Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 10 Science issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World in Class 10 Science provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World MCQ Questions Class 10 Science with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science
Question: A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light isincident on the prism as shown in below Figure. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
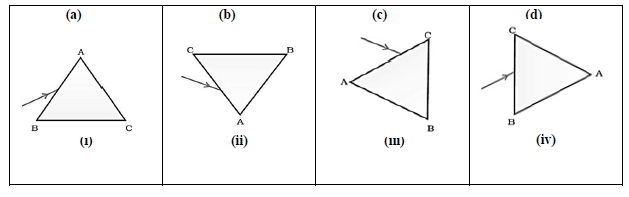
Answer
B
Question: For an equilateral prism the angle of the prism is
(a) 600
(b) 450
(c) 400
(d) None of these.
Answer
A
Question: The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
(a) The presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) Reflection of sky in water
(c) Scattering of light
(d) Absorption of light by the sea
Answer
C
Question: Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly
Answer
C
Question: When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
(a) Crystalline lens
(b) Outer surface of the cornea
(c) Iris
(d) Pupil
Answer
B
Question: When we enter a dark room coming from outside, immediately the things inside the room do not appear clear to our eyes. This is because
(a) Pupils do not open at all in the dark
(b) Pupils take time to adjust.
(c) Light travels slower in a dark room.
(d) Pupils open very quickly in the dark.
Answer
B
Question: The splitting of white light into its constituent colours is called
(a) Rainbow
(b) Atmospheric refraction
(c) Dispersion of light
(d) None of these.
Answer
C
Question: A liquid present between cornea and lens
(a) Aqueous humour
(b) Vitreous humour
(c) Water
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question: In a prism which colour deviated most
(a) Red
(b) Blue
(c) Green
(d) Violet
Answer
B
Question: Which phenomenon is not explained on scattering of light?
(a) Red colour of danger signals
(b) Blue colour of the sky
(c) White colour of clouds
(d) Advanced sun rise
Answer
D
Question: Astigmatism can be corrected by
(a) Concave lens
(b) Convex lens
(c) Double convex lens
(d) Cylindrical lens
Answer
D
Question: How many times does a ray of light bend on passing through a prism?
(a) Once
(b) Twice
(c) Thrice
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question: Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly
Answer
C
Question: Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset are explained on the basis of
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Tyndall effect
(d) Atmospheric refraction.
Answer
C
Question: At the point of blind spot there are no
(a) Cones
(b) Rods
(c) Cones and rods
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question: When looking at a distant object, the ciliary muscles of the eye are
(a) Relaxed
(b) Contracted
(c) Strained
(d) Both a and b
Answer
A
Question: A boy is wearing glasses and says that he cannot see the object kept at distance without glasses. He is suffering from
(a) Myopia
(b) Cataract
(c) Hypermetropia
(d) Presbyopia
Answer
A
Question: Which of the following is used to correct the eye defect presbyopia?
(a) Convex lens
(b) Concave lens
(c) Prismatic lens
(d) Bi-focal lens
Answer
D
Question: The danger signals are red in colour
(a) Least absorbed by fog or smoke
(b) Strongly absorbed by fog and smoke
(c) Least scattered by fog or smoke
(d) Strongly scattered by fog or smoke
Answer
C
Question: If the earth had no atmosphere then the sky would have appeared
(a) Blue
(b) Red
(c) Bright
(d) Dark
Answer
D
Question: The space between eye lens and the retina is filled with liquid called
(a) Aqueous humour
(b) Vitreous humour
(c) Water
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question: The colour of the scattered light depends on
(a) Size of the scattered particles
(b) Reflected light
(c) Reflected colour of light
(d) Intensity of light
Answer
A
Question: The amount of light entering the human light is controlled by
(a) Ciliary muscles
(b) Pupil
(c) cornea
(d) Iris
Answer
B
Question: What happens when white light is passed from air to glass prism
(a) Bends away from normal
(b) Bends towards normal
(c) Passes un deviated
(d) Reflects back
Answer
B
Question: At noon, sun appears white as
(a) Light is least scattered
(b) All the colours of the white light are scattered the most
(c) Blue colour is scattered the most
(d) Red colour is scattered the most
Answer
A
Question: Which light is easily scattered?
(a) Long wave length light
(b) Short wavelength light
(c) Sunlight
(d) Coherent light
Answer
A
Question: In the eye, the position of the image on the retina is adjusted by changing the
(a) Diameter of the pupil
(b) Position of the lens
(c) Focal length of the eye lens
(d) Size of the eye ball
Answer
C
Question: How does the eye change in order to focus on near or distant objects?
(a) The lens moves in or out
(b) The retina moves in or out
(c) The lens becomes thicker or thinner
(d) The pupil gets larger or smaller
Answer
C
Question: Which of the following changes occur when you walk out of bright sunshine into a poorly lit room?
(a) The pupil becomes larger
(b) The lens becomes thicker
(c) The ciliary muscle relaxes
(d) The pupil becomes smaller
Answer
A
Question: A person got his eyes tested. The optician’s prescription for the spectacles reads:
Left eye : – 3.00 D Right eye : – 3.50 D
The person is having a defect of vision called :
(a) presbyopia (b) myopia
(c) astigmatism (d) hypermetropia
Answer
B
Question: The human eye possesses the power of accommodation. This is the power to :
(a) alter the diameter of the pupil as the intensity of light changes
(b) distinguish between lights of different colours
(c) focus objects at different distances
(d) decide which of the two objects is closer.
Answer
C
Question: The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitudes mainly because :
(a) Scatterings of light is not enough at such heights.
(b) There is no atmosphere at great heights.
(c) The size of molecules is smaller than the wavelength of visible light.
(d) The light gets scattered towards the earth.
Answer
A
Question: A man driving a car can read a distant road sign clearly but finds difficulty in reading the odometer on the dashboard of the car. Which of the following statement is correct
about this man?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
(d) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
Answer
A
Question: A near sighted person cannot see distinctly beyond 50 cm from his eye. The power in diopter of spectacle lenses which will enable him to see distant objects clearly is
(a) +50
(b) –50
(c) +2
(d) –2
Answer
A
Question: Which of the following is not caused by the atmospheric refraction of light?
(a) Twinkling of stars at night
(b) Sun appearing higher in the sky than it actually is
(c) Sun becoming visible two minutes before actual sunrise
(d) Sun appearing red at sunset
Answer
D
Question: A student sitting on the last bench in the class cannot read the writing on the blackboard clearly but he can read the book lying on his desk clearly. Which of the following
statement is correct about the student?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
(d) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
Answer
D
Question: In the visible spectrum the colour having the shortest wavelength is
(a) Green
(b) Red
(c) Violet
(d) Blue
Answer
C
Question: When a mirror is rotated an angle the reflected ray moves through double that angle, the instrument based on the above principle is
(a) Periscope
(b) Odometer
(c) Refractometer
(d) Sextant
Answer
D
Question: The following one is not a primary colour
(a) Yellow
(b) Red
(c) Green
(d) Blue
Answer
A
Question: The splitting of white light into several colours on passing through a glass prism is due to
(a) refraction
(b) reflection
(c) interference
(d) diffraction
Answer
A
Question: At sun rise or at sun set the sun appears to be reddish while at mid-day it looks white. This is because
(a) Scattering due to dust particles and air molecules causes this phenomenon
(b) The sun is cooler at sun rise or at sunset
(c) Refraction causes this phenomenon
(d) Diffraction sends red rays to the earth at these times.
Answer
A
Question: 14
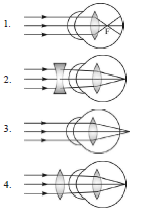
Identify the wrong description of the above figures
(a) 1 represents far-sightedness
(b) 2 correction for short sightedness
(c) 3 represents far sightedness
(d) 4 correction for far-sightedness
Answer
A
Question: On entering a glass prism, sun rays are
(a) Deviated but not dispersed
(b) Deviated and dispersed
(c) Dispersed but not deviated
(d) Neither deviated nor dispersed.
Answer
B
Question: A person 20 years old cannot see objects clearly which are nearer than 75 cms from his eyes, the disease he is suffering from is
(a) Astigmatism
(b) Myopia
(c) Hypermetropia
(d) Presbyopia
Answer
C
Question: A student can distinctly see the object upto a distance cm. He wants to see the black board at a distance of 3 m. Focal length and power of lens used respectively will be
(a) –4.8 cm, – 3.3 D
(b) –5.8 cm, –4.3 D
(c) –7.5 cm, –6.3 D
(d) –15.8 cm, –6.3 D
Answer
D
Question: A piece of cloth looks red in sun light. It is held in the blue portion of a solar spectrum, it will appear
(a) red
(b) black
(c) blue
(d) white
Answer
B
Question:To get line spectrum, the substances are excited in their
(a) solid state
(b) molecular state
(c) gaseous state
(d) atomic state
Answer
D
Question: What power lens is needed to correct for farsightedness where the uncorrected near point is 50 cm?
(a) + 2 diopters
(b) – 3 diopters
(c) + 4 diopters
(d) – 2 diopters
Answer
A
Question: The pupil of the eye changes in size to adjust for
(a) objects at different distances
(b) objects of different sizes
(c) different colors
(d) different amounts of light
Answer
D
Question: What power lens is needed to correct for nearsightedness where the uncorrected far point is 250 cm?
(a) +2.5 diopters
(b) –2.5 diopters
(c) + 0.4 diopters
(d) –0.4 diopters
Answer
D
Question: A man can see upto 100 cm of the distant object. The power of the lens required to see far objects will be
(a) + 0.5 D
(b) + 1.0 D
(c) + 1 D
(d) – 5.0 D
Answer
B
Question: Astigmatism can be corrected by
(a) Bifocal lenses
(b) Cylindrical lenses
(c) Concave lenses
(d) Planoconvex lenses
Answer
B
Question: In a room, artificial rain is produced at one end and a strong source of white light is switched on at the other end. To observe the rainbow an observer must
(a) Look anywhere in the room
(b) Look towards the source
(c) Look towards the raindrops
(d) Look in a direction equally inclined to the source of raindrops
Answer
C
Question: Dispersion is the term used to describe
(a) the propagation of light in straight lines
(b) The splitting of a beam of light into component colours
(c) The bending of a beam of light when it strikes a mirror
(d) The change that takes place in white light after passage through red glass.
Answer
B
Question: The least distance of vision of a longsighted person is 60 cm. By using a spectacle lens, this distance is reduced to 12 cm. The power of the lens is
(a) + 5.0 D
(b) + (20/3) D
(c) – (10/3) D
(d) + 2.0 D
Answer
B
Question: In a glass prism
(a) Blue light is dispersed more than red light
(b) Red light is dispersed more than blue light
(c) Both red light and blue light are equally dispersed
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question: An optician while testing the eyes finds the vision of a patient to be 6/12. By this he means that
(a) The person can read the letters of 6 inches from a distance of 12 m
(b) The person can read the letters of 12 inches from 6 m
(c) The person can read the letters of 6 m which the normal eye can read from 12 m
(d) The focal length of eye lens had become half that of the normal eye
Answer
C
Question: A person cannot see objects clearly beyond 50 cm. The power of the lens to correct the vision is
(a) +5 D
(b) –0.5 D
(c) –2 D
(d) +2 D
Answer
C
Question: If a person can see on object clearly when it is placed at 25 cm away from him, he is suffering from :
(a) myopia
(b) hyper metropia
(c) asitgmatism
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question: A Red object when seen through a thick blue glass appears:
(a) Green
(b) Violet
(c) Black
(d) Red
Answer
C
Question: To read a poster on a wall, a person with defective vision needs to stand at a distance of 0.4m from the poster. A person with normal vision can read the poster from a distance of 2.0 m. Which one of the following lens may be used to correct the defective vision?
(a) A concave lens of 0.5 D
(b) A concave lens of 1.0 D
(c) A concave lens of 2.0 D
(d) A convex lens of 2.0 D
Answer
C
Question: A person is suffering from some sight problem. From the given diagram say which defect he suffers from?
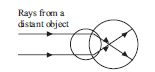
(a) Myopia
(b) Hypermetropia Rays from a distant object
(c) Cataract
(d) Astigmatism
Answer
A
Question: Various optical processes are involved in the formation of a rainbow. Which of the following provides the correct order in time in which these processes occur ?
(a) Refraction, total internal reflection, refraction
(b) Total internal reflection, refraction total internal reflection
(c) Total internal reflection, refraction, refraction
(d) Refraction, total internal reflection, total internal reflection.
Answer
A
Question: The figures represent three cases of a ray passing through a prism of angle A. The case corresponding to minimum deviation is
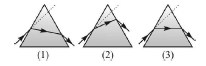
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question: Pick the wrong answer in the context with rainbow.
(a) When the light rays undergo two internal reflections in a water drop, a secondary rainbow is formed.
(b) The order of colours is reversed in the secondary rainbow.
(c) An observer can see a rainbow when his front is towards the sun.
(d) Rainbow is a combined effect of dispersion, refraction and reflection of sunlight.
Answer
C
Question: Select the correct statement about rainbow.
(a) We can see a rainbow in the western sky in the late afternoon
(b) The double rainbow has red on the inside and violet in the outside
(c) A rainbow has an arc shape, since the earth is round
(d) A rainbow on the moon is violet on the inside and red on the outside
Answer
B
Question: The reason for using red light in traffic signals to stop vehicles.
(a) Red light has shorter wavelength
(b) Red light has longer wavelength
(c) Red light is very bright and attractive
(d) Red light has highest angle of refraction
Answer
B
Question: If for a given prism the angle of incidence is changed from 0° to 90°, the angle of deviation
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) First decreases and then increases
(d) First increases and then decreases
Answer
C
ONE WORD ANSWERS
Question: The fluid present between the cornea and the pupil is called___________
Answer
Aqueous Humour
Question: For a person suffering from hypermetropia, the image of the object is formed ___________ the retina.
Answer
Infront
Question: For a person suffering from myopia, the image of the object is formed ___________ the Retina.
Answer
Behind
Question: The rear part of the eye where the light entering the eye is focused is calledthe ___________
Answer
Infron Retina
Question: Defect myopia can be corrected by using ___________
Answer
Concave Lens
Question: In order to correct astigmatism we can use ___________
Answer
Cylindrical Lens
Question: Defect hypermetropia can be corrected by using ___________
Answer
Convex Lens
Question: The Retina contains about ___________ number of rod cells that receive light signals.
Answer
125 Million

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.


