VBQs Coordination Compounds Class 12 Chemistry with Coordination Compounds has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Coordination Compounds. The following Coordination Compounds Class 12 Chemistry value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Coordination Compounds VBQs Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following has square planar structure?
(a) [Ni(CO)4]
(b) [NiCl4]2–
(c) [Ni(CN)4]2–
(d) [Ni(H2O) 6]2+
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following complex ions is diamagnetic?
(a) [FeF6]3–
(b) [CoF6]3–
(c) [Co(C2O4)3]3–
(d) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Answer
C
Question. The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral (Δ0) and tetrahedral (Δt) complexes is related as

Answer
B
Question. Which of the following options are correct for [Fe(CN)6 ]3- complex ?
(i) Possess d2sp3 hybridisation
(ii) Possess sp3d2 hybridisation
(iii) It is paramagnetic
(iv) It is diamagnetic
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of these statements about [Co(CN)6]3– is true ?
(a) [Co(CN)6]3– has four unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration.
(b) [Co(CN)6]3– has four unpaired electrons and will be in a high spin configuration.
(c) [Co(CN)6]3– has no unpaired electrons and will be in a high-spin configurtion.
(d) [Co(CN)6]3– has nounpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light ?
(a) [Ni(CN)4]2-
(b) [Cr(NH3)6]3+
(c) [Fe(H2O)6] 2+
(d) [Ni(H2O)6] 2+
Answer
A
Question. The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) is the highest for
(a) [CoF4]2–
(b) [Co(NCS)4]2–
(c) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(d) [CoCl4]2–
Answer
C
Question. The complex ion which has highest magnetic moment among the following is
(a) [CoF6]3–
(b) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(c) [Ni(NH3)4]2+
(d) [Ni(CN)4]2–
Answer
A
Question. In which of the following complexes of the Co (at. no. 27), will the magnitude of Δo be the highest?
(a) [Co(CN)6]3–
(b) [Co(C2O4)3]3–
(c) [Co(H2O)6]3+
(d) [Co(NH3)6]3+
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following correctly explains the fact that [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital complex whereas [CoF6]3– is an outer orbital complex?
(a) NH3 being a strong ligand results into pairing of 3d orbital electrons in Co3+.
(b) F– being a strong ligand results into pairing of 3d orbital electrons in Co3+.
(c) F– being a weak ligand cannot cause the pairing of electrons present in 3d orbital of Co3+.
(d) Both (a) and (c).
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) [MnCl6]3– is more paramagnetic than [Mn(CN)6]3–
(b) Both [Co(C2O4)3]3– and [CoF6]3– are paramagnetie.
(c) [Fe(CN)6]3– forms inner orbital complex whereas [FeF6]3– forms outer orbital complex.
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is an outer orbital complex and exhibits paramagnetic behaviour ?
(a) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
(b) [Zn(NH3)6)]2+
(c) [Cr(NH3)6]3+
(d) [Co(NH3)6]3+
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following are inner orbital complex (i.e., involving d2sp3 hybridisation) and is paramagnetic in nature?
(a) [Mn(CN)6]3– , [Fe(CN)6]3–, [Co(C2O4)3]3–
(b) [MnCl6]3–, [FeF6]3–, [CoF6]3–
(c) [Mn(CN)6]3–, [Fe(CN)6]3–
(d) [MnCl6]3– , [Fe(CN)6]3–, [Co(C2O4)3]3–
Answer
C
Question. Atomic number of Mn, Fe, Co and Ni are 25, 26, 27 and 28 respectively. Which of the following outer orbital octahedral complexes have same number of unpaired electrons ?
(i) [MnCl6 ]3-
(ii) [FeF6 ]3-
(iii) [CoF6 ]3-
(iv) [Ni(NH3 )6 ]2+
(a) (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the limitation of valence bond theory?
(a) It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands.
(b) It does not give quantitative interpretation of magnetic data.
(c) It does not explain the colour exhibited by coordination compounds
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Of the following complex ions, which is diamagnetic in nature?
(a) [NiCl4]2–
(b) [Ni(CN)4]2–
(c) [CuCl4]2–
(d) [CoF6]3–
Answer
B
Question. Among the ligands NH3, en, CN– and CO the correct order of their increasing field strength, is :
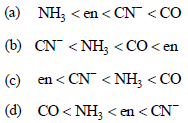
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
Coordination polyhedron Shape
(A) [Co(NH3)6]3+ Octahedral
(B) [Ni(CO)4] Square planar
(C) [PtCl4]2– Tetrahedral
(a) C
(b) B and C
(c) A and C
(d) B
Answer
B
Question. Among the following complexes the one which shows zero crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE):
(a) [Mn(H2O)6]3+
(b) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
(c) [Co(H2O)6]2+
(d) [Co(H2O)6]3+
Answer
B
Question. Which complex of Co2+ will have the weakest crystal field splitting –
(a) [CoCl6]4–
(b) [Co(CN)6]4–
(c) [Co(H3)6]2+
(d) [Co(en)3N]2+
Answer
A
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Square planar complexes of MABXL type show three isomers-two cis and one trans.
(ii) Complexes of Ma3B3 type show three isomers-two cis and one trans.
(iii) Optical isomerism is common in octahedral complexes involving bidentate ligands.
(iv) [Co(NH3)4Cl (NO2)]Cl show linkage isomerism.
(v) Hydrate isomerism is another name of solvate isomerism.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (v)
(d) (iii), (iv) and (v)
Answer
D
Question. Identify the correct statements for the behaviour of ethane- 1, 2-diamine as a ligand.
(i) It is a neutral ligand.
(ii) It is a didentate ligand.
(iii) It is a chelating ligand.
(iv) It is a unidentate ligand.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements regarding formulas and naming of coordination compounds are correct?
(i) During nomenclature names of neutral ligands are kept same except for H2O, NH3 and CO.
(ii) If the complex is anion, the name of the metal ends with the suffix–ate.
(iii) While writing formula of coordination compounds polydentate ligands are listed alphabeticaly.
(iv) The cation is named first in both positively and negatively charged coordination entities.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) When light of wavelength 600nm is absorbed by complex [Ti(H2O)6]3+ its configuration changes from

and it appears violet in colour.
(ii) Anhydrous CuSO4 is white but CuSO4 .5H2O is blue in colour as presence of H2O as a ligand causes crystal field spitting.
(iii) Ruby is aluminum oxide containing 0.5 – 1% Cr3+ ions with d3 configuration.
(iv) Crystal field theory predict correctly that anionic ligands should exert the greater splitting effect.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), and (ii)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Read the following statements
(i) Macromolecules cannot behave as a ligand.
(ii) [EDTA]4– can bind through two oxygen and four nitrogen atom.
(iii) Chelate complexes are more stable than similar complexes containing unidentate ligands.
(iv) Coordination number of the central atom/ion is determined only by the number of sigma bonds formed by the ligand with central atom/ion
Which of the following is the correct code for statements above?
(a) FFTT
(b) FTFT
(c) TFTF
(d) FFFT
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect?
(i) In metal carbonyls M–C σ bond is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons on the carbonyl carbon into a vacant orbital of metal.
(ii) M—C π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from a filled d orbital of metal into the vacant antibonding π* orbital of CO.
(iii) Bonding in metal carbonyls is called synergic bonding.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (ii) only
(d) None of these
Answer
D
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. According to IUPAC nomenclature sodium nitroprusside is named as
(a) Sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III)
(b) Sodium nitroferrocyanide
(c) Sodium nitroferricyanide
(d) Sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (II)
Answer
A
Question. Total number of electron count in Ni(CO)4 and Fe(CO)5 respectively are.
(a) 36, 36
(b) 34, 36
(c) 36, 34
(d) 34, 34
Answer
A
Question. [Co(NH3)4 (NO2)2] Cl exhibits
(a) linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and geometrical isomerism
(b) ionization isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
(c) linkage isomerism, geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism
(d) linkage isomerism, ionization isomerism and optical isomerism
Answer
A
Question. The terahedral complex [M(A)(B)(X)(Y)], where A,B,X and Y are different ligands and M is a metal ion is
(a) optically inactive
(b) rotate plane polarized light
(c) incomplete information
(d) can’t be said
Answer
B
Question. Atomic number of Mn, Fe and Co are 25, 26 and 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbital octahedral complex ions are diamagnetic ?
(i) [Co(NH3 )6 ] 3+
(ii) [Mn(CN)6 ] 3-
(iii) [Fe(CN)6 ] 4-
(iv) [Fe(CN)6 ] 3-
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. What is the secondary valence of following compounds PtCl2.2NH3, CoCl3.4NH3 and NiCl2.6H2O if moles of AgCl precipitated per mole of the given compounds with excess AgNO3 respectively are: 0, 1 and 2
(a) 6, 4, 4
(b) 4, 6, 6
(c) 4, 4, 6
(d) 2, 4, 6
Answer
B
Question. C63H88CoN14O14P is the formulae of the Cyanocobalamine,(vitamin B12) it contain CN– and CN– is very poisonous,than why this compound does not prove to be fatal for us? (it inhibit the electron transport chain ?
(a) CN– forms covalent bond
(b) CN– is coordinating to the cobalt as the ligand
(c) CN– hydrolysis immediately
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. The d-electron configurations of Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Co2+ are d4, d5, d6 and d7, respectively. Which one of the following will exhibit minimum paramagnetic behaviour?
(a) [Mn(H2O)6]2+
(b) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(c) [Co(H2O)6]2+
(d) [Cr(H2O)6]2+
(At, nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)
Answer
C
Question. Both [Ni(CO)4] and [Ni(CN)4]2– are diamagnetic. The hybridisations of nickel in these complexes, respectively, are
(a) sp3, sp3
(b) sp3, dsp2
(c) dsp2, sp3
(d) dsp2, sp2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following has an optical isomer
(a) [Co(en) (NH3)2]2+
(b) [Co(H2O)4(en)]3+
(c) [Co(en)2 (NH3)2]3+
(d) [Co(NH3)3Cl] +
Answer
C
Question. The value of the ‘spin only’ magnetic moment for one of the following configurations is 2.84 BM. The correct one is
(a) d5 (in strong ligand field)
(b) d3 (in weak as well as in strong fields)
(c) d 4 (in weak ligand fields)
(d) d 4 (in strong ligand fields)
Answer
D
Question. Among the following coordination compounds/ions

Which species exhibit geometrical isomerism?
(a) (ii) only
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. According to valence bond theory which of the following statement is correct about the complexes Ni(CO)4 and [Ni(CN)4]2– if both are diamagnetic in nature
(a) both are tetrahedral
(b) both are square planar
(c) one is square planar and other is tetrahedral
(d) one is tetrahedral and other is square planar
Answer
D
Question. The correct statement with respect to the complexes Ni(CO)4 and [Ni(CN)4]2– is
(a) nickel is in the same oxidation state in both
(b) both have tetrahedral geometry
(c) both have square planar geometry
(d) have tetrahedral and square planar geometry respectively
Answer
D
Question. In which of the following coordination entities the magnitude Δ0 (CFSE in octahedral field) will be maximum?
(a) [Co(H2O)6]3+
(b) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(c) [Co(CN)6]3–
(d) [Co (C2O4)3]3–
(At. No. Co = 27)
Answer
C
Question. The complex given is
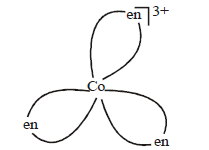
(i) non-superimposable on its mirror images
(ii) optically inactive
(iii) rotate plane polarised light
(iv) planar
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) only
Answer
C
Question. How many geometrical isomers are possible for following square planar compound [M (Cl) (Br) (I) (F)] (where M is a metal ion)
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 9
(d) 8
Answer
B
Question. Low spin complex of d6-cation in an octahedral field will have the following energy :

(Δ0= Crystal Field Splitting Energy in an octahedral field,P = Electron pairing energy)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following carbonyls will have the strongest C – O bond ?
(a) [Mn (CO)6]+
(b) [Cr (CO)6]
(c) [V (CO)6]–
(d) [Fe (CO)5]
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following complexes formed by Cu2+ ions is most stable ?
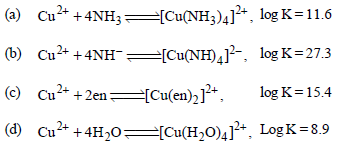
Answer
B
180. Which one of the following is an inner orbital complex as well as diamagnetic in behaviour? (Atomic number:
Zn = 30, Cr = 24, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
(a) [Zn(NH3)6]2+
(b) [Cr(NH3)6]3+
(c) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(d) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
Answer
C