Please refer to Biological Classification Class 11 Biology Important Questions with solutions provided below. These questions and answers have been provided for Class 11 Biology based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these problem solutions as it will help them to gain more marks in examinations. We have provided Important Questions for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your book. These Board exam questions have been designed by expert teachers of Standard 11.
Class 11 Biology Important Questions Biological Classification
Objective Questions
Question. Organisms of which of the following kingdom do not have nuclear membrane ?
(a) Protista
(b) Fungi
(c) Monera
(d) Plantae
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following pigment is present in cyanobacteria?
(a) Chlorophyll ‘a’
(b) Chlorophyll ‘b’
(c) Chlorophyll ‘c’
(d) Chlorophyll ‘d’
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following processes are involved in the reproduction of protists ?
(a) Binary fission and budding
(b) Cell fusion and zygote formation
(c) Spore formation and cyst formation
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is an example of amoeboid protozoans ?
(a) Trypanosoma
(b) Paramecium
(c) Gonyaulax
(d) Entamoeba
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is used extensively in biochemical and genetic work ?
(a) Agaricus
(b) Alternaria
(c) Neurospora
(d) Mucor
Answer
C
Question. Which group of fungi is commonly known as imperfect fungi ?
(a) Phycomycetes
(b) Ascomycetes
(c) Basidiomycetes
(d) Deuteromycetes
Answer
D
Question. The subunit of capsid is called
(a) core
(b) nucleotide
(c) amino acid
(d) capsomere
Answer
D
Question. The symbiotic association between fungi and algae is called
(a) lichen
(b) mycorrhiza
(c) rhizome
(d) endomycorrhiza
Answer
A
Question. Dikaryon formation is the characteristic feature of
(a) ascomycetes and basidiomycetes.
(b) phycomycetes and basidiomycetes.
(c) ascomycetes and phycomycetes.
(d) phycomycetes and zygomycetes.
Answer
A
Question. Plasmogamy is the fusion of
(a) two haploid cells including their nuclei.
(b) two haploid cells without nuclear fusion.
(c) sperm and egg.
(d) sperm and two polar nuclei.
Answer
B
Question. Fungi are filamentous with the exception of “X” which is unicellular. Identify X.
(a) Yeast
(b) Albugo
(c) Mucor
(d) Lichen
Answer
A
Statement Type Questions
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct for viruses?
(a) Viruses are obligate parasites.
(b) Viruses can multiply only when they are inside the living cells.
(c) Viruses cannot pass through bacterial filters.
(d) Viruses are made up of protein and DNA or RNA (never both DNA and RNA).
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct for methanogens?
(a) They are archaebacteria.
(b) They live in marshy areas.
(c) Methane is their preferred carbon source.
(d) They are present in guts of several ruminant animals (cow, buffaloes) and produce biogas (CH4) from the dung of these animals.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
(a) TMV has a double-stranded RNA molecule.
(b) Most plant viruses are RNA viruses.
(c) The bacteriophage has double-stranded DNA.
(d) Most animal viruses are DNA viruses.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is a characteristic feature of chrysophytes?
(a) They are parasitic forms which cause diseases in animals.
(b) They have a protein rich layer called pellicle.
(c) They have indestructible cell wall layer deposited with silica.
(d) They are commonly called dinoflagellates.
Answer
C
Question. Choose the correct statements (i – v) regarding mycoplasma
(i) Mycoplasma has no cell wall.
(ii) Mycoplasma is the smallest living organism known.
(iii) Mycoplasma cannot survive without O2.
(iv) Mycoplasma are pathogenic in animals and plants.
(v) A sort of sexual reproduction occurs in bacterium by adopting a primitive DNA transfer from one bacterium to the other.
(a) Only (iii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (v)
(c) (i), (ii), (iv), and (v)
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. T. O. Diener discovered a new infectious agent that was smaller than viruses and have the following characteristics.
(i) It causes potato spindle tuber disease.
(ii) It has free RNA.
(iii) Molecular weight of RNA is low.
Identify the infections agent.
(a) Viruses
(b) Viroids
(c) Virion
(d) Mycoplasma
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following are the characters of dinoflagellates?
(i) They are planktonic golden yellow algae with soap box like structure.
(ii) They are marine red biflagellated protista.
(iii) They appear yellow, green, brown, blue and red in colour.
(iv) They are biflagellated organisms with pellicle.
(v) They are saprophytic (or) parasitic unicellular forms.
(a) (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (v)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii), (iv) and (v)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following group of kingdom protista is being described in the statements given below ?
(i) This group includes diatoms and golden algae.
(ii) They are microscopic and float passively in water currents (plankton).
(iii) Most of them are photosynthetic.
(iv) They have deposits in their habitat; this accumulation over billion of years is referred to as ‘diatomaceous earth’.
(a) Dinoflagellates
(b) Chrysophytes
(c) Euglenoids
(d) Slime moulds
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following class of fungi is being described by the given statements ?
(i) They are found in aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist and damp places.
(ii) Mycelium is aseptate and coenocytic.
(iii) Asexual reproduction takes place by zoospores (motile) or by aplanospores (non-motile).
(iv) Some common examples are Mucor, Rhizopus and Albugo.
(a) Ascomycetes
(b) Phycomycetes
(c) Basidiomycetes
(d) Deuteromycetes
Answer
B
Question. Read the following statements and answer the question given below
(i) They are saprophytic protists.
(ii) Under suitable conditions, they form an aggregation (called plasmodium) which may grow and spread over several feet.
(iii) During unfavourable conditions, the plasmodium differentiates and forms fruiting bodies bearing spores at their tips.
Which of the following class of protists is being described by the above statements ?
(a) Euglenoids
(b) Dinoflagellates
(c) Slime moulds
(d) Protozoans
Answer
C
Question. Read the following statements and answer the question.
(i) Some members are saprophytes or parasites while a large number of them are decomposers of litter and help in mineral cycling.
(ii) They reproduce only by asexual spores known as conidia.
(iii) Mycelium is septate and branched.
(iv) Alternaria, Colletotrichum and Trichoderma are examples of this class.
Which of the following class of fungi is being described by the above statements ?
(a) Phycomycetes
(b) Deuteromycetes
(c) Basidiomycetes
(d) Ascomycetes
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements regarding cyanobacteria is incorrect?
(a) It is also called blue green algae.
(b) They are chemosynthetic autotrophs.
(c) It forms blooms in polluted water bodies.
(d) It is unicellular, colonial or filamentous, marine or terrestrial bacteria.
Answer
B
Assertion/Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Outside a living cell, viruses have must crystalline statements.
Reason : Viroids have a protein coat.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Lichen is important for chemical industries.
Reason : Litmus and Orcein are formed from lichens.
Answer
A
Matching Type Questions
Question. Match the class of fungi given in column-I with their common name given in column-II and select the correct option.
| Column-I (Class of fungi) | Column-II (Common name) |
| A. Phycomycetes | I. Sac fungi |
| B. Ascomycetes | II. Algal fungi |
| C. Basidiomycetes | III. Fungi imperfecti |
| D. Deuteromycetes | IV. Club fungi |
(a) A – II, B – I, C – IV, D – III
(b) A – II, B – IV, C – I, D – III
(c) A – IV, B – I, C – II, D – III
(d) A – IV, B – III, C – II, D – I
Answer
A
Question. Match the class of fungi given in column I with their examples given in column II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I (Class of fungi) | Column-II (Examples) |
| A. Ascomycetes | I. Rhizopus |
| B. Basidiomycetes | II. Penicillium |
| C. Deuteromycetes | III. Ustilago |
| D. Phycomycetes | IV. Alternaria |
(a) A – IV, B – III, C – I, D – II
(b) A – II, B – III, C – IV, D – I
(c) A – IV, B – I, C – II, D – III
(d) A – III, B – IV, C – II, D – I
Answer
B
Question. Match the scientists given in column I with their discovery given in column II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I (Scientists) | Column-II (Discovery) |
| A. Ernst Mayr | I. Discovered Viroids |
| B. Whittaker | II. Gave the name virus |
| C. Pasteur | III. Proposed five kingdom classification |
| D. Diener | IV. Darwin of the 20th Century |
(a) A – IV, B – III, C – II, D – I
(b) A – III, B – IV, C – II, D – I
(c) A – II, B – III, C – IV, D – I
(d) A – I, B – II, C – III, D – IV
Answer
A
Question. Match the type of protozoans given in column-I with their examples given in column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I (Type of Protozoans) | Column-II (Examples) |
| A. Amoeboid protozoans | I. Paramecium |
| B. Ciliated protozoans | II. Plasmodium |
| C. Flagellated protozoans | III. Amoeba |
| D. Sporozoans | IV. Trypanosoma |
(a) A – I, B – III, C – IV, D – II
(b) A – III, B – I, C – II, D – IV
(c) A – III, B – I, C – IV, D – II
(d) A – III, B – IV, C – I, D – II
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched ?
(a) Anabaena – Cyanobacteria
(b) Amoeba – Protozoa
(c) Gonyaulax – Dinoflagellates
(d) Albugo – Chrysophytes
Answer
D
Question. Select the correct match from the given option.
(a) Occurrence of dikaryotic stage – ascomycetes and basidiomycetes.
(b) Saprophytes – They are autotrophic and absorb soluble organic matter from dead substrates.
(c) Vegetative mean of reproduction in fungi – fragmentation, budding and sporangiophores.
(d) Steps involved in asexual cycle of fungi – plasmogamy, karyogamy and meiosis in zygote resulting in haploid spores.
Diagram Type Questions
Question. Choose the correct names of the different bacteria given below according to their shapes.
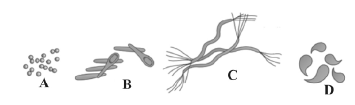
(a) A – Cocci, B – Bacilli, C – Spirilla, D – Vibrio
(b) A – Bacilli, B – Cocci, C – Spirilla, D – Vibrio
(c) A – Spirilla, B – Bacilli, C – Cocci, D – Vibrio
(d) A – Spirilla, B – Vibrio, C – Cocci, D – Bacilli
Answer
A
Question. The figure given below shows the structure of a bacteriophage. Identify its parts labelled as A, B, C and D.
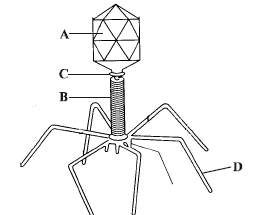
| A | B | C | D |
| (a) Tail fibres | Head | Sheath | Collar |
| (b) Sheath | Collar | Head | Tail fibres |
| (c) Head | Sheath | Collar | Tail fibres |
| (d) Collar | Tail fibres | Head | Sheath |
Answer
C
Question. The given figure shows some structures labelled as A, B, C and D. Which structure has the protein coat that encloses the nucleic acid?
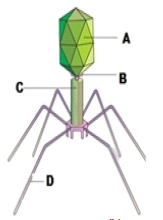
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Lichens indicate SO2 pollution because they
(a) show association between algae and fungi.
(b) grow faster than others.
(c) are sensitive to SO2.
(d) flourish in O2 rich environment.
Answer
C
Question. In some viruses, RNA is present instead of DNA indicating that
(a) their nucleic acid must combine with host DNA before replication.
(b) they cannot replicate.
(c) there is no hereditary information.
(d) RNA can transfer heredity material.
Answer
D
Question. A fungus contains cells with two nuclei from different genomes. The nuclei do not fuse but divide independently and simultaneously as new cells are formed. This fungus belongs to
(a) phycomycetes
(b) zygomycetes
(c) deuteromycetes
(d) basidiomycetes
Answer
D
Question. Bacteria are found to be primitive organisms because they
(a) are small, microscopic which are not seen with naked eye.
(b) cause serious diseases to human being, domestic animals and crop plants.
(c) produce endospores which are very resistant to adverse conditions.
(d) possess incipient nucleus and show amitotic division.
Answer
D
Question. Mycorrhizae are useful for plants because they
(a) fix atmospheric nitrogen.
(b) enhance absorption of nutrients from the soil.
(c) kill insects and pathogen.
(d) provide resistance against abiotic stresses.
Answer
B
Question. A specimen of fungus is brought by a student for identification. Upon close examination, he discovered that its hyphae are completely septate and it has gills on the underside of the pileus. To which fungal group does it most likely belong ?
(a) Basidiomycetes
(b) Zygomycetes
(c) Ascomycetes
(d) Chytrids
Answer
A
Question. Fungi show asexual reproduction by all of the following kinds of spores except
(a) conidia
(b) oospores
(c) sporangiospores
(d) zoospores
Answer
B
Question. Protozons are not included in kingdom animalia because they are
(a) mostly asymmetrical.
(b) unicellular eukaryotes.
(c) heterotrophic in nature.
(d) multicellular prokaryotes.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is the correct sequence of three steps in the sexual cycle of fungi?
(a) Mitosis → Meiosis → Fertilization
(b) Plasmogamy → Karyogamy → Meiosis
(c) Mitosis → Plasmogamy → Karyogamy
(d) Karyogamy →Plasmogamy → Meiosis
Answer
B
Question. Identify the basis of classification of fungi into phycomycetes, ascomycetes, basidiomycetes and deuteromycetes.
i. Fruiting bodies
ii. Nature of habitat
iii. Morphology of mycelium
iv. Mode of spore formation
(a) i & ii only
(b) ii & iii only
(c) i, iii, & iv only
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Refer to the statement and answer the question.
“Once the sexual stage of members of deuteromycetes were discovered, they were often moved to X and Y.” Identify X and Y.
(a) X – Monera ; Y – Protista
(b) X – Basidiomycetes ; Y – Phycomycetes
(c) X – Ascomycetes ; Y – Basidiomycetes
(d) X – Phycomycetes ; Y – Archaebacteria
Answer
C


