Please refer to Agriculture Class 10 Social Science Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 10 Social Science based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 10.
Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Agriculture
Objective Type Questions
Question. A type of millet rich in iron, calcium, other micro nutrients and roughage is _____________.
(a) Bajra
(b) Rajma
(c) Jowar
(d) Ragi
Answer
D
Question. Aus, aman and boro are types of which crop?
(a) Maize
(b) Paddy
(c) Jowar
(d) Bajra
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following methods have been changed depending upon the characteristics of physical environment, technological know-how and socio-cultural practice?
(a) Industrial activity
(b) Irrigation Pattern
(c) Cultivation
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. What is jhumming cultivation called in Andhra Pradesh?
(a) Dahiya
(b) Kumari
(c) Khil
(d) Podu or Penda
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area?
(a) Shifting agricultural
(b) Plantation agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive agriculture
Answer
B
Question. Jhumming in Brazil is called–
(a) Ladang
(b) Roca
(c) Masole
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the staple food crop of a majority of the people in India?
(a) Jowar
(b) Bajra
(c) Wheat
(d) Rice
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following farming practice depends upon monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and suitability of other environmental conditions?
(a) Commercial farming
(b) Internsive subsistence farming
(c) Plantation
(d) Primitive subsistence farming
Answer
D
Question. Tick the characteristic of commercial farming.
(a) Plots of land are fragmented.
(b) Transport and communication plays an important role.
(c) The yield is usually low.
(d) The pressure of population is high on land.
Answer
B
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the Primitive cultivation in India from the following options:
(a) Dahiya – Madhya Pradesh
(b) Kumari – Jharkhand
(c) Khil – Andhra Pradesh
(d) Koman – Karnataka
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Paddy
(b) Gram
(c) Jowar
(d) Soyabean
Answer
B
Question. Bewar: Madhya Pradesh, Penda: Andhra Pradesh,_________ : Odisha
(a) Kuruwa
(b) Podu
(c) Khil
(d) Bringa
Answer
D
Question. During which season/seasons important crops like watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber and vegetables crops are produced?
(a) Zaid season
(b) Kharif season
(c) Rabi season
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following countries is the largest producer of Horticulture crops?
(a) India
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Japan
(d) China
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following crops requires moist and humid climate with rainfall of more than 200 cm and temperature above 25°C?
(a) Jute
(b) Rice
(c) Rubber
(d) Wheat
Answer
C
Question. What is ‘Boro’?
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Zaid crop
(c) Rabi crop
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Name the farming that is also known as ‘slash and burn’ agricultural.
(a) Primitive subsistence farming
(b) Intensive subsistence farming
(c) Plantation farming
(d) Dairy farming
Answer
A
Question. Ragi is very rich in
(a) Zinc
(b) Iodine
(c) Iron
(d) Phosphorous
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) In the 19th century Indian spices were exported to different countries of the world.
(b) During the colonial period cotton was exported to Britain.
(c) Indian farmers have been exposed to new challenges after 2001.
(d) Organic farming does not affect environment negatively.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is an age-old economic activity?
(a) Fishing
(b) Tailoring
(c) Agriculture
(d) Weaving
Answer
C
Question. Rabi crops are sown in
(a) Winters
(b) Monsoon
(c) Summers
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a fibre crop grown in India?
(a) Silk
(b) Maize
(c) Hemp
(d) Cotton
Answer
B
Question. The crops grown in rabi season are
(a) Wheat, peas, barley and mustard
(b) Rice, jute, maize, soyabean
(c) Pulses, melons, vegetables
(d) Sugarcane and tobacco
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following are the two main beverage crops produced in India?
(a) Cocoa and sugarcane
(b) Rice and pulses
(c) Tea and coffee
(d) Jowar and Bajra
Answer
C
Question. Pulses: leguminous crop, watermelon: zaid crop, ____________: rabi crop
(a) Maize
(b) Jowar
(c) Bajra
(d) Barley
Answer
C
Question. In which months are the kharif crops harvested?
(a) April – June
(b) September – October
(c) January – February
(d) June – July
Answer
B
Question. Rearing and breeding of fishes: Pisciculture, Honey-bee farming: Apiculture, Rearing of silkworms: ______________
(a) Silkculture
(b) Sericulture
(c) Mulberryculture
(d) Wormculture
Answer
B
Question. Important crops like paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, etc. are grown during which of the following seasons?
(a) Spring
(b) Summer
(c) Monsoon
(d) Winter
Answer
C
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the slash and burn agriculture in other countries from the following options:
(a) Ray – Mexico
(b) Milpa – Vietnam
(c) Roca – China
(d) Conuco – Venezuela
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following crops is used both as food and fodder?
(a) Ragi
(b) Jowar
(c) Maize
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the largest producing country from the following options:
(a) Brazil – Pulses
(b) China – Rice
(c) India – Fruits and vegetables
(d) Sugarcane – Japan
Answer
B
Question. Which which of the following is the Operation Flood related?
(a) French Revolution
(b) White Revolution
(c) Green Revolution
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Barley: rabi crop, cotton: kharif crop, ________: zaid crop
(a) Wheat
(b) Mustard
(c) Soyabean
(d) Cucumber
Answer
D
Question. On black soil is ______________ grown.
(a) Cotton
(b) Maize
(c) Silk
(d) Mulberry
Answer
A
Question. Peas: rabi crop, Muskmelon: zaid crop, _________ : kharif crop
(a) Gram
(b) Bajra
(c) Wheat
(d) Barley
Answer
C
Question. Point out the India’s rural population as per census 2011?
(a) 833 million
(b) 250 million
(c) 200 million
(d) 900 million
Answer
A
Question. West Bengal: Rice, Punjab: Wheat ________: Maize
(a) Karnataka
(b) Uttarakhand
(c) Haryana
(d) Assam
Answer
A
Question. The largest sugarcane producing state of India is
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Bihar
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer
D
Question. After 1990, under , the Indian farmers have been exposed to new challenges.
(a) Privatisation
(b) Industrialisation
(c) Globalisation
(d) Capitalisation
Answer
C
Question. is a scheme introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers.
(a) Kisan Credit Card
(b) Mudra Yojana
(c) Farmer Scheme
(d) Jan Dhan Yojana
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following crops is grown once a year?
(a) Sugarcane
(b) Cotton
(c) Rice
(d) Pulses
Answer
A
Question. North-eastern region: Jhumming, Waltre: South-eastern Rajasthan,_________ : Odisha
(a) Valre
(b) Pama Dabi
(c) Kuruwa
(d) Podu
Answer
B
Question. Which crop is harvested in the months of September-October?
(a) Zaid
(b) Rabi
(c) Kharif
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the largest tea producer state in India?
(a) Punjab
(b) Haryana
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Assam
Answer
D
Question. Which type of agriculture practice is famous in North-Eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland?
(a) Jhumming
(b) Slash and burn farming
(c) Commercial farming
(d) Subsistence farming
Answer
A
Question. What population of India is engaged in agricultural activities?
(a) Two-third
(b) Three-fourth
(c) One-fourth
(d) Two-fourth
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following countries is the largest producer of sugarcane?
(a) China
(b) Brazil
(c) France
(d) India
Answer
B
Question. In which state of India ‘slash-and burn’ agriculture is called ‘Pamlou’?
(a) Meghalaya
(b) Manipur
(c) Mizoram
(d) Nagaland
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following varieties of coffee is grown in India?
(a) American
(b) Arabica
(c) Espresso
(d) Cappuccino
Answer
D
Question. India was the second largest producer of this crop after China in 2015.
(a) Barley
(b) Cotton
(c) Maize
(d) Sugarcane
Answer
B
Question. Cotton grows well in
(a) Arid soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Black soil
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is being used in making gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets and other artefacts?
(a) Jute
(b) Cotton
(c) Fibre
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Choose the correctly matched pair about the crops from the following options:
(a) Golden fibre – Jute
(b) Fibre crop – Rubber
(c) Food crop – Cotton
(d) Non-food crop – Tea
Answer
A
Question. Who was declared as spiritual heir of Mahatma Gandhi?
(a) Subhash Chandra Bose
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Vinoba Bhave
(d) Sardar Patel
Answer
C
Question. ______________ a major industrial raw material which is mainly grown in Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
(a) Coffee
(b) Rubber
(c) Coconut
(d) Rice
Answer
B
Question. Who initiated Bhoodan-Gramdan movement?
(a) Pt. Nehru
(b) Dr. Ambedkar
(c) Sardar Patel
(d) Vinoba Bhave
Answer
D
Question. Which out of the following is a zaid crop?
(a) Moong
(b) Mustard
(c) Urad
(d) Watermelon
Answer
D
Question. Agriculture contributes to the national income of India.
(a) 33%
(b) 22%
(c) 40%
(d) None of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is/are bio-diesel crops?
(a) Jatropha
(b) Jojoba
(c) Cactus
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following states is not a major sugarcane producing states in India?
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Rajasthan
Answer
D
Question. In the 19th century who among the following came to India?
(a) Asian traders
(b) European traders
(c) African traders
(d) American traders
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following crops is mainly grows in Kerala?
(a) Tea
(b) Coffee
(c) Rubber
(d) Jute
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following countries was the second largest producer of cotton in 2015, but now it is the largest cotton producing country in the world?
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Brazil
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer
A
Question. What are the challenges faced by the Indian farmers at present?
(a) International competition and reduction in public investment in irrigation, power infrastructure and other inputs.
(b) Decreased subsidy on fertilizers leads to higher cost of production and reduction in import duties on farmers’ produce.
(c) Nature of monsoon affects crops production.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. ________ is a slash and burn agriculture.
(a) Extensive farming
(b) Commercial subsistence farming
(c) Jhumming
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Groundnut is a zaid crop and accounts for about one-third of the major oilseeds produced in the country.
Reason (R): Castor seed is grown both as rabi and kharif crop.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production.
Reason (R): Doses of biochemical input are used to grow crops rapidly.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Crops are grown depending upon the variations in soil, climate and cultivation practices.
Reason (R): Crops are also grown according to availability of water.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Tea cultivation is a labour-intensive industry.
Reason (R): Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate throughout the year.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Globalisation is a latest phenomenon.
Reason (R): It was there at the time of colonisation when Europeon traders entered India.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): Plantation, a type of commercial farming, in this a single crop is grown on a large area.
Reason (R): Since the production is mainly for market, a well developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Staple food crop in India is rice and requires less rain.
Reason (R): Our country is the fourth largest producer of rice in the world.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): India’s primary activity is agriculture.
Reason (R): Two-thirds of India’s population is engaged in agricultural activities.Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Rubber is grown in tropical and sub-tropical areas.
Reason (R): It requires moist and humid climate with rainfall of more than 100 cm and temperature above 50°C
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): The Government of India embarked upon introducing agricultural reforms to improve Indian agriculture in the 1960s and 1970s.
Reason (R): KCC, PAIS are some schemes introduced by Government of India for the benefit of farmers.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Organic farming is much in vogue.
Reason (R): In organic farming, crops are grown using high doses to increase production.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
C
Question. Study the given graph releated to consumption of natural rubber and answer the question:
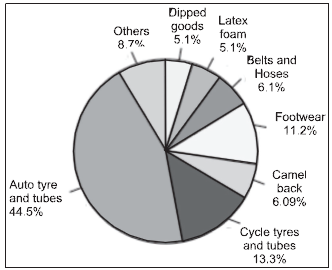
Which among the following sectors consume more natural rubber?
(a) Dipped Goods
(b) Camel Back
(c) Latex Foam
(d) Footwears
Answer
D
Case/Source Based Questions
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June. Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard. Through, these crops are grown in large parts of India, states from the north and north-western parts such as Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir (UT), Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are important for the production of wheat and other rabi crops. Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western temperate cyclones help in the success of these crops. However, the success of the green revolution in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and Parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the above mentioned rabi crops.
Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September-October. Important crops grown during this season are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean. Some of the most important rice growing regions are Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karala and Maharashtra, particularly the (Konkan coast) along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Recently, paddy has also become an important crop of Punjab and Haryana. In states like Assam, West Bengal and Odisha, three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are Aus, Aman and Boro.
Question. Which of the following crops grown in rabi season?
(a) Barely, soyabean, watermelon
(b) Rice, peas, bajra
(c) Gram, mustard, barley
(d) Jowar, urad, gram
Answer
C
Question. Read the following statements and find the INCORRECT from the given options.
I. Rabi crops are grown in summer and harvested from October to December.
II. Kharif crops are harvested in September-October.
III. West Bengal and Assam are major rice producing states of India.
Options:
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) I only
(d) III only
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not a kharif crop?
(a) Arhar
(b) Moong
(c) Cotton
(d) Mustard
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the main crop of rabi reason?
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Maize
(d) Jowar
Answer
A
Question. The three main cropping seasons of India are
(a) Pongal, Lohri and Onam
(b) Aus, Aman and Boro
(c) Rabi, Kharif and Zaid
(d) Chat, Baishakh and Lohri
Answer
C
Question. The staple food of India is
(a) Soyabean
(b) Rice
(c) Maize
(d) Gram
Answer
B
2. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area. The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry. Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers. All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
In India, tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana, etc., are important plantation crops. Tea in Assam and North Bengal coffee in Karnataka are some of the important plantation crops grown in these states. Since the production is mainly for market, a well developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays an important role in the development of plantations.
Question. Plantation is a type of commercial farming. Which of the following crops come under plantation farming?
(a) Rubber, coffee, wheat, banana, cotton
(b) Tea, rice, rubber, coffee, maize
(c) Sugarcane, tea, coffee, banana, rubber
(d) Jute, tea, coffee, maize, banana
Answer
C
Question. Plantation covers large tracts of land. Read the following statements and find the INCORRECT from the given options.
I. Planation is practised in areas where population pressure on land is high.
II. It has an interface of agriculture and industry.
III. It requires well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas.
Options:
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) III only
(d) I only
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following states of India is famous for spices and rubber?
(a) West Bengal
(b) Odisha
(c) Karnataka
(d) Kerala
Answer
D
Question. Laterite soil is useful for growing which of the following commercial crops?
(a) Rubber and sugarcane
(b) Cotton and jute
(c) Barley and gram
(d) Tea and coffee
Answer
D
Question. Which form of agriculture is plantation farming?
(a) Extensive farming
(b) Commercial farming
(c) Mixed farming
(d) Subsistence farming
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a major planation crop of India?
(a) Banana
(b) Grapes
(c) Rubber
(d) Tea
Answer
B
3. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
Agriculture has been practised in India for thousands of years. Sustained uses of land without compatible techno–institutional changes have hindered the pace of agricultural development. Inspite of development of sources of irrigation most of the farmers in large parts of the country still depend upon monsoon and natural fertility in order to carry on their agriculture. For a growing population, this poses a serious challenge. Agriculture which provides livelihood for more than 60 per cent of its population, needs some serious technical and institutional reforms. Thus, collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc. were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after Independence. ‘Land reform’ was the main focus of our First Five Year Plan. The right of inheritance had already lead to fragmentation of land holdings necessitating consolidation of holdings.
Question. belongs to sector.
(a) Construction; tertiary
(b) Agriculture; primary
(c) Smelting; primary
(d) Banking; secondary
Answer
B
Question. Arrange the correct sequence of Column I against the Column II.

Choose the correct answer.
(a) a-3, b-2, c-4, d-1
(b) a-4, b-1, c-2, d-4
(c) a-2, b-3, c-1, d-4
(d) a-2, b-1, c-4, d-3
Answer
D
Question. For irrigation, most of the Indian farmers depend on
(a) Monsoon
(b) Rivers
(c) Reservoirs
(d) Tube wells
Answer
A
Question. Grouping of small land holdings into a bigger one is called
(a) Collectivisation
(b) Cooperation and abolition of zamidari
(c) Consolidation of land holdings
(d) Institutional reforms
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following was the main forces of the First Five Year plan of India?
(a) Privatisation
(b) Globalisation
(c) Industrialisation
(d) Land reform
Answer
D
Question. Land reform is covered under which list?
(a) State list
(b) Concurrent list
(c) Central list
(d) Board list
Answer
A


