Please see below Case Study MCQ Questions Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science. These MCQ Questions with Answers for Case study have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines of Class 10 Science. Cased Study Based MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science are expected to come in the upcoming exams. We have provided a lot of case studies for all chapters in standard 10 science. Please solve the MCQ Questions and compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science Case Study MCQ Questions
Case-based Questions :
When the branches of a plant growing in the field are pulled towards the ground and a part of them is covered with moist soil (leaving the tips of the branches exposed above the ground), then after sometime new roots develop from the parts of branches buried in the soil. On cutting these branches from the parent plant, new plants are produced from the cut parts of branches which had developed roots.
Question. Name any two plants which are grown for their flowers and propagated by this method.
Answer
Jasmine and China rose
Question. Name any two plants which are grown for their fruits and propagated by this method.
Answer
Lemon and Guava
Question. Name one plant which gets propagated by this method naturally by forming runners (soft horizontal stems running above the ground).
Answer
Strawberry
Question. What is this method of propagation of plants known as?
Answer
Layering
Question. What type of branches should a plant have to be able to be propagated by this method?
Answer
Slender branches (Thin branches)
When an insect sits on the flower of a plant then some particles, present on the top of little stalks in the flower get stick to its body hair. When this insect now sits on the flower of another similar plant, then particles attached to the hair of insect are shifted to top of a flask-shaped organ at the centre of a flower. This particle grows a long tube B from the top of flask-shaped organ through which C moves down and reaches the bottom of the flask-shaped organ. Here C fuses with the nucleus of D, present in structure E. The fusion of C and D forms a new cell F which grows and develops into a seed of the plant.
Question. What is C which moves down through the tube B?
Answer
C is male gamete.
Question. Name D and E.
Answer
D is female gamete (ovum or egg); E is ovule
Question. What is F?
Answer
F is fertilised egg (zygote).
Question. What are these particles? Name the process by which these particles are transfered from one flower to other flower of another similar plant.
Answer
These particles are known as pollen grains; cross pollination
Question. What is the name of tube B?
Answer
Pollen-tube
I. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of population.
Question. Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
(a) Condoms
(b) Diaphragms
(c) Oral pills
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
C
Question. Which of these factor determines the size of a population?
(a) Birth rate
(b) Death rate
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys ?
(a) Broadening of shoulders
(b) Development of mammary glands
(c) Broadening of waist
(d) High pitch of voice
Answer
A
Question. Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is:
(a) Low pitch voice
(b) Appearance moustache and beard
(c) Development of mammary gland
(d) Broadening of shoulders
Answer
C
II. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions given below:
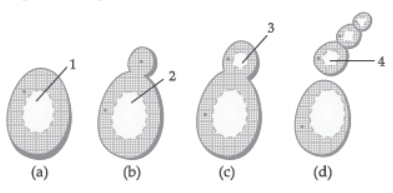
Question. Which organism uses the above method for reproduction?
(a) Yeast
(b) Amoeba
(c) Spirogyra
(d) Leishmania
Answer
A
Question. An organism capable of reproducing by two asexual reproduction methods one similar to the reproduction in yeast and the other similar to the reproduction in Planaria is:
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Hydra
(c) Bryophyllum
(d) Paramecium
Answer
B
Question. Identify the above process.
(a) Binary fission
(b) Budding
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Regeneration
Answer
B
Question. A Planaria worm is cut horizontally in the middle into two halves P and Q such that the part P contains the whole head of the worm. Another Planaria worm is cut vertically into two halves R and S in such a way that both the cut pieces R and S contain half head each. Which of the cut pieces of the two Planaria worms could regenerate to form the complete respective worms?
(a) Only P
(b) Only R and S
(c) P, R and S
(d) P, Q, R and S
Answer
D
III. Study the process depicted in the picture given below and answer the questions given below:
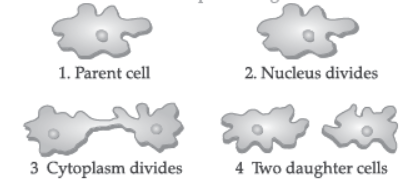
Question. Which of the following statement is correct about the above type of reproduction?
(a) It involves two individuals.
(b) It involves a mature parent cell.
(c) It involves union of two types of gametes.
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of these statement is correct about the fission in Leishmania?
(a) Splitting into two cells during division can take place in any plane.
(b) Binary fission occurs in a definite orientation in relation to the whip like structure.
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of these organisms divides by the above process?
(a) Amoeba
(b) Spirogyra
(c) Leishmania
(d) Yeast
Answer
A
Question. In multiple fission :
(a) Two daughter cells are produced.
(b) Many daughter cells are formed simultaneously.
(c) Two types of gametes fuse together
(d) None of these
Answer
B
IV. Study the given diagram and answer the questions given below:
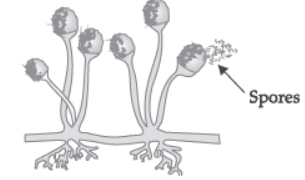
Question. The thread like non-reproductive structures is :
(a) Hyphae
(b) Rhizoids
(c) Sporangium
(d) Sporangiophores
Answer
A
Question. On maturation sporangia of given organism bursts and releases :
(a) Pollens
(b) Spores
(c) Seeds
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The above diagram depicts:
(a) Spore formation in Rhizopus
(b) Fragmentation in Spirogyra
(c) Binary fission in Amoeba
(d) Spore formation in Yeast
Answer
A
Question. ‘Blobs’ that develop at the tips of the nonreproductive thread is known as :
(a) Hyphae
(b) Sporangia
(c) Spores
(d) Pollens
Answer
A
V. The given diagram represent the structure of a flower. Study the structure and answer the questions given below :

Question. When an insect sits on the flower of a plant then some particles from the little stalks in the flowers sticks to its body and when this insect sits on the flower of another plant, the particles get deposited in that flower. What are these particles?
(a) Dust
(b) Pollens
(c) Grains
(d) Seeds
Answer
B
Question. A student decides to study the impact of removing certain flower parts on fruit formation in plant species X. He chooses three separate plants that are growing in the same plot under uniform conditions. The data is given in the table below.
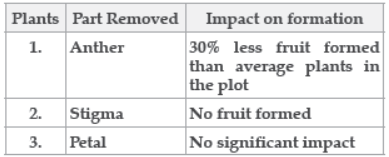
Which of the following can be inferred from the above data?
(a) Anthers and stigmas are crucial in sexual reproduction in species X.
(b) Pollen grains are probably unable to germinate if they land on other parts of the carpel besides the stigma.
(c) Species X is likely to be wind-pollinated.
(d) Species X relies completely on crosspollination.
Answer
C
Question. The labels A, B and C are
(a) Anther, Style and Ovary respectively.
(b) Stamen, Stigma and Ovule respectively.
(c) Anther, Style and Stigma respectively.
(d) Stamen, Fragment and Ovary respectively.
Answer
A
Question. Which of these is the function of part labelled as C?
(a) Contains ovules which develop into seeds.
(b) Attracts pollinators.
(c) Protect rising buds.
(d) Receive pollens
Answer
A
VI. Study the diagram and answer the questions given below:
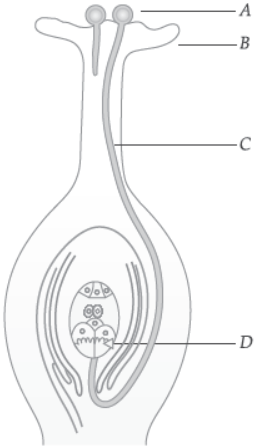
Question. The importance of the part “C” is :
(a) It carries female gametes.
(b) It carries male gametes.
(c) It carries food for the seeds.
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. What happens to the part marked ‘D’ after fertilization is over?
(a) Converted into seed.
(b) Converted into fruit
(c) Converted into embryo
(d) Converted into flower.
Answer
C
Question. The part labelled as A in the diagram is:
(a) Dust
(b) Germs
(c) Pollen
(d) Pollinators
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect about pollination?
(a) It precedes fertilization.
(b) It follows fertilization.
(c) It brings male and female gametes closer.
(d) It introduces variations in plants.
Answer
B
VII. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
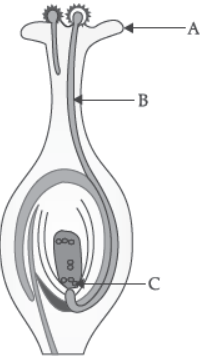
Question. What happens to the label A which falls on a suitable stigma?
(a) Pollen grain gradually disintegrates.
(b) Pollen grain directly reaches the embryo sac.
(c) Pollen grain starts germinating and forms a pollen tube.
(d) Pollen grain changes into ovules and then to fruit.
Answer
C
Question. In the given diagram showing the carpel of an insect pollinated flower, the most likely reason for the non-germination of pollen grain Z is :

(a) Pollen grains X and Y were brought to the stigma earlier, therefore, their germination inhibited the germination of pollen grain Z.
(b) Pollen grain Z was brought to the flower by wind, while pollen grains X and Y were brought to the flower by insects.
(c) Pollen grain Z lacks protrusions that allow it to adhere properly onto the stigma surface.
(d) Pollen grain Z comes from a flower of an incompatible species.
Answer
D
Question. The role of part labelled as B is:
(a) Transport of male gametes to the ovary.
(b) Transport of female gametes to the ovary
(c) Contains ovules which develop into seeds.
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. How many male gametes are produced by each pollen grain?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer
B
The male reproductive system consists of portions which produce the germ-cells and other portions that deliver the germ-cells to the site of fertilisation. The formation of germ-cells or sperms takes place in the testes. These are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature. We have discussed the role of the testes in the secretion of the hormone, testosterone, in the previous chapter. In addition to regulating the formation of sperms, testosterone brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. The sperms formed are delivered through the vas deferens which unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder. The urethra thus forms a common passage for both the sperms and urine. Along the path of the vas deferens, glands like the prostate and the seminal vesicles add their
secretions so that the sperms are now in a fluid which makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition.
The sperms are tiny bodies that consist of mainly geneticmaterial and a long tail that helps them to move towards the female germ-cell.
Question. Another name for Bulbourethral gland is
(a) Meibomian gland
(b) Prostate gland
(c) Perineal gland
(d) Cowper’s gland
Answer
D
Question. In man, Cryptorchidism is the condition when
(a) testes do not descent into the scrotum
(b) there are two testes in each scrotum
(c) testis degenerates in the scrotum
(d) testis enlarges in the scrotum
Answer
A
Question. The seminiferous tubules of the testes are lined by the germinal epithelium consisting of
(a) spermatids
(b) cells of Sertoli
(c) spermatogonium
(d) spermatocytes
Answer
B
Question. The seminiferous tubules of the testes are lined by the germinal epithelium consisting of
(a) sertoli cells
(b) cells of germinal epithelium
(c) cells of Leydig or interstitial cells
(d) secondary spermatocytes
Answer
A
Question. Which of these is an accessory reproductive gland in male mammals
(a) Inguinal gland
(b) Prostate gland
(c) Mushroom-shaped gland
(d) Gastric gland
Answer
B

