement is incorrect
(a) Generative cell is bigger
(b) Vegetative cell possess irregularly shaped nucleus
(c) Generative cell floats in cytoplasm of vegetative cell
(d) Vacuole is present in vegetative cell
Answer
A
Question. Endosperm is completely consumed by developing embryo in
(a) Castor
(b) Coconut
(c) Wheat
(d) Pea
Answer
D
Question. What will be the ploidy of the cells of functional megaspore and female gametophyte respectively:
(a) n, n
(b) 2n, 2n
(c) n, 2n
(d) 2n, n
Answer
A
Question. Regarding to cross pollination which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) Plants use two abiotic and one biotic agent
(b) Majority of plants use abiotic agents for pollination
(c) Production of enormous amount of pollen grains is concerned to compensate uncertainity and loss of pollens
(d) Pollination by wind is more common among abiotic pollinations
Answer
B
Question. About wind pollination which of the following is incorrect?
(a) Light and non sticky pollengrains
(b) Well exposed stamens
(c) Feathery stigma
(d)Highly scented flowers
Answer
D
Question. Chalaza represents the
(a) Tip of the ovule
(b) Base of the ovule
(c) Both (1) & (2)
(d) Stalk of the ovule
Answer
B
Question. Ovules generally differentiate a single megaspore mother cell in the
(a) Micropylar region
(b) Chalazal region
(c) Both 1 & 2
(d) Integument region
Answer
A
Question. In Castor plant :
(a) Autogamy is possible
(b) Geitonogamy is possible
(c) Both are possible
(d) Both are not possible
Answer
B
Question. Example of plants, which contains cleistogamous flowers :
(a) Oxalis
(b) Commelina
(c) Viola (Common pansy)
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. In embryosac, three cells are grouped together at the micropylar end to constitute
(a) Antipodals
(b) Synergids
(c) Egg apparatus
(d) Polar nuclei
Answer
C
Question. Cleistogamous flowers are invariably :
(a) Autogamous
(b) Xenogamous
(c) Geitonogamous
(d) All are possible
Answer
A
Question. A typical flower has ______different kinds of whorl.
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer
C
Question. The functions of tapetum is to
(a) produce ubisch bodies.
(b) produce pollen grains.
(c) provide nourishment to the developing pollen grains.
(d) store and protect pollen grains.
Answer
C
Question. Exine of pollen grain is formed of
(a) callose
(b) pecto-cellulose
(c) ligno-cellulose
(d) sporopollenin
Answer
D
Question. Pollen grain is liberated at
(a) one celled stage.
(b) two celled stage.
(c) three celled stage.
(d) two or three celled stage.
Answer
D
Question. Ovule is
(a) megasporangium
(b) megasporophyll
(c) integumented megasporangium
(d) rolled megasporophyll
Answer
A
Question. The point at which funiculus touches the ovule is
(a) chalaza
(b) hilum
(c) raphe
(d) endothelium
Answer
B
Question. The most common type of ovule is __________ .
(a) orthotropous
(b) hemitropous
(c) anatropous
(d) campylotropous
Answer
C
Question. Polygonum type of embryo sac/typical female gametophyte of angiosperms is
(a) 7-celled, 7-nucleate
(b) 7-celled, 8-nucleate
(c) 8-celled, 7-nucleate
(d) 8-celled, 8-nucleate
Answer
B
Question. Cleistogamous flowers are
(a) wind pollinated
(b) self-pollinated
(c) cross-pollinated
(d) insect pollinated
Answer
B
Question. Pollination by water occurs in
(a) Vallisneria
(b) Zostera
(c) Satvia
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Vegetative fertilization involves fusion of
(a) two polar nuclei
(b) a male gamete and a synergid
(c) a male gamete and antipodal cell
(d) nucleus of a male gamete and secondary nucleus
Answer
D
Question. Endosperm is generally
(a) diploid
(b) triploid
(c) haploid
(d) polyploid
Answer
B
Question. Scutellum is present in the embryo of
(a) pea
(b) Ranunculus
(c) Triticum
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. False fruits (thalamus also contributes to fruit formation) are found in
(a) apple and pear
(b) strawberry
(c) cashewnut
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The seed in which endosperm is used by embryo is called __________ seed.
(a) single
(b) albuminous
(c) endospermic
(d) non-endospermic
Answer
D
Question. Nucellar polyembryony is reported in species of
(a) Brassica
(b) Gossypium
(c) Triticum
(d) Citrus
Answer
D
Statement Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect about emasculation?
(a) During emasculation process, stigma is removed.
(b) Emasculated flowers are bagged in order to prevent self-pollination.
(c) Emasculation is the removal of stamens before the maturation of selected bisexual flowers.
(d) It is one of the steps for artificial hybridization.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement about sporopollenin is incorrect?
(a) Exine is made up of sporopollenin.
(b) Sporopollenin is one of the resistant organic materials.
(c) Exine has apertures called germ pores where sporopollenin is present.
(d) Sporopollenin can withstand high temperatures and strong acids.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following statement is correct?
(a) Sporogenous tissue is haploid.
(b) Endothecium produces the microspores.
(c) Tapetum nourishes the developing pollen.
(d) Hard outer layer of pollen is called intine.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about self-incompatibility ?
(i) It is a device to prevent inbreeding.
(ii) It provides a biochemical block to self-fertilization.
(iii) It ensures cross-fertilization.
(iv) It is governed by pollen-pistil interaction.
(v) It is governed by series of multiple alleles.
(vi) It prevents self-pollen (from the same flower of other flowers of the same plant) from fertilizing the ovules by inhibiting pollen germination of pollen tube growth in the pistil.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (iv) and (v)
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements are correct for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant?
(i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity.
(ii) It is free-nuclear during the development.
(iii) It is situated inside the integument but outside the nucellus.
(iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Seeds are adaptively important because
(i) they maintain dormancy.
(ii) they protect young plants during vulnerable stages.
(iii) they store food for young plants, and facilitate dispersal.
Identify the correct reasons.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Assertion/Reason Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : If a pollen mother cell has 42 chromosomes, the pollen has only 21 chromosomes.
Reason : Pollens are formed after meiosis in pollen mother cell.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Photomodulation of flowering is a phytochrome regulated process.
Reason : Active form of phytochrome (PFR) directly induces floral induction in shoot buds.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Chasmogamous flowers require pollinating agents.
Reason : Cleistogamous flowers do not expose their sex organs.
Answer
B
Matching Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. Match the parts of gynoceium given in column I with their definition given in column II. Choose the correct combination from the options given below.‘
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Funicle | I. Mass of cells within ovule with more food |
| B. Hilum | II. Basal part of ovule |
| C. Integument | III. One or Two protective layers of ovule |
| D. Chalaza | IV. Region where body of ovule fuses with funicle |
| E. Nucellus | V. Stalk of ovule |
(a) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV; E – V
(b) A – V; B – IV; C – III; D – II; E – I
(c) A – IV; B – II; C – I; D – III; E – V
(d) A – I; B – III; C – V; D – II; E – IV
Answer
B
Question. Match the items given in column-I with those given in column-II and choose the correct option given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Parthenocarpy | I. Inactive state |
| B. Polyembryony | II. Meiosis and syngamy are absent |
| C. Apomixis | III. Occurrence of more than one embryo |
| D. Dormancy | IV. Seedless fruit |
(a) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
(b) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(d) A – III; B – II; C – I; D – IV
Answer
B
Question. Match the items given in column-I with their examples given in column-II and identify the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Coleorhiza | I. Grapes |
| B. Food storing tissue | II. Mango |
| C. Parthenocarpic fruit | III. Maize |
| D. Single seeded fruit developing | IV. Radicle from monocarpellary superior ovary |
| E. Membranous seed coat | V. Endosperm |
(a) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II; E – V
(b) A – IV; B – II; C – V; D – I; E – III
(c) A – V; B – I; C – III; D – IV; E – II
(d) A – IV; B – V; C – I; D – II; E – III
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is a mismatched pair?
(a) Storage of pollen grains – – 196°C
(b) Pollen allergy – Carrot grass
(c) Chasmogamous flowers – Exposed anthers and stigmas
(d) Xenogamy – Self-pollination
Answer
D
Diagram Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. The given figure shows a typical stamen (a) and three dimensional cut section of an anther. Identify A to D respectively marked in the figures (a & b)

(a) Anther, Petiole, Pollen sac and Megaspore
(b) Anther, Petiole, Megasporangium and Pollen grains
(c) Anther, Pedicel, Megasporangium and Pollen grains
(d) Anther, Filament, Pollen sac and Pollen grains
Answer
D
Question. Identify A, B, C, D and E structures marked in the given figure of a mature embryo sac.
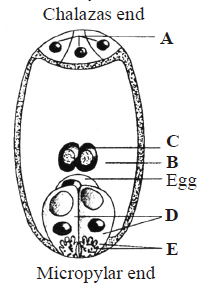
Answer
B
Question. Diagram given below shows the stages in embryogenesis in a typical dicot plant (Capsella). Identify the structures

(a) Suspensor, Radicle, Plumule, Cotyledons
(b) Hypophysis, Radicle, Plumule, Cotyledons
(c) Suspensor, Plumule, Radicle, Cotyledons
(d) Suspensor, Radicle, Plumule, Hypocotyls
Answer
A
Question. In the given figure of pollen grain tetrad, identify the parts marked as A, B, C, D and E.

(a) A – Germ pore, B – Generative cell, C – Intine, D – Exine, E – Vegetative cell
(b) A – Germ pore, B – Generative cell, C – Exine, D – Intine, E – Vegetative cell
(c) A – Intine, B – Exine, C – Germ pore, D – Generative cell, E – Vegetative cell
(d) A – Exine, B – intine, C – Vegetative cell, D – Germ pore, E – Generative cell
Answer
D
Question. Choose the option showing the correct labelling A, B, C and D in the given figure of a dicot embryo.
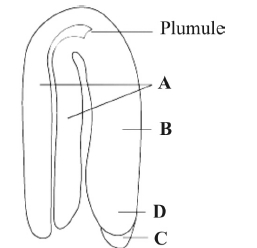
(a) A – Hypocotyl; B – Cotyledons; C – Root cap; D – Radicle
(b) A – Cotyledons; B – Hypocotyl; C – Root cap; D – Radicle
(c) A – Cotyledons; B – Hypocotyl; C – Radicle; D – Root cap
(d) A – Cotyledons; B – Radicle; C – Hypocotyl; D – Root cap.
Answer
B
Question. The given figure shows a diagrammatic view of a typical anatropous ovule, in which some parts are typical anatropous ovule, in which some parts are marked as A, B, C, & D. Identify the correct labelling of A, B, C & D from the options given below.

(a) A – Chalazal pole; B – Micropyle; C – Embryo sac; D –Nucellus
(b) A – Micropyle; B – Chalazal pole; C – Embryo sac; D – Nucellus
(c) A – Micropyle; B – Chalazal pole; C – Nucellus; D – Embryo sac
(d) A – Micropyle; B – Nucellus; C – Embryo sac;D – Chalazal pole
Answer
D
Critical Thinking Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. Which one of the following is not related to other three?
(a) Archaegonium
(b) Oogonium
(c) Ovule
(d) Antheridium
Answer
D
Question. Seed coat is not thin, membranous in
(a) coconut
(b) groundnut
(c) gram
(d) maize
Answer
A
Question. Product of sexual reproduction generally generates
(a) prologned dormancy.
(b) new genetic combination leading to variation.
(c) large biomass.
(d) longer viability of seeds.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following processes is necessary for the complete development of male gametophyte?
(a) One meiotic cell division and two mitotic cell divisions.
(b) One meiotic cell division and one mitotic cell division.
(c) Two meiotic cell divisions and one mitotic cell division.
(d) Two mitotic cell divisions.
Answer
A
Question. How many meiotic division are required for the formation of 100 functional megaspores?
(a) 100
(b) 50
(c) 75
(d) 25
Answer
A
Question. Unisexuality of flowers prevents
(a) geitonogamy but not xenogamy.
(b) autogamy and geitonogamy.
(c) autogamy but not geitonogamy.
(d) both geitonogamy and xenogamy.
Answer
C
Question. Pollination occurs in
(a) bryophytes and angiosperms.
(b) pteridophytes and angiosperms.
(c) angiosperms and gymnosperms.
(d) angiosperms and fungi.
Answer
C
Question. Point out the odd one from the given options.
(a) Nucellus
(b) Embryo sac
(c) Micropyle
(d) Pollen grain
Answer
D
Question. In the embryos of a typical dicot and a grass, true homologous structures are
(a) coleorhiza and coleoptile.
(b) coleoptile and scutellum
(c) cotyledons and scutellum
(d) hypocotyl and radicle
Answer
C
Question. The endosperm found in angiospermic seed is different from that of gymnosperms in the sense that, in the former
(a) it is formed before fertilization while in the latter it is formed after fertilization.
(b) it is formed after fertilization.
(c) it is cellular while in the latter it is nuclear.
(d) it is nutritive while in the latter it is protective.
Answer
B
Question. If a diploid female plant and a tetraploid male plant are crossed, the ploidy of endosperm shall be
(a) tetraploid
(b) triploid
(c) diploid
(d) pentaploid
Answer
A
Question. How many pollen grains will be formed after meiotic division in ten microspore mother cells?
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 40
(d) 80
Answer
C
Question. Through which part of the embryo sac, does the pollen tube enter the embryo sac?
(a) Egg cell
(b) Persistent synergid
(c) Degenerated synergid
(d) Central cell
Answer
C
