Please refer to Directing Class 12 Business Studies Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 12 Business Studies based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 12 Business Studies for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 12.
Class 12 Business Studies Important Questions Directing
Question: Define directing as a function of management.
Answer: Directing is the process of instructing, guiding, counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation to achieve its objectives.
Question: Explain any three points of importance of directing as the function of management.
Answer: The three importance of directing are:
- Initiate action: It enables employees to initiate action in the organisation towards the attainment of different objectives.
- Integrates employees’ efforts: It integrates employees’ efforts in the organisation so that every individual effort contributes to the organisational performance.
- Means of motivation: It guides employees to fully realise their potential and capabilities by motivating and providing effective leadership.
Question: Why is directing known as the execution function of management?
Answer: Directing is known as the execution function of management because it converts plans into action. While the other functions prepare a setting for action, it initiates action in the organisation for the achievement of pre-determined goals.
Question: Why is it said that directing flows from top to bottom?
Answer: Directing is said to flow from top to bottom because directions are given by the superior to the subordinates. It starts from top level and flows to lower level.
Question: What are the elements of Directing?
Answer: The elements of directing are
- Supervision,
- Motivation,
- Leadership and
- Communication.
Question: Define the term supervision.
Answer: Supervision is the process of guiding the efforts of employees another resources to accomplish the desired objectives. It means overseeing what is being done by subordinates and giving instructions to ensure optimum utilisation of resources and achievement of work targets.
Question: Define the term of motivation.
Answer: Motivation is the process of stimulating, inspiring and inducing the employees to perform to their best capacity to accomplish desired goals.
Question: Define the term leadership.
Answer: Leadership is the process of influencing the behaviour of people by making them strive voluntarily towards achievement of organisational goals.
Question: Define the term communication
Answer: Communication is the process of exchange of ideas, views, facts, feelings, etc., between or among people to create common understanding.
Question: Define the terms ‘motive’, ‘motivation’ and ‘motivator’.
Answer:
- Motive: Motive is an inner state that energises, activates or move sand directs behaviour towards goals.
- Motivation: Motivation is the process of stimulating people to action to accomplish desired goals.
- Motivator: Motivator is the technique used to motivate people in an organisation like pay, bonus, promotion, recognition, praise, responsibility etc.
Question: What are the features of motivation?
Answer: Features of motivation:
- Motivation is a psychological phenomenon: Motivation is an internal feeling. It cannot be seen or touched. This internal feeling urges employees to behave in a particular manner.
- Motivation produces goal-oriented behaviour: Motivation induce people to behave in such a manner so that they can achieve their goal.
- Motivation can be positive as well as negative: Positive motivation can take the form of appraisal or promotion. On the other hand, negative motivation can take the form of pay-cut and demotion.
- Motivation is a complex process: Different individuals have different needs and expectations. Hence, all employees get motivated for different reasons at different
Question: Explain the process of motivation.
Answer: Process of motivation:

An unsatisfied need of an individual creates tension which stimulates his or her drives. These drives generate search behaviour to satisfy such need. If such need is satisfied, the individual is relieved of tension.
Question: Explain Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory.
Answer: Maslow’s need hierarchy was based on human needs. He felt that within every human Being, there exists a hierarchy of five needs. These are:
- Basic Physiological Needs: Theseneeds are most basic in the hierarchy and corresponds to primary needs. Hunger, thirst, shelter, sleep and sex are some examples of these needs. In the organisational context, basic salary helps to satisfy these needs.
- Safety/Security Needs:These needs provide security and protection from physical and emotional harm. Examples: job security, stability of income, Pension plans etc.,
- Affiliation/Belonging Needs: These needs refer to affection, sense of belongingness, acceptance and friendship.
- Esteem Needs: These include factors such as self-respect, autonomystatus, recognition and attention.
- Self Actualisation Needs: It is the highest level of need in the hierarchy. It refers to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming. These needs include growth, self-fulfilment and achievement of goals.
Question: What are financial incentives? Explain any three types of financial incentives.
Answer: Financial incentives refer to the direct monetary benefits given to employees by an organisation with the objective of providing motivation to improve performance. The three financial incentives are:
- Salary and allowances: It is the most basic form of financial incentive. Regular increment in salaries and other allowances act as good motivation for employees.
- Performance-based incentives: Sometimes monetary incentives can be given based on the performance of employees. In other words, they can be suitably rewarded for good performance. This motivates workers to improve work efficiency.
- Bonus: Bonus refers to the monetary reward which is over and above the basic salary. It can be in the form of cash and gifts. It is given to employees in order to recognise their exemplary performance in the organisation.
Question: What are non-financial incentives? Explain any three types of non-financial incentives.
Answer: Non-financial incentives are incentives which cater to the non-monetary needs of employees such as social and psychological needs. The three non-financial incentives are:
- Status or Position: Employees often require a rise in the status in terms of power and authority. It provides them psychological satisfaction.
- Organisational Climate: Various organisational characteristics such as employee freedom and recognition of performance play an important role in motivating employees. For example, if an employee’s work is recognised and praised, it would encourage him to further improve performance.
- Job enrichment: Challenging work endowed with greater responsibility and requiring higher knowledge and skill enhances the interest of employees. It provides employees prospects for personal growth. Thus, it proves to be a good source of motivation
- Job security: Employees need a certain degree of job security in the sense that they must be certain about their income in the future. This is would enable them to work with greater passion.
Question: What are the various types of leadership styles? Briefly explain.
Answer: The various types of leadership styles are Autocratic Leadership, Democratic Leadership and Laissez Faire / Free-rein Leadership.
- Autocratic (or Authoritative) Leadership: It is a leadership style where a leader has complete control over his subordinates and all the decisions are taken by himself without consulting the subordinates.
- Democratic (or Participative) Leadership: It is a leadership style where the leader takes decisions in consultation with his subordinates and follows the opinion based on the majority.
- Laissez faire (or Free-rein leader): It is a leadership style where subordinates take decisions and resolve issues themselves. are given a high degree of freedom to formulate their own objectives and ways to achieve them. This type of leader does not believe in the use of power unless it is absolutely essential.
Question: Describe the concept of Authoritative leadership and state its merits and demerits.
Answer: Autocratic (or Authoritative) Leadership: It is a leadership style where a leader has complete control over his subordinates and all the decisions are taken by himself without consulting the subordinates.
Merits:
- Decision-making is quicker under this leadership style.
- This leadership style is effective in many situations like in a factory where the supervisor is responsible for production on time and has to ensure labour productivity.
Demerits:
- This leader rarely or does not takes inputs, advice nor suggestions from subordinates/followers. Therefore, decision is based on the leader’s own beliefs.
- This leader does not delegate authority but centralises power in himself.
- This leader gives orders and expects his subordinates to obey those orders.
- There is only one-way communication with the subordinate, only acting according to the command given by the leader.
Question: Describe the concept of Democratic leadership and state its merits and demerits.
Answer: Democratic (or Participative) Leadership: It is a leadership style where the leader takes decisions in consultation with his subordinates and follows the opinion based on the majority.
Merits:
- He will encourage the subordinates to participate in decision-making.
- This leader delegates and decentralises authority.
- They also need to respect the other’s opinion and support subordinates to perform their duties and accomplish organisational objectives. They exercise more control by using forces within the group.
Demerits:
- Decision making is time taking.
- It is difficult at the time of emergency.
Question: Describe the concept of Laissez-faire leadership and state its merits and demerits.
Answer: Laissez faire (or Free-rein leader): It is a leadership style where subordinates take decisions and resolve issues themselves. Subordinates are given a high degree of freedom to formulate their own objectives and ways to achieve them. This type of leader does not believe in the use of power unless it is absolutely essential.
Merits:
- Subordinates are given a high degree of freedom.
- More job satisfaction and morale among subordinates.
- Maximum scope of development of subordinates.
Demerits:
- Subordinates do not get the guidance and support of the leader.
- It ignores the contribution of leader.
- Subordinates may work in different directions and result in chaos.
Question: What is meant by communication? Explain how communication is an important function of management.
Answer: Communication: Communication is the exchange of information, facts and feelings such that a common understanding is created. The importance of communication are:
- Provides coordination: Communication is the key to good coordination among various departments in an organisation. Communication promotes coordination by making clear the goals to be achieved and how they would be achieved.
- Enables smooth operations: Clear and effective communication enables smooth operations in the organisation. Various interactions in the organisation depend on effective communication. Working efforts of individuals and departments can be united towards common goals and objectives through proper communication.
- Facilitates decision making: Taking meaningful decisions requires a pool of information which can be provided through good communication.
- Increases efficiency: Goals, objectives, instructions and targets are conveyed effectively through good communication. In this way, it enables smooth operations and improves efficiency.
- Enables effective leadership: Communication forms a basis for effective leadership. Communication also helps in influencing subordinates in a positive manner.
- Helps in motivation: Good communication is the basic tool for motivation. It is only with good communication that the needs of employees can be recognised and accordingly worked upon.
Question: Explain the elements involved in communication process.
Answer: The elements involved in communication process are explained below:
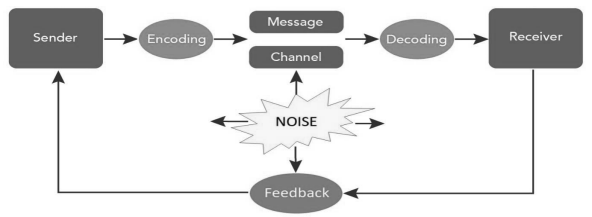
- Sender: Sender means person who conveys his thoughts or ideas to the receiver. The sender represents source of communication.
- Message: Content of ideas, feelings, suggestions, order, etc., intended to be communicated to the receiver.
- Encoding: Process of converting the message into communication symbols such as words, pictures, gestures etc.
- Media: It is the path or way through which encoded message is transmitted to receiver. The channel may be in written form, face to face, phone call, Internet, mail etc.,
- Decoding: Process of converting/translating encoded message into message that is easily understood by the receiver.
- Receiver: The person who receives the message and understands it.
- Feedback: All those actions or responses of receiver indicating that he has received and understood message of sender.
- Noise: Noise means some disturbance or interruption to communication. This hindrance may be caused to sender, message or receiver. Some examples of noise are:
(a) Ambiguous symbols that lead to faulty encoding.
(b) A poor telephone connection.
(c) An inattentive receiver.
Question: Give some example of “Noise” in the process of communication.
Answer: Some examples of noise in the process of communication are:
- Ambiguous symbols that lead to faulty encoding.
- A poor telephone connection.
- An inattentive receiver.
- Faulty decoding (attaching wrong meanings to message).
- Prejudices obstructing the poor understanding of message.
- Gestures and postures that may distort the message.
Question: What is formal communication? State the merits and demerits of formal communication.
Answer: Formal communication: It refers to official channels of communication (formal line of communication) designed in the organisational chart.
Merits:
- Formal communication is systematic and ensures orderly flow of information.
- Source of information can be easily located.
- It is easy to fix responsibilities of different employees as there is proof for the information.
Demerits:
- Information is conveyed or passed in impersonal manner.
- Although very systematic in passing information, it delays decision making.
Question: What is informal communication? State the demerits of formal communication.
Answer: Communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication is said to be informal communication. It is also called as ‘grapevine’ because it spreads throughout the organisation with its branches going out in all directions regardless of the levels of authority.
Demerits:
- Actual information may possibly get distorted.
- Difficult to detect the source of such communication.
- It leads to generate rumours which are not authentic.
- People’s behaviour is affected by rumours and informal discussions may hamper work environment.
Question: Explain the advantages of informal communication.
Answer: The advantages of informal communication are:
- Spread of information through informal channels is faster. It may be useful to the manager at times.
- Provides emotional relief to employees and results in reducing union and management problems.
- Managers can get true and accurate response of subordinates on various policy matters.



