See below CBSE Class 12 Economics Term 1 Sample Paper Set B with solutions. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics as per the latest paper pattern issued by CBSE for the current academic year. All sample papers provided by our Class 12 Economics teachers are with answers. You can see the sample paper given below and use them for more practice for Class 12 Economics examination.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Economics Term 1 Set B
Section A
1. Money is the most liquid form of asset due to which of the following reasons?
(a) It can be exchanged easily
(b) It can be stored without any additional cost
(c) Its value remains constant overtime
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
2. Government has no role to play in which of the ……… policies.
(a) fiscal
(b) monetary
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
B
3. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Social discrimination intensifies the incidence of poverty in the country.
Statement II People are generally discriminated on economic ground and hence not able to earn sufficient income.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
4. Short-term objectives vary from plan to plan to depend on current needs of the country. For example, first plan (1951-56) focused on higher agricultural production while in second plan (1956-61) shifted the focus from agriculture to industry. In India, growth and equity are the objectives of all the five-year plans. The goal of 12th five-year plan, 2012-17 was
(a) inclusive development
(b) exclusive development
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
A
5. The regulatory body set up for the medical research and development in India is ICMR. Its full form is ……… .
(a) International Council of Medical Research
(b) Indian Council of Medical Resources
(c) International Council of Medical Resources
(d) Indian Council of Medical Research
Answer
B
6. Which of the following factors has led to low economic growth in the country?
(a) Changing economic structure
(b) Jobless growth
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
7. India’s foreign trade policy have changed many times since independence. In the initial phase, India followed a closed macroeconomic model and tried to fulfil the domestic demand by domestically produced goods. This strategy was technically known as
(a) Export promotion
(b) Import substitution
(c) Inward looking trade
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
B
8. ……… is/are advantage(s) of loans taken from moneylenders.
(a) Easy procedure of lending
(b) Available for both productive and unproductive purposes
(c) Loans are non-collateralised
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
9. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I The value of money remains constant overtime making it the most preferred medium of exchange.
Statement II General price level and purchasing power of money are inversely proportional.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
10. WTO is ……… based organisation as compared to GATT, also the trade under WTO is based on bilateral and multi-lateral agreements.
(a) rule
(b) agreement
(c) international
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
11. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Fines and penalties imposed by the government are part of non-tax revenue of the union budget.
Statement II Non-tax revenue is the major component of governments receipts.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
A
12. ……… concept of poverty is used in a comparative aspect.
(a) Absolute poverty
(b) Relative poverty
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
B
13. Export of goods and services lead to ……… in the stock of foreign exchange reserves.
(a) rise
(b) fall
(c) no change
(d) None of these
Answer
A
14. ……… is excluded from current account of BoP.
(a) Investment incomes
(b) Invisible trade
(c) Merchandise trade
(d) Investment from rest of the world
Answer
D
15. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Reserve Bank of India issues all currencies in the country except one-rupee notes.
Statement II Intrinsic value of coins must be less than the denominated value of the same.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
A
16. In agriculture marketing, when the price of goods is set by government, it is known as ……… .
(a) Minimum support price
(b) Regulated price
(c) Market price
(d) None of these
Answer
B
17. Recently, government of India merged several public sector banks due to strategic reasons. This step leads to which of the following impact on the money supply in the economy?
(a) Increase in money supply
(b) Decrease in money supply
(c) No change in money supply
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer
C
18. The price of one currency in terms of another is known as ……… .
(a) Foreign exchange
(b) Foreign exchange rate
(c) Interest rate
(d) Trade rate
Answer
B
19. Poverty alleviation programmes in the country faced a major setback due to which of the following reasons?
(a) Gender discrimination
(b) Caste system
(c) Inefficient macroeconomic policies
(d) All of these
Answer
D
20. The fraction by which money is multiplied in the economy is known as ……… .
(a) Primary deposit
(b) Legal reserve ratio
(c) Money multiplier
(d) None of these
Answer
C
21. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Under the fixed exchange rate system, the price of currency once fixed cannot be changed ever.
Statement II Managing exchanging rate brings stability in the system.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
22. Operation flood leads to increase in production milk through organising milk cooperative. This shows ……… .
(a) agricultural marketing
(b) diversification of agriculture
(c) centralisation
(d) commercialisation
Answer
B
23. Choose the correct pair from given below
Column I Column II
A. Export and import of goods (i) Balance of invisibles
B. Unilateral receipts (ii) Capital account
C. Increase in for-ex reserves (iii) Debit item of BoP
D. Import of machinery (iv) Credit item of BoP
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) D – (iv)
Answer
C
24. ……… is a central government scheme which focused upon financial inclusion to target poverty by promoting self-employment.
(a) MGNERGA
(b) Jan Dhan Yojana
(c) PMGSY
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Section B
25. Opening of Suez Canal served as a direct route between India and Britain, when was it started?
(a) 1869
(b) 1881
(c) 1907
(d) 1909
Answer
A
26. ……… is/are the component(s) of globalisation process under the new economic policy of 1991.
(a) Partial convertibility of the Indian rupee
(b) Increase in equity limit of foreign investment
(c) Reduction in tariffs
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
27. Assertion (A) The primary objective of the central bank is welfare of the general public.
Reason (R) Commercial banks are the financial institutions which works for the motive of maximising the profit.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
28. ……… is among the economist who estimated per capita income during colonial period.
(a) William Digby
(b) Findley Shirras
(c) Dadabhai Naoroji
(d) All of these
Answer
C
29. Which of the following is not a function of a commercial bank?
(a) Creation of credit
(b) Advancement of loans
(c) Custodian of foreign exchange
(d) Accepting deposits
Answer
C
30. Assertion (A) Foreign investment from abroad to India will be recorded on the debit side of the capital account in the balance of payments account.
Reason (R) Foreign investment in India is of capital nature which leads to inflow of foreign currency.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
C
31. ……… refers to migration of people between country and considered as problem of human capital formation.
(a) Relative poverty
(b) Illiteracy
(c) Brain drain
(d) None of these
Answer
C
32. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Poor life expectancy during colonial rule is attributed to poor health andfamines.
Statement II Life expectancy rate of India during colonial rule was 44 years.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
33. Assertion (A) Economic inequality has created more poor people in the country than unemployment.
Reason (R) The changing structure of the economy leads to displacement of people from employment as they are not able to adapt to the latest techniques.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
34. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Although there is a steady decline in poverty over the last two decades, but total number of the poor people have remained constant.
Statement II Poverty in urban areas have decreased at a slower pace as compared to urban areas.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
35. Choose the correct statement from given below related to Indian economy between 1950-90.
(a) The share of agricultural products in country’s exports increased
(b) The share of agricultural products increased while that of manufacturers decreased
(c) The share of manufactured goods in country’s exports increased
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
36. Assertion (A) Governor of RBI gives advise to central government regarding tax revenue.
Reason (R) It is imperative for the central government to follow the advise of RBI.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Both are false
Answer
D
37. Choose the correct pair from given below.
Column I Column II
A. Migration (i) Physical capital
B. Knowledge resource (ii) Labour supply
C. Employment exchange (iii) Getting information regarding jobs
D. Property (iv) Working in another city
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) D – (iv)
Answer
C
38. Assertion (A) Rapid growth of the banking system had a positive impact on rural farm and non-farm output.
Reason (R) The institutional credit arrangement continues to be inadequate.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
39. The vegetable and fruit market in Andhra Pradesh is called as ……… .
(a) Apni Mandi
(b) Hadaspar Mandi
(c) Rythu Bazars
(d) Uzhavar Sandies
Answer
C
40. Assertion (A) Accommodating items of trade are undertaken to bring BoP to surplus.
Reason (R) Accommodating items are net consequences of autonomous transactions that are undertaken to correct imbalance in autonomous items of BoP.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
C
41. Choose the correct pair from given below.
Column I Column II
A. Prior to 1921 (i) Death rate
B. After 1921 (ii) First stage of demography
C. The number of death per 1,000 persons in a year (iii) Second stage of demography
D. The number of births per 1,000 person in a year (iv) Birth rate
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) D – (iv)
Answer
D
42. Assertion (A) Modernisation as an objective of planning means adoption of new technology along with a change in the social and economic outlook.
Reason (R) With the progress of the economy, techniques of production along with preference of people also changes.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
43. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Import of services leads to increase in supply of foreign exchange.
Statement II Import of both goods and services is part of current account of BoP.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
44. Assertion (A) Role of RBI changed from being a regulator to a facilitator during the new economic reforms.
Reason (R) The financial market of the country is regulated by RBI.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
45. Kerala, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and Haryana have good HDIs. But states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Odisha have HDIs close to nearly one-half to that of Kerala. Which of the following reasons can be attributed for good HDIs of Kerala, Punjab, etc?
(a) Better education facility
(b) Proper implementation of policies
(c) People participation
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
46. Assertion (A) The high default rate of agricultural loans has led to lower sanction rate of agricultural credit.
Reason (R) Agriculture has remained a risky occupation due to natural constraint in farming.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
47. Choose the incorrect statement from given below.
(a) Demand deposits with commercial banks are a liquid component of money supply
(b) Increase in M1 indicates increase in money supply in the economy
(c) Time deposits are most liquid measure of money supply
(d) RBI controls the ability of commercial bank to create money
Answer
C
48. Observe the image graph below.
Assuming that the above curve shows the demand curve for foreign exchange, the movement from point A to B represents which of the following?
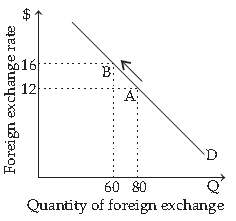
(a) Appreciation of domestic currency
(b) Depreciation of domestic currency
(c) Depreciation of foreign currency
(d) Revaluation of domestic currency
Answer
B
Section C
Direction Read the following case study and answer questions 49 to 54 on the basis of the same.
On 8th November, 2016, Prime Minister Narendra Modi in a surprise announcement said the existing higher denomination currency (₹ 500 and ₹ 1,000) will cease to be legal tenders. PM said this is government’s biggest push to fight black money and end corruption. The opposition, however, criticised the government for poor implementation of the scheme and said a lot of people have died standing in queues trying to get their hands on the new currency.
The government introduced new ₹ 500 and ₹ 2,000 notes and urged people to move towards cash-less economy. This is not the first time that demonetisation has been implemented in India. In 1936, ₹10,000, which was the highest denomination note, was introduced but was demonetised in 1946. Though, it was re-introduced in 1954 but later, in 1978, the then Prime Minister Morarji Desai in his intensive move to counter the black money, introduced The High Denomination Banks Act (Demonetisation) and declared ₹ 500, ₹ 1,000 and ₹ 10,000 notes illegal.
49. Which of the following is true about the demonetisation policy?
(a) It refers to the removal of legal tender status of the existing currency notes
(b) The exchange of goods and services is not possible using the existing currency notes
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
50. The recent demonetisation was carried with which of the following objectives?
(a) Removing black money from the economy
(b) To bring transparency in the system
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
51. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Demonetisation resulted in increase in digital modes of payments.
Statemant II Digitalisation brings transparency in the system.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
52. Before 2016, how many times demonetisation policy was adopted in India?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Answer
B
53. Assertion (A) Demonetisation increases the economic growth of the country by increasing number of tax payers.
Reason (R) Post-demonetisation, many shall companies were identified and shut down leading to increase in money supply.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of
Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation
of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
54. First demonetisation in India happened in which year?
(a) 1936
(b) 1946
(c) 1954
(d) 1978
Answer
A
Direction : – Read the following case study and answer questions 55 to 60 on the basis of the same.
In India, there is a constitutional requirement as per Article 112 to present before the Parliament a statement of estimated receipts and expenditures of the government in respect of every financial year, which runs from 1st April to 31st March.
This ‘Annual Financial Statement’ constitutes the main budget document of the government. Although the budget document relates to the receipts and expenditures of the government for a particular financial year, the impact of it will be there in subsequent years. There is a need therefore to have two accounts, i.e. those that relate to the current financial year only are included in the revenue account (also called revenue budget) and those that concern the assets and liabilities of the government into the capital account (also called capital budget). In order to understand the accounts, it is important to first understand the objectives of the government budget.
55. Which of the following components of government budget is based upon influencing the burden of future liability?
(a) Revenue budget
(b) Capital budget
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
B
56. Which of the following is not a component of revenue budget?
(i) Capital receipts
(ii) Revenue receipts
(iii) Capital expenditure
(iv) Revenue expenditure
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
A
57. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Corporate profit tax will be a part of revenue budget.
Statement II Revenue budget is non-recurring in nature.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
A
58. Assertion (A) The union budget in India is presented before the Parliament twice during the fiscal year.
Reason (R) Budget presented by the government is comprised of revenue budget and capital budget in its estimated form.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
C
59. Which of the following is a form of indirect tax as a component of revenue receipts of the budget?
(a) Wealth tax
(b) Income tax
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
D
60. All the components of revenue budget are in ……… terms.
(a) actual
(b) potential
(c) estimated
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
C

