See below CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Term 1 Sample Paper Set B with solutions. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry as per the latest paper pattern issued by CBSE for the current academic year. All sample papers provided by our Class 12 Chemistry teachers are with answers. You can see the sample paper given below and use them for more practice for Class 12 Chemistry examination.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry Term 1 Set B
Section ‘A’
1. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) Melting point of Phosphorous is less than that of Nitrogen
(B) N2 is highly reactive while P4 is inert
(C) Nitrogen shows higher tendency of catenation than P
(D) N-N is weaker than P-P
Answer
D
2. Which of the following is a non-stoichiometric defect?
(A) Frenkel defect
(B) Schottky defect
(C) Metal deficiency defect
(D) Interstitial defect
Answer
C
3. Identify the law which is stated as:
“For any solution, the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction.”
(A) Henry’s law
(B) Raoult’s law
(C) Dalton’s law
(D) Gay-Lussac’s Law
Answer
B
4. Pink colour of LiCl crystals is due to:
(A) Schottky defect
(B) Frenkel defect
(C) Metal excess defect
(D) Metal deficiency defect
Answer
B
5. Which of the following isomer has the highest melting point?
(A) 1,2-Dicholorbenzene
(B) 1,3 -Dichlorobenzene
(C) 1,4-Dicholorbenzene
(D) All isomers have same melting points
Answer
C
6. Which one of the following reactions is not explained by the open chain Structure of glucose:
(A) Formation of pentaacetate of glucose with acetic anhydride.
(B) Formation of addition product with 2,4 DNP reagent
(C) Silver mirror formation with Tollen’s reagent
(D) Existence of alpha and beta forms of glucose.
Answer
D
7. Williamson’s synthesis of preparing dimethyl ether is an:
(A) SN1reaction
(B) Elimination reaction
(C) SN2reaction
(D) Nucleophilic addition reaction
Answer
C
8. Chlorine water loses its yellow colour on standing because:
(A) HCl gas is produced, due to the action of sunlight.
(B) A mixture of HOCl and HCl is produced in the presence of light
(C) HOCl and hydrogen gas is produced
(D) A mixture of HCl and ClO3 is produced, due to the action of sunlight
Answer
B
9. During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with concentrated H2SO4, the initiation step is:
(A) Protonation of alcohol molecule
(B) Formation of carbocation
(C) Elimination of water
(D) Formation of an ester
Answer
A
10. Amorphous solids are:
(A) Isotropic
(B) Anisotropic
(C) Isotopic
(D) Isomeric
Answer
A
11. Which of the following reactions is used to prepare salicylaldehyde?
(A) Kolbe’s reaction
(B) Étard’s reaction
(C) Reimer-Tieman reaction
(D) Stephen’s reduction.
Answer
C
12. Which of the following is an example of a solid solution?
(A) Sea water
(B) Sugar solution
(C) Smoke
(D) 22 carat gold
Answer
D
13. The boiling points of alcohols is higher than those of hydrocarbons of comparable masses due to presence of:
(A) Hydrogen bonding
(B) Ion – dipole interaction
(C) Dipole- dipole interaction
(D) Van der Waal’s forces.
Answer
A
14. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
(A) H2O
(B) H2S
(C) H2Se
(D) H2Te
Answer
B
15. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) Fibrous proteins are generally soluble in water.
(B) Albumin is an example of fibrous proteins.
(C) In fibrous proteins, the structure is stabilised due to formation of hydrogen bonds and disulphide bonds.
(D) pH does not affect the primary structure of protein.
Answer
D
16. Major product obtained on reaction of 3-Phenyl propene with HBr in presence of organic peroxide:
(A) 3- Phenyl 1- bromopropane
(B) 1 –Phenyl -3- bromopropane
(C) 1-Phenyl -2-bromopropane
(D) 3-Phenyl -2- bromopropane
Answer
B
17 Which of the following is a correct statement for C2H5Br?
(A) It reacts with metallic Na to give ethane.
(B) It gives nitroethane on heating with aqueous solution of AgNO2.
(C) It gives C2H5OH on boiling with alcoholic potash.
(D) It forms diethyl thioether on heating with alcoholic KSH.
Answer
B
18. Covalency of nitrogen is restricted to:
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer
C
19. Solubility of gases in liquids decreases with rise in temperature because dissolution is an:
(A) Endothermic and reversible process
(B) Exothermic and reversible process
(C) Endothermic and irreversible process
(D) Exothermic and irreversible process
Answer
B
20. All elements of Group 15 show allotropy except:
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Arsenic
(C) Antimony
(D) Bismuth
Answer
A
21. Which of the following is a polysaccharide?
(A) Glucose
(B) Maltose
(C) Glycogen
(D) Lactose
Answer
C
22. Substance having the lowest boiling point:
(A) Hydrogen
(B) Oxygen
(C) Nitrogen
(D) Helium
Answer
D
23 Lower molecular mass of alcohols are:
(A) Miscible in limited amount of water
(B) Miscible in excess of water
(C) Miscible in water in all proportions
(D) Immiscible in water
Answer
C
24. Maximum oxidation state exhibited by Chlorine is:
(A) +1
(B) +3
(C) +5
(D) +7
Answer
D
25. In which of the following cases blood cells will shrink:
(A) When placed in water containing more than 0.9% (mass/ volume) NaCl solution.
(B) When placed in water containing less than 0.9% (mass /volume) NaCl solution.
(C) When placed in water containing 0.9% (mass/volume) NaCl solution.
(D) When placed in distilled water.
Answer
A
Section ‘B’
26. How much ethyl alcohol must be added to 1 litre of water so that the solution will freeze at– 14°C ?
(Kf for water = 1.86°C/mol).
(A) 7.5 mol
(B) 8.5 mol
(C) 9.5 mol
(D) 10.5 mol
Answer
B
27. Which reagents are required for one step conversion of chlorobenzene to toluene?
(A) CH3Cl / AlCl3
(B) CH3Cl, Na, Dry ether
(C) CH3Cl/Fe dark
(D) NaNO2/ HCl /0-5°C
Answer
B
28. On partial hydrolysis, XeF6 gives:
(A) XeO3 +4HF
(B) XeO2F + HF
(C) XeOF4+ 2HF
(D) XeO2F2 + 4HF
Answer
C
29. Which one of the following statement is correct about sucrose :
(A) It can reduce tollen’s reagent however cannot reduce fehling’s reagent
(B) It undergoes mutarotation like glucose and fructose
(C) It undergoes inversion in the configuration on hydrolysis
(D) It is laevorotatory in nature .
Answer
C
30. Phenol does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction easily due to:
(A) Acidic nature of phenol
(B) Partial double bond character of C-OH bond
(C) Partial double bond character of C-C bond
(D) Instability of phenoxide ion
Answer
B
31. Which of the following has highest ionisation enthalpy?
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Phosphorus
(C) Oxygen
(D) Sulphur
Answer
A
32. Metal M ions form a ccp structure. Oxide ions occupy ½ octahedral and ½ tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the oxide?
(A) MO
(B) MO2
(C) MO3
(D) M2O3
Answer
D
33. The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in presence of FeCl3 gives ‘X’ while the toluene with Cl2 in presence of light gives ‘Y’. Thus ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are:
(A) X = benzyl chloride Y = o and p – chlorotoluene
(B) X = m – chlorotoluene Y = p – chlorotoluene
(C) X = o and p–chlorotoluene Y = trichloromethyl benzene
(D) X= benzyl chloride, Y = m-chlorotoluene
Answer
D
34. Ozone is a/ an ______________molecule and the two O-O bond lengths in ozone are (i) ______________ and (ii) ______________
(A) Linear ,110pm ; 148pm
(B) Angular, 110pm ; 148pm
(C) Linear, 128pm ; 128pm
(D) Angular, 128pm ; 128pm
Answer
D
35. Water retention or puffiness due to high salt intake occurs due to:
(A) Diffusion
(B) Vapour pressure difference
(C) Osmosis
(D) Reverse osmosis
Answer
C
36. In the following reaction, identify A and B:

(A) A= COOH – (CH2)4 – COOH, B= OHC – (CHOCOCH3)4 – CH2OCOCH3
(B) A= COOH – (CH2)4 – CHO, B=OHC – (CHOCOCH3)4 – CH2OCOCH3
(C) A= OHC – (CHOCOCH3)3 – CH2OCOCH3 B=COOH – (CH2)4 – CHO,
(D) A= OHC – (CHOCOCH3)4 – CH2OCOCH3 B=COOH – (CHOH)4 – COOH
Answer
D
37. In lake test for Al3+ ions, there is the formation of coloured ‘floating lake’. It is due to:
(A) Absorption of litmus by [Al(OH)4]–
(B) Absorption of litmus by Al(OH)3
(C) Adsorption of litmus by [Al(OH)4]–
(D) Adsorption of litmus by Al(OH)3
Answer
D
38. A unit cell of NaCl has 4 formula units. Its edge length is 0.50 nm. Calculate the density if molar mass of NaCl = 58.5 g/mol.
(A) 1 g/cm3
(B) 2 g/cm3
(C) 3 g/cm3
(D) 4g/cm3
Answer
C
39. Which one of the following are correctly arranged on the basis of the property indicated?
(A) I2< Br2<F2<Cl2 [ increasing bond dissociation enthalpy]
(B) H2O > H2S<H2Te<H2Se [increasing acidic strength]
(C) NH3 < N2O< NH2OH<N2O5 [ increasing oxidation state]
(D) BiH3<SbH3<AsH3<PH3<NH3 [ increasing bond angle]
Answer
D
40. What would be the reactant and reagent used to obtain 2, 4-dimethyl pentan-3-ol ?
(A) Propanal and propyl magnesium bromide
(B) 3-methylbutanal and 2-methyl magnesium iodide
(C) 2-dimethylpropanone and methyl magnesium iodide
(D) 2- methylpropanal and isopropyl magnesium iodide
Answer
D
41. o-hydroxy benzyl alcohol when reacted with PCl3 gives the product as (IUPAC name)
(A) o- hydroxy benzyl chloride
(B) 2- chloromethylphenol
(C) o-chloromethylchlorobenzene
(D) 4-hydroxymethylphenol
Answer
B
42. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) Ammonia is the weakest reducing agent and the strongest base among Group 15 hydrides.
(B) Ammonia is the strongest reducing agent as well as the strongest base among Group 15 hydrides.
(C) Ammonia is the weakest reducing agent as well as the weakest base among Group 15 hydrides.
(D) Ammonia is the strongest reducing agent and the weakest base among Group 15 hydrides.
Answer
A
43. Identify the secondary alcohols from the following set :
(i) CH3CH2CH(OH) CH3
(ii) (C2H5)3COH

(A) (i) and (iv)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (i) and (ii)
(D) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
44. Alkenes decolourise bromine water in presence of CCl4 due to formation of:
(A) Allyl bromide
(B) Vinyl bromide
(C) Bromoform
(D) Vicinal dibromide
Answer
D
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
45. Assertion (A): Electron gain enthalpy of oxygen is less than that of Flourine but greater than Nitrogen.
Reason (R): Ionisation enthalpies of the elements follow the order Nitrogen > Oxygen > Fluorine.
Answer
C
46. Assertion (A): Alkyl halides are insoluble in water.
Reason (R): Alkyl halides have halogen attached to sp3 hybrid carbon.
Answer
B
47. Assertion(A): Molarity of a solution changes with temperature.
Reason (R): Molarity is a colligative property.
Answer
C
48. Assertion(A): SO2 is reducing agent while TeO2 is an oxidising agent.
Reason(R):Reducing property of dioxide decreases from SO2 to TeO2.
Answer
A
49. Assertion (A): Cryoscopic constant depends on nature of solvent.
Reason(R): Cryoscopic constant is a universal constant.
Answer
C
Section ‘C’
50. Match the following:
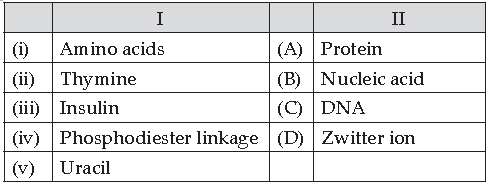
Which of the following is the best matched options?
(A) i-A, v- D, iii- C, iv-B
(B) i-D, ii-C, iii- A, iv-B
(C) i-D, v- D, iii- A, iv-B
(D) i-A, ii- C, iii- D, iv-B
Answer
51. Which of the following analogies is correct?
(A) Nitrogen: 1s22s22p3 :: Argon:1s22s22p6
(B) Carbon: maximum compounds :: Xenon: no compounds
(C) XeF2: Linear :: ClF3: Trigonal planar
(D) Helium: meteorological observations :: Argon: metallurgical processes
Answer
D
52. Complete the following analogy:
Same molecular formula but different structures: A:: Non superimposable mirror images: B
(A) A:Isomers, B: Enantiomer
(B) A: Enantiomers, B: Racemic mixture
(C) A: Stereoisomers, B: Retention
(D) A: Isomers, B: Sterioisomers
Answer
A
CASE 1 : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55.
Early crystallographers had trouble solving the structures of inorganic solids using X-ray diffraction because some of the mathematical tools for analyzing the data had not yet been developed. Once a trial structure was proposed, it was relatively easy to calculate the diffraction pattern, but it was difficult to go the other way (from the diffraction pattern to the structure) if nothing was known a priori about the arrangement of atoms in the unit cell. It was important to develop some guidelines for guessing coordination numbers and bonding geometries of atoms in crystals. The first such rules were proposed by Linus Pauling, who considered how one might pack together oppositely charged spheres with different radii. Pauling proposed from geometric considerations that the quality of the “fit” depended on the radius ratio of the anion and the cation.
If the anion is considered as the packing atom in the crystal, then the smaller cation fills the interstitial sites (“holes”). Cations will find arrangements in which they can contact the largest number of anions. If the cation can touch all of its nearest neighbouring anions then the fit is good. If the cation is too small for a given site, that coordination number will be unstable and it will prefer a lower coordination structure. The table below gives the ranges of cation/anion radius ratios that give the best fit for a given coordination geometry.

53. The radius of Ag+ ion is 126 pm and of I-ion is 216 pm. The coordination number of Ag+ion will be :
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 6
(D) 8
Answer
C
54. A solid AB has square planar structure. If the radius of cation A+ is 120 pm, calculate the maximum
possible value of anion B-.
(A) 240 pm
(B) 270 pm
(C) 280 pm
(D) 290 pm
Answer
D
55. A “good fit” is considered to be one where the cation can touch:
(A) All of its nearest neighbouring anions
(B) Most of its nearest neighbouring anions
(C) Some of its nearest neighbouring anions
(D) None of its nearest neighbouring anions
Answer
A

