See below CBSE Class 10 Science Term 1 Sample Paper Set C with solutions. We have provided CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science as per the latest paper pattern issued by CBSE for the current academic year. All sample papers provided by our Class 10 Science teachers are with answers. You can see the sample paper given below and use them for more practice for Class 10 Science examination.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Science Term 1 Set C
Section – A
1. Write the molecular formula of the following compounds and draw their electron-dot structures:
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethene
Ans. (a) Ethane : The Molecular Formula is C2H6
(b) Ethene : The molecular formula is C2H4
2. Elements have been arranged in the following sequence on the basis of their increasing atomic masses.
F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K
(a) Pick two sets of elements which have similar properties.
(b) The given sequence represents which law of classification of elements?
Ans. (a) (i) F and Cl, (ii) Na and K
(b) Newland’s law of octaves
3. Reproduction is one of the biological processes that are commonly carried out by an organism. In fact, the ability to reproduce is one of the major characteristics of a living organism. There are two major modes of reproduction : sexual and asexual. The given diagram represents a mode of reproduction,
wherein a cell divides to produce two identical cells.

(a) Name the organism that divides by the above process. State the type of reproduction.
(b) How the above process is different from multiple fission?
Ans. (a) Amoeba reproduces asexually by binary fission.
4. In biology class, a teacher taught his student about male reproductive part. He taught that tail.
(a) What is the role of the long tail?
(b) How are the sperms delivered from the site of their production?
Ans. Sperms are male gametes that fuse with ovum to form zygote
5. In an experiment, Mendel obtained 1014 plants out of which 787 were having round seeds and 227 had wrinkled seeds in F2 generation.
(a) What is the approximate ratio obtained in F2-generation? Under which law of Mendel do you find this ratio?
(b) Why is this law so called?
Ans. Recall the 2nd law of Mendel = (Law of Segregation).
OR
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
Ans. Mendel used pea plant for his experiment. When Mendel performed a cross between tall plant and dwarf plant he found that all the plants in F1 generation are tall. In F2 generation 75% of plants were tall while 25% of plants were dwarf. The ratio obtained in F2 generation is 3 : 1.
6. A student drew three magnetic field lines 1, 2 and 3 of a bar magnet with the help of a compass needle as shown in the figure.

(a) Is this configuration possible? If not, then what is wrong in the given figure and why?
(b) List any two characteristics of these magnetic field lines.
Ans. (a) Magnetic field lines do not intersect.
(b) 1. The direction of the magnetic field at any point is given by the tangent to the field lines at that point .
2. Magnetic field lines never cross each other.
OR
(a) What kind of energy transformation takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil and a galvanometer is connected at the two ends of the coil?
(b) What is the name of this phenomenon?
Ans. (a) Mechanical energy (Motion ) changes into electrical energy.
(b) This phenomenon is called as electromagnetic induction
7. During a class test teacher asked student to identify the correct image of the different trophic levels given bellow along with reasons.

Ans. Fig. A is correct.
OR
Observe the figure and answer the below questions.
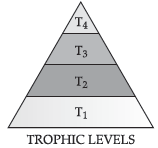
(a) Which trophic level has maximum number of organisms? Why?
(b) In which trophic level chemicals like DDT are accumulated in highest concentration? Why?
Ans. (a) Trophic level 1 has maximum number of organisms because it includes producers.
(b) DDT is accumulated at Trophic level 4. It occupies the topmost place in the given food chain.
Section – B
8. An element X (atomic number 17) reacts with an element Y (atomic number 20) to form a divalent halide.
(a) Where in the periodic table are elements X and Y placed?
(b) Classify X and Y as metal (s), non-metal (s) or metalloid (s).
(c) What will be the nature of oxide of element Y? Identify the nature of bonding in the compound formed.
Ans. (a) X belongs to Group 17 and 3rd period Y belongs to Group 2 and 4th period
(b) X-Non-metal and Y metal
(c) Basic oxide; Ionic bonding
9. A homologous series is a series of organic compounds which belong to the same family (i.e., possess same functional group) and show similar chemical properties. The members of this series are called homologous and differ from each other by the number of –CH2 units in the main carbon chain.
(a) What is the difference between two consecutive members in a homologous series in alkanes in terms of:
(i) Molecular mass
(ii) Number of atoms of elements.
(b) The molecular formula of ‘A’ is C10H18 and ‘B’ is C18H36. Name the homologous series to which they belong.
Ans. (a) (i) Molecular mass : In term of molecular mass each successive member in a homologous series differ by molecular mass of 14 Dalton by the preceding member.
(ii) Number of atoms : There is a difference of one carbon atom and two hydrogen atom between two consecutive members of homologous series that is of one CH2 molecule or three atoms.
(b) ‘A’ belongs to alkyne and ‘B’ belongs to alkene
OR
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are called isomers and the phenomenon is called isomerism. When the isomerism is due to the difference in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space, the phenomenon is called structural isomerism.
(a) Draw the structures of two isomers of butane, C4H10.
(b) Why can’t we have isomers of first three members of alkane series?
Ans. (b) because they will have the same structural formula.
10. Piyu saw a female being blamed by the family members for producing a girl child. She approached them and explained the genetic basis of sex determination of human beings. She explained them that mother is not responsible for the girl child. The family members agreed to her argument and felt sorry for their act. Based on the above case, answer the following questions:
(a) What is the basis of sex determination in human beings?
(b) What are the chances of the birth of a boy or a girl during sexual reproduction in human beings?
Ans. (a) A chromosome is considered as the basis of sex determination in humans
(b) There should be a 50% chance of conceiving a boy or girl
11. Vaani connected a hot plate to a 220 V line, which has two resistance coils A and B, each of 22W resistances. Now she wants to calculate the amount of electric current flowing when these coil are :
(a) used individually.
(b) connected in series.
(c) connected in parallel.
Ans. Use the formula, I = V/R, in parallel connection Req = R1R2 / R1 + R2 ,in series connection, Req = R1 + R2
12. Consider the given electric circuit and find potential difference across each resistor.
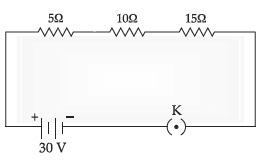
Ans. Req = 5 + 10 + 15 = 30 Ω
V = IR
30 = i (30)
i = 1 ampere
Now as all resistors are in series so current in all will be same. So,
V15 = (1 x 15) = 15 V
Across 15 Ω potential difference is 15 Volt.
13. We observe heaps of garbage lying along the roads while passing through a highway. Open dumping is the most common method of waste disposal in India. The trash heaps are usually left open to the environment and the elements. These seldom have a sparse covering which can often attract pests or vermin. According to Priyanka’s father, it is the responsibility of the government to arrange for the management and disposal of waste.
(a) As an individual you have no role to play. Do you agree? Support your answers with two reasons.
(b) Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Ans. (b) 1. Non-Degradable means a compound that cannot be broken down into basic molecules easily.
2. While non-degradable refers to a compound that cannot be converted into basic molecules by natural methods
Section – C
14. A dihybrid cross describes a mating experiment between two organisms that are identically hybrid for two traits. A hybrid organism is one that is heterozygous, which means that it carries two different alleles at a particular genetic position, or locus. Therefore, a dihybrid organism is one that is heterozygous at two different genetic loci. In 1865, Gregor Mendel studied the inheritance pattern of traits in a pea plant. According to this study, he obtained 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio of certain traits in progeny of F2 generation. Based on the given information, answer the questions given below:
(a) What trait did he study? How do they represent themselves?
(b) What was the trait of F1 progeny?
(c) Which rule does this inheritance pattern suggest? Explain.
Ans. Recall dihybrid cross.
OR
How did Mendel’s experiments show that different traits are inherited independently? Explain.
Ans. According to Mendel’s law of independent assortment, during the inheritance of two or more characters, the assortment of individual traits takes place independently during gamete formation. Thus each allele of a pair segregates independently and each gamete formed contains one allele of that trait. This law is inapplicable for linked genes.
Mendel performed the dihybrid cross from which he showed that the traits are inherited independently.
The genotype of the F1 plants is RrYy. These plants were self-crossed by Mendel. In his dihybrid cross the F2 plants were obtained in the phenotypic ratio 9 (round yellow):3 (round green) :3 (wrinkled yellow):1 (wrinkled green) as shown in the Punnett square. The seed colour is inherited independently of the seed shape. Thus round green seeds, as well as yellow wrinkled seeds both were formed along with round yellow seeds and green wrinkled seeds.
15. Study the figure of a current carrying straight conductor passing perpendicularly through a horizontal cardboard. Answer the following questions:
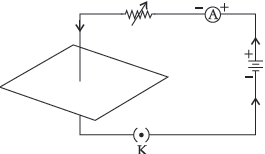
(a) Why does a compass needle show deflection when brought near a current carrying conductor?
(b) State right-hand thumb rule to mark the direction of the field lines.
(c) How will the strength of the magnetic field change when the point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the straight conductor? Give reason to justify your answer.
Ans. (a) Due to generation of magnetic field.
(c) As the distance increases, magnetic field strength decreases
OR
Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines produced around a current carrying straight conductor
passing perpendicularly through a horizontal cardboard as shown in figure.
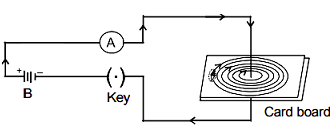
Ans. Right hand thumb rule : If we hold the current carrying conductor in the right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of current, then the fingers encircle the wire in the direction of magnetic lines of force.
The strength of the magnetic field will reduce when the point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the straight conductor as B ∝ r
