Please refer to Concept of Programming and Programming Languages Class 11 Computer Science Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Computer science based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Computer Science for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Computer Science Important Questions Concept of Programming and Programming Languages
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question: What are Procedure Oriented Programming Languages?
Ans: Procedure Oriented Languages are considered as third generation programming languages (3GLs). To create programs in these languages, it is divided into small procedures or subroutines. Each procedure contains a series of instructions for carrying out a specific task. After creating the procedure, we can use them one or more times anywhere in the program. The sequence of program instructions in these languages is very important. FORTRAN, COBOL, Pascal, C, etc. are examples of some popular procedural languages.
Question: What are Syntax Errors?
Ans: These are the errors that occur when we develop programs that do not follow the rules or syntax of programming language. These types of errors are automatically detected by compilers during the compilation process. A program cannot be successfully compiled until all syntax errors in the program have been corrected. Some examples of syntax errors in C language are: Missing Semicolon, Variable not declared, etc.
Question: Write the names of different symbols used in flowcharts.
Ans: Following are the different symbols used in the flow chart:
• Terminal (Oval symbol)
• Input / Output (parallelogram)
• Processing (rectangle)
• Diamond (rhombus)
• Flow lines (arrows)
• Connectors (circles)
Question: What is Programming?
Ans: Programs are a set of instructions that a computer can understand to perform a task. The process of writing these instructions into a program is called programming. The person who writes the program is called the programmer.

Question: Write the steps used in Programming Process.
Ans: The steps used in the programming process are as follows:
1. Define the problem to be solved
2. Develop a plan for solving problem
3. Coding the solution in high level language
4. Compile the program
5. Test and debug the program
6. Documenting the program
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question: What are Language Translators? Explain any one translator in detail.
Ans: Language translators are also called language processors. These are system-programs. The purpose of developing language translators is to accomplish two main tasks: first, to translate source programs into Object Code, and second, to detect syntax errors in the source program. Each language has its own translator program that can only translate programs written in that particular language. Examples of language translators are: assemblers, compilers and interpreter.
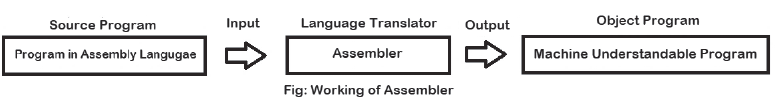
Assembler: This is a language translator that converts programs written in assembly language into machine language. A program written in assembly language is called a source program. This source program cannot be directly understood by the computer. Therefore, it is necessary to translate it into a machine-understandable format. It is the assembler that converts the source program of the assembly language into a machine-understandable program. The code generated after translation is called the object program, which is used to execute the program.
Question: What are low level programming languages? Explain their advantages and disadvantages.
Ans: Machine and assembly languages are called low-level languages. These are explained below:
• Machine language: Machine language is also called binary language. It is the fundamental language of computer systems because it is understood directly by the computer system. The computer does not require any translation to understand this language. This language is made up of only two binary digits 0 and 1.
• Assembly Language: This language is also called Symbolic Language because it uses the symbolic names of the instructions instead of the binary code. The symbolic names of the assembly language instructions can be easily remembered.
Advantages of Low-Level Languages:
• These languages can communicate / interact directly with computer hardware
• These languages work faster than computers.
Disadvantages of Machine Language:
• For programming in low level languages, the programmer needs to know the internal structure of the hardware.
• Programs created in low level languages are machine dependent.
Question: Explain different types of errors found in the computer programs.
Ans: There are two common types of errors in programs:
• Syntax Errors: These are the errors that occur when we develop programs that do not follow the rules or syntax of programming language. These types of errors are automatically detected by compilers during the compilation process. A program cannot be successfully compiled until all syntax errors in the program have been corrected. Some examples of syntax errors in C language are: Missing Semicolon, Variable not declared, etc.
• Logical Errors: These errors occur when there are the errors in the logic of the program. If there are logical errors in our program, it will be successfully compiled but it will produce incorrect results / output. Such errors cannot be detected by the compiler. These can be easily found with the help of debugging tools.
Question: What is algorithm? Explain the different features that an algorithm should have.
Ans: Creating algorithms is a basic requirement in computer programming. This is a step-by-step description of how to solve a given problem. An algorithm has limited steps and it should always produce some (right or wrong) result. Before creating a program, a programmer first sets the algorithm. An algorithm should have the following features:
• Every step must be accurate.
• Every step should be clear, which means it should not be ambiguous.
• Input and output should be carefully determined.
• Steps should not be repeated indefinitely.
• After implementing the steps, the required output should be obtained in any case.


