Please refer to Production and Costs Class 12 Economics Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 12 Economics based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 12 Economics for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 12.
Class 12 Economics Important Questions Production and Costs
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question. Define variable costs. Explain the behaviour of total variable cost as output increases.
Ans. Variable costs are those costs, which vary directly with the quantity of output produced.
Total variable cost increases with increase in output. Initially, it increases at decreasing rate. Eventually, it increases at an increasing rate.
Question. Explain the concepts of the short-run and the long-run.
Ans. Short-run Short-run refers to a period in which output can be changed by changing only variable factors. In the short- run, fixed inputs like land, building, plant machinery etc, cannot be changed. It means, production can be raised by increasing only variable factors, but till the extent of fixed factors.
Long- run Long-run refers to a period in which output can be changed by changing all factors of production. In the long run, firm can change its factory size, techniques of production, purchase new plant machinery, patents etc.
Question. ‘‘Average revenue curve represents law of demand’’. Discuss.
Ans. Average revenue is determined by dividing total revenue by the quantity sold which indicates price of the commodity. Hence, average revenue curve shows the relationship between price of a commodity and quantity demanded.
It is downward sloping curve because to increase its sales, firms have to lower their prices. So, it possesses all the characteristics of the demand curve. Therefore, we can say that Average Revenue curve represents law of demand.
Question. A producer borrows money and opens a shop. The shop premises is owned by him. Identify implicit cost and explicit cost from this information. Also, explain.
Ans. In the above example, interest paid on borrowed money will be explicit cost, whereas, the imputed rent of the shop premises is implicit cost. Explicit Cost These are those cash payments, which firms make to outsiders for their services and goods. e.g. wages, payment for raw material, rent, interest, etc.
Implicit Cost These are the costs of self-owned and self-employed resources. e.g. entrepreneur may utilise his own building for factory use, interest on self-capital, etc.
Question. What is meant by returns to a factor? State the law of diminishing returns to a factor.
Ans. Returns to a Factor It refers to the behaviour of output when only one variable factor of production is increased in short-run and fixed factors remain constant.
Law of Diminishing Returns to a Factor It refers to a situation in which total output increases at a diminishing rate when more and more variable factor is combined with the fixed factor of production. In this situation, Marginal Product of the variable factor must be diminishing.
Question. Explain the relationship between Marginal Cost and Average Cost using diagram.
Ans. Relationship between Marginal Cost (MC) and Average Cost (AC) is stated below
(i) When AC falls, MC is lower than AC.
(ii) When AC rises, MC is greater than AC.
(iii) When AC is constant and minimum, MC is equal
(iv) MC is always to the left of AC and cuts AC from its lowest point.

Question. ‘‘Fixed cost of input is ignored in the study of the law of increasing return’’. Do you agree?
Ans. No, it is not correct. In fact, fixed cost plays an important role in deriving increasing returns from variable inputs. A firm can leverage its fixed cost to derive better returns due to improved productivity of resources.
e.g. rent is paid every month for the factory space which is fixed cost.
By employing more labours, the production can be maximised and returns of paying rent as fixed cost can be increased. Hence, fixed cost is not ignored in the analysis of law of increasing returns to variable factor.
Question. A firm can sell as many units of a good as it wants to sell at a given price. Prepare a schedule showing total revenue, average revenue and marginal revenue of such a firm.
Ans. TR = AR × Q, MRnth = TRn − TRn−1

Question. Explain the concept of a production function.
Ans. It is the technological knowledge that determines the maximum levels of output that can be produced using different combinations of inputs.
If the technology improves, the maximum levels of output obtainable for different input combinations increase. Then we have a new production function. e.g., A firm produce a product (Y) by using two inputs X1 and X2. Then production function can be expressed as
qy = f (X1 . X2 )
Question. Complete the following data
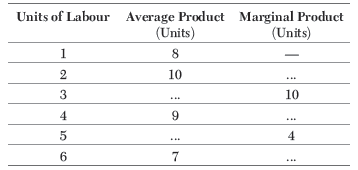
Ans.

Question. Complete the following table
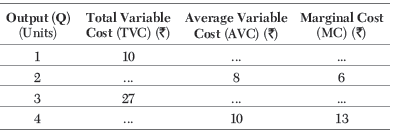
Ans.

Question. ‘‘Average product can never be zero while marginal product can be’’. Comment.
Ans. MP can become zero when production does not increase with increase in the number of variable factor. On the other hand, AP can never be zero as it is calculated on the basis of TP and variable units of input. Both TP and variable units cannot be zero which makes it impossible for AP to be zero. Hence, it is clear that MP can be zero, but AP will never be zero.
Question. Why AC curve is ‘U’ shaped?
Ans. The main reason for this ‘U’ shaped AC curve is the operation of the law of variable proportion. We know as output increases, law of increasing return operates in the initial stages. At this stage, when a firm increases its output, it gets economies and the result is decline in average cost. After the point of optimum combination, economies turn into diseconomies and result in increase in output and average cost. This is the stage of law of diminishing returns.
Question. State giving reasons, whether the following statements are true or false
(i) When Total Revenue is constant, Average Revenue will also be constant.
(ii) When Marginal Revenue falls to zero, Average Revenue becomes maximum.
(iii) Marginal Revenue is always the price at which the last unit of the commodity is sold.
(iv) WhenMarginal Revenue is positive and constant, Average Revenue and Total Revenuewill both increase at constant rate.
Ans. (i) False, when Total Revenue is constant, Average Revenue will be diminishing.
(ii) False, when Marginal Revenue is zero, Average Revenue will be diminishing.
(iii) False, Marginal Revenue can never be the price at which the last unit of the commodity is sold. It simply refers to additional revenue, when an additional unit of output is sold.
(iv) False, because when Marginal Revenue is positive and constant, Total Revenue increases at constant rate but Average Revenue tends to be equal to Marginal Revenue.
Question. State giving reasons, whether the following statements are true or false.
(i) When there are diminishing returns to a factor, total product first increases and then starts falling?
(ii) When marginal product falls, average product will also fall?
Ans. (i) False, this is because of decline in marginal product. Falling marginal product implies that total product continues to increase at a diminishing rate.
(ii) False, Average product can rise even when marginal product falls.
Question. Explain the relationship between AP and MP.
Ans. Relationship between AP and MP is stated below
(i) AP increases when MP is greater than AP.
(ii) AP is maximum when both MP and AP are equal.
(iii) AP decreases when MP is less than AP.
(iv) AP continues to be positive even when MP is zero or negative.
(v) AP may rise even when MP falls but lies above AP.
Question. Complete the following table

Ans.

Question. Complete the following table
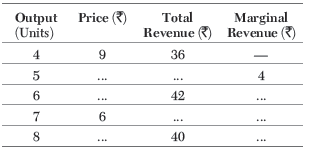
Ans.

Question. The following table gives the marginal product schedule of labour. It is also given that total product of labour is zero at zero level of employment.
Calculate the total and average product schedules of labour.
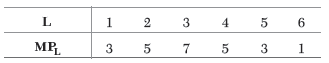
Ans.
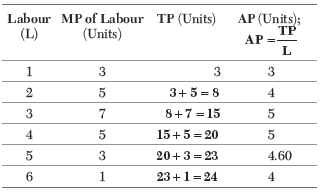
Question. Calculate total revenue from the following data

Ans.

Question. Why the total revenue curve of a competitive firm faces a straight line passing through origin?
Ans. A competitive firm sells its output at the uniform price. The price or AR is constant and MR is also constant which is equal to AR.
The Total Revenue is the sum total of MR corresponding to different levels of output. Since, MR is constant, TR increases at a constant rate. Thus, TR curve is a straight line. It passes through the origin because when sale is zero, TR is also zero.

Question. The following table gives the Average Product (AP) schedule of labour.
Find the Total Product (TP) and Marginal Product (MP) schedules. It is given that the Total Product is zero at zero level of labour employment.

Ans.

Question. Complete the following table

Ans.

Long Answers Type Questions:
Question. Distinguish between
(i) Fixed Cost and Variable Cost with examples.
(ii) Average Cost and Marginal Cost with examples.
Ans. (i) Difference between Fixed Cost and Variable Cost
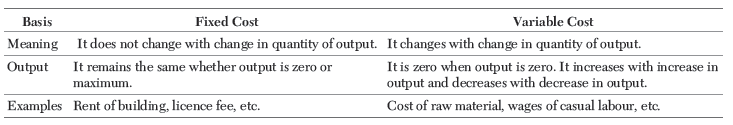
(ii) Difference between Average Cost and Marginal Cost

Question. Discuss the causes of increasing returns to a factor.
Ans. Increasing returns to a factor occur because of the following factors
(i) Fuller Utilisation of the Fixed Factor In the initial stages, fixed factor remains underutilised. Its fuller utilisation is possible by adding additional units of the variable factor to total output and the Marginal Product of the variable factor tends to increase.
(ii) Increased Efficiency of the Variable Factor Additional application of the variable factor causes process based division of labour that raises efficiency of the factor. Accordingly, marginal productivity of the factor tends to rise.
(iii) Better Coordination between the Factors So long as fixed factor remains underutilised, additional application of the variable factor tends to improve. As a result, total output increases at an increasing rate.
Question. State giving reasons, whether the following statements are true or false
(i) Average Variable Cost falls even when Marginal Cost is rising.
(ii) The difference between Total Cost and Total Variable Cost falls with increase in output.
(iii) As soon as Marginal Cost starts rising, Average Variable Cost also starts rising.
(iv) Average Cost falls only when Marginal Cost falls.
(v) The difference between Average Total Cost and Average Variable Cost is constant.
(vi) As output is increased, the difference between Average Total Cost and Average Variable Cost falls and ultimately becomes zero.
Ans. (i) True, Average Variable Cost can fall even when Marginal Cost is rising as minimum point of MC lies to the left of AVC.
(ii) False, because the difference between Total Cost and Total Variable Cost is equal to Total Fixed Cost which remains constant at all levels of output.
(iii) False, Average Variable Cost can fall even when Marginal Cost is rising.
(iv) False, Average Cost can fall even when Marginal Cost is rising.
(v) False, the difference between AVC and ATC is AFC which can never be constant. Since, AFC tends to decline with increase in output, the difference between ATC and AVC must reduce as output increases.
(vi) False, because as output increases, the difference between ATC and AVC falls but can never be zero. The difference is equal to AFC, which must remain positive, even when it is falling.
Question. Discuss the causes of diminishing returns to a factor.
Ans. Diminishing returns to a factor or the law of diminishing returns may be explained in terms of the following factors
(i) Fixity of the Factor It is the principal cause behind the law of diminishing returns. As more and more units of the variable factor is combined with the fixed factor, the latter gets
excessively utilised, leading to decrease in its productivity.
(ii) Imperfect Factor Substitutability Factors of production are imperfect substitutes of each other. e.g. more and more of labour cannot be continuously used in place of additional capital. Accordingly, diminishing returns to the variable factor become inevitable.
(iii) Poor Coordination between the Factors Continuous increasing application of the variable factor alongwith fixed factors beyond a point, crosses the limit of ideal factor ratio.
This results in poor coordination between the fixed and variable factors.
Question. What are the total fixed cost, total variable cost and total cost of a firm? How are they related?
Ans. Total Fixed Cost The cost which does not change with the change in output. Even when output is zero. In other words, fixed costs are the sum total expenditure on the purchase or hiring of fixed factors of production.
Total Variable Cost The cost which change with the change in output. In other words, variable costs are the expenditure incurred on the use of variable factors of production.
Total Cost Total cost is the sum total of total fixed cost and total variable cost at various level of output.

(i) TC = TFC + TVC.
(ii) TFC is constant at all levels of output.
(iii) TVC increases as output increases.
(iv) TC is parallel to TVC.

Numerical Problems with Solutions:
Question. Answer the following
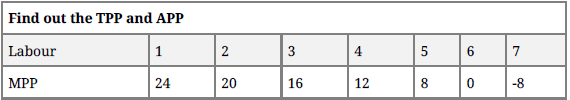
Answer :

Question. The following table gives APP of a factor. It is also known that (TPP) total product at O level of employment is O. Determine its total product and marginal product.

Answer :
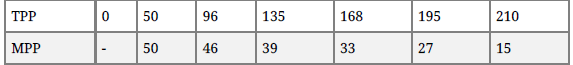
Cost
Question. Answer the following

Answer :
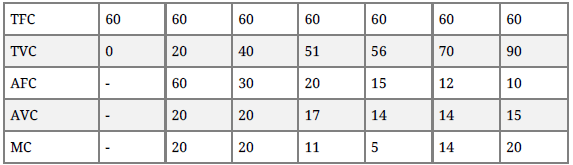
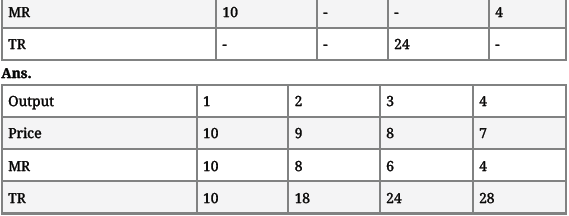
Question. Answer the following

Elasticity of Supply:
Question. If price elasticity of supply of a commodity is 5. A producer supplies 500 units of this product at a price of Rs. 5 per unit. How much quantity of this product will be supplied, at the price of Rs. 6 per unit?
Answer :

Question. The quantity supplied of a commodity at a price of Rs. 8 per unit is 400 units. Its price elasticity of supply is 2. Calculate the new price at which its quantity supplied will be 600 units?
Answer : es=2

2 (X – 8) = 4
2 x – 16 = 4
2 x = 4+16
2 x = 20
x = 10
Hence the new price is Rs. 10
Question. If es = 3, A seller supplies 20 units of the commodity at a price of Rs.8 per unit. How much quantity of the commodity will the seller supply when price rises by Rs.2 per unit?
Answer : es = 3
q = 20
p = 8
Δp = 2

8 Δq = 120
Δq = 15
(change in quantity)
Quantity supplied at increased price = 20 + 15 = 35 units

