Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter 6 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Biology Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Assignments Class 12 Biology
Question. Which of the following pyrimidine base is common in both DNA and RNA
(a) Adenine
(b) Guanine
(c) Cytosine
(d) Thymine
Answer
C
Question. The backbone in a polynucleotide chain is formed due to
(a) Sugars and nitrogenous bases
(b) Phosphates and nitrogenous base
(c) Nitrogenous bases and histones
(d) Sugar and phosphates
Answer
D
Question. In RNA, every nucleotide residue has an additional – OH group at which of the following position
(a) 2′ position of deoxyribose
(b) 1′ possition of ribose sugar
(c) 3′ position of ribose sugar
(d) 2′ position of ribose sugar
Answer
D
Question. DNA as an acidic substance present in nucleus was first identified by
(a) Wilkins and Franklin
(b) Watson and Crick
(c) Friedich meischer
(d) Altmann
Answer
C
Question. In addition to hydrogen bonding which of the following feature confers stability to helical structure
(a) Phosphodiester bond
(b) Pairing between one purine and one pyrimidine
(c) Glycosidic linkage between sugar and nitrogenous base
(d) The plane of one base pair stacks over the other
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is responsible for constant distance between two polynuclestide chains in DNA
(a) Antiparallel polarity of two polynucleotide strands
(b) Hydrogen bonding
(c) Pairing between one purine and one pyrimidine
(d) All the above
Answer
C
Question. In prokaryotes predominant site for control of gene expression is the
(a) Control of rate of processing of primary transcript
(b) Control of rate of transcription initiation
(c) Control of transport of m-RNA from nucleus to cytoplasm
(d) Control of Translation
Answer
B
Question. HGP was closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called as
(a) Biofortification
(b) Bioinformatics
(c) Biomining
(d) Biotransformation
Answer
B
Question. Phosphoric acid remain associated with which of the following carbon of sugar in a nucleotide :-
(a) Ist
(b) 3rd
(c) 4th
(d) 5th
Answer
D
Question. In there are 3.3 x 109 bp present in genome, then what would be the length of the DNA of any somatic cell
(a) 1.1 meter
(b) 2.2 meter
(c) 3.3 meter
(d) 6.6 meter
Answer
B
Question. Positive charge and basic nature of histone is due to abundance of
(a) Lysines and tryptophanes
(b) Arginines & threonines
(c) Lysines and arginines
(d) Tryptophanes and threonines
Answer
C
Question. Negative charge of DNA is due to which of the following constituent
(a) Sugar
(b) Nitrogenous base
(c) Phosphoric acid
(d) Hydroxyl group (-OH) present on sugar
Answer
C
Question. A typical nucleosome contains how much amount of DNA
(a) 100 bp
(b) 146 bp
(c) 200 bp
(d) 346 bp
Answer
C
Question. In a mammalian somatic cell how many nucleosomes are present
(a) 6.6 x 109
(b) 3.3 x 109
(c) 3.3 x 107
(d) 3.3 x 105
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is actual sequence of packaging of DNA in eukaryotic cells
(a) DNA → Chromatin → Nucleosome → Chromosome
(b) DNA → Nucleosome → Chromosome → Chromatin
(c) DNA → Nucleosome → Chromatin → Chromosome
(d) DNA → Chromosome → Chromatin → Nucleosome
Answer
C
Question. The packaging of chromatin at higher level requires additional set of proteins that is known as
(a) Histone proteins
(b) NHC proteins
(c) Homeotic proteins
(d) Domain proteins
Answer
B
Question. The unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material came from the experiments of
(a) Griffith
(b) Avery, Macleod & Mccarty
(c) Hershey and Chase
(d) Watson and Crick
Answer
C
Question. Radioactive (S35) was detected in
(a) Supernatant
(b) Sediment
(c) Both
(d) Either 1 or 2
Answer
A
Question. Regarding to RNA which of the following feature is wrong
(a) Catalytic property
(b) Labile and easily degradable
(c) Absence of thymine
(d) Presence of methylated uracil
Answer
D
Question. Which fo the folloiwng reason is suitable to expalin that RNA is best for expression of characters
(a) It shows catalytic properties
(b) Presence of 2′-OH group on ribose sugar
(c) It can directly code for the synthesis of protein
(d) Presence of uracil
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not the feature of human genome ?
(a) Less than 2 percent of the genome code for protein
(b) Chromosome 1 has fewest gene (231)
(c) Repetitive sequences make up very large portion of human genome
(d) The functions are unknown for over 50% of the discovered genes
Answer
B
Question. The sequence of which chromosome number was completed in May 2006 ?
(a) Chromosome number 1
(b) Chromosome number 2
(c) Chromosome number 5
(d) Chromosome number 10
Answer
A
Question. The repressor of the operon is synthesized :
(a) All the time
(b) Certain time
(c) Non constitutively
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is responsible for short life span and fast rate of mutation and evolution
(a) Presence of DNA
(b) Presence of highly reactive RNA
(c) Double stranded genetic material
(d) Single stranded genetic material
Answer
B
Question. Double helix model of DNA proposed by watson and crick was based on
(a) X-ray diffraction data of Meischer
(b) X-ray crystallography data of Wilkins and Franklin
(c) X-ray diffraction data of Watson and Crick
(d) X-ray diffraction data of Chargaff
Answer
B
Question. Approach of HGP focused on identifying all the genes that expressed as RNA is known as
(a) Expressed sequence tags
(b) Sequence annotation
(c) Polymerase chain reaction
(d) Dermatoglyphics
Answer
A
Question. Automated DNA sequencers worked on the principle of a method developed by
(a) Watson
(b) Chargaff
(c) Frederick sanger
(d) Singer and Nicolson
Answer
C
Question. Regarding to features of double helix struture of DNA which of the following is wrong
(a) Two polynucleotide chains have antiparallel polarity
(b) The bases in two strands are paired through phosphodiester bonds
(c) Adenine form two hydrogen bonds with thymine
(d) The pitch of the helix is 3.4 nm
Answer
B
Question. A m-RNA also has some additional sequences that are not translated called UTR. The function of UTR is
(a) Charging of t-RNA
(b) Formation of peptide bond
(c) Helps in efficient translation
(d) Helps in translocation
Answer
C
Question. The t-RNA move away from ribosomes after translocation of ribosome in relation to m-RNA, is known as
(a) Acylated t-RNA
(b) Peptidyle t-RNA
(c) Deacylated t-RNA
(d) Charged t-RNA
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following evidence suggests that essential life processes evolved around RNA
(a) RNA used to act as genetic material
(b) RNA can act as catalyst
(c) RNA is highly reactive
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer
D
Question. Regarding to Meselson and Stahl experiment for semi conservative nature of DNA replication select out the wrong statement
(a) 15N of 15NH4Cl was incorporated in DNA and other compounds
(b) 15N & 14N can be differentiate on the basis of radioactive activity
(c) Heavy and normal DNA molecules could be distinguished by CsCl density gradient centrifugation
(d) 15N used in 15NH4Cl was not a radioactive isotope
Answer
B
Question. Nucleotide arrangement in DNA can be seen by
(a) X-ray crystallography
(b) electron microscope
(c) ultracentrifuge
(d) light microscope
Answer
A
Question. One turn of DNA possesses
(a) one base pair
(b) two base pairs
(c) five base pairs
(d) ten base pairs
Answer
D
Question. Information flow or central dogma of modern biology is
(a) RNA → Proteins → DNA
(b) DNA → RNA → RNA
(c) RNA → DNA → Proteins
(d) DNA → RNA → Proteins
Answer
D
Question. Genetic information is carried out by long chain molecule made up of
(a) amino acids
(b) enzymes
(c) nucleotides
(d) histone proteins
Answer
C
Question. In Meselson and Stahl’s experiments, heavy DNA was distinguished from normal DNA by centrifugation in
(a) CsOH gradient
(b) 14NH4Cl
(c) 15NH4Cl
(d) CsCl gradient
Answer
D
Question. The scientists involved in discovery of DNA as chemical basis of heredity were
(a) Hershey and Chase
(b) Griffith and Avery
(c) Avery, Mac Leod and McCarty
(d) Watson and Crick
Answer
C
Question. If a double stranded DNA has 20% of cytosine, what will be the percentage of adenine in it?
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 30%
(d) 60%
Answer
C
Question. A bacterium grown over medium having radioactive 35S incorporates radioactivity in
(a) carbohydrates
(b) proteins
(c) DNA
(d) RNA
Answer
B
Question. DNA replication is
(a) conservative and discontinuous.
(b) semi-conservative and semi-discontinuous.
(c) semi-conservative and discontinuous.
(d) conservative.
Answer
C
Question. Genetic code is
(a) triplet, universal, ambiguous and degenerate.
(b) triplet, universal, non-ambiguous and nondegenerate.
(c) triplet, universal, non-ambiguous and degenerate.
(d) triplet, universal, ambiguous and non-degenerate.
Answer
C
Question. Frame shift mutation occurs when
(a) base is deleted or added.
(b) base is added.
(c) base is deleted.
(d) anticodons are not present.
Answer
A
Question. In eukaryotes, mRNA is synthesized with the aid of
(a) RNA polymerase III.
(b) RNA polmerase II.
(c) RNA polymerase I.
(d) reverse transcriptase.
Answer
B
Question. In Escherichia coli, lac operon is induced by
(a) lactose
(b) promotor gene
(c) b-galactosidase
(d) I-gene
Answer
A
Question. Lac operon is
(a) arabinose operon
(b) repressible operon
(c) inducible operon
(d) overlapping genes
Answer
C
Question. Which process is used for amplication or multiplication of DNA for finger printing ?
(a) Polymerse chain reaction (PCR)
(b) Nesslerisation
(c) Southern blotting
(d) Northern blotting
Answer
A
Question. VNTRs are
(a) Variable Number of Tandem Repeats.
(b) Very Narrow Tandem Repeats.
(c) Variable Non-cistronic Transposon Repeats.
(d) Valuable Non-cistronic Transposon Regions.
Answer
A
Question. Human Genome Project (HGP) is closely associated with the rapid development of a new area in biology called as
(a) biotechnology
(b) bioinformatics
(c) biogeography
(d) bioscience
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. Which of the following statement forms the basis of DNA fingerprinting?
(a) The relative proportions of purines and pyrimidines in DNA.
(b) Satellite DNA occurring as highly repeated short DNA segments.
(c) The relative difference in the DNA occurrence in blood, skin and saliva.
(d) The relative amount of DNA in the ridges and grooves of the fingerprints.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) VNTR belong to a class of mini satellite DNA.
(b) DNA sequences work on the principle developed by F. Sanger.
(c) HGP was coordinated by US Department of Energy and the National Institute of Health.
(d) DNA fingerprinting involves identifying similarities in repetitive DNA.
Answer
D
Question. Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) In prokaryotes, the structural gene is polycistronic.
(b) In eukaryotes, structural genes have interrupted coding sequences.
(c) Eukaryotes have split gene arrangement.
(d) Intervening sequences appear in mature RNA.
Answer
D
Question. Find out the incorrect statement.
(a) Uracil is present in RNA at the place of thymine.
(b) The complex of DNA and protein in chromosome is called chromatin.
(c) Heterochromatin is the most highly condensed form of chromatin.
(d) The process involved in the RNA formation on the DNA template is called replication.
Answer
D
Question. How many of the given statements (i-iv) is/are correct?
(i) In transcription, adenosine pairs with uracil.
(ii) Regulation of lac operon by repressor is referred to as positive regulation.
(iii) The human genome has approximately 50,000 genes.
(iv) Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease.
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) One
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements about RNA polymerase are correct?
(i) RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNAs.
(ii) RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNAs.
(iii) RNA polymerase III transcribes hnRNA.
(iv) RNA polymerase II transcribes hnRNAs.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. Read the following statements and choose the incorrect statements.
(i) Nitrogenous base is linked to the pentose sugar through a N-glycosidic linkage.
(ii) Phosphate group is linked to 5’–OH of a nucleoside through phosphoester linkage.
(iii) Two nucleosides are linked through 3’–5’N-glycosidic linkage.
(iv) Negatively charged DNA is wrapped around positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.
(v) The chromatin that is more densely packed and stains dark is called euchromatin.
(a) (i) only
(b) (iv) only
(c) (iii) and (v)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
C
Assertion / Reason Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : A single mRNA strand is capable of forming a number of different polypetide chains.
Reason : The mRNA strand has terminator codon.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Replication and transcription occur in the nucleus but translation takes place in the cytoplasm.
Reason : mRNA is transferred from the nucleus into cytoplasm where ribosomes and amino acids are available for protein synthesis.
Answer
A
Matching Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. Match the enzymes (given in column I) with their function (given in column II) and choose the correct combination from the given options.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Helicase | I. Joining of nucleotides |
| B. Gyrase | II. Opening of DNA |
| C. Primase | III. Unwinding of DNA |
| D. DNA polymerase III | IV. RNA priming |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
D
Question. Match the column-I with column-II and choose the correct combination from the given options.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Operator site | I. Binding site for RNA polymerase |
| B. Promoter site | II. Binding site for repressor molecule |
| C. Structural gene | III. Codes for enzyme protein |
| D. Regulator gene | IV. Codes for repressor molecules |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
(b) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – I; D – IV
Answer
A
Question. Match the column-I with column-II and select the correct combination from the given options.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Griffith | I. Nucleoid |
| B. Hershey and Chase | II. Active chromatin |
| C. Prokaryotic DNA | III. Transduction |
| D. Euchromatin | IV. Transformation |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
(b) A – III; B – I; C – IV; D – II
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – I; D – II
(d) A – II; B – III; C – I; D – IV
Answer
C
Question. Match the enzymes given in column -I with its function given in column -II and select the correct option.

(a) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(b) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
(c) A – II; B – IV; C – I; D – III
(d) A – I; B – II; C – IV; D – III
Answer
B
Question. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct combination from the given options.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Sigma factor | I. 5′ – 3′ |
| B. Capping | II. Initiation |
| C. Tailing | III. Termination |
| D. Coding strand | IV. 5′ end |
| V. 3′ end |
(a) A – III; B – V; C – IV; D – II
(b) A – II; B – IV; C – V; D – I
(c) A – II; B – IV; C – V; D – III
(d) A – III; B – V; C – IV; D – I
Answer
B
Question. Match the following
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) f x 174 | (i) 48502 bp |
| (B) Lambda phage | (ii) 5386 Nucleotides |
| (C) E.Coli | (iii) 6.6 x 109 bp |
| (D) Human somatic cell | (iv) 4.6 x 106 bp |
(a) A(i), B(ii), C(iv), D(iii)
(b) A(ii), B(i), C(iv), D(iii)
(c) A(i), B(ii), C(iii), D(iv)
(d) A(iv), B(iii), C(ii), D(i)
Answer
D
Question. Match the following
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. SNPs | i. 3164.7 million |
| B. Genes of | ii. 1.4 Million chromosome No. 1 |
| C. Total No. of Human | iii. 30000 genes |
| D. Total nucleotides of | iv. 2968 human genome |
A B C D
(a) ii iii iv i
(b) ii iv iii i
(c) ii iv i iii
(d) iv ii iii i
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. The given figure shows the structure of nucleosome with their parts labelled as A, B & C. Identify A, B and C.
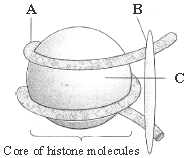
(a) A – DNA; B – H1 histone; C – Histone octamer
(b) A – H1 histone; B – DNA; C – Histone octamer
(c) A – Histone octamer; B – RNA; C – H1 histone
(d) A – RNA; B – H1 histone; C – Histone octamer
Answer
A
Question. The given figure represents the double stranded polynucteotide chain. Some parts are labelled as A, B, C, D and E. Identify the correct labelling of A, B, C, D & E.
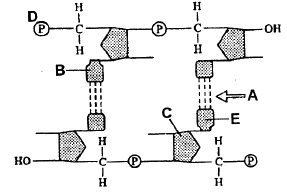
(a) A–Hydrogen bonds, B–Pyrimidine, C–Hexose (deoxyribose) sugar, D–5′ end, E–Purine base
(b) A–Hydrogen bonds, B–Purine base, C–Hexose (deoxyribose) sugar, D–5′ end, E–Pyrimidine
(c) A–Hydrogen bonds, B–Pyrimidine, C–Pentose (deoxyribose) sugar, D–5′ end, E–Purine base
(d) A–Hydrogen bonds, B–Purine base, C–Pentose (deoxyribose) sugar, D– 5′ end, E– Pyrimidine
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following correctly represents the manner of replication of DNA ?
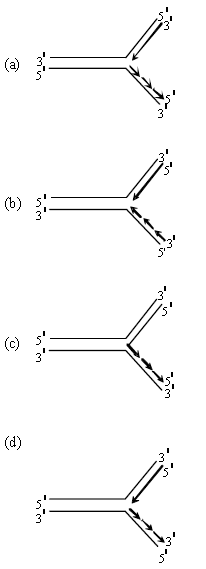
Answer
D
Question. Given diagram represents the schematic structure of a transcription unit with some parts labelled as A, B, C and D. Select the option which shows its correct labelling.

Answer
C
Question. The given figure represent one of the step in the process of transcription in bacteria. Identify the step and label A, B & C marked in the figure.
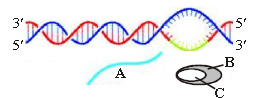
(a) Initiation; A – DNA, B – RNA, C – Promoter
(b) Termination; A – RNA, B – RNA polymerase,C – Rho factor
(c) Elongation; A – RNA, B – RNA polymerase, C – Sigma factor
(d) Elongation; A – DNA, B – DNA polymerase,C – RNA
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question. In tertiary structure of DNA, what is a histone octamer ?
(a) A complex consisting of eight positively charged histone proteins (two of each H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) that aid in the packaging of DNA.
(b) A complex consisting of eight negatively charged histone proteins (two of each H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) that aid in the packaging of DNA.
(c) A complex consisting of nine positively charged histone proteins (H1 and two of each H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) that aid in the packaging DNA.
(d) A complex consisting of nine negatively charged histone proteins (H1 and two of each H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) that aid in the packaging of DNA.
Answer
A
Question. The most abundant type of RNA in the cell is
(a) rRNA
(b) mRNA
(c) t RNA
(d) hn RNA
Answer
A
Question. DNA exists in a double-stranded form whereas RNA is mainly a single stranded molecule. What is the likely reason for DNA being double stranded ?
(a) RNA strands cannot form base pairs.
(b) Double stranded DNA is a more stable structure.
(c) DNA cannot exist in the single stranded form.
(d) It is easier to replicate double stranded DNA than single stranded RNA.
Answer
B
Question. Which step of translation does not consume high energy phosphate bond?
(a) Translocation
(b) Peptidyl transferase reaction
(c) Amino acid activation
(d) Aminoacyl tRNA binding to A-site
Answer
B
Question. Determination of one amino acid by more than one codon is due to
(a) redundancy of genetic code.
(b) continuous nature of genetic code.
(c) punctuation in genetic code.
(d) universal nature of genetic code.
Answer
A
Question. Clover leaf secondary structure of tRNA has a loop for
(a) three nucleotides of a codon.
(b) three nucleotides of an anticodon.
(c) no nucleotides.
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Mutations which alter nucleotide sequence within a gene are called
(a) frame shift mutations
(b) base pair substitutions
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following group of codons is called as degenerate codons?
(a) UAA, UAG and UGA
(b) GUA, GUG, GCA, GCG and GAA
(c) UUC, UUG, CCU, CAA and CUG
(d) UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA and CUG
Answer
A
Question. Transcription
(a) starts at initiator region and ends at stop region.
(b) starts at operator region and ends at telomeric end.
(c) starts at promoter region and ends at terminator region.
(d) starts at CAAT box and ends at TATA box.
Answer
C
Question. Nucleotides are linked by
(a) hydrogen bonds.
(b) phosphodiester bonds.
(c) peptic bonds.
(d) ionic bonds.
Answer
B
Question. A DNA strand with the sequence AACGTAACG is transcribed. What is the sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized ?
(a) AACGTAACG
(b) UUGCAUUGC
(c) AACGUAACG
(d) TTGCATTGC
Answer
B
Question. What role does messenger RNA play in the synthesis of proteins ?
(a) It catalysis the process.
(b) It translates the genetic code to a specific amino acid.
(c) It provides the genetic blue print for the protein.
(d) It modifies messenger RNA molecules prior to protein synthesis.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following molecule contains the genetic code?
(a) DNA
(b) mRNA
(c) tRNA
(d) rRNA
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following would you expect to find in an inducible system ?
(a) A repressor protein, which is bound to DNA in absence of any other factor.
(b) A repressor protein, which is bound to DNA in the presence of a co-repressor.
(c) An activator protein, which is bound to DNA in the absence of any other factor.
(d) An activator protein, which is bound to DNA only in the absence of air inhibitor.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is Not a goal of the human genome project ?
(a) To sequence the genomes of selected model organisms.
(b) To eliminate all diseases.
(c) To consider social, ethical and legal aspects of genetic information.
(d) To develop computational tools for analyzing sequence information.
Answer
C
Question. Each individual has a unique DNA fingerprint as individuals differ in
(a) number of minisatellites on chromosome.
(b) location of minisatellites on chromosome.
(c) size of minisatellites on chromosome.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. The okazaki fragments in DNA chain
(a) result in transcription.
(b) polymerize in the 3′ to 5′ direction and forms replication form.
(c) prove semi-conservative nature of DNA replication.
(d) polymerize in the 5′ to 3′ direction and explain 3′ to 5′ DNA replication.
Answer
D


