VBQs Amines Class 12 Chemistry with Amines has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Amines. The following Amines Class 12 Chemistry value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Amines VBQs Class 12 Chemistry
Question. The amine that does not react with acetyl chloride is
(a) CH3NH2
(b) (CH3)2NH
(c) (CH3)3N
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. –NH2 group in aniline is
(a) only o-directing
(b) only p-directing
(c) only m-directing
(d) o-and p-directing
Answer
D
Question.
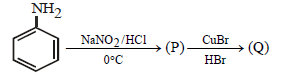
The compound Q is –
(a) bromobenzene
(b) chlorobenzene
(c) benzyl bromide
(d) benzyl chloride
Answer
A
Question. Ethylamine reacts with HNO2 giving :
(a) C2H5OH
(b) C2H5NO2
(c) NH3
(d) C2H6
Answer
A
Question. When benzenediazonium chloride in hydrochloric acid reacts with cuprous chloride, then chlorobenzene is formed.
The reaction is called
(a) Gattermann reaction
(b) Perkin reaction
(c) Etard reaction
(d) Sandmeyer reaction
Answer
D
Question. In the reaction sequence
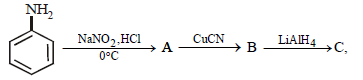
the product ‘C’ is:
(a) benzonitrile
(b) benzaldehyde
(c) benzoic acid
(d) benzylamine
Answer
D
Question. The reaction,
C6H5NH2+ ClCOC6H5 → C6H5NHCOC6H5 is called:
(a) Friedel-crafts reaction
(b) Claisen condensation
(c) Benzoylation or Schotten Baumann reaction
(d) None of these
Answer
D
Question. When phenol and benzene diazonium chloride are coupled, the main product is :
(a) aniline
(b) p-hydroxyazobenzene
(c) azobenzene
(d) chlorobenzene
Answer
B
Question. In the chemical reactions,
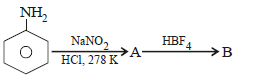
the compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ respectively are
(a) nitrobenzene and fluorobenzene
(b) phenol and benzene
(c) benzene diazonium chloride and fluorobenzene
(d) nitrobenzene and chlorobenzene
Answer
C
Question. In the chemical reactions :
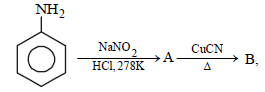
the compounds A and B respectively are :
(a) benzene diazonium chloride and benzonitrile
(b) nitrobenzene and chlorobenzene
(c) phenol and bromobenzene
(d) fluorobenzene and phenol
Answer
A
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength?
p–nitroaniline(1); m–nitroaniline (2); 2,6–trimethylaniline(3);
3–methylanline(4).
(a) 1, 3, 2, 4
(b) 2, 3, 4, 1
(c) 3, 1, 2, 4
(d) 1, 2, 4, 3
Answer
D
Question. Product of the following reaction is
C6H5–N2Cl+C6H5–NH2 →
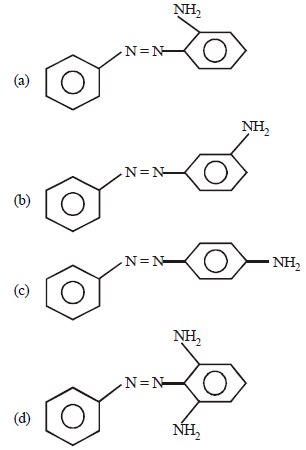
Answer
C
Question. In the diazotization of arylamines with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid, an excess of hydrochloric acid is used primarily to
(a) Supress the concentration of free aniline available for coupling
(b) Supress hydrolysis of phenol
(c) Ensure a stoichiometric amount of nitrous acid
(d) Neutralise the base liberated
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds cannot be identified by carbylamine test?
(a) CH3CH2NH2
(b) CHCl3
(c) C6H5NH2
(d) C6H5–NH–C6H5
Answer
D
Question. Hinsberg reagent is
(a) C6H5SO3H
(b) C6H5NO
(c) C6H5SO2Cl
(d) C6H5N2Cl
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reagent can be used to convert benzenediazonium chloride into benzene?
(a) CH3OH
(b) H3PO2
(c) Br2–H2O
(d) LiAlH4
Answer
B
Question.
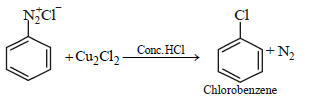
Above reaction is known as:
(a) Strecker’s reaction
(b) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(c) Wohl-Ziegler reaction
(d) Stephen’s reaction
Answer
B
Question.
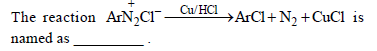
(a) Sandmeyer reaction
(b) Gatterman reaction
(c) Claisen reaction
(d) Carbylamine reaction
Answer
B
Question. The reagents that can be used to convert benzenediazonium chloride to benzene are _________.
(i) SnCl2/HCl
(ii) CH3CH2OH
(iii) H3PO2
(iv) LiAlH4
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following cannot be prepared by Sandmeyer’s reaction?
(i) Chlorobenzene
(ii) Bromobenzene
(iii) Iodobenzene
(iv) Fluorobenzene
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. The acylation reaction of amines is carried out in presence of pyridine because
(i) pyridine is stronger base than amine.
(ii) pyridine is weaker base than amine.
(iii) pyridine removes HCl formed and shifts the equilibrium to the right hand side.
(iv) pyridine removes HCl formed and shifts the equilibrium to the left hand side.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
A
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Ammonolysis (p) Amine with lesser number of carbon atoms
(B) Gabriel phthalimide (q) Detection test for primary amines.
synthesis
(C) Hoffmann bromamide (r) Reaction of Phthalimide with KOH and R–X
reaction
(D) Carbylamine reaction (s) Reaction of alkylhalides with NH3
(a) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (r), D – (s)
(c) A – (q), B – (r), C – (s), D – (p)
(d) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) ArN2+ Cl– → ArOH (p) HBF4 / NaNO2
(B) ArN2+ Cl–→ ArNO2 (q) H2O
(C) ArN2+ Cl– → ArH (r) HBF4
(D) ArN2+ Cl– → ArF (s) CH3CH2OH
(a) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(b) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r)
(c) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(d) A – (q), B – (s), C – (r), D – (p)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Gabriel phthalimide (p) C6H5CH2NH2
reaction
(B) Reduction with (q) C6H5NH2
LiAlH4
(C) Reaction with (r) C6H5CN
alc. KOH + CHCl3
(D) 1° Amide with (s) CH3CH2NH2
Br2 + KOH
(a) A – (p, s); B – (p, s); C – (p, q, s); D – (p, q, s)
(b) A – (s); B – (p); C – (q); D – (p, q)
(c) A – (p, s); B – (r); C – (q); D – (s)
(d) A – (p, q); B – (p); C – (p, q); D – (s)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Benzene sulphonyl (p) Zwitter ion
chloride
(B) Sulphanilic acid (q) Hinsberg reagent
(C) Alkyl diazonium salts (r) Dyes
(D) Aryl diazonium salts (s) Conversion to alcohols
(a) A – (s), B – (q), C – (r), D – (p)
(b) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(c) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
(d) A – (s), B – (p), C – (r), D – (q)
Answer
B
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
RCONH2 is converted into RNH2 by means of Hoffmann bromamide degradation. During the reaction amide is treated with Br2 and alkali to get amine. This reaction is used to descend the series in which carbon atom is removed as carbonate ion (CO32–). Hoffmann bromide degradation reaction can be written as :
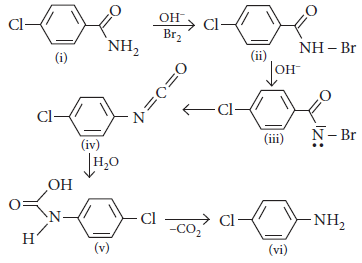
Question. Which is the rate determining step in Hoffmann bromamide degradation?
(a) Formation of (i)
(b) Formation of (ii)
(c) Formation of (iii)
(d) Formation of (iv)
Answer
D
Question. Hoffmann bromamide degradation is used for the preparation of
(a) primary amines
(b) secondary amines
(c) tertiary amines
(d) secondary aromatic amines.
Answer
A
Question. What are the constituent amines formed when the mixture of (i) and (ii) undergoes Hoffmann bromamide degradation?
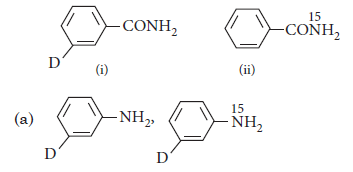
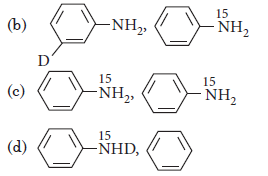
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is used for the conversion of (i) to (ii)?
(a) KBr
(b) KBr + CH3ONa
(c) KBr + KOH
(d) Br2 + KOH
Answer
D
Case II : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
The amines are basic in nature due to the presence of a lone pair of electron on N-atom of the –NH2 group, which it can donate to electron deficient compounds. Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than NH3 because of the +I effect of the alkyl groups. Greater the number of alkyl groups attached to N-atom, higher is the electron density on it and more will be the basicity. Thus, the order of basic nature of amines is expected to be 3° > 2° > 1°, however the observed order is 2° > 1° > 3°. This is explained on the basis of crowding on N-atom of the amine by alkyl groups which hinders the approach and bonding by a proton, consequently, the electron pair which is present on N is unavailable for donation and hence 3° amines are the weakest bases.
Aromatic amines are weaker bases than ammonia and aliphatic amines. Electron-donating groups such as –CH3, –OCH3, etc. increase the basicity while electron-withdrawing substitutes such as – NO2, –CN, halogens, etc. decrease the basicity of amines. The effect of these substituents is more at p than at m-positions.
Question. Which of the following order of basicity is correct?
(a) Aniline > m-toluidine > o-toluidine
(b) Aniline > o-toluidine > m-toluidine
(c) o-Toluidine > aniline > m-toluidine
(d) o-Toluidine < aniline < m-toluidine
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is the strongest base in aqueous solution?
(a) Methyl amine
(b) Trimethyl amine
(c) Aniline
(d) Dimethyl amine
Answer
D
Question. The order of basic strength among the following amines in benzene solution is
(a) CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH
(b) (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2
(c) CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
(d) (CH3)3N > CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH
Answer
B
Question. What is the decreasing order of basicity of primary, secondary and tertiary ethylamines and NH3?
(a) NH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2NH > (C2H5)3N
(b) (C2H5)3N > (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3
(c) (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)3N > NH3
(d) (C2H5)2NH > (C2H5)3N > C2H5NH2 > NH3
Answer
D
Case III : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
When the mixture contains the three amine salts (1°, 2° and 3°) along with quaternary salt, it is distilled with KOH solution. The three amines distill, leaving the quaternary salt unchanged in the solution. Then the mixture of amines is separated by fractional distillation, Hinsberg’s method and Hoffmann’s method.
(1°, 2° and 3° amines in mixture)
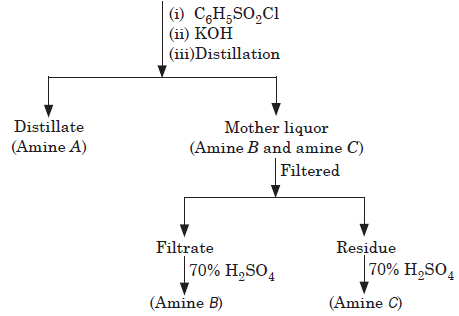
Question. Primary amine with Hinsberg’s reagent forms
(a) N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide soluble in KOH solution
(b) N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide insoluble in KOH solution
(c) N,N-dialkyl benzene sulphonamide soluble in KOH solution
(d) N,N-dialkyl benzene sulphonamide insoluble in KOH solution.
Answer
A
Question. 3° amines with Hinsberg’s reagent give
(a) no reaction
(b) product which is same as that of 1° amine
(c) product which is same as that of 2° amine
(d) products which is a quaternary salt.
Answer
A
Question. To separate amines in a mixture, Hoffmann’s method is used. The Hoffmann’s reagent is
(a) benzenesulphonyl chloride
(b) diethyl oxalate
(c) benzeneisocyanide
(d) p-toulenesulphonic acid.
Answer
B
Question. Hinsberg reagent is
(a) aliphatic sulphonyl chloride
(b) phthalamide
(c) aromatic sulphonyl chloride
(d) anhydrous ZnCl2 + conc. HCl.
Answer
C
Case IV : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
Amines are basic in nature. The basic strength of amines can be expressed by their dissociation constant, Kb or pKb.
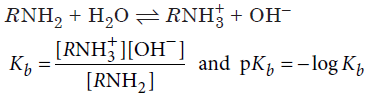
Greater the Kb value or smaller the pKb value, more is the basic strength of amine. Aryl amines such as aniline are less basic than aliphatic amines due to the involvement of lone pair of electrons on N-atom with the resonance in benzene. In derivatives of aniline, the electron releasing groups increase the basic strength while electron withdrawing groups decrease the basic strength. The base weakening effect of electron withdrawing group and base strengthening effect of electron releasing group is more marked at p-position than at m-position. o-Substituted aniline is less basic than aniline due to ortho effect and is probable due to combination of electronic and steric effect.
Question. Which of the following has lowest pKb value?
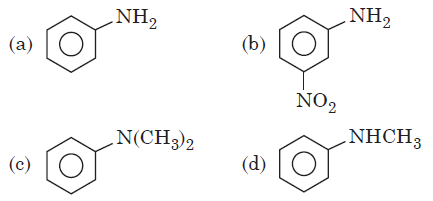
Answer
C
Question. Which among the following shoes maximum pKb value ?
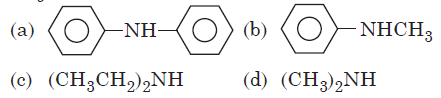
Answer
A
Question. The strongest base among the following is
(a) C6H5NH2
(b) p-NO2 – C6H4NH2
(c) m-NO2 – C6H4NH2
(d) C6H5CH2NH2
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Methylamine is more basic than NH3.
(b) Primary amines form hydrogen bonds.
(c) Ethylamine has higher boiling point than propane.
(d) Dimethylamine is less basic than methylamine.
Answer
D