Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Surface Chemistry Chapter 5 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Surface Chemistry Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm, the amount of gas adsorbed at very high pressure
(A) reaches a constant limiting value
(B) goes on increasing with pressure
(C) goes on decreasing with pressure
(D) increase first and decreases later with pressure
Answer
A
Question. Adsorption due to strong chemical forces is called
(A) Chemisorption
(B) Physisorption
(C) Reversible adsorption
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer
A
Question. At the critical micelle concentration (CMC) the surfactant molecules
(A) decompose
(B) dissociate
(C) associate
(D) become completely soluble
Answer
C
Question. Adsorption of gases on solid surface is exothermic reaction because
(A) free energy increases
(B) enthalpy is positive
(C) entropy increases
(D) enthalpy is negative
Answer
D
Question. The gas which is least adsorbed on charcoal (under identical conditions) is
(A) HCl
(B) O2
(C) CO2
(D) NH3
Answer
B
Question. Which one is an example of multimolecular colloid system
(A) Soap dispersed in water
(B) Protein dispersed in water
(C) Gold dispersed in water
(D) Gum dispersed in water
Answer
C
Question. Adsorption is accompanied by
(A) decrease in enthalpy and increase in entropy
(B) increase in enthalpy and increase in entropy
(C) decrease in enthalpy and decrease in entropy
(D) increase in enthalpy and decrease in entropy
Answer
C
Question. Choose the incorrect statement in respect of physisorption?
(A) It is not specific in nature
(B) It arises because of van der Waal’s force
(C) It is reversible in nature
(D) Enthalpy of adsorption is in the range 80-240 kJ mol–1
Answer
D
Question. Extent of physisorption of a gas increases with _______.
(A) increase in temperature.
(B) decrease in temperature.
(C) decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
(D) decrease in strength of van der Waal’s forces.
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following impurities present in colloidal solution cannot be removed by electrodialysis?
(A) Sodium chloride
(B) Potassium sulphate
(C) Urea
(D) Calcium chloride
Answer
C
Question. Extent of adsorption of adsorbate from solution phase increases with _________.
(A) increase in amount of adsorbate in solution.
(B) decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
(C) increase in temperature of solution.
(D) decrease in amount of adsorbate in solution.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a favourable condition for physical adsorption ?
(A) High pressure
(B) Negative ΔH
(C) Higher critical temperature of adsorbate
(D) High temperature
Answer
D
Question. Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with ________.
(A) decrease in temperature
(B) increase in temperature
(C) increase in surface area of adsorbent
(D) decrease in surface area of adsorbent
Answer
B
Question. In physisorption adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because _________.
(A) involved van der Waal’s forces are universal.
(B) gases involved behave like ideal gases.
(C) enthalpy of adsorption is low.
(D) it is a reversible process.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is an example of absorption ?
(A) Water on silica gel .
(B) Water on calcium chloride.
(C) Hydrogen on finely divided nickel.
(D) Oxygen on metal surface.
Answer
B
Question. For adsorption of a gas on a solid, the plot of log x/m vs log P is linear with slope equal to (n being whole number)
(A) k
(B) log k
(C) n
(D) 1/n
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is most powerful to coagulate the negative colloid?
(A) ZnSO4
(B) Na3PO4
(C) AlCl3
(D) K4[Fe(CN)6]
Answer
C
Question. If x is amount of adsorbate and m is amount of adsorbent,which of the following relations is not related to adsorption process ?
(A) x / m = f (p) at constant T.
(B) x / m = f (T) at constant p.
(C) p = f (T) at constant (x / m).
(D) x/m = p x T
Answer
D
Question. In Freundlich adsorption isotherm, the value of 1/n is :
(A) between 0 and 1 in all cases
(B) between 2 and 4 in all cases
(C) 1 in case of physical adsorption
(D) 1 in case of chemisorption
Answer
A
Question. The efficiency of an enzyme in catalysing a reaction is due to its capacity
(A) to form a strong enzyme-substrate complex
(B) to decrease the bond energies of substrate molecule
(C) to change the shape of the substrate molecule
(D) to lower the activation energy of the reaction
Answer
D
Question. Which is not correct regarding the adsorption of a gas on surface of solid?
(A) On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously
(B) Enthalpy and entropy changes are –ve
(C) Adsorption is more for some specific substance
(D) This Phenomenon is reversible
Answer
A
Question. Identify the correct statement regarding enzymes
(A) Enzymes are specific biological catalysts that cannot be poisoned.
(B) Enzymes are normally heterogeneous catalysts that are very specific in their action.
(C) Enzymes are specific biological catalysts that can normally function at very high temperatures (T = 1000K).
(D) Enzymes are specific biological catalysts that possess well-defined active sites.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is related to adsorption?
(i) ΔH = – ve (ii) ΔS = – ve
(iii) –TΔS = – ve (iv) ΔG = – ve
(A) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) only
(D) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. The role of a catalyst in a reversible reaction is to
(A) increase the rate of forward reaction
(B) decrease the rate of backward reaction
(C) alter the equilibrium constant of the reaction
(D) allow the equilibrium to be achieved quickly
Answer
D
Question. Adsorbed acetic acid on activated charcoal is:
(A) adsorber
(B) absorber
(C) adsorbent
(D) adsorbate
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is an example of homogeneous catalysis ?
(A) Haber’s process of synthesis of ammonia
(B) Catalytic conversion of SO2 to SO3 in contact process
(C) Catalytic hydrogenation of oils
(D) Acid hydrolysis of methyl acetate.
Answer
D
Question. A catalyst :
(A) lowers the activation energy
(B) changes the rate constant
(C) changes the product
(D) itself destroyed in the reaction
Answer
A
Question. Active charcoal is a good catalyst because it
(A) is made up of carbon atoms.
(B) is very reactive.
(C) has more adsorption power.
(D) has inert nature toward reagents.
Answer
C
Question.Which of the following kind of catalysis can be explained by the adsorption theory ?
(A) Homogeneous catalysis
(B) Acid – base catalysis
(C) Heterogeneous catalysis
(D) Enzyme catalysis
Answer
C
Question.According to the adsorption theory of catalysis, the speed of the reaction increases because-
(A) Adsorption lowers the activation energy of the reaction
(B) The concentration of reactant molecules at the active centres of the catalyst becomes high due to strong adsorption
(C) In the process of adsorption, the activation energy of the molecules becomes large
(D) Adsorption produces heat which increases the speed of the reaction
Answer
A
Question. Catalyst increases the rate of reaction by
(A) decreasing threshold energy
(B) decreasing activation energy
(C) increasing activation energy
(D) decreasing equilibrium constant
Answer
B
Question. A catalyst can affect reversible reaction by
(A) changing equilibrium constant
(B) slowing forward reaction
(C) attaining equilibria in both directions
(D) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a property of colloidal solution?
(A) Heterogenity
(B) Particle size > 100 nm
(C) Tyndall effect
(D) Brownian movement
Answer
B
Question. When a strong beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, the light will
(A) be reflected
(B) be scattered
(C) be refracted
(D) give a rainbow
Answer
B
Question. A biological catalyst is
(A) an enzyme
(B) a carbohydrate
(C) an amino acid
(D) a nitrogenous base
Answer
A
Question. The term ‘sorption’ stands for ___________.
(A) absorption
(B) adsorption
(C) both absorption and adsorption
(D) desorption
Answer
C
Question. The charge on colloidal particles is due to
(A) presence of electrolyte
(B) very small size of particles
(C) adsorption of ions from the solution
(D) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which is not correct regarding the physical adsorption of a gas on surface of solid ?
(A) On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously
(B) Enthalpy and entropy changes are negative
(C) Adsorption is more for some specific substance
(D) Reversible
Answer
A
Question. Hydrolysis of urea is an example of
(A) homogenous catalysis
(B) heterogenous catalysis
(C) biochemical catalysis
(D) zeolite catalysis
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is correctly matched ?
(A) Emulsion – curd
(B) Foam – mist
(C) Aerosol – smoke
(D) Solid sol – cake
Answer
C
Question. What is the role of molybdenum in Haber’s process for manufacture of ammonia?
(A) As catalytic poison
(B) As a catalytic promoter
(C) As a catalyst
(D) As a reactant
Answer
B
Question. Adsorption is always
(A) endothermic
(B) exothermic
(C) exothermic in case of physical and endothermic in case of chemical
(D) Either (A) or (B)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following step(s) is/are not involved in the mechanism of adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalyst?
(i) Diffusion of reactants to the surface of the catalyst.
(ii) Sorption of reactant molecules on the surface of the catalyst.
(iii) Occurrence of chemical reaction on the catalyst’s surface through formation of an intermediate.
(iv) Desorption of reaction products from the catalyst’s surface.
(v) Diffusion of reaction products away from the catalyst’s surface.
(A) (i) only
(B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (ii) only
(D) (i), (ii) and (v)
Answer
C
Question. Blood may be purified by
(A) Dialysis
(B) Electro-osmosis
(C) Coagulation
(D) Filtration
Answer
A
Question. Milk is a colloid in which a
(A) liquid is dispersed in a liquid
(B) solid is dispersed in a liquid
(C) gas is dispersed in a liquid
(D) sugar is dispersed in a liquid
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following electrolytes is least effective in coagulating ferric hydroxide solution?
(A) KBr
(B) K2SO4
(C) K2CrO4
(D) K4 [Fe(CN)6]
Answer
A
Question. The size of colloidal particles is between
(A) 10–7 – 10–9 cm
(B) 10–9 – 10–11 cm
(C) 10–5 – 10–7 cm
(D) 10–2 – 10–3 cm
Answer
C
Question. Peptization involves
(A) precipitation of colloidal particles
(B) disintegration of colloidal aggregates
(C) evaporation of dispersion medium
(D) impact of molecules of the dispersion medium on the colloidal particles
Answer
B
Question. An example of dispersion of a liquid in a gas is :
(A) milk
(B) vegetable oil
(C) foam
(D) mist
Answer
D
Question. Extent of adsorption of adsorbate from solution phase increases with:
(A) increase in amount of adsorbate in solution.
(B) decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
(C) increase in temperature of solution.
(D) decrease in amount of adsorbate in solution.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a favourable condition for Physical adsorption?
(A) High pressure
(B) Negative dH
(C) Higher critical temperature of adsorbate
(D) High temperature
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is an example of absorption?
(A) Water on Silica gel
(B) Water on Calcium Chloride
(C) Hydrogen on highly divided Nickel
(D) Oxygen on Metal surface
Answer
B
Question. Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by:
(A) coagulation.
(B) electrolysis.
(C) diffusion.
(D) peptisation.
Answer
D
Question. Which is the example of emulsions?
(A) Smoke
(B) Starch
(C) Gold Sol
(D) Hair Cream
Answer
D
Question. The values of colligative properties of colloidal solution are of small order in comparison to those shown by true solutions of same concentration because of colloidal particles _____________.
(A) exhibit enormous surface area.
(B) remain suspended in the dispersion medium.
(C) form lyophilic colloids.
(D) are comparatively less in number.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following interface cannot be obtained?
(A) Liquid-liquid
(B) Solid-liquid
(C) Liquid-gas
(D) Gas-gas
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following will show Tyndall effect?
(A) Aqueous solution of soap below critical micelle concentration.
(B) Aqueous solution of soap above critical micelle concentration.
(C) Aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
(D) Aqueous solution of sugar.
Answer
B
Question. In physisorption, adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because :
(A) involved Van der Waals forces are universal.
(B) gases involved behave like ideal gases.
(C) enthalpy of adsorption is low.
(D) it is a reversible process.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is most effective in coagulating negatively charged hydrated Ferric Oxide sol?
(A) NaNO3
(B) MgSO4
(C) AlCl3
(D) KCl
Answer
C
Question. On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?
Gas CO2 SO2 CH4 H2
Critical temp/K 304 630 190 33
(A) CO2
(B) SO2
(C) CH4
(D) H2
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the most effective in coagulating positively charged methylene blue sol?
(A) Na3PO4
(B) K4 [Fe(CN)6]
(C) Na2SO4
(D) Al2(SO4)3
Answer
B
Question. A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is classified as .
(A) Solid sol
(B) Gel
(C) Emulsion
(D) Sol
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is not applicable to the phenomenon of adsorption?
(A) ΔH > 0
(B) ΔG < 0
(C) ΔS < 0
(D) ΔH < 0
Answer
A
Question. Method by which lyophobic sol can be protected :
(A) by addition of oppositely charged sol.
(B) by addition of an electrolyte.
(C) by addition of lyophilic sol.
(D) by boiling.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is most effective in coagulating positively charged hydrated Ferric Oxide sol?
(A) NaNO3
(B) Na2SO4
(C) (NH4)3PO4
(D) LiAlH4
Answer
C
Question. The stability of lyophobic sols is due to
(A) adsorption of covalent molecules on the colloid
(B) the size of the particles
(C) the charge on particles
(D) Tyndall effect.
Answer
C
Question. Which is favorable for physical adsorption?
(A) High T and high P
(B) High T and low P
(C) Low T and high P
(D) T and P do not affect
Answer
C
Question. When a small amount of FeCl3 is added to a freshly precipitated Fe (OH)3 a reddish-brown colloidal solution is obtained. This phenomenon is known as
(A) dialysis
(B) peptization
(C) protection
(D) dissolution
Answer
B
Question. Colloidion is 4% solution of which one of the following in alcohol-ether mixture.
(A) Nitroglycerin
(B) Cellulose acetate
(C) Glycol dinitrate
(D) Nitrocellulose
Answer
D
Question. The term ‘sorption’ stands for ___________ .
(A) absorption
(B) adsorption
(C) both absorption and adsorption
(D) desorption
Answer
C
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question. Assertion (A): Detergents with low CMC are more economical to use.
Reason (R): Cleansing action of detergents involves the formation of micelles. These are formed when the concentration of detergents becomes equal to CMC.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Extent of physisorption of a gas increases with decrease in temperature.
Reason (R): Extent of physiorption increases due to decrease in strength of Van der Waals forces.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Colloidal solutions show colligative properties.
Reason (R): Colloidal particles are large in size.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Activated adsorption is also known as chemical adsorption or chemisorption.
Reason (R): Adsorption involves formation of chemical bonds between adsorbent and reactants.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Colloidal solution are stable sols.
Reason (R): Brownian movement has a stirring effect, which does not allow the particles to settle down.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): An ordinary filter paper impregnated with colloidal solution stops the flow of colloidal particles.
Reason (R): Pore size of the filter paper becomes more than the size of colloidal particle.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Extent of adsorption of adsorbate from solution phase increases with increase in amount of adsorbate in solution.
Reason (R): Freundlich’s equation describes the behaviour of adsorption from a solution.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Colloidal solutions do not show brownian motion.
Reason (R): Brownian motion is responsible for stability of Sols.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (A): At the equilibrium position in the process of adsorption ∆H = T∆S.
Reason (R): Adsorption is accompanied by decrease in surface energy.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Coagulation power of Al3+ is more than Na+ in the coagulation of negative sol.
Reason (R): Greater the valency of the flocculating ion added, greater is its power to cause precipitation (Hardy-Schulze rule).
Answer
A
Case-based MCQs
I. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The amount of moisture that leather adsorbs or loses is determined by the temperature, relative humidity, degree of porosity and the size of the pores. Moisture has great practical significance because its amount affects the durability of leather and the comfort of the wearer in articles such as shoes, gloves and other garments. High moisture content accelerates deterioration and promotes mildew action. On the other hand, a minimum amount of moisture is required to keep leather properly lubricated and thus, prevent cracking. The study indicates that adsorption of moisture by leather is a multi-molecular process and is accompanied by low enthalpies of adsorption. Further at 75 percent relative humidity, the adsorption is a function of surface area alone. Untanned hide and Chrome tanned leathers have the largest surface areas. The leathers tanned with vegetable tanning materials have smaller surface areas since they are composed of less hide substance and the capillaries are reduced to smaller diameters in some cases probably completely filled by tanning materials. This process of tanning occurs due to mutual coagulation of positively charged hide with negatively charged tanning material. The result of the study indicated that untanned hide and Chrome tanned leather adsorb most of the water vapour.
In these questions a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(A) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion (A): Adsorption of moisture by leather is physisorption.
Reason (R): It is a multimolecular process and is accompanied by low enthalpies of adsorption.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Leather absorbs different amount of moisture.
Reason (R): Some moisture is necessary to prevent cracking of leather.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Animal hide soaked in tannin results in hardening of leather.
Reason (R): Tanning occurs due to mutual coagulation.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Vegetable tanned leather cannot adsorb a large amount of moisture.
Reason (R): Porous materials have higher surface area.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Leathers tanned with vegetable tanning materials have smaller surface areas.
Reason (R): The capillaries present in leather are reduced to smaller diameters.
Answer
A
II. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Some colloids are stable by their nature, i.e., gels, alloys, and solid foams. Gelatin and jellies are the two common examples of a gel. The solid and liquid phases in a gel are interpersed with both phases being continuous. In most systems, the major factor influencing the stability is the charge on the colloidal particles. If a particular ion is preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the particles, the particles in suspension will repel each other, thereby preventing the formation of aggregates that are larger than colloidal dimensions. The ion can be either positive or negative depending on the particular colloidal system, i.e., air bubbles accumulate negative ions. Sulphur particles have a net negative charge in a sulphur sol, and the particles in a metal hydroxide sol are positively charged. Accumulation of charge on a surface is not as usual phenomenon of dust attracted to furniture surfaces by electrostatic forces. When salts are added to lyophobic colloidal systems the colloidal particles begin to form larger aggregates and a sediment forms as they settle. This phenomenon is called flocculation, and the suspension can be referred to as flocculated, or colloidally unstable. If the salt is removed, the suspension can usually be restored to its original state; this process is called Deflocculation or Peptization. The original and restored colloidal systems are called deflocculated, peptized, or stable sols.
Addition of small amount of salt affects the stability of colloidal system because of attractive and repulsive forces that exist between colloidal particles. Van der Waals forces are responsible for the attractions, while the repulsive forces are due to the surface charge on the particles. In a stable colloid, the repulsive forces are of greater magnitude than the attractive forces. The magnitude of the electrical repulsion is diminished by addition of ionized salt, which allows the dispersed particles to aggregate and flocculate. River deltas provide an example of this behaviour.
Question. The particles in suspension will repel each other, thereby preventing the formation of aggregates that are larger than colloidal dimensions. This statement explains:
(A) formation of delta.
(B) river water as a colloidal solution of clay particles.
(C) effect of salt on lyophobic colloid.
(D) phenomenon of flocculation.
Answer
A,B
Question. Settling down of colloidal particles to form a suspension is called:
(A) Flocculation
(B) Precipitation
(C) Aggregation
(D) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Gelatin is a ________________ colloidal system.
(A) Solid in solid
(B) Solid in gas
(C) Liquid in solid
(D) Liquid in gas
Answer
C
Question. When Van der Waals forces are greater than forces due to the surface charge on the particles:
(A) Flocculation occurs.
(B) The colloid is stable.
(C) Peptization takes place.
(D) Deflocculation occurs.
Answer
A
Question. Colloidal solutions are stable due to:
(A) presence of charges on the colloidal particles.
(B) formation of aggregates by colloidal particles.
(C) preferential adsorption on the surface.
(D) preferential absorption on the surface.
Answer
A
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Read the following statements related to chemisorption
(i) It is highly specific.
(ii) It increases with increase in temperature and pressure.
(iii) It is reversible.
(iv) It increases with increase in surface area of adsorbent.
Which of the following is correct code for the statements above?
(a) TTFT
(b) TFFT
(c) FTFT
(d) FFTF
Answer
A
Question. Read the following statements related to physisorption.
(i) Adsorbent shows preference for gases with high molecular weight.
(ii) Easily liquefiable gases gets readily adsorbed.
(iii) Adsorption varies with change in temperature and pressure.
(iv) Finely divided and solid metals adsorb gases equally.
(v) It is exothermic with low value of enthalpy of adsorption.
Which of the following is the correct code for the statements above ?
(a) TFFTF
(b) FTTFT
(c) TFFTT
(d) FTTTF
Answer
B
Question. Read the following statements regarding enzyme catalysis
(i) Enzyme catalysis is highly specific in nature.
(ii) Enzyme catalysis to work effectively requires optimum temperature (298-310 K) and optimum pH (3-5)
(iii) Metal ions like Na+, Mn2+, Co2+, Cu2+ etc. increases the activity of enzymes.
(iv) Catalyst used in Ostwald’s process is platinised asbestos at 673 K.
(v) Catalyst used in contact process is platinised asbestos or V2O5 at 673-723 K.
Which of the following is the correct coding for the above statements?
(a) FTFTF
(b) TFTFT
(c) TTFFF
(d) FTTFT
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about solid catalyst?
(i) Same reactants may give different product by using different catalysts.
(ii) Catalyst is required in large quantities to catalyse reactions.
(iii) Catalyst does not change ΔH of reaction.
(iv) Catalytic activity of a solid catalyst does not depend upon the strength of chemisorption.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) only
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Read the following statements regarding adsorption and choose the correct option.
(i) It is a surface phenomenon.
(ii) The material which is adsorbed is termed as adsorbate.
(iii) The material on the surface of which the adsorption .
takes place is called adsorbent.
(iv) Adsorption is a bulk phenomenon.
(a) Only (iv) is correct
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(i) Zeolites are good shape selective catalysts because of their honeycomb-like structures.
(ii) All zeolites are naturally occurring substance.
(iii) An important zeolite catalyst used in the petroleum industry in ZSM-5.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
C
Question. Read the following statements
(i) Tyndall effect is used to distinguish between a colloidal and true solution.
(ii) Values of colligative properties are same for true and colloidal solutions.
(iii) Random bombardment of the colloidal particles by the molecules of the dispersion medium does not allow colloids to settle thereby providing stability to them.
(iv) Most acceptable phenomena to account for the charge of sol particles is electrodispersion.
Which of the following is the correct code for statements above?
(a) TFTF
(b) TTFF
(c) FTFT
(d) TFFT
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Gelatine sol if evaporated off it can be reobtained simply by mixing gelatine obtained on evaporation with suitable dispersion medium.
(ii) Metal sulphide sols need stabilising agents for their preservation
(iii) S8 being a macromolecule forms macromolecular colloid.
(iv) Starch and proteins are natural whereas polythene and polystyrene are man-made macromolecules.
(v) Micelles are formed above kraft temperature at any concentration
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii), (iv) and (v)
(d) (ii), (iv) and (v)
Answer
B
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Why is it necessary to remove CO when ammonia is obtained from Haber’s process?
Answer.Because CO act as poison.
Question. Name the type of colloid of cheese.
Answer.Gel
Question. What is peptization?
Answer.Conversion of a freshly prepared precipitate into colloidal sol by the addition of electrolyte.
Question.Define Brownian movement.
Answer.It involves the motion of colloidal particles in zigzag path.
Question. What is protective colloid?
Answer. lyophilic colloid that protect any colloid from coagulation.
Question. Define Electrophoresis.
Answer.The movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an electric field.
Question.Which will adsorb more gas, a lump of charcoal or its powder and why?
Answer.Powdered form of charcoal, because of greater surface area.
Question. Which one of this will be better reagent to coagulate blood a) FeCl3 b) NaCl c) CaCl2?
Answer.FeCl3because of greater valence of iron according to Hardy Schulz rule
Question. Explain the following:
(i) Same substance can act both as colloids and crystalloids.
(ii) Artificial rain is caused by spraying salt over clouds.
Answer.(i) The nature of the substance whether colloid or crystalloid depends upon size of the solute particles. When the size of solute particles lies between 1 nm to 1000 nm, it behaves as a colloid. Whereas size of particles is less than 1 nm, it behaves as crystalloids.
(ii) The colloidal particles of the clouds that carry charges, get neutralized and coagulated to bigger water drops by spraying salt over clouds and as a result artificial rain is occurred.
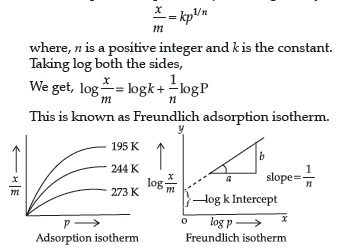
Question. What do you understand by an adsorption isotherm? Give a brief description of Freundlich’s isotherm.
Answer. A graph drawn between extent of adsorption of gas on the adsorbent and the pressure of the gas at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherm. An empirical relationship between the amount of gas adsorbed by unit mass of solid adsorbent (x/m) and the equilibrium pressure (p) can be given by
Question. (i) How does the precipitation of colloidal smoke take place in Cottrell precipitator?
(ii) Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression x/m = kp1/n What conclusions can be drawn from this expression?
Answer. (i) In Cottrell precipitator, charged smoke particles are passed through a chamber containing plates with charge opposite to the smoke particles. Smoke particles lose their charge on coming in contact to the plates and get precipitated. Hence, particles settle down on the floor of the chamber.
(ii) Following conclusions can be drawn from the equation:
(a) When 1/ n = 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure.
(b) When n = 1, x/m vs p graph is a straight line with slope 1. This show xm∝ p, means adsorption is dependent upon the pressure directly.(or any other correct conclusion)
Question. Give reasons for the following observations:
(i) Leather gets hardened after tanning.
(ii) Lyophilic sol is more stable than Lyophobic sol.
Answer.
(i) Animal hides are colloidal in nature. When a hide which has positively charged particles, is soaked in tannin, which contains negatively charged colloidal particles, mutual coagulation takes place. This results in the hardening of leather.
(ii) Lyophilic colloids have great affinity for the Dispersion medium i.e., Dispersed phase particles are solvated to a greater extent in case of lyophilic colloids. Hence, lyophilic sols are relatively more stable than lyophobic sols.
Question. (i) Why is Chemisorption referred to as activated adsorption?
(ii) What type of colloid is formed when a liquid is dispersed and a solid is in dispersion? Give an example.
Answer. (i) Chemisorption involves formation of bonds between the solid surface (adsorbent) and gaseous atoms/molecules (adsorbate). Since formation of chemical bonds requires high activation energy, it is known as activated adsorption.
(ii) Gel is a colloidal solution in which liquid is dispersed in a solid dispersion medium. Example- Cheese / butter.
Question. Define Brownian movement. What is the cause of Brownian movement in colloidal particles? How is it responsible for the stability of Colloidal sol?
Answer. Brownian movement: The particles of the dispersed phase of colloidal solution execute a continuous zigzag motion. This phenomenon is called Brownian movement. Cause of Brownian movement: The dispersed phase particles of the colloidal solution are constantly collided by the molecules of the dispersion medium. Brownian movement opposes the force of gravity on the colloidal particles. So, these particles always remain in a state of motion and do not settle.
Question. Write one difference in each of the following:
(a) Multimolecular colloid and associated colloid
(b) Coagulation and peptization
Answer.
(a) Multimolecular colloids are formed by the aggregate of a large number of molecules which generally have diameter less than nm. e.g.; Sols of gold.
Associated colloids are formed by aggregation of a large number of ions in concentrated solution. e.g., Soap sol.
(b) Coagulation is a process of agitating together the colloidal particles so as to change them into large sized particles which ultimately settle as precipitate. Peptization is the process of converting a fresh precipitate into colloidal particles by shaking it with the dispersion medium in the presence of a small amount of suitable electrolyte.
Question. (i) Why are medicines more effective in colloidal state?
(ii) What is the difference between an emulsion and a gel?
Answer. (i) Due to large surface area these are easily assimilated or adsorbed.
(ii) Emulsion – Both dispersed phase and dispersion medium are liquid. Example – Milk.
Gel- Dispersed phase is liquid while Dispersion medium is solid. Example – Butter.
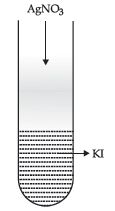
Question. (a) A colloidal sol is prepared by the method in given figure. What is the charge of AgI colloidal particles in the test tube? How is the sol formed, represented?
(b) Which of the following electrolytes is the most effective for the coagulation of Fe(OH)3 sol which is a positively charged sol ?
NaCl, Na2SO4, Na3PO4
Answer. (a) Negative charge is developed on the sol,
Sol is represented as AgI /I–
(b) Na3PO4
Hardy-Schulze rule.
Question. (i) Define adsorption with an example.
(ii) Write one similarity between Physiorption and Chemisorption.
Answer. (i) The phenomenon of accumulation of higher concentration of the molecular species on the surface of the solid than in the bulk is called adsorption. e.g.
Activated charcoal adsorbs a number of gases like ammonia, phosgene etc.
(ii) Both are surface phenomenon / both increase with increase in surface area (or any other correct similarity).
Question. Write the main reason for the stability of colloidal sols.
Answer. The colloidal particles carry same charge which can be either positive charge or negative charge.The similar charged colloidal particles repel each other. This prevents from aggregating when these particles come closer to each other.
Question. With the help of an example, explain how physisorption changes to chemisorption with rise in temperature? Give the reason for the change.
Answer. Adsorption of hydrogen gas on finely divided nickel is physisorption at low temperatures as it involves weak Van der Waals forces. With the rise in temperature, hydrogen molecules dissociate to form hydrogen atoms which are held on the surface by chemisorption.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Desorption
(ii) Critical Micelle Concentration
Answer. (i) The process of removing an adsorbed substance from a surface on which it is adsorbed.
(ii) The formation of micelles takes place only above a particular concentration called CMC.
Question. Write one difference in each of the following:
(i) Lyophobic sol and Lyophilic sol
(ii) Solution and Colloid
Answer. (i) Lyophobic sols are liquid (dispersion medium)- hating and lyophillic sols are liquid (dispersion medium)-loving colloids.
(ii) Solution is a homogeneous mixture while colloid is heterogeneous mixture/does not show Tyndall effect.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Protective colloid
(ii) Zeta potential
Answer. (i) Protective colloid: The process by which the lyophobic sols are protected from coagulation
by electrolytes due to the previous addition of a lyophilic colloid is called protection and the colloids are called Protective colloids.
(ii) Zeta potential: It is the potential difference between the dispersion medium and the stationary layer of fluid attached to the dispersed particle.
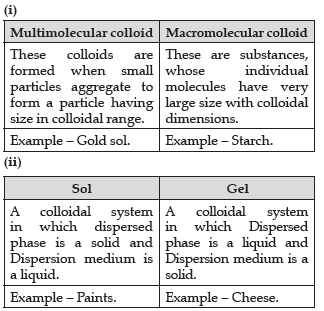
Question. Write one difference between each of the following:
(i) Multimolecular colloid and Macromolecular colloid
(ii) Sol and Gel
Answer.
Question. (i) Write the expression for Freundlich’s equation to describe the behaviour of adsorption from solution phase.
(ii) What causes charge on sol particles?
Answer. (i) Frendlich adsorption isotherm, x/m = kC1/n
Where, x/m = quantity of gas adsorbed in unit mass of solid adsorbent
C = equilibrium concentration k, n = constants at a given temperature
(ii) The charge on the sol particles is due to:
(a) Electron capture by sol particles during electrodispersion.
(b) Preferential adsorption of ions from solution.
(c) Formulation of electrical double layer.
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. (i) Differentiate between Adsorption and Absorption.
(ii) Out of MgCl2 and AlCl3, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged sol and why ?
(iii) Out of sulphur sol and proteins, which one forms multimolecular colloids ?
Answer.

(ii) AlCl3 is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged sol because according to Hardy and Schulze rule, greater the valency of the flocculating ion, greater is its ability to bring coagulation.
(iii) Sulphur sol forms multimolecular colloids.
Question. Write three differences between lyophobic sol and lyophilic sol.
Answer. Differences between lyophobic and lyophilic sol:

Question. (a) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of dust.
(b) Why does Physisorption reversible whereas Chemisorption is irreversible?
(c) A colloidal sol is prepared by the method given in the figure. What is the charge on AgI colloidal particles formed in the test tube?
How is this sol represented?
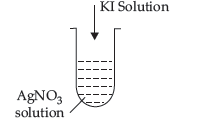
Answer. (a) Dispersed phase = Liquid;
Dispersion medium = Gas
(b) Due to weak Van der Waal’s forces in physisorption whereas strong chemical forces in chemisorption.
(c) Positively charged , AgI/Ag+
Question. What happens when
(a) a freshly prepared precipitate of Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a small amount of FeCl3 solution ?
(b) persistent dialysis of a colloidal solution is carried out ?
(c) an emulsion is centrifuged ?
Answer.
(a) When a freshly prepared precipitate of Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a small amount of FeCl3 solution, peptisation occurs by converting the Fe(OH)3 precipitate into colloidal solution of positively charged Fe(OH)3.
(b) On persistent dialysis, the electrolyte present is completely removed resulting in the coagulation of the colloidal solution.
(c) On centrifugation, an emulsion gets separated into its constituent liquids.
Question. (a) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk.
(b) Write one similarity between physisorption and chemisorption.
(c) Write the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3
Answer.
(a) Dispersed phase of milk: Liquid
Dispersion medium of milk: Liquid
(b) Physisorption and chemisorption depend on the nature of the gas / both are exothermic processes.
(c) A red sol of Fe(OH)3 is obtained by adding some ferric chloride to a beaker of boiling water.
FeCl3 + 3H2O → Fe(OH)3 + 3HCl
Question. Write any three differences between Physisorption and Chemisorption.
OR
Write three differences between Physisorption and Chemisorption.
Answer.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Lyophilic colloid,
(ii) Zeta potential,
(iii) Associated colloids.
Answer. (i) Lyophilic colloid: Liquid loving colloidal sols directly formed by mixing substances like gum, gelatin, starch, rubber, etc., with a suitable liquid (the dispersion medium) are called lyophilic sols.e.g., muddy water.
(ii) Zeta potential: The potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charges is called the Electrokinetic potential or Zeta potential.
(iii) Associated colloids: There are some substances which at low concentrations behave as normal strong electrolytes, but at higher concentrations exhibit colloidal behaviour due to the formation of aggregates. The aggregated particles thus formed are called Associated colloids or Micelles.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(a) Which of the following electrolytes is most effective for the coagulation of AgI/Ag+ sol?
MgCl2, K2SO4, K4[Fe(CN)6]
(b) What happens when a freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a little amount of dilute solution of FeCl3?
(c) Out of Sulphur sol and Proteins, which one forms Macromolecular colloids?
Answer.
(a) According to the Hardy-Schulze rule, greater the valence of the flocculating ion, greater is its ability to bring coagulation. Thus,
K4[Fe(CN)6] is most effective in coagulation of AgI/Ag+ sol.
(c) Macromolecular colloids are molecularly dissolved solutions of a polymer with particle size of colloidal range. Proteins are polymers of amino acids and form macromolecular colloids.
Question. Answer the following questions:
(i) What happens when a freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a little amount of dilute solution of FeCl3 ?
(ii) Why are lyophilic colloidal sols more stable than lyophobic colloidal sols ?
(iii) What form Freundlich adsorption equation will take at high pressure ?
Answer. (i) A reddish brown coloured colloidal solution is obtained.
(ii) Stability of lyophilic sols is due to:
(a) same charge on all the colloidal particles.
(b) solvation of the colloidal particles.
(iii) At high pressure amount of gas adsorbed (x/m) becomes independent of pressure (p).
x/m = k × p°
Freundlich isotherm fails at high pressure, because rate of adsorptions saturates at high pressure.
Question. (a) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk.
(b) Why is adsorption exothermic in nature?
(c) Write Freundlich adsorption isotherm for gases at high pressure.
Answer. (a) Dispersed phase = liquid
Dispersion medium = liquid
(b) Due to the formation of new bonds / force of attraction between adsorbate and adsorbent
(c) x/m = kp° = k
Question. (a) Write the dispersed phase and Dispersion medium of butter.
(b) Why does physisorption decrease with increase in temperature?
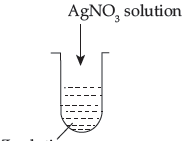
(c) A colloidal sol is prepared by the method given in the figure. What is the charge on AgI colloidal particles formed in the test tube?
How is this sol represented?
Answer.
(a) Dispersed phase: Liquid Dispersion medium: Solid
(b) Physisorption decrease with increase in temperature because it is an exothermic reaction.
(c) When AgNO3 solution is added to KI solution, negatively charged sol of AgI is formed due to elective adsorption of I– ion from the dispersion medium. It is represented as given below.
AgI/I– is Negatively charged.
Question. Give reason for the following observations:
(i) When silver nitrate solution is added to Potassium Iodide solution, a negatively charged colloidal solution is formed.
(ii) Finely divided substance is more effective as an adsorbent.
(iii) Lyophilic colloids are also called reversible sols.
Answer. (i) The precipitated Silver Iodide adsorbs Iodide ions from the Dispersion medium resulting in the negatively charged colloidal solution.
(ii) Due to large surface area.
(iii) If the dispersion medium is separated from the dispersed phase, the sol can be reconstituted by simply remixing with the dispersion medium. That is why, these sols are also called
reversible sols.
Question. (i) What is the role of activated charcoal in gas mask?
(ii) A colloidal sol is prepared by the given method in figure. What is the charge on hydrated Ferric Oxide colloidal particles formed in the test tube?
How is the sol represented?
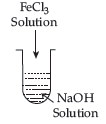
(iii) How does Chemisorption vary with temperature?
Answer.
(i) The activated charcoal adsorbs the poisonous gases rather than oxygen and provides fresh oxygen for inhaling.
(ii) When ferric chloride is added to NaOH, a negatively charged sol is formed with adsorption of OH– ions.
The sol is represented as [Fe(OH)3]OH–.
(iii) Adsorption is an exothermic process. According to Le-Chatelier’s principle at low temperature, forward reaction is favourable. As temperature increases, enough energy is being provided for the molecules to reach the activation energy. Therefore, initially as temperature increases chemisorption increases. As the high temperature helps in bond breaking after certain temperature, chemisorption decreases.
Question. Explain the following phenomenon giving reasons:
(i) Chemical adsorption increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Alum is applied on a cut to stop bleeding.
(iii) Sky appears blue in colour.
Answer.
(i) Increase in temperature provides high energy of activation required in chemical adsorption to form chemical bonds.
(ii) It is due to coagulation of blood. Alum acts as an electrolyte which coagulates blood because blood is a colloidal solution.
(iii) The light gets incident on the atmospheric particles scatters the sunlight. Due to larger scattering of blue colour, sky appears blue in colour.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Define the following:
(i) Gold Number
(ii) Hardy-Schulze rule
(iii) Zeta Potential
(iv) CMC
(v) Electrophoresis
Answer. (i) The number of milligram of protective collides which must be added to 10 ml of given gold sol to prevent it from coagulation by addition of 1 ml of 10% of NaCl.
(ii) The coagulating power of electrolyte increases with increase in charge on the ions used for coagulation
e.g., Al3+ > Ba2+ > Na+ for negatively charged colloids.
[Fe(CN)6]4– > PO43– SO42– > Cl– for positively charge d colloids.
(iii) The potential difference between the fixed layer and diffused payer of opposite charges is called Zeta Potential.
(iv) Critical micelle concentration is the concentration of a surfactant in the bulk phase above which aggregates of surfactant molecules start formation of micelle.
(v) The movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an electric field where negatively charged particles move towards the cathode and positively charged particles move towards anode.
Question. Differentiate between multi-molecular and macro- molecular colloids. Name one example of each. How does associated colloids differ fro these two colloids?
Answer. (i) In multi-molecular colloids, the colloidal particles are aggregate of atoms or small molecules with a diameter of less than 1nm. The molecules in the aggregate are held together by Van der Waals forces of attraction. Examples of such colloids include Gold sol and Sulphur sol.
(ii) In macro-molecular colloids, the colloidal particles are large molecules having colloidal dimensions. These particles have a high molecular mass. When these particles are dissolved in a liquid, sol is obtained.
For example : Starch, Nylon, Cellulose, etc.
(iii) Certain substances tend to behave like normal electrolytes at lower concentrations.
However, at higher concentrations these substances behave as colloidal solutions due to the formation of aggregated particles. Such colloids are called aggregated colloids.


