Please refer to the Analysis of Financial Statement Revision Notes given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 12th Accountancy book. We have provided chapter wise Notes for Class 12 Accountancy as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 4 Analysis of Financial Statement
Students of Class 12 Accountancy will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 12 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Meaning
♦ It is the process of critical evaluation of the financial information contained in the financial statement, to understand & make decisions regarding the operations of the business.
♦ It involves study of relationship among various facts & figures underlying the financial statements & interpretation thereof. Thus, it includes both, Analysis & Interpretation.
Objectives
♦ To assess profitability & operational efficiency.
♦ To assess the financial position (or financial health) of the company.
♦ To ascertain the relative importance of different components of the financial position of the company.
♦ To ascertain the reasons for change in profitability & financial position.
♦ To assess the short-term & long-term liquidity & solvency (i.e. ability of the business to repay its debts) position of the business.
Analytical Tools
♦ Comparative Statements: It shows profitability & financial position of an entity over different periods of time in a comparative form. It is commonly used for Balance Sheet & Statement of P&L. It will be covered in detail as a separate chapter.
♦ Common Size Statement: It is also known as component percentage statement. It is used to study key changes & trends in the financial position & operating results of a company. Each component in the statement is stated as a % of a base (i.e. revenue from operations for income statement & total assets/liabilities for balance sheet). To be covered as a separate chapter.
♦ Trend Analysis: It helps in studying the operational results & financial position over a series of years, by observing the % change over time.
♦ Ratio Analysis: To be covered in a separate chapter.
♦ Cash Flow Analysis: It is done by preparing a cash flow statement (separate chapter)
Types of FS Analysis
♦ External Analysis – It is done by those who do not have detailed financial records or information i.e. outsiders. It is done on the basis of published accounts like Balance Sheet, Statement of P&L, Auditor’s Report etc. It is mostly done by investors, lenders, creditors, govt agencies etc.
♦ Internal Analysis – It is done by management, as they have access to all the financial information. It is more detailed, comprehensive, extensive & accurate.
♦ Horizontal/Dynamic Analysis – It involves analysis of FS for more than 1 year (i.e. multiple years). It is useful for Trend Analysis & Long-term Planning. Eg: Comparative Balance Sheet & Statement of P&L.
♦ Vertical/Static Analysis – It involves analysis of FS of 1 year only (i.e. of different items for same period). For eg: Ratio Analysis, Common Size Statement.
Inter-Firm & Intra-Firm Comparison
♦ Intra Firm Comparison – It means comparison of different items of an entity over a period of time. It is also known as Time Series Analysis or Trend Analysis.
♦ Inter Firm Comparison – It means comparison of 2 or more entities to determine their competitive position. It is also known as Cross-sectional analysis.
Importance of FS Analysis for Different Users
♦ Management – To assess the efficiency of business & for better decision making, controlling, budgeting etc.
♦ Employees – They are interested in profitability & financial performance for better remuneration & bonus.
♦ Shareholders / Investors – To ascertain the profitability & safety of their investment, and growth potential of the business.
♦ Potential Investors – To ascertain present profitability & financial position, and future prospects of the business, to decide whether to invest or not.
♦ Suppliers / Creditors – To analyse short term solvency / liquidity position to decide whether to provide/extend credit facilities & period or not.
♦ Bankers / Lenders / Other Financial Institutions – To judge short-term solvency & liquidity position (for short-term loans) & long-term solvency & liquidity position (for long-term loans).
♦ Tax Authorities – To ensure proper & correct assessment of tax liabilities.
♦ Customers – To ascertain the potential for long-term continuance of business, especially for dependent & loyal customers.
Limitations of FS Analysis
♦ Historical analysis
♦ Price level changes & inflation effects are ignored
♦ Qualitative Aspects are ignored
♦ Suffers from all limitations of FS
♦ Window dressing
♦ Different accounting policies/practices followed by different companies affects comparability. Moreover, it may be misleading without the knowledge of the changes in accounting procedure followed by the company.
♦ It is just a study of reports of the company
♦ Financial statements are prepared on the basis of accounting concepts, and as such does not reflect the current position.
MCQs Questions Financial Statements Of a Company Class 12 Accountancy
Question: Debit Balance of Profit & Loss Statement will be shown on:
(a) Assets Side of Balance Sheet
(b) Liabilities Side of Balance Sheet
(c) Under the head Reserve & Surplus
(d) Under the head Reserves and Surplus as a negative item
Answer
D
Question: A company has an operating cycle of 12 months. It has accounts payable amounting to Rs.10,00,000 out of which Rs.7,00,000 have a maturity period of 15 months. How would this information be presented in the Balance sheet?
(a) Rs.7,00,000 as current liabilities and Rs.3,00,000 as non-current liabilities
(b) Rs.3,00,000 as current liabilities and Rs.7,00,000 as non-current liabilities
(c) Rs.10,00,000 as non-current liabilities
(d) Rs.10,00,000 as non-current liabilities
Answer
B
Question: Dividend is usually paid :
(a) On Authorised Capital
(b) On Issued Capital
(c) On Paid-up Capital
(d) On Called-up Capital
Answer
C
Question: Contingent Liabilities are exhibited under the heading:
(a) Non-current Liabilities
(b) Current Liabilities
(c) In the Notes to Accounts
(d) Current assets
Answer
C
Question: Match the items given in Column I with the headings/ subheadings (Balance sheet) as defined in Schedule III of Companies Act2013.
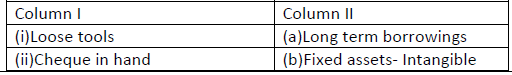

Choose the correct option:
(a) (i)-(c ),(ii)-(d),(iii)- (a ), (iv)-(b)
(b) (i)-(d), (ii)-(c),(iii)- (b), (iv)- (a)
(c) (i)-(a),(ii)-(b),(iii)-(c) ,(iv)-(d)
(d) (i)-(b),(ii)-(a),,(iii)-(d), (iv)-(c )
Answer
A
Question: What will be the correct sequence of arrangement of items in the Notes to Accounts (i)Subscribed but not fully paid up capital (ii) Authorised Capital (iii) Subscribed and fully paid up capital (iv)Issued capital Options:
(a) (ii),(iv),(iii), (i)
(b) (i) ,(ii),(iii), (iv)
(c) (iii),(i),(iv), (iii)
(d),(ii),(i), (iii)
Answer
A
Question: Match the items given in Column I with the headings/ subheadings (Statement of Profit & Loss) as defined in Schedule III of Companies Act2013.
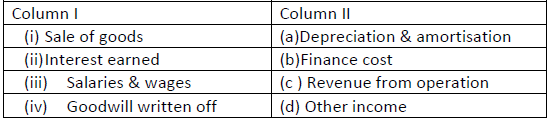
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i)-(a),(i)- (b), (iii)-(c ), (iv)- (d)
(b) (i)-(c ),(ii)-(d), (iii)-(b), (iv)- (a)
(c) (i)- (d),(ii)-(c),(iii)-(a) ,(iv)- (b)
(i)-(b) ,(ii)- (a),(iii)-(d), (iv)-(c)
Answer
B
Question: With the permission of Registrar of Companies,, accounting period can be extended up to
(a) 12 months
(b) 15 months
(c) 15 months
(d) 18 months
Answer
D
Question: Match the items given in Column I with the headings/ subheadings ( Balance sheet & Statement of Profit & Loss) as defined in Schedule III of Companies Act2013.
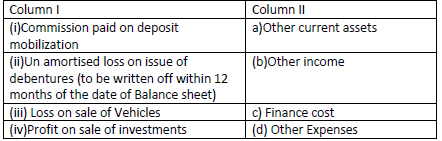
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i)-(b),(ii)-(a) ,(iii)- (d), (iv)-(c )
(b) (i)-(a),(ii)-)b), (iii)-(c ), (iv)- (d)
(c) (i)-(d), (ii)- (c ),(iii)-(b), (iv)- (a)
(i)-(c),(ii)- (a) ,(iii)-(d) ,(iv)-(b)
Answer
D
Question: What will be the correct sequence of arrangement of items
(i) Profit before tax
(ii) Revenue from operations
(iii) Profit after tax
(iv) Expenses
Options:
(a) (i),(ii),(iii),(iv)
(b) (ii),(i),(iv),(iii)
(c) (ii),(iv),(i),(iii)
(d) (iv), (iii),(ii),(i)
Answer
C


