Please see below Case Study MCQ Questions Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science. These MCQ Questions with Answers for Case study have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines of Class 10 Science. Cased Study Based MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science are expected to come in the upcoming exams. We have provided a lot of case studies for all chapters in standard 10 science. Please solve the MCQ Questions and compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science Case Study MCQ Questions
The table given below refers to the elements of the periodic table with atomic number from 3 to 18. These elements are shown by letters. (not by the usual symbols of the elements).
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
A B C D E F G H
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
I J K L M N O P
Question. Which of the following elements have valency 4?
(a) F and N
(b) C and K
(c) D and L
(d) H and P
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are noble gases?
(a) H and P
(b) G and O
(c) D and L
(d) A and I
Answer
A
Question. Which are halogens?
(a) H and L
(b) C and M
(c) G and O
(d) E and P
Answer
C
Group VII A elements are strong non-metals because they can easily accept an electron to form an anion whereas group 1 A element are strong metals because they can very easily lose one electron to form cation. Metals have the tendency to lose their valence electrons and form positive ions, so metallic character is related to the ionisation potential. Elements having low ionisation potential, lose electrons easily. Thus, metallic character generally decreases across a period and increases down a group.
Question. Which of the following is the correct decreasing order of metallic character?
(a) Ca > Sc > Ti > K
(b) K > Ca > Sc > Ti
(c) K > Sc > Ca > Ti
(d) Ti > Sc > Ca > K
Answer
B
Question. The non metallic character on moving along a period –
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) depends on the period
(d) remains the same
Answer
A
Question. Group 1 and group 2 elements are considered as strong metals because
(a) they have incomplete octet.
(b) they can easily gain electrons.
(c) they can easily lose electrons.
(d) they form anions.
Answer
C
Question numbers 1 – 3 are based on the periodic table. Study the part of the modern periodic table presented below in which the alphabets represent the symbols of elements and answer the following questions.

Question. Study the data of the following three categories A, B and C.
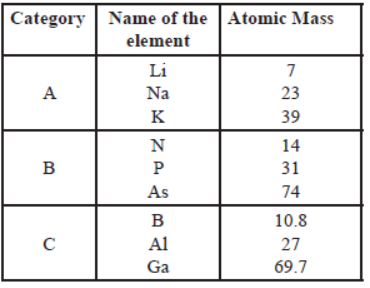
(i) From the given three categories A, B and C, Pick the one which forms Dobereiner’s Triads.
Answer
Dobereiner’s Triads is A.
(ii) Why did Mendeleev placed elements of category A, B and C in three different groups?
Answer
Mendeleev placed elements of category A,B and C in three different groups because they have different physical and chemical properties.
(iii) Is Newland law of octaves applicable to all the three categories?
Answer
No, Newland’s Law of octaves is not applicable for all three categories.
Because the law of octaves states that every eighth element has similar properties when the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses.
Question. Consult the above part of the periodic table to predict which of the given combination is a covalent compound: RQ2, AT, JQ, JX2.
Answer
R and Q are members of group 16th having elements, O, S, Se, Te etc. RQ2 is characterised by showing the formation of covalent bond.
Question. Considering the above part of the periodic table, which of the given element is the most electropositive element?
Answer
Element ‘G’ is the most electropositive element.
Question. Which of the given element is the most electronegative element?
Answer
Element ‘V’ is the most electronegative element
Read the passage and answer the questions given below :
Mendeleev was a Russian chemist, who contributed the most for the development of periodic table of elements wherein the elements were arranged on the basis of their fundamental property, the atomic mass and also on the similarity of chemical properties.
Only 63 elements were known at his time. He arranged the 63 elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and found that there was a periodic recurrence of elements with similar physical and chemical properties. He observed that elements with similar properties fall in the same vertical column. These vertical columns are called groups and horizontal rows of elements are called periods. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium
Question. The elements eka aluminium and eka silicon discovered by Mendeleev later found place in periodic table. Both of these elements belong to:
(a) Period 2
(b) Group 13
(c) Group 14
(d) Period
Answer
D
Question. How do we classify these newly discovered elements (eka-aluminium and eka-silicon)?
(a) Metals
(b) Non metals
(c) Metalloids
(d) Inert gases
Answer
C
Question. Mendeleev arranged the periodic table on the basis of which fundamental property?
(a) Atomic mass
(b) Atomic number
(c) Number of neutrons
(d) Valence electrons
Answer
A
Question. Eka aluminium and eka silicon were later replaced respectively as :
(a) Germanium and gallium
(b) Gallium and scandium
(c) Gallium and germanium
(d) Germanium and scandium
Answer
C
Using the given part of the periodic table, answer the questions given below :

Question. Identify the elements which have similar chemical properties as the element X.
(a) Y and Z.
(b) Y and B
(c) All Y, Z and B
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of them will have largest atomic radii?
(a) E
(b) X
(c) C
(d) D
Answer
B
Question. Which of these elements have smallest atomic size?
(a) B
(b) C
(c) D
(d) E
Answer
D
Question. What is the valency of element E?
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 0
Answer
C
Read the passage and answer the questions given below :
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells as K, L and M. But are different in their outermost shells.
It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. Oxides of the elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and F are acidic. The oxide of elements D is almost neutral.
Question. Which two of these elements could definitely be metals ?
(a) E and F
(b) A and B
(c) D
(d) G
Answer
B
Question. Which two elements amongst these are likely to be the non–metals ?
(a) A and G
(b) D and F
(c) E and F
(d) A and B
Answer
C
Question. To which period the listed elements belong?
(a) 2nd
(b) 7th
(c) 8th
(d) 3rd
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature ?
(a) A
(b) H
(c) D
(d) B
Answer
B
From the following table of the periodic table, answer the questions given:

Question. Which of the following element belongs to group 2?
(a) Sodium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Aluminium
(d) Carbon
Answer
B
Question. Which other element is likely to present in the group in which fluorine is present?
(a) Neon
(b) Aluminium
(c) Chlorine
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which is the most reactive metal ?
(a) Lithium
(b) X
(c) Y
(d) Z
Answer
D
Question. Name the family of fluorine, Q, R, T:
(a) Alkali metals
(b) Noble gas
(c) Halogens
(d) Alkaline metals
Answer
C
Metallic Character The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ion (cation) is known as electropositivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size. Non-Metallic Character The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electro-negativity have a higher tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electronegativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.

Question. Identify the reason for the gradual change in electronegativity in halogens down the group.
(a) Electronegativity increases down the group due to decrease in atomic size
(b) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to decrease in tendency to lose electrons
(c) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/ tendency to gain electron decreases
(d) Electronegativity increases down the group due to increase in forces of attractions between nucleus & valence electrons
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following correctly represents the decreasing order of metallic character of Alkali metals plotted in the graph?
(a) Cs > Rb > Li > Na > K
(b) K > Rb > Li > Na > Cs
(c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li
(d) Cs > K > Rb > Na > Li
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reason correctly justifies that “Fluorine (72pm) has smaller atomic radius than Lithium (152pm)”?
(a) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size increases down the group
(b) F and Li are in the same period. Atomic size increases across the period due to increase in number of shells
(c) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size decreases down the group
(d) F and Li are in the same period and across the period atomic size/radius decreases from left to right.
Answer
D
Question. Hydrogen is placed along with Alkali metals in the modern periodic table though it shows non-metallic character
(a) as Hydrogen has one electron & readily loses electron to form negative ion
(b) as Hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion
(c) as Hydrogen can gain one electron easily like Halogens to form negative ion
(d) as Hydrogen shows the properties of non-metals
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following has highest electronegativity?
(a) F
(b) Cl
(c) Br
(d) I
Answer
A



