Please refer to Anatomy of Flowering Plants Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Objective Type Questions
Question. Meristemsare present in
(a) Root apex and shoot apex
(b) Bases of leaves
(c) Axillarybuds
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. A branch or a flower is developed in the axilof leaves by
(a) Apical bud
(b) Axillarybud
(c) Apical meristem
(d) Shoot apical meristem
Answer
B
Question. All are lateral meristemexcept
(a) Fascicular/vascular cambium
(b) Interfascicularcambium
(c) Apical and intercalary meristem
(d) Phellogen
Answer
C
Question. Secondary tissues of a plant
(a) Add to the length of roots and shoots
(b) Add to the diameter of existing roots and shoots
(c) Are found only in the embryo
(d) Are found only in seedling
Answer
B
Question. Meristem helps in
(a) Absorption of water
(b) Growth of plants
(c) Absorption of minerals
(d) Transpiration
Answer
B
Question. Meristematic activity occurs at
(a) Vascular tissue
(b) Stem apex
(c) Leaf
(d) Root hair
Answer
B
Question. Axillary and terminal buds develop by activity of
(a) Lateral meristem
(b) Intercalary meristem
(c) Apical meristem
(d) Parenchyma
Answer
C
Question. The following characters are shown by which of the following tissues
A. Occurs as layers or patches
B. Cell wall-unevenly thickened due to pectocellulosic deposition
C. Cells-spherical, oval or polygonal
D. Often has chloroplast
E. Living mechanical tissue
F. Occurs in hypodermis of young dicotstem and petiole
Options :
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Vascular tissue
Answer
B
Question. Angiospermic xylem consists of
(a) Vessels + tracheids only
(b) Tracheids+ fibres only
(c) Vessel, tracheids, fibres and parenchyma
(d) Parenchyma and fibres only
Answer
C
Question. Tracheid, vessel and sclereids are similar in that they all
(a) Lack secondary walls
(b) Conduct water and mineral
(c) Function when dead
(d) Have open ends
Answer
C
Question. The is the centre most tissue in a dicot stem
(a) Pith
(b) Xylem
(c) Phloem
(d) Pericycle
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is living element of xylem?
(a) Fibre
(b) Parenchyma
(c) Tracheid
(d) Vessel
Answer
B
Question. Ray parenchyma cells
(a) Are living
(b) Are dead
(c) Perform radial conduction of water
(d) (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect about companion cell?
(a) It is specialised parenchyma cell
(b) Its nucleus controls the function of sieve tube
(c) It helps in maintaining the pressure gradient in sieve tube
(d) It is present in all vascular plants having phloem
Answer
D
Question. At maturity, sieve tubes do not possess
(a) Cell wall
(b) Nucleus
(c) Cytoplasm
(d) Vacuoles
Answer
B
Question. Complex tissue comprises
(a) Xylem and phloem
(b) Heterogeneous tissue
(c) Conductive tissue
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Companion cell are associated with
(a) Sieve cells
(b) Sieve tubes
(c) Albuminous cells
(d) Vessels
Answer
B
Question. Griitiness of fruits like pears is due to
(a) Presence of silica
(b) Presence of stone cells/sclereids
(c) Presence of raphids
(d) Formation of cystolith
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following cell is described by following characters?
I. Sclerenchymatous cells
II. Much elongated, unbranched and tapering ends
III. Needle like shape
IV. Cell wall thick
V. Dead cells
VII. Found in secondary phloem
Options :
(a) Sieve tubes
(b) Phloem parenchyma
(c) Phloem firbes/blast fibres
(d) Comapnionor albuminouscells
Answer
C
Question. Epidermis is derived form
(a)Ground meristem
(b)Procambium
(c)Protoderm
(d)Corpus
Answer
C
Question. Epidermis consists of _____ and is _____ (layered)
(a)Sclerenchyma, multi
(b)Collenchyma, single
(c)Parenchyma, multi
(d)Parenchyma, single
Answer
D
Question. Trichomes, hairs, stomata etc are included under
(a)Ground tissue system
(b)Vascular tissusesystem
(c)Epidermal tissue system
(d)None
Answer
C
Question. Guard cell differ from epidermal cells in having
(a)Specific shape
(b)Chloroplast
(c)Heterogeneous nature of cell wall
(d)All
Answer
D
Question. The stomatal apparatus includes
(a)Only stomatal aperture
(b)Stomatal aperture and guard cells
(c)Only guard cell
(d)Stomatal aperture, guard cells and surrounding subsidiary cells
Answer
D
Question. Ground/fundamental tissue system is made up of
(a)Parenchyma
(b)Collenchyma
(c)Sclerenchyma
(d)All
Answer
D
Question. In leaves, ground tissue consists of
(a)Mesophyll
(b)Epidermis
(c)Vascular tissues
(d)Guard cells
Answer
A
Question. One of the primary function of the ground tissue in a plant is
(a)Photosynthesis
(b)To protect the plant
(c)Two anchor the plant
(d)Water and sugar conduction
Answer
A
Question. Vascular bundle without cambium is called
(a)Closed vascular bundle
(b)Open vascular bundle
(c)Conjoint vascular bundle
(d)Radial vascular bundle
Answer
A
Question. The description refers to which of the following
A. Unicellular hair
B. Endodermis with passage cell
C. Pith-small/inconspicuous
D. Radial vascular bundle
E. 2-4 xylem and phloem
Options :
(a)Monocot root
(b)Dicotroot
(c)Monocot stem
(d)Dicotstem
Answer
B
Question. In young dicotstem, cambium is
(a)Single layered
(b)2 layered
(c)Multi-layed
(d)Absent
Answer
A
Question. Well developed pith is seen in
(a)Monocot root and monocot stem
(b)Dicotroot and anddicotstem
(c)Monocot root and dicotstem
(d)Dicotroot and monocot stem
Answer
C
Question. In leaves, protoxylemelements
(a)Face towards adaxialside
(b)Face towards abaxialside
(c)Are surrounded by metaxylem
(d)Are scattered in the middle
Answer
D
Question. In stem, starch sheath is equivalento
(a)Pericycle
(b)Endodermis
(c)Bundle sheath
(d)Bundle cap
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. One of the primary function of the ground tissue in a plant is
(a) photosynthesis.
(b) to protect the plant.
(c) to anchor the plant.
(d) water and sugar conduction.
Answer
A
Question. Why grafting is successful in dicots ?
(a) In dicots vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
(b) Dicots have cambium for secondary growth.
(c) In dicots vessels with elements are arranged end to end.
(d) Cork cambium is present in dicots
Answer
B
Question. As secondary growth proceeds, in a dicot stem, the thickness of
(a) sapwood increases.
(b) heartwood increase.
(c) both sapwood and heartwood increases.
(d) both sapwood and heartwood remains the same.
Answer
C
Question. Some vascular bundles are described as open because these
(a) are surrounded by pericycle but not endodermis.
(b) are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem.
(c) possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem.
(d) are not surrounded by pericycle.
Answer
B
Question. Sieve tubes are suited for translocation of food because they possess
(a) bordered pits.
(b) no ends walls.
(c) broader lumen and perforated cross walls.
(d) no protoplasm.
Answer
C
Question. In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having
(a) cytoskeleton.
(b) mitochondria.
(c) endoplasmic reticulum.
(d) chloroplasts.
Answer
D
Question. Tissue(s) present in an annual ring is/are
(a) secondary xylem and phloem.
(b) primary xylem and phloem.
(c) secondary xylem only.
(d) primary phloem and secondary xylem.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are present in monocot root ?
(a) conjoint, collateral, open polyarch vascular bundle.
(b) exodermis, endarch, tetrarch closed vascular bundles.
(c) suberized exodermis, casparian strip, passage cells, cambium.
(d) suberized exodermis, polyarch xylem, pith.
Answer
D
Question. A common structural feature of vessel elements and sieve tube elements are
(a) pores on lateral walls.
(b) presence of p-protein.
(c) enucleate condition.
(d) thick secondary walls.
Answer
C
Question. A student was given a tissue to observe under the microscope. He observes the tissue and concludes that the tissue is a type of simple plant tissue and provides mechanical support to young stem and petiole of leaf. Identify the tissue.
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Xylem parenchyma
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following process helps the trichomes in preventing water loss?
(a) Where companion cells helps in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
(b) Where plants absorb water through the roots and then give off water vapor through pores in their leaves.
(c) Where activity of cork cambium builds pressure on the remaining layers peripheral to phellogen and
ultimately these layers dies and slough off.
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions
Question. Identify A, B and C in the given figure of shoot apical meristem
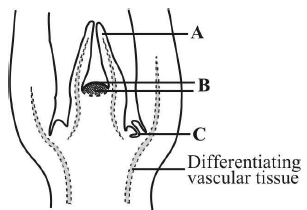
(a) A – Leaf primordium, B – Shoot apical meristem, C – Axillary bud
(b) A – Leaf primordium, B – Shoot apical meristem, C – Apical bud
(c) A – Root hair primordium, B – Root apical meristem, C – Axillary bud
(d) A – Root hair primordium, B – Root apical meristem, C – Terminal bud
Answer
A
Question. The given figures are types of elements (A and B) which constitute one type of complex tissue (c) of a plant . Identify A, B and C.
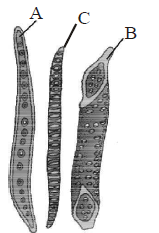
(a) A – Tracheid, B – Vessel, C – Xylem
(b) A – Vessel, B – Tracheild, C – Phloem
(c) A – Fibre, B – Tracheid, C – Bark
(d) A – Fibre, B – Sclereid, C – Casparian strips
Answer
A
Question. The given diagrams show stomatal apparatus in dicots and monocots. Which one is correct option for A, B and C?
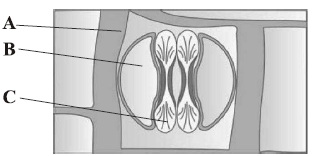
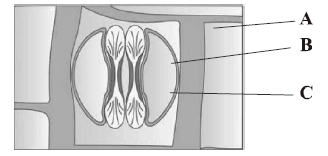
(a) A – Epidermal cells; B – Subsidiary cells; C – chloroplast
(b) A – Guard cells; B – Subsidiary cells; C – Stomatal pore
(c) A – Guard cells; B – Epidermal cells; C – Guard cells
(d) A – Epidermal cells; B – Subsidiary cells; C – Guard cells
Answer
D
Question. Choose the correct labelling of (A – J) in the given figure of T.S. of monocot root.
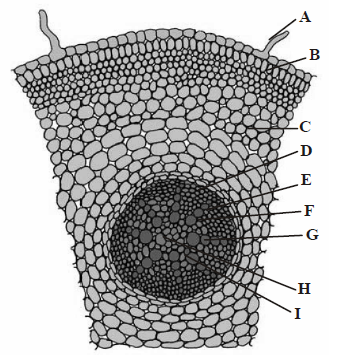
(a) A – Root hair, B – Epiblema, C – Cortex, D – Endodermis, E – Passage cell, F – Pericycle, G – Pith, H – Phloem, I – Metaxylem.
(b) A – Root hair, B – Epiblema, C – Cortex, D – Endodermis, E – Passage cell, F – Pith, G – Pericycle, H – Metaxylem, I – Phloem.
(c) A – Root hair, B – Epiblema, C – Cortex, D – Endodermis, E – Pericycle, F – Phloem, G – Protoxylem, I – Metaxylem
(d) A – Root hair, B – Cortex, C – Epiblema, D – Pericycle, E – Endodermis, F – Pith, G – Phloem, H – Protoxylem, I – Metaxylem
Answer
C
Question. T.S. of dicot stem is given below, certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A – I). Choose the option which shows their correct labelling.
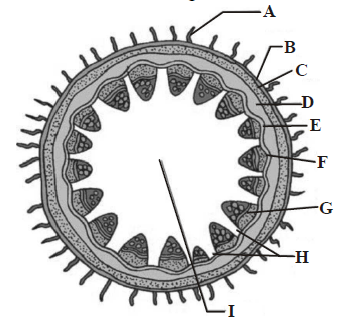
(a) A – Epidermis, B – Epidermal hair, C – Parenchyma, D – Starch sheath, E – Hypodermis (collenchyma), F – Vascular bundle, G – Bundle cap, H – Medulla or pith, I – Medullary rays
(b) A – Epidermal hair, B – Epidermis, C – Hypodermis (collenchyma), D – Parenchyma, E – Endoderm is (Starch Sheath), F – Pericycle, G – Vascular bundle, H – Medullary rays, I – Medulla or pith
(c) A – Epidermal hair, B – Epidermis, C – Hypodermis (collenchyma), D – Starch sheath, E – Parenchyma, F – Vascular bundle, G – Bundle cap, H – Medulla or pith, I – Medullary rays
(d) A – Epidermal hair, B – Epidermis, C – Parenchyma, D – Hypodermis (collenchyma), E – Starch sheath, F – Vascular bundle, G – Bundle cap, H – Medulla or pith, I – Medullary rays
Answer
B
Question. T.S. of dicot leaf passing through the midrib is given below. Certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A to H). Choose the option showing their correct labelling.
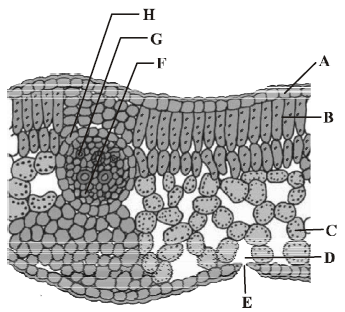
(a) A–Epidermis, B–Spongy mesophyll, C– Palisade mesophyll, D – Stomata, E– Guard cells, F–Phloem, G–Metaxylem, H–Protoxylem
(b) A–Epidermis, B–Palisade mesophyll, C– Spongy mesophyll, D–Sub-stomatal cavity, E–Stoma, F–Phloem, G– Xylem, H– Bundle sheath
(c) A – Epidermis, B – Palisade mesophyll, C–Spongy mesophyll, D–Stomata, E– Guard cells, F–Epidermis, G– Xylem, H–Phloem
(d) A–Epidermis, C–Palisade mesophyll, C–Spongy mesophyll, D– Stomata, E– Guard cells, F–Phloem, G– Metaxylem, H– Protoxylem
Answer
B
Question. The given figure shows the secondary growth in a dicot stem. Their parts are marked as A, B, C, D, E & F. Choose the correct labelling of the parts marked as A to F.
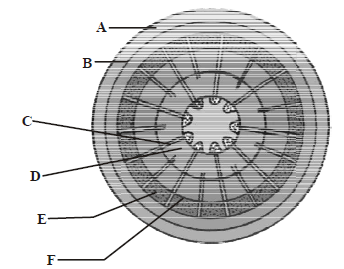
(a) A – Phellem, B – Phellogen, C – Medullary rays, D – Secondary xylem, E – Secondary phloem, F – Cambium ring
(b) A – Phellem, B – Phellogen, C – Medullary rays, D – Secondary phloem, E – Secondary xylem, F – Cambium ring
(c) A – Phellogen, B – Phellem, C – Medullary rays, D – Secondary xylem, E – Secondary phloem, F – Cambium ring
(d) A – Phellem, B – Phellogen, C – Cambium ring, D – Secondary xylem, E – Secondary phloem, F – Medullary rays
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following option shows the correct labelling of the parts marked as A, B, C and D in the given figure of a typical dicot root?

(a) A – Primary phloem, B – Vascular cambium, C – Secondary phloem, D – Primary xylem
(b) A – Secondary phloem, B – Vascular cambium, C – Primary phloem, D – Primary xylem
(c) A – Primary phloem, B – Primary xylem, C – Secondary phloem, D – Vascular cambium
(d) A – Secondary phloem, B – Primary xylem, C – Primary phloem, D – Vascular cambium
Answer
A



