VBQs Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry with Alcohols Phenols and Ethers has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Alcohols Phenols and Ethers. The following Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Chemistry value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Alcohols Phenols and Ethers VBQs Class 12 Chemistry
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect.
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : In case of phenol, bromination takes place even in absence of Lewis acid whereas bromination of benzene takes place in presence of Lewis acid like FeBr3.
Reason : – OH group attached to benzene ring is highly deactivating.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : With HI at 373 K, ter-butyl methyl ether gives ter-butyl iodide and methanol.
Reason : The reaction occurs by SN2 mechanism.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Reimer-Tiemann reaction of phenol with CCl4 in NaOH at 340 K gives salicyclic acid as the major product.
Reason : The reaction occurs through intermediate formation of dichlorocarbene.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Phenol is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Reason : In the case of phenol, the intermediate carbocation is more resonance stabilized.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Ethyl phenyl ether on reaction with HBr form phenol and ethyl bromide.
Reason : Cleavage of C–O bond takes place on ethyloxygen bond due to the more stable phenyl-oxygen bond.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
Reason : In alcohols, the oxygen of –OH group is attached to sp3 hybridized carbon atom.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Ethers behave as bases in the presence of mineral acids.
Reason : Due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on oxygen.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : In Lucas test, 3º alcohols react immediately.
Reason : An equimolar mixture of anhyd. ZnCl2 and conc.HCl is called Lucas reagent.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : With HI, anisole gives iodobenzene and methyl alcohol.
Reason : Iodide ion combines with smaller group to avoid steric hindrance.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : ter – Butyl methyl ether is not prepared by the reaction of ter-butyl bromide with sodium methoxide.
Reason : Sodium methoxide is a strong nucleophile.
Answer
B
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Propene, CH3CH = CH2 can be converted into 1-propanol by oxidation. Indicate which set of reagents amongst the following is ideal to effect the above conversion ?
(a) KMnO4 (alkaline)
(b) Osmium tetraoxide (OsO4/CH2Cl2)
(c) B6H6 and alk. H2O2
(d) O3/Zn
Answer
C
Question.

In the above sequence X can be
(a) H2 / Ni
(b) NaBH4
(c) K2Cr2O7 /H+
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?

Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reactions will yield phenol?

(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity :

(a) II > IV > I > III
(b) I > II > III > IV
(c) III > I > II > IV
(d) IV > III > I > II
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reagents can be used for preparation of cumene ?
(i) C6H6, Cl2, hv; Mg.THF; acetone.
(ii) C6H6, CH3CH2CH2Cl, AlCl3.
(iii) C6H6, CH3CHClCH3, AlCl3.
(iv) C6H6, CH3CH2Cl, AlCl3;
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Phenol is less acidic than
(a) acetic acid
(b) p-methoxyphenol
(c) acetylene
(d) ethanol
Answer
A
Question. The hydroboration of an alkene is carried out, then on oxidation with hydrogen peroxide, the alcohol so obtained is achiral. Possible structure of alkene is (are) :
(i) 2, 3– dimethylbut–2–ene.
(ii) 3, 4–dimethylbut –3–ene.
(iii) 2–methyl–but–2–ene.
(iv) 2–methylpropene.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. Vinyl carbinol is
(a) HO — CH2 — CH = CH2
(b) CH3C(OH) = CH2
(c) CH3 — CH = CH —OH
(d) CH3 — C(CH2OH) = CH2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following shows structure of allylic alcohol?

(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. The correct order of acid strength of the following compounds :
(A) Phenol
(B) p–Cresol
(C) m–Nitrophenol
(D) p–Nitrophenol
(a) D > C > A > B
(b) B > D > A > C
(c) A > B > D > C
(d) C > B > A > D
Answer
A
Question. ClCH2CH2OH is stronger acid than CH3CH2OH because of:
(a) – I effect of Cl increases negative charge on O atom of alcohol
(b) – I effect of Cl disperses negative charge on O atom to produce more stable cation
(c) – I effect of Cl disperses negative charge on O atom to produce more stable anion
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes?
(i) CrO3 in anhydrous medium.
(ii) KMnO4 in acidic medium.
(iii) Pyridinium chlorochromate.
(iv) Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. The major product of the reaction between tert-butyl chloride and sodium ethoxide is
(a) 2-methylprop-1-ene
(b) 1-butene
(c) 2-butene
(d) ethene
Answer
A
Question. Consider the following reaction:

The product Z is
(a) benzaldehyde
(b) benzoic acid
(c) benzene
(d) toluene
Answer
B
Question. An aromatic ether is not cleaved by HI even at 525 K. The compound is
(a) C6H5OCH3
(b) C6H5OC6H5
(c) C6H5OC3H7
(d) Tetrahydrofuran
Answer
B
Question. When phenol is reacted with CHCl3 and NaOH followed by acidification, salicylaldehyde is obtained. Which of the following species are involved in the above mentioned reaction as intermediate?
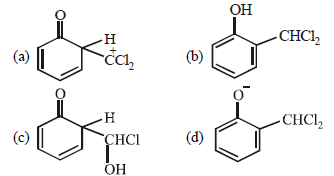
Answer
D
Question. The alcohol which does not give a stable compound on dehydration is
(a) ethyl alcohol
(b) methyl alcohol
(c) n-Propyl alcohol
(d) n-Butyl alcohol
Answer
B
Question.

Answer
D
Question. A compound of the formula C4H10O reacts with sodium and undergoes oxidation to give a carbonyl compound which does not reduce Tollen’s reagent, the original compound is
(a) Diethyl ether
(b) n-Butyl alcohol
(c) Isobutyl alcohol
(d) sec-Butyl alcohol
Answer
D
Question. The product of the following reaction is
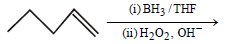
(a) 1-Pentanol
(b) 2-Pentanol
(c) Pentane
(d) 1,2-Pentanediol
Answer
A
Question. In the following sequence of reactions,
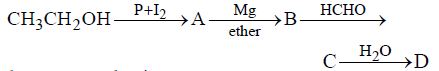
the compound D is
(a) propanal
(b) butanal
(c) n-butyl alcohol
(d) n-propyl alcohol.
Answer
D
Question. Hydration of styrene is carried out in presence of acid as catalyst. The major product is.
(a) 1–hydroxy–2–phenylethane.
(b) 1–hydroxy–1–phenylethane.
(c) 2–hydroxy–1–phenylethane.
(d) 2–hydroxy–2–phenylethane.
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily attacked by an electrophile ?
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Benzene
(c) Phenol
(d) Toluene
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is most reactive towards aqueous HBr ?
(a) 1-Phenyl-1-propanol
(b) 1-Phenyl-2-propanol
(c) 3-Phenyl-1-propanol
(d) All are equally reactive
Answer
A
Question. The reagent used for dehydration of an alcohol is
(a) phosphorus pentachloride
(b) calcium chloride
(c) aluminium oxide
(d) sodium chloride
Answer
C
Question. In Williamson synthesis if tertiary alkyl halide is used than
(a) ether is obtained in good yield
(b) ether is obtained in poor yield
(c) alkene is the only reaction product
(d) a mixture of alkene as a major product and ether as a minor product forms.
Answer
C
Question. In the reaction:

Answer
C
Question. Mechanism of acid catalysed hydration reaction involves
(i) Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by electrophilic attack of H3O+
(ii) Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
(iii) Deprotonation to form alcohol.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following will show the highest pH value ?
(a) m–nitrophenol.
(b) p–nitrophenol.
(c) o–nitrophenol.
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following fact(s) explain as to why p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol?
I. –I Effect of nitro group.
II. Greater resonance effect of p-nitrophenoxy group
III. Steric effect of bulky nitro group
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) II alone
Answer
A