Please refer to MCQ Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below. These multiple-choice questions have been developed based on the latest NCERT book for class 12 Chemistry issued for the current academic year. We have provided MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. Students should learn the objective based questions for Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids in Class 12 Chemistry provided below to get more marks in exams.
Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Questions
Please refer to the following Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry with solutions for all important topics in the chapter.
MCQ Questions Answers for Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which reaction is used for the preparation of acetophenone?
(a) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(b) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
(c) Friedel-Craft’s reaction
(d) Cannizaro’s reaction
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds will give positive iodoform test with I2 and NaOH?
(a) C6H5COCC6H5
(b) CH3CH2CHO
(c) C6H5COCH2CH3
(d) C6H5—CH—CH3
l
OH
Answer
D
Question. The compound C6H5CH = N—N = CHC6H5 is produced by the reaction of an excess of benzaldehyde with which compound?
(a) NH3
(b) NH2NH2
(c) Hydroxyl amine
(d) Phenyl hydrazine
Answer
B
Question. The reagent used in Gatte1mann Koch aldehyde synthesis is
(a) Pb/BaSO4
(b) alkaline KMnO4
(c) acidic KMnO4
(d) CO + HCl
Answer
D
Question. X →(Reductive)Ozonolysis Y + Z
Y can be obtained by Etard’s reaction, Z undergoes disproportionation reaction with concentrated alkali. X could be
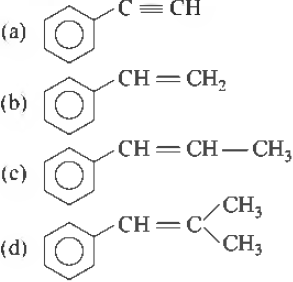
Answer
B
Question. When CH2 = CH—O—CH2—CH3 reacts with one mole of HI, one of the products formed is
(a) ethane
(b) ethanol
(c) iodoethene
(d) ethanal
Answer
D
Question. HCHO was treated with a reagent X . The product formed upon hydrolysis in the presence of an acid gave C2H5 OH The reagent X is
(a) alcoholic KOH
(b) alcoholic KCN
(c) CH3MgI
(d) aqueous KOH
Answer
C
Question. Upon treatment with AI(OEt)3 followed by usual reactions (work up) CH3CHO will produce
(a) Only CH3COOCH2CH3
(b) a mixture of CH3COOH and EtOH
(c) Only CH3COOH
(d) Only EtOH
Answer
A
Question. Acetophenone cannot be prepared easily starting from
(a) C6H5CH(OH)CH3
(b) C6H5CH3
(c) C6H5C= CH
(d) C6H6
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following, compounds is the reactant in Rosenmund’s reduction?
(a) CH3CO2H
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3CH2Cl
(d) CH3COCl
Answer
D
Question. In the given transformation, which of the following is the most appropriate reagent?

(a) NH2NH2 , OH
(b) Zn—Hg/HCI
(c) Na, Liq. NH3
(d) NaBH4
Answer
B
Question. How many enols (including stereo isomers) exist for 3-hexanone?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Six
Answer
C
Question. What will be the order of reactivity of the following carbony I compounds with Grignard’ s reagent?
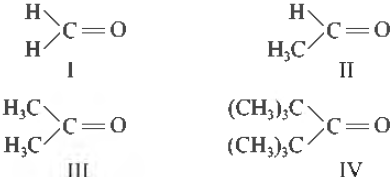
(a) I > II > III > IV
(c) II > I > IV> III
(b) IV > III > II > I
(d) III > II > I > IV
Answer
A
Question. What will be the product/s ifbenzyl chloride is heated with a concentrated aqueous KOH solution?
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) Benzyl alcohol and sodium benzoate
(d) An aldol
Answer
A
Question. Which set of products is expected on reductive ozonolysis of the following di olefin?
CH3
l
CH3CH = C—CH= CH2
(a) CH3CHO; CH3COCH = CH2
(b) CH3CH = C(CH3 )CHO; CH2O
(c) CH3CHO; CH3COCHO;CH2O
(d) CH3CHO; CH3COCH3 ; CH2O
Answer
C
Question. By combining the two calcium salts of carboxylic acids we are preparing 2-butanone. Find the correct pair from the following.
(a) Calcium formate + calcium propanoate
(b) Calcium acetate + calcium propanoate
(c) Calcium acetate + calcium acetate
(d) Calcium formate + calcium acetate
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following on heating with aqueous KOH, produces acetaldehyde?
(a) CH3COCl
(b) CH3CH2CI
(c) CH2ClCH2CI
(d) CH3CHCI2
Answer
D
Question. When a mixture of calcium benzoate and calcium acetate is dry distilled, the resulting compound is
(a) acetophenone
(b) benzaldehyde
(c) benzophenone
(d) acetaldehyde
Answer
A
Question. The compound which is not formed during the dry distillation of a mixture of calcium formate and calcium acetate is
(a) methanal
(b) propanal
(c) propanone
(d) ethanal
Answer
B
Question. The compound which forms acetaldehyde when heated with dilute NaOH, is
(a) 1, 1-dicholoroethane
(b) 1, 1, 1 -trichloroethane
(c) 1-chloroethane
(d) 1, 2-dichloroethane
Answer
A
Question. The most suitable reagent for the conversion of
R—CH2—OH→ R—CHO is
(a) KMnO4
(b) K2Cr2O7
(c) CrO3
(d) PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate)
Answer
D
Question. Shown below are four possible synthesis of propionaldehyde. Which one would not work?
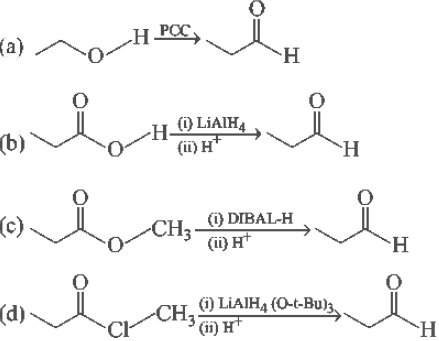
Answer
B
Question.
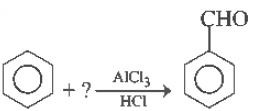
Identify the reactant.
(a) H2O
(b) HCHO
(c) CO
(d) CH3CHO
Answer
A
Question. The product P in the reaction,
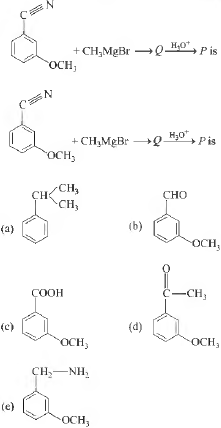
Answer
D
Question. Stephen’s reduction is used to prepare aldehyde from
(a) alcohol
(b) alkyl cyanides
(c) alkanones
(d) acid chlorides
Answer
B
Question. 3-pentanol on reaction with aluminium tertiary butoxide in the presence of acetone gives
(a) 3-pentanal
(b) 2-pentanal
(c) 3-pentanone
(d) 2-pentanone
Answer
C
Question. The reagents to carry out the following conversion are
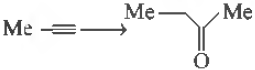
(a) HgSO4 / dil. H2SO4
(b) BH3 ; H2O2/Na0H
(c) OsO4 ; HIO4
(d) NaNH2/CH3I; HgSO4 /dil. H2SO4
Answer
D
Question.

The above ketone will not be formed by
(a) reaction of benzene and acetyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3
(b) reaction of acetonitrile with phenyl magnesium bromide in ether followed by hydrolysis
(c) treatment ofacetyl chloride with dibenzyl cadmium
(d) addition of water to phenyl acetylene in the presence of mercuric sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer
C
Question. The reaction of H2 is given below
H2 + CO+ R—CH = CH2 →
R—CH2—CH2—CHO is specifically called as
(a) hydrogenation
(b) reduction
(c) hydroformylation
(d) dehydration
(e) formylation
Answer
C
Question.

Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following product is formed when calcium salt of adipic acid is heated?

Answer
B
Question. When calcium acetate is distilled, it will produce which of the following compound?
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Calcium formate on distillation gives
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3COOH
(c) CH3CHO
(d) HCHO
Answer
D
Question. The best reagent to convert pent-3-en-2-ol into pent-3-en-2-one is
(a) pyridinium chlorochromate
(b) chromic anhydride in glacial acetic acid
(c) acidic di chromate
(d) acidic permanganate
Answer
B
Question. The major product in the following reaction is
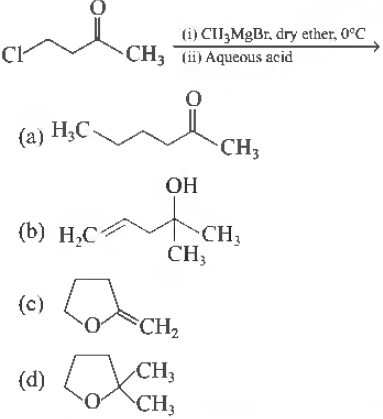
Answer
D
Question. How many chiral centre are possible for the product of following reaction?

(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 3
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of nucleophilic addition reaction
I. HCHO
II. CH3COCH3
III. C6H5COCH3
IV. C6H5CO6H5
(a) I < II < III < IV
(b) IV < III < II < I
(c) IV < II < III < I
(d) III < IV < II < I
Answer
B
Question. Silver min-or test is given by which one of the following compounds?
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Acetone
(c) Formaldehyde
(d) Benozophenone
Answer
A,C
Question. Which of the following statements is not true for acetaldehyde?
(a) It will undergo an aldol condensation reaction
(b) It will undergo a Cannizaro reaction
(c) It will undergo a haloform reaction
(d) Enolisation is catalysed by acid or base
Answer
B
Question.
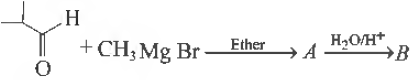
The IUPAC name of B is
(a) 3-methylbutan-2-ol
(b) 2-methylbutan-3-ol
(c) 2-methylbutan-2-ol
(d) pentan-2-ol
Answer
A
Question. The catalyst used in Rosenmund reaction is
(a) Zn/Hg
(b) Pd/BaSO4
(c) Raney Ni
(d) Na in ethanol
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following can be oxidised to the coITesponding carbonyl compound?
(a) 2-hydroxypropane
(b) ortho-nitrophenol
(c) Phenol
(d) 2-methyl-2-hydroxypropane
Answer
A
Question. The compound of molecular formula C5H10O(A) reacts will Tollen’s reagent to give silver minor but does not undergo aldol condensation. The compound A is
(a) 3-pentanone
(b) 2, 2-dimethylpropanal
(d) 3-methylbutanal
(e) 3-methyl-2-butanone
Answer
B
Question. The intermediate J in the following Wittig reaction is
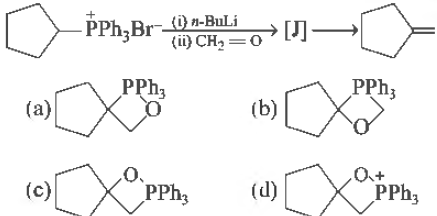
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following process is used for the preparation of acetone?
(a) Haber’s process
(b) Wacker’s process
(c) Wolff-Kishner reaction
(d) Gatterman-Koch synthesis
Answer
B
Question. An organic compound ‘A’ burns with a sooty flame. It is neagtive towards Tollen’s reagent test and positive for Brady’s reagent test. The compound ‘A’ is
(a) Acetophenone
(b) Acetone
(c) Salicylic acid
(d) Bezaldehyde
Answer
A
Question. The order of compounds in their reactivity towards HCN is
(a) acetaldehyde < ketone < methyl tert-butyl ketone < di-tert-butyl ketone
(b) di-tert-butyl ketone < methyl tert-butyl ketone < acetone < acetaldehyde
(c) di-tert-butyl ketone < acetone < methyl tert-butyl ketone < acetaldehyde
(d) Acetone < acetaldehyde < di-tert-butyl ketone < methyl tert-butyl ketone
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following does not give Cannizzaro’s reaction?
(a) CCI3CHO
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) HCHO
(d) CH3CHO
Answer
D
Question. In the following reaction, the product E is
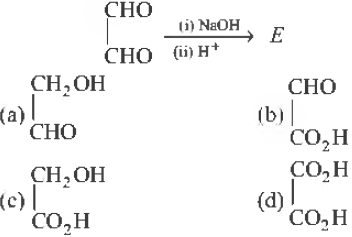
Answer
C
Question. The major product of the following reaction is
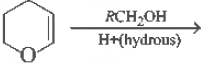
(a) a hemiacetal
(b) an acetal
(c) an ether
(d) an ester
Answer
B
Question. Reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction of
I. HCHO
II. CH3CHO
III. CH3COCH3 is
(a) II > III > I
(b) III > II > I
(c) I > II > III
(d) I > III > II
Answer
C
Question. What kind of isomerism is exhibited by the compounds CH3CH2CHO and CH3COCH3?
(a) Geometrical isomerism
(b) Functional isomers
(c) Tautomers
(d) Metamers
Answer
B
Question. Trichloroacetaldehyde was subjected to Cannizzaro’s reaction by using NaOH. The mixture of the products contains sodium trichloroacetate ion and another compound. The other compound is
(a) 2, 2, 2-trichlorethanol
(b) trichloromethanol
(c) 2, 2, 2-trichloropropanol
(d) chloroform
Answer
A
Question. An organic compounds with the molecular formula C8H8O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. The organic compound is
(a) 2-ethylbenzaldehyde
(b) 2-methylbenzaldehyde
(c) acetophenone
(d) 3-methylbenzaldehyde
(e) phenylacetaldehyde
Answer
B
Question. Among the following structures the one which is not a resonating stmcture of others is
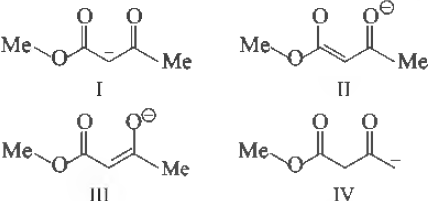
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Only III
(d) Only IV
Answer
D
Question. In the scheme given below, the total number of intramolecular aldol condensation products formed from ‘Y’ is
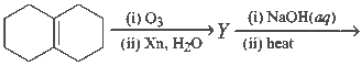
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
A
Question. The reagent with which both acetaldehyde and acetone react is
(a) Fehling’s solution
(b) I2 /NaOH
(c) Tollen’s reagent
(d) carbonic acid
Answer
B
Question. An important industrial solvent, also a laboratory reagent, called 2-butanone, is nothing but
(a) methyl ethyl ketone
(b) dimethyl ketone
(c) diethyl ketone
(d) propyl ketone
(e) methyl propyl ketone
Answer
A
Question. The number of aldol reaction(s) that occurs in the given transformation is
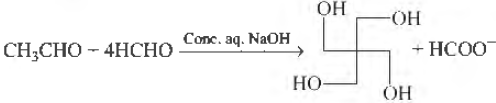
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
D
Question. What type of compound is shown below?
O
ll
H—C—CH2—CH3
(a) An alcohol
(c) A ketone
(b) An aldehyde
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. When a mixture of calcium acetate and calcium formate is dry distilled, the product formed as
(a) ethanal
(b) butanone
(c) methanal
(d) acetophenone
Answer
A
Question. If formaldehyde and KOH are heated, we get
(a) methane
(b) methyl alcohol
(c) ethyl formate
(d) acetylene
Answer
B
Question. Carbonyl compounds are constituents of
(a) fabrics, drugs
(b) fabrics, plastics
(c) flavourings, plastics
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. After completion of the reactions (I and II), the organic compound(s) in the reaction mixtures is
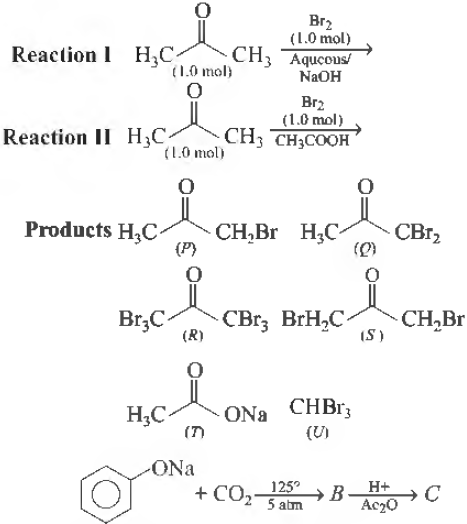
(a) Reaction I P and Reaction II P
(b) Reaction I U, acetone and Reaction II Q, acetone
(c) Reaction I T, U acetone and Reaction II P
(d) Reaction I R acetone and reaction II S acetone
Answer
C
Question. Oxidation of aldehydes gives
(a) esters
(b) acids
(c) ethers
(d) alcohols
(e) esters and acids
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following gives an aldehyde on dry distillation?
(a) Calcium formate + calcium acetate
(b) Calcium acetate + calcium benzoate
(c) Calcium acetate
(d) Calcium benzoate
Answer
A
Question. Collin’s reagent is used to convert
(a) C = O → CHOH
(b) —CH2OH→ CHO
(c) —CHO→ —COOH
(d) —CHO→ —CH2OH
Answer
B
Question. lodoform can be prepared form all except
(a) ethyl methyl ketone
(b) iso-propyl alcohol
(c) 3-methyl-2-butanone
(d) iso-buty1 alcohol
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% sodium hydroxide solution to give the corresponding alcohol and acid?
(a) Phenol
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Butanal
(d) Benzoic acid
Answer
B
Question. Among H—CHO,CH3CHOand C6H5CHO, which will undergo Cannizzaro’s reaction?
(a) HCHO and CH3—CHO
(b) CH3—CHO and C6H5CHO
(c) C6H5CHO and HCHO
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. The compound obtained when acetaldehyde reacts with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide exhibits
(a) geometrical isomerism
(b) optical isomerism
(c) neither optical nor geometrical isomerism
(d) both optical and geometrical isomerism
Answer
D
Question. Reaction of formaldehyde and ammonia gives
(a) hexamethylene tetramine
(b) bakelite
(c) urea
(d) triethylene tetramine
Answer
A
Question. Identify the combination of compounds that undergo aldol condensation followed by dehydration to produce but-2-enal
(a) methanal and ethanal
(b) two moles of ethanal
(c) methanal and propanone
(d) ethanol and propanone
(e) two moles of ethanol
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following organic compounds answers both iodoform test and Fehling’s test?
(a) Methanal
(b) Ethanol
(c) Propane
(d) Ethanal
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following reactions convert acetone into hydrocarbon having same number of carbon atoms?
(a) Wolff-Kishner reaction
(b) Hofmann reaction
(c) Grignard reaction
(d) Reduction with LiAIH4
Answer
A
Question. When acetaldehyde is heated with dilute sodium hydroxide solution, the product is
(a) ethanol and sodium acetate
(b) paraldehyde
(c) aldol
(d) brown resin
Answer
C

We hope you liked the above provided MCQ Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry with solutions. If you have any questions please ask us in the comments box below.


