Please refer to Acids Bases Salts Class 10 Science Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 10 Science based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 10.
Class 10 Science Important Questions Acids Bases Salts
Question: State the reason for the following statements:
a. Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not.
b. Dry hydrogen chloride gas does not turn blue litmus red whereas dilute hydrochloric acid does.
c. During summer season, a milkman usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
d. For dilution of an acid, acid is added to water and not water to acid.
e. Ammonia is a base but it does not contain hydroxyl group.
Answer
a. Tap water contains ions which makes it a good conductor whereas distilled water does not contain any ions.
b. Dry HCl gas does not dissociate into ions, so it has no effect on the litmus. Hydrochloric acid form ions, so it turns blue litmus red.
c. Baking soda prevents the formation of lactic acid when milk turns sour.
d. Acid is added to water slowly because the reaction is highly exothermic. If water is added to acid, then glass container may break due to lot of heat evolved.
e. NH3 dissolves in H2O forming NH4OH, therefore it acts as base:
NH3 + H2O → NH4OH → NH4 + OH-
Question: a. State the chemical properties on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid,
(ii) as a soda acid fire extinguisher,
(iii) to make bread and cake soft and spongy.
b. How is washing soda obtained from baking soda?
Write the relevant balanced chemical equation.
Answer
a. (i) It is basic in nature.
(ii) It liberates CO2 with acid which extinguishes fire.
(iii) It releases CO2 gas on heating which makes bread and cake soft and spongy.
b. Washing soda is obtained by heating baking soda followed by crystallisation:
2NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O
Na2CO310H2O→Na2 CO3 ·10H2O
(Washing soda)
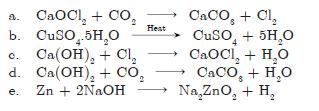
Question: Write balanced chemical equations for the following:
a. Bleaching powder is kept open in air.
b. Blue crystals of copper sulphate are heated.
c. Chlorine gas is passed through dry slaked lime.
d. Carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water.
e. NaOH solution is heated with zinc granules.
Answer
Question: a. Define indicator. Name two indicators obtained from plants.
b. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place when sodium oxide reacts with water. How will this solution behave towards phenolphthalein and red litmus paper?
c. State what happens when sodium hydroxide solution reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Answer
a. Indicator is a substance which give different colour or odour in acid and base e.g., litmus and turmeric are indicators obtained from plants.
b. Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
Solution will turn phenolphthalein pink and red litmus paper blue.
c. Sodium chloride and water are formed:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Question: The metal salt ‘A’ is blue in colour. When salt ‘A’ is heated strongly over a burner, then a substance ‘B’ present in it is eliminated and a white powder ‘C’ is left behind. When a few drops of a liquid ‘D’ is added to powder ‘C’, it becomes blue again.
a. Identify A, B, C and D.
b. Write the chemical equations involved.
c. Give an example of the salt which also shows the above property
Answer
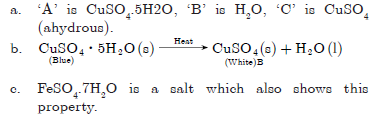
Question: Equal length of magnesium ribbon are taken in two test tubes A and B. H2SO4 is added to test tube ‘A’ and H2CO3 is added in test tube ‘B’ in equal amounts:
a. Identify the test tube showing vigorous reaction.
b. Give reason to support your answer.
c. Name the gas liberated in both the test tubes.
How will you prove its liberation?
d. Write chemical equations for both the reactions.
e. Out of two acids taken above, which one will have lower pH value and lower H+ ion concentration respectively?
Answer
a. ‘A’ will show vigorous reaction.
b. H2SO4 is a strong acid, it reacts faster than H2CO3,
a weak acid.
c. H2 gas. If we bring a burning splinter near the gas,
it will burn with ‘pop’ sound.
d. Mg + H2SO4→MgSO4 + H2
Mg + H2CO3 → MgCO3 + H2
e. H2SO4 will have lower pH. H2CO3 will have lower H+ ion concentration
Question: Write chemical equations when zinc granules react with
a. Sulphuric acid,
b. Hydrochloric acid,
c. Aluminium chloride,
d. Sodium hydroxide,
e. Nitric acid
Answer

Question: a. Explain why is hydrochloric acid a strong acid and acetic acid, a weak acid. How can it be verified?
b. Explain why aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity.
c. You have four solutions A, B, C and D. The pH of solution A is 6, B is 9, C is 12 and D is 7.
(1) Identify the most acidic and most basic solutions respectively.
(2) Arrange the above four solutions in the increasing order of H+ ion concentration.
(3) State the change in colour of pH paper on dipping in solution C and D.
Answer
a. Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid because it is completely ionised in its aqueous solution. Acetic acid is only partially ionised. HCl reacts with
Mg vigorously whereas acetic acid reacts less vigorously.
b. Aqueous solution of acid contain ions which carry current, it conducts electricity.
c. (1) With pH = 6 ‘A’ is most acidic, With pH = 12, ‘C’ is most basic.
(2) C < B < D < A is the increasing order of H+ ion concentration.
(3) pH paper will turn blue in ‘C’ with pH = 12, basic pH paper will turn green in D with pH = 7, neutral.
Question: a. Explain the following chemical properties of acids with the help of balanced chemical equations only:
(1) when an acid reacts with a metal carbonate,
(2) when an acid reacts with a metal bicarbonate,
(3) when an acid reacts with a metal oxide.
b. You are given three solutions A, B and C with pH values, 2,10 and 13 respectively. Which solution has the highest hydrogen ion concentration among the three and state the nature ‘acidic or basic’ of each solution.
Answer

Question: a. Identify the acid and the base whose combination forms the common salt that you use in your food.
Write its chemical formula and chemical name of the salt.
b. What is rock salt? Mention its colour and the reason due to which it has this colour.
c. What happens when electricity is passed through brine? Write chemical equation for it.
Answer
a. NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) and HCl (Hydrochloric
acid) form common salt. NaCl is common salt, sodium chloride.
b. Rock salt is sodium chloride found in the form of rocks. It is yellowish in colour due to the presence of impurities.
c. Sodium hydroxide, H2 gas and chlorine gas will be formed:
2NaCl (aq) 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) H2(g) Cl2(g)
Question: a. A metal compound ‘X’ reacts with dilute H2SO4 to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. If one of the compound formed is calcium sulphate, then what is ‘X’ and the gas evolved? Also write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which has occurred.
b. (i) Name one antacid. How does it help to relieve indigestion in stomach?
(ii) A farmer treats the soil with quicklime or calcium carbonate. What is the nature of the soil? Why does the farmer treat the soil with quicklime?
Answer
This is is calcium carbonate
CaCO3(s) H2SO4(dill)→ CaSO4(aq) +H2O(l) CO2(g)
The gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2).
b. (i) NaHCO3(baking soda) is an antacid. If neutralises excess of HCl in stomach and gives relief.
(ii) The nature of soil is acidic. The farmer treats the soil with quicklime (basic in nature) to neutralise the acidity of soil and make it fit for crops.
Question: a. Tooth enamel is one of the hardest substance inour body. Explain the changes in pH of mouth which indicates tooth decay. How does tooth paste help in preventing it?
b. What is the nature of salt if pH of its aqueous solution is greater than 7? Name the acid and base that would be used to prepare the following salts:
(i) Potassium sulphate, (ii) Ammonium chloride
Answer
a. Tooth enamel is made up of Ca3(PO4)2 calcium phosphate. pH = 5.5 causes tooth decay because Ca3(PO4)2 reacts with acid. Tooth paste are basic,
neutralises the acid in mouth and prevents tooth decay.
b. The salt is basic if pH > 7.
(i) KOH and H2SO4 are needed to prepare K2SO4.
(ii) NH4OH and HCl are needed to prepare NH4Cl.
Question: (a) A salt is produced by reaction between an acid and a base. Identify the acid and base from which the following salts have been formed:
(i) Na2SO4, (ii) NH4Cl, (Hi) KNO3, (iv) NaCl
(b) Which one of these will have pH less than 7 and why?
Answer
(a) (i) Na2SO4 is prepared from NaOH and H2SO4
(ii) NH4Cl is formed by NH4OH and HCl.
(iii) KNO3 is formed by KOH and HNO3.
(iv) NaOH is formed by NaOH and HCl.
(b) NH4Cl has pH less than 7 because it is a salt of
weak base NH4OH and strong acid, HCl, therefore the salt is acidic.
Question: (a) Dry pellets of a base ‘X’ when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also formed by chlor-alkali process. Write the chemical name and formula of X. Describe chloralkali process with balanced chemical equations.
Name the type of reaction occurs when X is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid. Write the relevant chemical equation.
(b) While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer
a. ‘X’ is NaOH. It is a base which is hygroscopic i.e., absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and turns sticky. It is also formed by the electrolysis of
aqueous solution of brine by chlor alkali process: 2NaCl (aq) 2H2O(l)Heat→ 2NaOH(aq) H2 (g Neutralisation reaction will take place between
NaOH and HCl: NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
b. It is because the process is highly exothermic. If we add H2O to acid, the glass container may break due to excess heat evolved.
Question: What are strong acids and weak acids? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids: hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Answer
Strong acids are those acids which are completely ionised in aqueous solution e.g.-,
HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Weak acids do not ionise completely in aqueous solution:
CH3COOH(aq) CH3OO–(aq)⇌ + H+(aq)
Strong acids: Hydrochloric acid, Nitric acid, Sulphuric acid
Question: Describe an activity with diagram to illustrate that the reaction of metal carbonates or metal bicarbonateswith acid produces carbon dioxide. Write the relevant equations of all the reactions that take place. Name any two forms in which calcium carbonate is found in nature.
Answer
Activity: To show reaction of metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates with dilute acids.
1. Take marble chips in Woulfe bottle.
2. Set the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
3. Add dilute HCl with the help of thistle funnel.
4. Collect the gas and pass through lime water and bring a burning matchstick near the gas.
5. Observe what happens.
Observation: Lime water turns milky. The burning matchstick gets extinguished.
Conclusion: Metal carbonates react with dilute acids to liberate carbon dioxide.
Repeat the experiment with NaHCO3 taken in Woulfe bottle.
Observation:
CO2 gas will be evolved which turns lime water milky. Conclusion: Metal hydrogen carbonates give CO2 with
dilute acids.
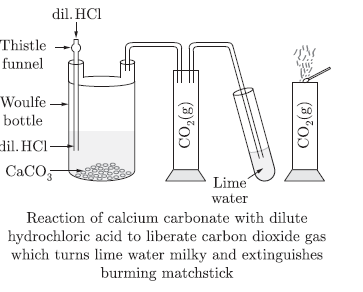
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
Na2CO3 + 2HCl $ 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
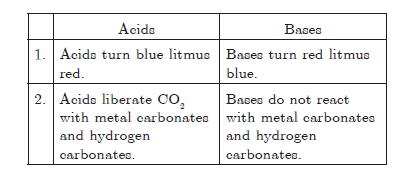
Question: List two differences between acids and bases on the basis of chemical properties.
Answer
Question: A substance ‘X’ is used as antacid reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce a gas W which is used in fire extinguishers:
a. Name the substance X and ‘Y’.
b. Write a balanced equation of the reaction between X and hydrochloric acid.
Answer
a. ‘X’ is NaHCO3 (Sodium hydrogen carbonate). ‘Y’
is CO2 gas, which is used in fire extinguishers.
b. NaHCO3(s) HCl (aq) NaCl (aq) H2O(l) CO2(g) + $ + +
Question: “Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a basic salt.” Justify the statement. How is it converted into washing soda?
Answer
NaHCO3 is a salt of NaOH which is a strong base and H2CO3 (Carbonic acid) which is a weak acid, therefore
it is a basic salt. It can be converted into washing soda by heating followed by crystallisation:
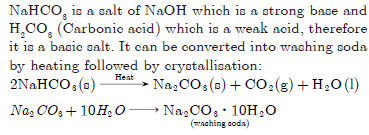
Question: What is neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer
The reaction in which acid reacts with base to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction e.g.,
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
2KOH + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2H2O
CaCO3 (Marble), CaCO3(Chalk) are the two forms in which calcium is found in nature.
Question: Five solutions A, B, C, D, and E showed pH as 4, 7, 1, 11 and 9 respectively when tested with universal indicator. Which solution is
a. Neutral,
b. Strongly alkaline,
c. Strongly acidic,
d. Weakly acidic,
e. Weakly alkaline.
Arrange the pH in increasing order of H+ ion concentration.
Answer
a. ‘B’ is neutral,
b. D is strongly alkaline,
c. ‘C’ is strongly acidic,
d. A is weakly acidic,
e. ‘E’ is weakly basic. D<E<B<A<C is the
increasing order of H+ ion concentration.
Question: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contains an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus, how will you identify the contents 5 of each test tube?
Answer
Add red litmus to each of them. The test tube in which it turns blue contains the base.
Add blue litmus to the remaining two test tubes.
The one in which it turns red contains the acid. The other one in which blue litmus and red litmus do not change contains distilled water,
Question: Name the products formed in each case when:
a. Hydrochloric acid reacts with caustic soda.
b. Granulated zinc reacts with caustic soda.
c. Carbon dioxide is passed through lime water.
Answer
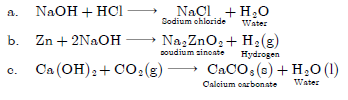
Question: While constructing a house, a builder selects marble flooring and marble table top for the kitchen where vinegar and lemon juice, tamarind etc., and re often used for cooking are to be kept. Will you agree to this selection and why?
Answer
No, he has taken wrong decision. Marble will react with vinegar and other acids and get corroded.
CaCO3 +2CH3COOH→ (CH2COO)2Ca+ H2O +CO2
Question: Two solutions ‘A’ and ‘B’ have pH value 3.0 and 10.5 respectively. Which of these will turn a. Blue litmus solution to red, b. Phenolphthalein from colourless to pink? Justify your answer in each case.
Answer
a. ‘A’ with pH = 3, will turn blue litmus red because it is acidic in nature.
b. “B’ with pH = 10.5, will turn phenolphthalein colourless to pink because ‘B’ is basic in nature.
Question: The pH of soil ‘A’ is 7.5, while that of soil “B is 4.5. Which of the two soils A or B should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust the pH and why?
Answer
Soil ‘B’ is acidic, therefore it needs to be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH because chalk is basic, which will make soil neutral.
Question: A white chemical compound becomes hard on mixing proper quantity of water. It is also used to maintain joints in fixed position. Name the chemical compound and write its chemical formula. Write the chemical equation to show what happens when water is added to this compound in proper quantity.
Answer
CaSO4. 1/2H2O is the formula of the compound. The name of compound is ‘Plaster of Paris’ (Calcium sulphate hemihydrate).
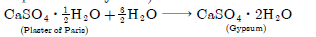
Question: What is chlor-alkali process? Write a balancedchemical equation for the reaction involved in this
Answer
When brine solution is electrolysed we get alkali
(NaOH) and chlorine (Cl2) gas, this process is called chlor-alkali process.
2NaCl (aq) 2H2O(l)→ 2NaOH(aq) H2(g) Cl2(g)
Question: Write the chemical equation to describe how baking soda is produced on a large scale. Also write the chemical name of the products formed in the reaction.
Answer
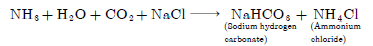
Question: Mention the pH of aqueous solution of the following salts as 7, more than 7, less than 7. KCl, Na2CO3, NH4C1, NaNO3 (Sodium nitrate)
Answer
KCl and NaNO3 has pH = 7
Na2CO3 has pH > 7
NH4Cl has pH < 7
Question: You have two solutions A and B. The pH of solution ‘A’ is 6 and the pH of solution ‘B’ is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which one of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer
‘A’ has more H+ ion concentration. ‘A’ is acidic while ‘B’ is basic.
Question: What is meant by the term water of crystallisation? How would you show that copper sulphate crystals contains water of crystallisation?
Answer
The molecules of water associated with a crystalline substance are called water of crystallisation. When hydrated copper sulphate is heated its colour
changes from blue to dirty white and water droplets are formed.
CuSO4.5H2O Heat→ CuSO4 + 5H2O
If we add little water to anhydrous CuSO4, we get blue colour again. It is the presence of molecules of water of crystallisation which was lost on heating.
CuSO4 + 5H2O $ CuSO4.5H2O
(Anhydrous)
Question: What is the difference between slaked lime and lime water?
Answer
The solid Ca(OH)2 is slaked lime whereas clear solution of Ca(OH)2 in water is lime water.
Question: Write a balanced chemical equation for the neutralisation reaction, mentioning the physical state of reactants and products.
Answer
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Question: During summer season, a milkman usually adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. Give one reason.
Answer
Baking soda is basic in nature, it will not allow milk to turn sour due to the formation of lactic acid.
Question: Curd is not kept in copper and brass utensils, why?
Answer
Curd contains lactic acid which can make poisonous compounds with brass and copper vessels.
Question: Oxides of metals are basic while those of non-metals are acidic. Explain
Answer
Metal oxides dissolve in water to form base basic in nature. On the other hand non-metals dissolve in water to form acids, acidic in nature.ns lactic acid which can make poisonous compounds with brass and copper vessels.
Question: Fresh milk has pH = 6. When it changes to curd will its pH value increase or decrease
Answer
pH value will decrease when milk changes to curd.
Question: On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to copper oxide powder, the solution formed is blue green. Predict the new compound formed which imparts a blue green colour to the solution.
Answer
Copper chloride imparts blue green colour to the solution.
Question: How does flow of acid rain water into river makes the survival of aquatic life in the river difficult?
Answer
Acidic water makes aquatic species uncomfortable. Aquatic species are more comfortable in the pH 7 to 7.8.
Question: What would be the colour of litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate?
Answer
The red litmus will turn blue in Na2CO3 solution.
Question: Arrange the following in an increasing order of their pH values: NaOH solution, Blood, Lemon juice.
Answer
Lemon juice < Blood < NaOH solution.
Question: How does the pH change when solution of a base is diluted?
Answer
When solution of a base is diluted, its pH decreases.
Question: At what pH in the mouth is tooth decay faster and why?
Answer
At pH lower than 5.5, tooth decay becomes faster because calcium phosphate (enamel) reacts with acid and gets corroded.
Question: Give two uses of baking soda and washing soda each.
Answer
Use of baking soda:
a. It is used in making of bread, biscuits, cakes.
b. It is used as an antacid.
Use of washing soda:
a. It is used as a cleansing agent.
b. It is used to remove hardness of water.
Question: Name the natural source of each of the following acid:
a. Citric acid,
b. Oxalic acid,
c. Lactic acid,
d. Tartaric acid.
Answer
a. Citric acid—Lemon, Orange.
b. Oxalic acid—Tomato, Guava
c. Lactic acid—Curd, Sour milk
d. Tartaric acid—Tamarind
Question: A compound ‘X’ of sodium is commonly used for making crispy pakoras. It is also used for curing acidity in the stomach. Identify ‘X’. Write the formula and its chemical name. State the reaction which takes place when it is heated.
Answer
X’ is NaHCO3, sodium hydrogen carbonate. It is used in cooking and for curing acidity in stomach.
2NaHCO3 Heat→ Na2CO3 + CO2 +H2O
The colour changes due to the loss of molecules of water of crystallisation. Colour is regained by absorbing water molecules from the atmosphere
containing water vapours.
Question: (a) Write the name given to the bases that are highly soluble in water. Give an example.
(b) Why does bee sting causes pain and irritation? Rubbing of baking soda on the sting area gives relief. How?
Answer
(a) Highly soluble bases are called alkalies e.g., KOH.
(b) Bee sting contains HCOOH, formic acid which causes irritation. Baking soda (basic) neutralises HCOOH, therefore it gives relief from pain on
rubbing it on sting area,
Question:The pH of the mouth of a person is lower I than 5.5. What changes will occur in his mouth? How these changes can be controlled? Write any two measures.
Answer
Acid will be formed in the mouth which causes tooth decay.
a. Wash your mouth with water after every meal.
b. Brush your teeth after meal. Toothpastes are basic in nature and it will neutralise the acid formed in mouth
Question: Write the chemical name of Plaster of paris. Write a chemical equation to show the reaction between Plaster of paris and water.
Answer
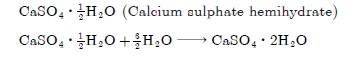
Question: Crystals of a substance changes their colour on heating in a closed vessel but regained it after sometime, when they were allowed to cool down.
a. Name one such substance.
b. Explain the phenomenon involved.
Answer

Question: State in brief the preparation of washing soda from baking soda. Write balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Answer
When sodium hydrogen carbonate (Baking soda) Download more materials in free at : is heated sodium carbonate is formed which on crystallisation forms washing soda

Question: What is colour of FeSO4.7H2O crystals? How does this colour change upon heating? Give a balanced chemical equation for the change.
Answer
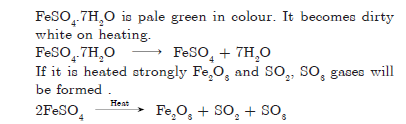
Question: What is a neutralisation reaction? Give one example.
Answer
The reaction in which acid reacts with a base to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction e.g.,
KOH(aq) + HNO3(aq)→KNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
Question: Classify the following salts into acidic, basic and neutral salts: Potassium sulphate, ammonium chloride, sodium carbonate, sodium chloride
Answer
Acidic: Ammonium chloride,
Basic: Sodium carbonate,
Neutral: Potassium sulphate, sodium chloride.
Question: A white powder is added while baking breads and while making cakes to make them soft and fluffy.
What is the name of that powder? What are the main ingredients in it? What are the functions of each ingredient?
Answer
The powder is baking powder. It consist of sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid.
NaHCO3 gives CO2 on heating which makes the bread cake soft and fluffy. Tartaric acid neutralises Na2CO3 which is bitter in taste.
Question: HCl and HNO3 show acidic characteristics in aqueous solution while alcohol and glucose solutions do not. Give reasons.
Answer
HCl and HNO3 form H+ or H3O+ ions in aqueous solution whereas alcohol and glucose do not dissociate into ions.
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl–
HNO3 + H2O $ H3O+ + NO3 –
Question: Write the chemical formulae of washing soda and baiting soda. Which one of these two is an ingredient of antacids? How does it provide relief in stomachache?
Answer
Na2CO3 ·10H2O $ is washing soda, NaHCO3 is baking soda. NaHCO3 is an ingredient of antacid. It neutralises hyper acidity in stomach and gives relief.
Question: What is bleaching powder chemically? Give a reaction for its preparation. State one of its use.
Answer
Bleaching powder is chemically CaOCl2, calcium oxychloride
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O (Dry slaked lime)
It is used as a disinfectant i.e., it makes water fit for drinking.
Question: A student dropped few pieces of marble in dilute HCl contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was passed through lime water.
a. What change would be observed in lime water?
b. Write a balanced chemical equation for the above change.
Answer
a. Lime water will turn milky.
b. Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
Question: What are olfactory indicators? Dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus. Give reason.
Answer
Olfactory indicators: They give different smell in acids and bases.
Dry HCl(g) does not form ions, so there is no effect on litmus.
Question: Answer the following:
a. Why is Plaster of paris written as CaSO4·1/2H2O?
How is it possible to have a half water molecule attached with CaSO4?
b. Why is sodium hydrogen carbonate an essential ingredient in antacids?
Answer
a. It has one molecule of water associated with 2 molecules of CaSO4. Water molecules are present as water of crystallisation.
b. It is a mild base and it can neutralise hyper acidity without harming our body.
Question: What happens when chlorine is passed over slaked lime at 313 K? Write chemical equation of the reaction involved and state two uses of the product.
Answer
Bleaching powder, CaOCl2 is formed:

a. It is used as an oxidising agent.
b. It is used as a disinfectant.
Question: What is meant by ‘water of crystallisation’ of a substance? Describe an activity to show that blue copper sulphate crystals contains water of crystallisation.
Answer
The molecules of water associated with a crystalline substance are called ‘water of crystallisation.’
CuSO4 ·5H2O→ CuSO4 5H2O
When hydrated copper sulphate is heated its colour changes from blue to dirty white and water droplets are formed. If we add little quantity of water to
anhydrous CuSO4, we get blue colour again. It is those presence of molecules water of crystallisation which was lost on heating.
Activity: To study the effect of heat on hydrated crystalline salts.
i. Take 2 g of CuSO4 5H2O $ in a test tube.
ii. Observe the initial colour of the salt.
iii. Heat the test tube at top of burner carefully as shown in the diagram.
iv. Record your observations.
v. Cool the crystals and add few drops of water.
vi. Record your observations again.
Observations: Blue colour of CuSO4 ·5H2O $ is changed to dirty white anhydrous CuSO4 and water droplets were formed. On adding water, blue colour of salt was restored.
Conclusion: CuSO4· 5H2O $ is a hydrated salt which loses water of crystallisation, which on heating becomes dirty white and regains its colour when it comes in contact with water.
Chemical reactions involved:
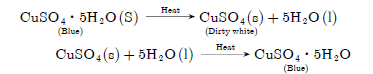
Question: What is baking powder? How does it make the cake soft and spongy?
Answer
Baking powder is made up of NaHCO3 and tartaric acid. NaHCO3, on heating gives CO2 which makes the cake soft and spongy

