Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Chapter 9 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Coordination Compounds Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following is the most stable complex?
(A) [Fe(CO)5]
(B) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
(C) [Fe(C2O4)3]3–
(D) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following will give a white precipitate upon reacting with AgNO3?
(A) K2 [Pt(en)2Cl2]
(B) [Co(NH3)3Cl3]
(C) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(D) [Fe(H2O)3Cl3]
Answer
C
Question. Amongst the following, the most stable complex is:
(A) [Fe(H2O)6]3+
(B) [Fe(NH3)6]3+
(C) [Fe(C2O4)3]3−
(D) [FeCl6]3−
Answer
C
Question. How many ions are produced from the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 in solution?
(A) 4
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 5
Answer
C
Question. The oxidation of Ni in [Ni(CO)4] is:
(A) 0
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer
A
Question. Ambidentate ligands like NO2– and SCN– are:
(A) unidentate
(B) didentate
(C) polydentate
(D) has variable denticity
Answer
D
Question. The colour of the coordination compounds depends on the crystal field splitting. What will be the correct order of absorption of wavelength of light in the visible region for the complexes,
[Co(NH3)6]3+, [Co(CN)6]3–, [Co(H2O)6]3+?
(A) [Co(CN)6]3– > [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(H2O)6]3+
(B) [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(H2O)6]3+ > [Co(CN)6]3–
(C) [Co(H2O)6]3+ > [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(CN)6]3–
(D) [Co(CN)6]3– > [Co(NH3)6]3+ > [Co(H2O)6]3+
Answer
C
Question. The formula of the coordination compound Tetraammineaquachloridocobalt(III) chloride is:
(A) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl2
(B) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl3
(C) [Co(NH3)2(H2O)Cl]Cl2
(D) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl
Answer
A
Question. The formula of the complex triamminetri(nitrito-O) cobalt (III) is:
(A) [Co(ONO)3(NH3)3]
(B) [Co(NO2)3(NH3)3]
(C) [Co(ONO2)3(NH3)3]
(D) [Co(NO2)(NH3)3]
Ans. Option (A) is correct.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the complex compounds give 2 moles of AgCl on reaction with AgNO3?
(A) 1 mole of CoCl3.6NH3
(B) 1 mole of CoCl3.5NH3
(C) 1 mole of CoCl3.4NH3
(D) All of the above
Answer
B
Question. How many ions are produced from the complex Co(NH3)6Cl2 in solution?
(A) 6
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 2
Answer
C
Question. The crystal field splitting energy for octahedral (Do) and tetrahedral (Dt) complexes is related as:

Answer
C
Question. The coordination number of ‘Co’ in the complex [Co(en)3]3+ is:
(A) 3
(B) 6
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer
B
Question. Atomic number of Mn, Fe and Co are 25, 26, 27 respectively. Which of the following inner orbital octahedral complex ions are diamagnetic?
(A) [Co(NH3)6]3+
(B) [Mn(CN)6]3−
(C) [Fe(CN)6]3−
Answer
A
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): [Fe(CN)6]3− ion shows magnetic moment corresponding to the two unpaired electrons.
Reason (R): [Fe(CN)6]3– it has d2sp3 type of hybridisation.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature.
Reason (R): Due to presence of unpaired electrons,complexes are reducing in nature.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Low spin tetrahedral complexes are rarely observed.
Reason (R): Crystal field splitting is less than pairing energy for tetrahedral complexes.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Among [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(en)3]3+,coordination compound [Co(en)3]3+ is a more stable complex.
Reason: en is a chelating ligand/bidentate ligand.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): NF3 is weaker ligand than N(CH3)3.
Reason (R): NF3 ionizes to give F– ions in aqueous solution.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature.
Reason (R): Unpaired electrons are present in their d-orbitals.
Answer
B
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to be ionic arising purely from electrostatic interactions between the metal ion and the ligand. Ligands are treated as point charges in case of anions or dipoles in case of neutral molecules. The five d orbitals in an isolated gaseous metal atom/ion have same energy, i.e., they are degenerate. This degeneracy is maintained if a spherically symmetrical field of negative charges surrounds the metal atom/ ion. However, when this negative field is due to ligands (either anions or the negative ends of dipolar molecules like NH3 and H2O) in a complex, it becomes asymmetrical and the degeneracy of the d orbitals is lifted. It results in splitting of the d orbitals.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Question. The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4− is 18,000 cm−1.
The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2− will be
(A) 18,000 cm−1
(B) 16,000 cm−1
(C) 8,000 cm−1
(D) 20,000 cm−1
Answer
C
Question. Consider the coordination compound,Na2[Pt(CN)4], identify the lewis acid.
(A) [Pt (CN)4]2–
(B) Na+
(C) Pt+2
(D) CN–
Answer
C
Question. An aqueous pink solution of cobalt(II) chloride changes to deep blue on addition of excess of HCl.This is because _____________.
(A) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl6]4−.
(B) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is transformed into [CoCl4]2−.
(C) tetrahedral complexes have larger crystal field splitting than octahedral complex.
(D) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?
(A) thiosulphato
(B) oxalato
(C) glycinato
(D) ethane-1,2-diamine
Answer
A
II. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
According to Valence Bond Theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n − 1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridisation to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with the ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
In these questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is NOT correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion (A): [NiCl4]2− is an inner orbital complex.
Reason (R): An inner orbital or low spin or spin paired complex uses inner d orbitals of the metal ion for hybridisation.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): In the diamagnetic octahedral complex, [Co(NH3)6]3+, the cobalt ion is in +3 oxidation state.
Reason (R): Six pairs of electrons, one from each NH3 molecule, occupy the six hybrid orbitals.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): The paramagnetic octahedral complex, [CoF6]3− uses outer orbital (4d) in hybridisation (sp3d2).
Reason (R): It is a high spin complex.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): [Ni(CN)4]2– is square planar complexes, the hybridisation involved is dsp2.
Reason (R): In [Ni(CN)4]2−, nickel is in +2 oxidation state and has the electronic configuration 3d8.
Answer
B
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) Write the formula for the following:
(ii) Write the formula for the following:
Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum(II)
Answer. (i) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl] (NO3)2
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)]
Question. Out of [CoF6]3− and [Co (en)3]3+ , which one complex is,
(i) Paramagnetic,
(ii) More stable,
(iii) Inner orbital complex and
(iv) High spin complex
(Atomic number of Co = 27)
Answer. (i) [CoF6]3–
(ii) [Co(en)3]3+
(iii) [Co(en)3]3+
(iv) [CoF6]3–
Question. (i) Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed?
(ii) Low spin configuration are rarely observed in tetrahedral coordination entity formation. Explain.
Answer. (i) Orbital splitting energies are not sufficiently large for forcing pairing of electrons.
(ii) The orbital splitting energies, Δ are not sufficiently large for forcing pairing of electrons in the tetrahedral coordination entity formation.
Question. (i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex:
[Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine)
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex:
Pentaamminenitrito-O-Cobalt (III).
Answer. (i) Diamminedichloridobisethylenediaminechromium (III) chloride
(ii) [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Sodium dicyanidoaurate (I)
(ii) Tetraamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (IV) sulphate
Answer. (i) Na[Au(CN)2]
(ii) [Pt(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]SO4
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Pentaammine nitrito-o-cobalt (III) Chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate (II)
Answer.
(i) [Co(NH3)5ONO]Cl2
(ii) K2[Ni(CN4)]
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
(ii) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)
Answer. (i) K3[Al(C2O4)3]
(ii) [CoCl2(en)2]+
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the following complex:
[Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl
(ii) Write the formula for the following:
Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) chloride
Answer. (i) Tetraamminechloridonitrito-N-cobalt (III) chloride.
(ii) [CoCl2(en)2]Cl
Question. (i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following
complex: [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex:
Potassium tetrachloridonickelate (II)
Answer. (i) Pentaamminechloridocobalt (III) ion
(ii) K2[NiCl4]
Question. (i) What is the IUPAC name of the complex [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2?
(ii) What is meant by chelate effect?
Answer. (i) Hexaamminenickel (II) Chloride.
(ii) Formation of stable complex with a polydentate ligand due to stronger bonding is known as chelate effect.
OR
Formation of stable complex with a polydentate ligand due to stronger bonding than the non chelate complexes is known as chelate effect.
Question. When a coordination compound CoCl3.6NH3 is mixed with AgNO3, 3 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write
(i) Structural formula of the complex,
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex.
Answer. (i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3

(ii) IUPAC name: Hexamminecobalt (III) chloride.
Question. Discuss the bonding in the coordination entity [Co(NH3)6]3+ on the basis of valence bond theory.
Also, comment on the geometry and spin of the given entity.
Answer.
Bonding in [Co(NH3)6]3+
d2sp3 hybridisation

Question. (a) Although both [NiCl4]2– and [Ni(CO)4] have sp3 hybridisation yet [NiCl4]2– is paramagnetic and [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic. Give reason. (Atomic no. of Ni = 28)
(b) Write the electronic configuration of d5 on the basis of crystal field theory when:
(i) Δo < P and (ii) Δo > P
Answer.(a) In [NiCl4]2– Ni is in +2 oxidation state and each Cl– donates a pair of electron. So, Cl – acts as a weak ligand and does not cause any forced pairing. Thus, electrons remains unpaired making it paramagnetic. In [Ni(CO)4], Ni is in zero oxidation state and CO acts as a strong ligand causing forced pairing. Thus, no electron remains unpaired making it diamagnetic.
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(ii) Potassium trioxalatochromate(III)
Answer.
(i) [Co(NH3)6]2(SO4)3
(ii) K3[Cr(C2O4)3]
Question. Using IUPAC norms, write the formula for the following complexes:
(a) Tetraamminediaquacobalt(III) chloride
(b) Dibromidobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
Answer. (i) [Co(NH3)4(H2O)2]Cl3
(ii) [Pt Br2(en)2](NO3)2
Question. Define the following terms with a suitable example of each:
(a) Polydentate ligand
(b) Homoleptic complex
Answer. (i) A ligand having several donor atoms. Example- EDTA.
(ii) A complex in which a metal is bound to only one kind of donor groups / ligands. Example- [Co(NH3)6]3+.
(or any other correct example)
(b) Complexes in which a metal is bound to only one kind of donor groups are known as homoleptic complexes. Example, [Co(NH3)6]3+.
Question. Using IUPAC norms, write the formulae for the following complexes:
(a) Potassium tri(oxalato)chromate(III)
(b) Hexaaquamanganese(II) sulphate
Answer.(i) K3[Cr(C2O4)3]
(ii) [Mn(H2O)6]SO4
Question.(i) A coordination compound with molecular formula CrCl3.4H2O precipitates one mole of AgCl with AgNO3 solution. Its molar conductivity is found to be equivalent to two
ions. What is the structural formula and name of the compound?
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d6 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when Δ0 < P. A
Answer. (i) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl
Tetraaquadichloridochromium (III) chloride.
(ii) t32ge3g.
Question. Using IUPAC norms, write the formulae for the following complexes:
(a) Hexaaquachromium(III) chloride
(b) Sodium trioxalatoferrate(III)
Answer. (a) Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(b) Na3[Fe(ox)3]
Question.(i) Which of the following is more stable complex and why?
[Co(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(en)3]3+.
(ii) How many ions are produced from the complex, [Co(NH3)6]Cl2 in solution?
Answer. (i) [Co(en)3]3+: Because (en) is a chelating ligand/ bidentate ligand.
(ii) Three ions [Co(NH3)6]2+, 2Cl–
Question. (a) Write the IUPAC name and hybridisation of the complex [Fe(CN)6]3–.
(Given: Atomic number of Fe = 26)
(b) What is the difference between an ambidentate ligand and a chelating ligand?
Answer.

(b) Ambidentate ligand can bond through different atoms to form different coordination compounds. e.g. NO2– can bind to the central atom or ion at either the nitrogen atom or one
of the oxygen atom.
Chelating ligand: If the ligands with two or more electron donor groups positioned in such a way that they form five or six membered ring with central metal ion are called chelating ligands. e.g., ethane – 1, 2-diamine (en).
Question. (i) Predict the geometry of [Ni(CN)4]2−.
(ii) Calculate the spin only magnetic moment of
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ ion.
Answer. (i) Square planar.
(ii) In Cu2+, electronic configuration (3d9) has one unpaired electron so, magnetic moment
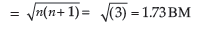
Question. Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine)chromium(III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetrahydroxozincate(II)
Answer. (i) [Cr(en)3]Cl3
(ii) K2[Zn(OH)4]
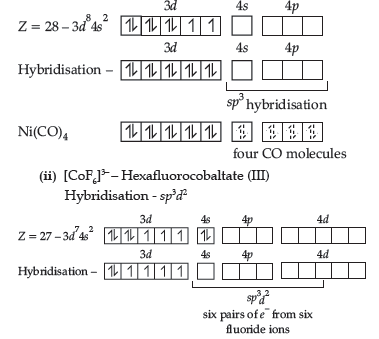
Question. Write IUPAC name and hybridisation of the following complexes:
(i) [Ni(CO)4] , (ii) [CoF6]3– (Atomic number Ni = 28, Co = 27)
Answer. (i) [Ni(CO)4] – Tetracarbonylnickel
Hybridisation – sp3
Question. (i) Using crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of iron ion in the following complex ion. Also predict its magnetic behaviour:
[Fe(H2O)6]2+
(ii) Write the IUPAC name of the coordination complex: [CoCl2(en)2]NO3
Answer. (i) t2g4eg 2, Paramagnetic
(ii) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III) nitrate
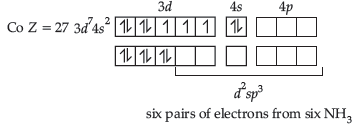
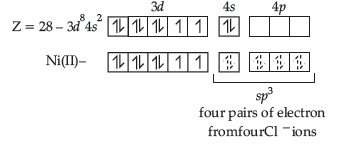
Question. 25. Write IUPAC name and hybridisation of the following complexes:
(i) [Co(NH3)6]3+ (ii) [NiCl4]2–
(Atomic number Ni = 28, Co = 27)
Answer. (i) [Co(NH3)6]3+: Hexaamminecobalt (III)
Hybridisation – d2sp3
(ii) [NiCl4]2– – Tetrachloronickelate (II)
Hybridization – sp3
Question. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compound [NiCl4]2–.
(ii) Write IUPAC name of the complex: [CoCl2(en)2]2+.
Answer. (i) Tetrachloridonickelate (II) ion.
(ii) Dichloridobis (ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt (III) ion.
Question. (i) Write IUPAC name of the complex:
[Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]+.
(ii) Write the coordination number and oxidation state of Platinum in the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2].
Answer. (i) Tetraamminechloridonitrocobalt (III) ion.
(ii) Coordination Number = 6,
Oxidation State = +2
Question. Out of [CoF6]3− and [Co (C2O4)]3- which one complex is:
(i) diamagnetic,
(ii) more stable,
(iii) outer orbital complex and
(iv) low spin complex.
(Atomic number of Co = 27)
Answer. (i) [Co(C2O4)3]3–
(ii) [Co(C2O4)3]3–
(iii) [CoF6]3–
(iv) [Co(C2O4)3]3–
Question. When a coordination compound CrCl3.6H2O is mixed with AgNO3, 2 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write
(i) Structural formula of the complex.
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex.
Answer. (i) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O
(ii) Pentaaquachloridochromium (III) chloride monohydrate.
Question. Write the hybridisation and magnetic character of the following complexes:
(i) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(ii) [Fe(CO)5]
Answer. (i) sp3d2, Paramagnetic
(ii) sp3d2, Paramagnetic
Detailed Answer:
(i) In [Fe(H2O)6]2+the oxidation state of Fe is +2.
The outermost electronic configuration of Fe is 3d64s24p0. H2O is weak field ligand and do not cause pairing up of electrons.
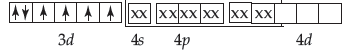
In this complex, there are 4 unpaired electrons. that makes it paramagnetic in nature. And, it involves sp3d2 hybridisation.
(ii) In [Fe(CO)5] the oxidation state of Fe is zero.
The outermost electronic configuration of Fe is 3d64s24p0. CO is strong field ligand, causes pairing up of 4s electrons into the 3d orbitals.
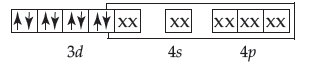
In this complex, there is no unpaired electron.
Therefore, it involves dsp3 hybridisation and is diamagnetic.
Question. Define the following terms with a suitable example of each:
(a) Chelate complex
(b) Ambidentate ligand
Answer.
(a) Chelate complex is the complex formed when a di – or polydentate ligand uses its two or more donor atoms to bind a single metal atom.
(b) Ligand which can ligate through two different atoms is called ambidentate ligand.
Question. (a) Using valence bond theory, write the hybridisation and magnetic character of the complex [Fe(CN)6]4- . (Atomic no. of Fe=26)
(b) Write the electronic configuration of d6 on the basis of crystal field theory when:
(i) Δo < P and
(ii) Δo > P
Answer. (a) d2sp, diamagnetic
(b) (i) t2g4eg2
(ii) t2g6eg0
(a) Oxidation number of Fe is + 2 in [Fe (CN) 6]4-
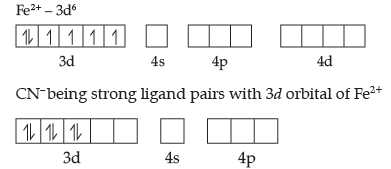
Six CN– ions give their six pairs of electron to the empty orbitals. The orbitals utilized for hybridisation is d2 sp3.
Magnetic character – Diamagnetic
Question. Write the IUPAC name and hybridisation of the following complexes:
(i) [Ni(CN)4]2–
(ii) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(Given: Atomic number of Ni = 28, Fe = 26)
Answer. (i) [Ni(CN)4]2– – Tetracyanonickelate (II)
hybridisation – dsp2
(ii) [Fe(H2O)6]2+ – Hexaquairon (II)
hybridisation – sp3d2
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. (a) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3)5 (SCN)]2+?
(b) Why is [NiCl4]2– paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2– is diamagnetic ? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
(c) Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes rarely observed ?
Answer. (a) Linkage isomerism.
(b) In [NiCl4]2–, due to the presence of Cl–, a weak
field ligand no pairing occurs whereas in [Ni(CN)4]2–, CN– is a strong field ligand and pairing takes place.
(c) Because of very low CFSE which is not able to pair up the electrons.
Question. (a) (i) For the complex [Fe(CN)6]4−, write the hybridisation, magnetic character and spin type of the complex. (At. number: Fe = 26).
(b) (i) Write the hybridisation and magnetic character of [Co(C2O4)3]3–. (At. no. of Co = 27)
Answer. (a) (i) Hybridization: d2sp3 Magnetic character: Diamagnetic Spin type: Low spin complex.
(b) (i) d2sp3, diamagnetic
Question. For the complex ion [CoF6]3– write the hybridisation type, magnetic character and spin nature. [Atomic number: Co = 27]
Answer. Hybridisation: sp3d2
Magnetic character: Paramagnetic
Spin nature: High spin
Question. For the complex ion [Ni(CN)4]2– write the hybridisation type, magnetic character and spin nature. [Atomic number: Ni = 28]
Answer. Hybridisation: dsp2
Magnetic character: Diamagnetic Spin nature: Low spin
Question. (i) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3?
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo > P.
(iii) Write the hybridization and shape of [CoF6]3−.
(Atomic number of Co = 27)
Answer. (i) Hydrate isomerism [1]
(ii) Electronic configuration is t4 2g or by diagram.
(iii) Hybridisation is sp3d2 and shape is octahedral.
Question. When a coordination compound CrCl3.6H2O is mixed with AgNO3 solution, 3 moles of AgCl are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write:
(i) Structural formula of the complex
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex
(iii) Magnetic and spin behaviour of the complex
Answer. (i) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(ii) Hexaaquachromium(III) chloride
(iii) Paramagnetic and high spin
Question. Write the IUPAC name of the following:
(i) [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
(ii) [NiCl4]2–
(iii) K3[Fe(CN)6]
Answer. (i) Hexaamminecobalt (III) chloride.
(ii) Tetrachloridonickelate (II) ion.
(iii) Potassiumhexacyanoferrate (III)
Question.A metal complex having composition
Cr(NH3)4Cl2Br has been isolated in two forms
A and B. The form A reacts with AgNO3 to give a white precipitate readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia whereas B gives a pale yellow precipitate soluble in concentrated ammonia.
Answer. (i) Isomer A: [Cr(NH3)4BrCl]Cl
Isomer B: [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Br
(ii) Hybridisation of Cr in isomer A and B is d2sp3.
(iii) Number of unpaired electrons in Cr3+(3d3) is 3
Magnetic moment = √n(n + 2)
= √3(3 + 2)
= 3.87 BM
Question. Write IUPAC name for each of the following complexes:
(i) [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
(ii) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(iii) [Co(en)3]3+
Answer. (i) Hexaamminenickel (II) chloride
(ii) Potassium hexacyanidoferrate (III)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt (III) ion
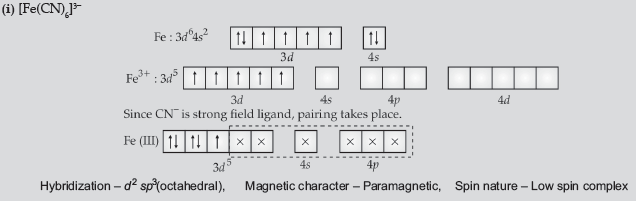
Question. (i) For the complex [Fe(CN)6]3−, write the hybridisation, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex. (At. number: Fe = 26).
(ii) Arrange the following complexes in increasing order of conductivity:
[Co(NH3)Cl3], [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl, [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
Answer.
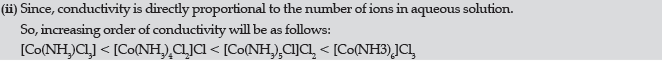
Question. (a) Write the formula of the following coordination compound:
Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
(b) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 ?
(c) Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex [CoF6]3-.
(Atomic No. of Co = 27)
Answer. (a) Fe4[Fe (CN)6]3
(b) Ionisation isomerism
(c) sp3d2, octahedral complex with 4 unpaired electrons
Question. Write the hybridisation, shape and magnetic character of [Fe(CN)6]4−.
Answer. Hybridisation: d2sp3
Shape: Octahedral
Magnetic character: Diamagnetic
Question. A metal complex having composition Cr(NH3)4Cl2Br has been isolated in two forms A and B. The form A reacts with AgNO3 to give a white precipitate readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia whereas B gives a pale yellow precipitate soluble in concentrated ammonia.
(i) State the hybridisation of chromium in each of them.
(ii) Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only value) of the isomer
Answer. (i) Hybridisation of Cr in isomer A and B is d2sp3.
(ii) Number of unpaired electrons in Cr3+(3d3) is 3
Magnetic moment = n(n+2)
= 3(3+2)
= 3.87 BM
(deduct half mark for wrong unit/unit not written)
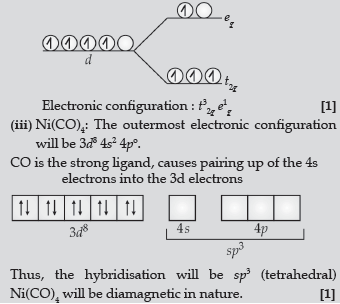
Question. (i) Write IUPAC name of the following complex [Cr(NH3)3Cl3].
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo < P.
(iii) Write the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Ni(CO)4]. (At. no. of Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) Triamminetrichloridochromium (III)
(ii) When Δo < P, it is weak field and high spin situation. As a result, one electron entered in eg orbital and 3 electrons in t2g.
Question. (i) For the complex [Fe (CN)6]3–, write the hybridisation, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex. (At. number: Fe = 26).
(ii) Give the limitations of valence bond theory.
Answer. (i) Hybridization: d2sp3
Magnetic character: Paramagnetic Spin nature of the complex: Low spin.
(ii) (a) No explanation for magnetic properties of complex compound.
(b) No explanation for absorption spectra, difference between square planar and tetrahedral in nature.
(c) Failed to distinct between strong and weak field ligands.
Question. (i) Define crystal field splitting energy. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo < P.
(ii) [Ni(CN)4]2– is colourless whereas [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green. Why? (At. no. of Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) It is the magnitude of difference in energy between the two sets of d orbital i.e., t2g and eg t32ge1g
(ii) In [Ni(H2O)6]2+, Ni+2(3d8) has two unpaired electrons which do not pair up in the presence of weak field ligand H2O.
Question. (i) For the complex [Fe(H2O)6]3+, write the hybridisation, magnetic character and spin of the complex. (At. number: Fe = 26).
(ii) Which of the following will not behave as ligand?
H2O, NH3, CO and CH4
Answer.[Fe(H2O)6]3+

Thus, it is strongly paramagnetic (due to presence of unpaired electrons).
In [Fe(H2O)6]3+ outer d-orbitals are used in hybridisation
to form high spin complex.
(ii) CH4 will not act as ligand because it does not contain lone pair of electrons.
Question. (i) Define crystal field splitting energy. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δo > P.
(ii) [Ni(CN)4]2– is diamagnetic whereas [NiCl4]2– is paramagnetic. Give reason. (At. no. of Ni = 28)
Answer. (i) It is the magnitude of difference in energy between the two sets of d orbital i.e. t2g and eg [1] t42geg0.
(ii) In [Ni(CN)4]2-, CN- is a strong field ligand and pairing takes place whereas in [NiCl4]2-, due to the presence of Cl–, a weak field ligand no pairing occurs/diagrammatic representation.
Question. (a) Write the formula of the following coordination compound: Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
(b) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4?
(c) Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex [CoF6]3-. (Atomic No. of Co = 27)
Answer. (a) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
(b) Ionisation isomerism
(c) sp3d2, 4
Question. A metal ion Mn+ having d4 valence electronic configuration combines with three bidentate ligands to form a complex compound. Assuming
Δo > P.
(i) Write the electronic configuration of d4 ion.
(ii) What type of hybridisation will Mn+ ion has?
(iii) Name the type of isomerism exhibited by this complex.
Answer. (i)t42geg0
(ii) sp3d2
(iii) Optical isomerism

