Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare Chapter 10 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Biology Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Microbes in Human Welfare Assignments Class 12 Biology
MCQs for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Question. Nutritionally curd is more suitable then milk. Which of the following reason not supporting to this view
(a) It increasing vitamin B12
(b) It checks disease causing microbes
(c) LAB convert lactose into lactic curd
(d) It provide additional proteins
Answer
D
Question. Full potential of penicillin as an effective antibiotic was established by
(a) Alexander Flemming
(b) Ernest chain
(c) Howard florey
(d) Both 2 and 3
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is “Clot buster”
(a) Citric acid
(b) Streptokinase
(c) Cyclosporin
(d) Statins
Answer
B
Question. Large holes in “Swiss cheese” are due to production of large amount of CO2 by _______ bacterium
(a) Leuconostoc mesenteroides
(b) Propionibacterium sharmanii
(c) Thermococcus proteus
(d) Staphylococcus thermophilus
Answer
B
Question. Functioning of statin is based on
(a) Competitive inhibition
(b) Endproduct inhibition
(c) Allosteric inhibition
(d) Negative feed back inhibition
Answer
A
Question. The technology of biogas production was developed in India mainly due to efforts of
(a) IARI
(b) KVIC
(c) IPM
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following bacteria was associated with discovery of penicillin
(a) Streptococus
(b) Staphylococcus
(c) Saccharomyces cerveisiae
(d) Propionobacterium
Answer
B
Question. Bacillus thuringiensis show their inhibitory effect on which part of the insect body
(a) Gut
(b) Respiratory tract
(c) Nervous system
(d) Circulatory system
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following biological agents are used for species specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications
(a) Adenoviruses
(b) Nucleopolyhedrosis viruses
(c) Retroviruses
(d) Trichoderma
Answer
B
Question. Members of which of the following fungal genus mainly participate in the mycorrhiza formation
(a) Azotobacter
(b) Fusarium
(c) Rhizopus
(d) Glomus
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not an advantage of mycorrhiza
(a) Phosphorus absorption
(b) Resistance to root borne pathogens
(c) Nitrogen fixation
(d) Tolerance to salinity and draught
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following chemicals, used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplantation
(a) Streptokinase
(b) Cyclosporin – A
(c) Statins
(d) Citric acid
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is one of the advantage of application of viruses as bioinsecticides
(a) They are less effective
(b) They are host specific
(c) They are costly
(d) They can not obtain easily
Answer
D
Question. In which of the following conditions use of baculoviruses is desirable
(a) When they are used as part of IPM
(b) When an ecologically sensitive area is being treated
(c) When beneficial insects are being conserved
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a product of distillation
(a) Whisky
(b) Brandy
(c) Wine
(d) Rum
Answer
C
Question. Find out odd one with refrence to distillation
(a) Beer
(b) Wine
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Vodka
Answer
D
Question. Use of biofertilizer is the part of
(a) Inorganic farming
(b) Organic farming
(c) Energy cropping
(d) Energy plantation
Answer
B
Question. Cultivation of which of the following crop plant specially get benif itted by application of cyanobacteria
(a) Maize
(b) legumes
(c) Wheat
(d) Rice
Answer
D
Question. Identify the organism shown in the given diagram.

(a) Bacteria
(b) Bacteriophage
(c) TMV
(d) HIV
Answer
C
Question. Yeast is used in the production of
(a) bread and beer
(b) cheese and butter
(c) citric acid and lactic acid
(d) lipase and pectinase.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is not used in organic farming?
(a) Glomus
(b) Earthworm
(c) Oscillatoria
(d) Snail
Answer
D
Question. The microbial biocontrol agent for butterfly caterpillar is
(a) Bacillus thuringiensis
(b) Saccharomyces
(c) Lactobacillus
(d) Cyanobacteria
Answer
A
Question. A nitrogen-fixing microbe associated with Azolla in rice fields is
(a) Spirulina
(b) Anabaena
(c) Frankia
(d) Tolypothrix.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is wrongly matched in the given table?
(a) Streptococcus Streptokinase Removal of clot from blood vessel
(b) Clostridium butylicum Lipase Removal of oil stains
(c) Trichoderma polysporum Cyclosporin A Immunosuppressive drug
(d) Monascus purpureus Statins Lowering of blood cholesterol
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following microbes is used for the commercial production of ethanol?
(a) Clostridium butylicum
(b) Trichoderma polysporum
(c) Monascus purpureus
(d) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Answer
B
Question. A person admitted to hospital as he had myocardial infarction. A cardiologist injected him ‘streptokinase’, why?
(a) It stimulates heart beat.
(b) It reduces hypertension.
(c) It acts as clot buster.
(d) It reduces the level of blood cholesterol.
Answer
C
Question. Select the correct pair of microorganism and the product obtained from it.
(a) Monascus purpureus – produces large holes in Swiss cheese.
(b) Saccharomyces cerevisiae – used for making wine and beer after distillation.
(c) Streptococcus – produces streptokinase which is used to remove clots.
(d) Aspergillus niger – produces citric acid and butyric acid.
Answer
C
Question. ‘Roquefort cheese’ is ripened by using a
(a) bacterium
(b) yeast
(c) cyanobacteria
(d) fungus.
Answer
D
Question. Which among these are produced by distillation of fermented broth?
(i) Whisky
(ii) Wine
(iii) Beer
(iv) Rum
(v) Brandy
(a) (ii) and (iii) only
(b) (i) and (ii) only
(c) (iii) and (v) only
(d) (i), (iv) and (v) only
Answer
D
Question. The primary treatment of sewage water involves
(a) anaerobic bacterial activity
(b) sludge digestion
(c) filtration and sedimentation
(d) aerobic bacterial activity.
Answer
C
Question. What gases are produced in anaerobic sludge digesters?
(a) Methane and CO2 only
(b) Methane, Hydrogen sulphide and CO2
(c) Methane, Hydrogen sulphide and O2
(d) Hydrogen sulphide and CO2
Answer
B
Question. When domestic sewage mixes with river water
(a) small animals like rats will die after drinking river water
(b) the increased microbial activity releases micronutrients such as iron
(c) the increased microbial activity uses up dissolved oxygen
(d) the river water is still suitable for drinking as impurities are only about 0.1%.
Answer
C
Question. Refer to the given diagram and choose the correct option for it.

(a) Bacteriophage – Tobacco mosaic disease
(b) Adenovirus – Respiratory disease
(c) Viroid – Potato spindle tumour disease
(d) Prion – Alzheimer’s disease
Answer
B
Question. Select the correct statement from the following.
(a) Biogas is produced by the activity of aerobic bacteria on animal waste.
(b) Methanobacterium is an aerobic bacterium found in rumen of cattle.
(c) Biogas, commonly called gobar gas, is pure methane.
(d) Activated sludge-sediment in settlement tanks of sewage treatment plant is a rich source of aerobic bacteria.
Answer
D
Question. Select the correct group of biocontrol agents.
(a) Nostoc, Azospirillum, Nucleopolyhedrovirus
(b) Bacillus thuringiensis, Tobacco mosaic virus, Aphids
(c) Trichoderma, Baculovirus, Bacillus thuringiensis
(d) Oscillatoria, Rhizobium, Trichoderma
Answer
B
Question. Select the mismatch.
(a) Rhodospirillum – Mycorrhiza
(b) Anabaena – Nitrogen fixer
(c) Rhizobium – Alfalfa
(d) Frankia – Alnus
Answer
A
Case Based MCQs for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Case I : Read the following passage and answer questions given below:
Yeast and certain bacteria play a key role fermentation to breakdown carbohydrates into ethanol and carbon dioxide which then further used to prepare acetic acid with the help of bacterium Acctobacter aceti. Alcoholic fermentation in anaerobic process, but the conversion of alcohol to acetic acid is aerobic one.
This process can be represented by following equation :
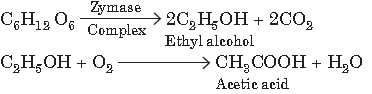
Question. A number of chemicals are produced at the time of alcoholic fermentation with the change of nutrient media, pH and aeration. Select such by-product from the following.
(a) Butanol
(b) Succinic acid
(c) Acetaldehyde
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Distilled alcohol with 95% ethanol content is called
(a) absolute alcohol
(b) rectified spirit
(c) gin
(d) brandy.
Answer
B
Case II : Read the following passage and answer the questions given below.
Villagers in a place near Chambur started planning to make power supply for agricultural purposes from cow dung. They have started a biogas plant for the purpose. Study the flow chart for biogas production given below and answer the following questions

Question. Biogas is composed of majorly
(a) methane, CO2 and O2
(b) CO2, H2S and H2O
(c) methane, CO2 and H2S
(d) H2S, H and O2.
Answer
C
Question. What is represented by ‘B’ in the flow chart?
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Protein polymers
(c) Organic acids
(d) Fat globules
Answer
C
Question. If ‘A’ is not added in the procedure
(a) methane will not be formed
(b) CO2 will not be formed
(c) organic compounds will not be converted to H2S
(d) O2 will not be formed.
Answer
A
Case Based MCQs for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Azolla is used as a biofertiliser in rice fields.
Reason : Azolla shows the presence of N2 – fixing bacteria in its leaf cavities.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : An organism which acts as herbicide is called bioherbicide.
Reason : Phytophthora palmivora is a mycoherbicide.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Curdling is required in the manufacture of cheese.
Reason : Lactic acid bacteria and rennet is used for the purpose.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Aspergillus niger produces lactic acid.
Reason : Aspergillus niger carry out fermentation.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Champagne gives off bubbles.
Reason : Alcoholic content is 12 – 16% in champagne.
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Question. Which one of the following statement regarding BOD is true?
(a) The greater the BOD of waste water, more is its polluting potential.
(b) The greater the BOD of waste water, less is its polluting potential.
(c) The lesser the BOD of waste water, more is its polluting potential.
(d) The lesser the BOD of waste water, less is its polluting potential.
Answer
A
Question. Pollution from animal excreta and organic wastes from kitchen can be most profitably minimised by
(a) storing them in underground storage tanks.
(b) using them for producing biogas.
(c) vermiculture.
(d) using them directly as biofertilizers.
Answer
B
Question. Organic farming includes
(a) use of fertilizers and pesticides of biological origin.
(b) IPM (integrated pest management programme).
(c) locally developed pest resistant varieties.
(d) all of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is correct ?
(a) Methanobacterium is an aerobic bacterium found in rumen of cattle.
(b) Biogas (commonly called gobar gas) is pure methane.
(c) Activated sludge sediment in settlement tanks of sewage treatment plants is rich source of aerobic
bacteria.
(d) Biogas is produced by the activity of aerobic bacteria on animal waste.
Answer
C
Question. Consider the following statements about organic farming.
(i) It utilizes genetically modified crops like Bt cotton.
(ii) It uses only naturally produced inputs like compost.
(iii) It does not use pesticides and urea.
(iv) It produces vegetables rich in vitamins and minerals.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv) only
(c) (ii) and (iii) only
(d) (i) and (ii) only
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Question. Match the columns and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Aspergillus niger | I. Ethanol |
| B. Clostridium | II. Statins butydicum |
| C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae | III. Citric acid |
| D. Trichoderma polysporum | IV. Butyric acid |
| E. Monascus purpureus | V. Cyclosporin A |
(a) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I; E – V
(b) A – V; B – IV; C – I; D – II; E – III
(c) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – V; E – II
(d) A – III; B – IV; C – V; D – I; E – II
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns and choose the correct combination.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Escherichia coli | I. ‘nif ’ gene |
| B. Rhizobium meliloti | II. Digests (hydrocarbons of crude) oil |
| C. Bacillus thuringiensis | III. Human insulin production |
| D. Pseudomonas putida | IV. Biocontrol of fungal disease |
| V. Biodegradable insecticide |
(a) A – III; B – I; C – V; D – II
(b) A – III; B – I; C – V; D – IV
(c) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
(d) A – II; B – I; C – III; D – IV
Answer
A
Question. The given table contains type of microbe (Column I),
Scientific name (Column II) and commercial product (Column III). Some names are replaced by A, B, C and D.
Identify the correct names.
| Type of Microbe | Scientific Name | Commercial Product |
| Bacterium | A | Lactic acid |
| Fungus | B | Cyclosporin A |
| C | Monascus purpureus | Statins |
| Fungus | Penicillium notatum | D |
(a) A – Lactobacillus, B – Trichoderma polysporum, C – Yeast (fungus), D – Penicillin
(b) A – Lactobacillus, B – Trichoderma polysporum, C – Yeast (algae), D – Penicillin
(c) A – Lactobacillus, B – Trichoderma polysporum, C – Yeast (prokaryote), D – Penicillin
(d) A – Lactobacillus, B – Trichoderma polysporum, C – Agaricus (fungus), D – Penicillin
Answer
A
Question. Identify the blank spaces marked A, B, C and D from the table given below.

(a) A–Trichoderma polyspora, B – Organ transplant patients, C – Yeast (fungus), D – Lowering of blood
cholesterol.
(b) A–Lowering of blood cholesterol, B – Trichoderma polyspora, C – Organ transplant patients, D – Yeast
(fungus).
(c) A – Yeast (fungus), B – Lowering of blood cholesterol, C – Trichoderma polyspora, D – Organ transplant patients.
(d) A – Organ transplant patients, B – Yeast (fungus), C – Lowering of blood cholesterol, D – Trichoderma
polyspora.
Answer
A
Question. Match the following
| A. Pectinases | i. Blood cholesterol lowering agents |
| B. Streptokinases | ii. Immunosuppressive agents |
| C. Cyclosporin – A | iii. Clot-busters |
| D. Statin | iv. Clearifying agents |
A B C D
(a) iv iii ii i
(b) iv iii i ii
(c) iii iv ii i
(d) i ii iii iv
Answer
A
Question. Match the following
| A. Citric acid | i. Haemolytic streptococcus |
| B. Streptokinase | ii. Aspergillus niger |
| C. Cyclosporin – A | iii.Monascus purpureus |
| D. Statins | iv.Trichoderma polysporum |
A B C D
(a) i ii iii iv
(b) ii i iii iv
(c) ii i iv iii
(d) iv ii iii i
Answer
C
Question. Match the microbes in column I with their commercial/industrial products in column II and choose the correct answer.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Aspergillus niger | 1. Ethanol |
| B. Clostridium butylicum | 2. Statins |
| C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 3. Citric acid |
| D. Trichoderma polysporum | 4. Butyric acid |
| E. Monascus purpureus | 5. Cyclosporin A |
(a) A – 4, B – 5, C – 2, D – 1, E – 3
(b) A – 5, B – 4, C – 1, D – 2, E – 3
(c) A – 3, B – 4, C – 1, D – 5, E – 2
(d) A – 3, B – 4, C – 5, D – 1, E – 2
Answer
C
Question. Match the following organisms with the products they produce.
| (A) Lactobacillus | (i) Cheese |
| (B) Saccharomyces | (ii) Curd cerevisiae |
| (C) Aspergillus niger | (iii) Citric acid |
| (D) Acetobacter aceti | (iv) Bread |
| (v) Acetic acid |
Select the correct option.
(A) (B) (C) (D)
(a) (ii) (i) (iii) (v)
(b) (ii) (iv) (v) (iii)
(c) (ii) (iv) (iii) (v)
(d) (iii) (iv) (v) (i)
Answer
C
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The diagram below shows a typical biogas plant. With few structure labelled as A, B and C. Identify A, B and C.

(a) A – Sludge, B – Methane, Oxygen, C – Dung, water
(b) A – Sludge, B – Methane, Carbon dioxide, C– Dung,water
(c) A – Sludge, B – Ethylin, Carbon dioxide, C – Dung,water
(d) A – Sludge, B – Methane, Carbon dioxide, C – Sewage
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Which of the following is the pair of biofertilizers?
(a) Azolla and blue green algae
(b) Nostoc and legume
(c) Rhizobium and grasses
(d) Salmonella and E. coli
Answer
A
Question. Microbes are present in
I. soil
II. air
III. water
IV. thermal springs
(a) I, III, IV
(b) I, II, III, IV
(c) I, II
(d) III, IV
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is used as biofertilizer ?
I. Cyanobacteria
II. Yeast
III. Symbiotic bacteria
IV. Free living bacteria
(a) I, II, III
(b) I, II, IV
(c) I, III, IV
(d) II, III, IV
Answer
C
Question. Methanogens grow anaerobically on cellulosic material and produces which of the following gases ?
I. Methane
II. Oxygen
III. Carbon dioxide
IV. Hydrogen
(a) I, III, IV
(b) I, II, III, IV
(c) II, III, IV
(d) I, II
Answer
A
Question. Antibiotics are drugs commonly used to cure diseases of
(a) fungi
(b) viruses
(c) protozoans
(d) bacteria
Answer
D
Question. Lactobacillus mediated change of milk to curd occurs due to
(a) coagulation and partial digestion of milk fats.
(b) coagulation and partial digestion of milk proteins.
(c) coagulation of milk proteins and complete digestion of milk fats.
(d) coagulation of milk fats and complete digestion of proteins.
Answer
B
Question. Choose the correct sequence of microbes involved in biogas production.
(a) Fragmentative microbes, decomposers, methanogens.
(b) Decomposers, methanogens, putrefying microbes.
(c) Putrefying microbes, methanogens, saprophytic microbes.
(d) Decomposers, fermentative microbes, methanogens.
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the micro-organism is used for production of citric acid in industries?
(a) Lactobacillus bulgaricus
(b) Penicillium citrinum
(c) Aspergillus niger
(d) Rhizopus nigricans
Answer
C
Question. A genetically engineered micro-organism used successfully in bioremediation of oil spills is a species of
(a) Pseudomonas
(b) Trichoderma
(c) Xanthomonas
(d) Bacillus
Answer
A
Question. Microbes are used in the
I. primary treatment of sewage.
II. secondary treatment of sewage.
III. anaerobic sludge digester.
IV. production of bioactive molecules.
Choose the correct option showing the uses of microbes.
(a) I, III, IV
(b) I, II, III, IV
(c) II, III, IV
(d) IV, I, II
Answer
C
Question. A lake with an inflow of domestic sewage rich in organic waste may result in
(a) drying of the lake very soon due to algal bloom.
(b) an increased production of fish due to lot of nutrients.
(c) death of fish due to lack of oxygen.
(d) increased population of aquatic food web organization.
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Question. BOD of two samples of water A and B were 120 mg/L and 400 mg/L respectively. Which sample is more polluted?
Answer : Water body having high BOD is more polluted as compared to water body having low BOD. Hence water sample having BOD 400 mg/L is more polluted as compared to water sample having BOD 120 mg/L.
Question. Name the metabolic pathway associated with the rising of dough in making bread. What makes the dough rise?
Answer : When Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker’s yeast) is added to dough it causes its fermentation and releases CO2 gas which is responsible for puffed up appearance of dough.
Question. Name the nutrient that gets enhanced while curdling of milk by Lactobacillus.
Answer : The curdling of milk by Lactobacillus changed milk into curd and its nutritional quality is enhanced due to increase in vitamin B12 content.
Question. List two advantages that a mycorrhizal association provides the plant.
Answer : Mycorrhiza perform following functions for the plant :
(i) Absorption of water and minerals like phosphorus from the soil and passing it to the plants.
(ii) Solubilisation of organic matter of the soil humus and their transfer to roots.
Question. Which of the following is a free living bacteria that can fix nitrogen in the soil?
Spirulina, Azospirillum, Sonalika
Answer : Azospirillum is a free living nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Short Answer Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Question. Why are some molecules called bioactive molecules? Give two examples of such molecules.
Answer : Bioactive compounds are those compounds that have an effect on living organisms tissues or cells. Bioactive compounds are found in both plant and animal products or can be synthetically produced. Two examples of bioactive compounds are cyclosporin A and statins.
Question. Name the blank spaces a, b, c and d in the table given below.

Answer : a = Lactobacillus bulgaricus
b = Trichoderma polysporum
c = Yeast (Fungus)
d = Penicillin
Question. How does the application of the fungal genus, Glomus, to the agricultural farm increase the farm output?
Answer : Many members of the genus Glomus form symbiotic associations with plants to form mycorrhiza. Glomus helps to absorb phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plant.
Plants having such associations show other benefits also, such as resistance to root-borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity and drought and an overall increase in plant growth and development. Therefore, Glomus increases the farm yield.
Question. Your advice is sought to improve the nitrogen content of the soil to be used for cultivation of a non-leguminous terrestrial crop.
(a) Recommend two microbes that can enrich the soil with nitrogen.
(b) Why do leguminous crops not require such enrichment of the soil?
Answer : (a) Azotobacter and Azospirillum.
(b) Leguminous crops have symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria such as Rhizobium that live in the root nodules of these plants. These bacteria obtain food and shelter from the plant and in return they trap nitrogen directly from the atmosphere which they provide to the plant.
Question. Name the organism that fixes nitrogen in symbiotic association with a water fern. Where does it live in such plant?
Answer : Anabaena azollae (blue green alga) fixes nitrogen in symbiotic association with a water fern. It resides in the leaf cavities of the fern.
Question. (a) Why are the fruit juices bought from market clearer as compared to those made at home?
(b) Name the bioactive molecules produced by Trichoderma polysporum and Monascus purpureus.
Answer : (a) The fruit juices sold in market or bottled juices are treated with pectinases and proteases which makes them clearer than those made at home.
(b) Cyclosporin A is obtained from fungus Trichoderma polysporum whereas statin is obtained from yeast Monascus purpureus.
Cyclosporin A has immunosuppressive properties. It inhibits activation of T cells and therefore prevents rejection of transplants. Statin inhibits cholesterol synthesis and is therefore used in lowering blood cholesterol.
Question. During the production of curd, a small amount of curd is added as a starter to the fresh milk at a suitable temperature. Explain the changes the milk undergoes when it sets into curd.
Answer : The starter or inoculum used in preparation of milk products actually contains millions of lactic acid bacteria.
Curd is prepared by inoculating cream and skimmed milk with Lactobacillus acidophilus at a temperature of about 40° C or less. Lactobacillus converts lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid which causes coagulation and partial digestion of milk protein casein and milk gets changed into curd, which also improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12 content.
Question. Describe the functions of anaerobic sludge digester in a sewage treatment plant.
Answer : In secondary sewage treatment, the sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge. A part of it is used as inoculum in aeration tank. The remaining is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sludge digester. It is designed for continuous operation. The aerobic microbes present in the sludge get killed. Anaerobic microbes digest the organic mass as well as aerobic microbes of the sludge. They are of two types, nonmethanogenic and methanogenic. Methanogenic bacteria produce a mixture of gases containing methane, H2S and CO2.
The mixture called biogas is inflammable and is a source of energy. The spent sludge can be used as manure or part of compost.
Question. Explain the role of baculoviruses as biological control agents. Mention their importance in organic farming.
Answer : Baculoviruses (a group of viruses) are known to infect the larval stages of many harmful insects such as ants, wasps, gnats and beetles. These biological weapons are not only effective as potential biological control of these insects, but are also harmless to non-target organisms (plants, mammals, birds, fish, or even non-target insects). Majority of baculoviruses belong to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus and are used as biopesticides during organic farming. Organic farming is a technique of raising crops through the use of manure, fertilizers and pesticides of biological origin.
Question. (a) Organic farmers prefer biological control of diseases and pests to the use of chemicals for the same purpose. Justify.
(b) Give an example of a bacterium, a fungus and an insect that are used as biocontrol agents.
Answer : (a) Chemical pesticides used in agricultural fields are toxic and they kill even useful organisms along with harmful ones, harm human beings and animals, pollute soil, water and crop plants. It is estimated that despite the use of chemical pesticides 30% of the agricultural produce is lost to pathogens and pests because these continue to develop resistance against various pesticides. Now, organic farmers prefer biological control of diseases and pests to the use of chemicals. Biopesticides are the biological agents that control the growth of weeds, insects and pathogens in an agricultural field. They have targeted actions and are harmless to the crop plants, other beneficial field animals and humans. In organic farming, pests and pathogens are not eradicated but kept at manageable levels by a system of checks and balances as operating in ecosystem. An organic farmer holds the view that eradicating pests is undesirable because without them the beneficial predatory and parasitic organisms which depend upon them for food would also be annihilated.
(b) Bacterium as a biocontrol agent : Bacillus thuringiensis is effective against the cabbage looper.
Fungi as a biocontrol agent : Trichoderma found in root ecosystem exerts biocontrol over several plant pathogens.
Insect as a biocontrol agent : Lady bird beetle and dragonflies feeds on aphids and prey upon mosquitoes, respectively.
Long Answer Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Microbes In Human Welfare
Question. Name the site of nitrogen fixation in legumes.
List and describe the biochemical components at this site.
Answer : Symbiotic nitrogen fixation is carried out by bacteria frequently found in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
The different components and their role in symbiotic nitrogen fixation are as follows:-
(i) Rhizobium : They are symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria commonly present in root nodules of leguminous plants and carry out conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous salts to make it available for absorption by plants.
(ii) Lectin : Lectins are the key proteins involved in the Rhizobium-legume symbiotic association. Bauer (1981) proposed that these lectins interact selectively with microbial cell carbohydrates (or glycoproteins) found in the capsule of bacteria and serve as determinants of recognition or host specificity.
(iii) Tryptophan : Leguminous plants release tryptophan in the soil which is absorbed by Rhizobium and is metabolised to produce IAA.
(iv) Root hair curling factor : The rhizobia produce another characteristic substance called root hair curling factor that causes deformation and twisting of root hairs.
(v) Leghaemoglobin : The nodule contains a pink coloured pigment leghaemoglobin which is like true haemoglobin combines with oxygen and CO2 gets readily oxidised into brown form with a trivalent iron.
(vi) Nitrogenase : Process of nitrogen fixation, involves reduction of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia (NH3) by the enzyme nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is made up of two protein components, one containing iron and molybdenum, known as Mo-Fe protein or molybdo-ferredoxin (component I) and the other containing only iron called Fe-protein or azoferredoxin. Nitrogenase is extremely sensitive to oxygen.
The enzyme remains active under anaerobic conditions. The leghaemoglobin binds with oxygen and protect nitrogenase from O2 inactivation. At the same time it is able to make O2 available to bacteroids for ATP production, required for nitrogen fixation.
Question. (a) Explain the process of sewage water treatment before it can be discharged into natural water bodies.
(b) Why is this treatment essential?
Answer : (a) Sewage water can be purified by passing it through sewage treatment plants with the action of microorganisms.
A sewage treatment plant separates solids from liquids by physical processes and purifies the liquid by biological processes. There are three stages of this treatment; primary, secondary and tertiary. Primary treatment is physical, secondary biological and tertiary chemical.
Primary treatment phase of sewage treatment removes floating and suspended solids from sewage through two processes of filtration and sedimentation. First floating matter is removed through sequential filtration. The filtrate is kept in large open settling tanks where grit settles down. Aluminium or iron sulphate is added in certain places to flocculation and settling down of solids. The sediment is called primary sludge while the supernatant is called effluent. The primary sludge traps a lot of microbes and debris. It is subjected to composting or land fill where anaerobic digestion removes the organic matter.
During secondary treatment, the primary effluent is taken to aeration tanks. A large number of aerobic heterotrophic microbes grow in the aeration tank. They form flocs which are masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh like structures. The microbes digest a lot of organic matter, converting it into microbial biomass and releasing a lot of minerals. As a result the BOD of the waste matter is reduced to 10-15% of raw sewage, which is then passed into settling tank. In settling tank, the bacterial flocs are allowed to undergo sedimentation. The effluent or supernatant is generally passed into natural water bodies and sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge.
(b) This treatment prevents water pollution and water borne diseases. So, it is essential in order to protect the natural water bodies from sewage pollution.



