Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation Chapter 5 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Biology Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Class 12 Biology have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Principles of Inheritance and Variation Assignments Class 12 Biology
Question. In monohybrid cross the allele do not show any blending and that both the characters are recovered as such in F2 generation. This statement is explained on the basis of :
(a) Dominance
(b) Segregation
(c) Independent assortmant
(d) All the above
Answer
B
Question. Recessive traits are seen due to :
(a) Formation of non functional enzyme
(b) Enzyme is not produced
(c) 1 and 2 both
(d) Formation of functional enzyme
Answer
C
Question. Multiple alleles can be found only when :
(a) Population studies are made
(b) Individual study is made
(c) Mutation is absent
(d) Dominance is present
Answer
A
Question. Which symbol of pedigree is correctly matched ?

Answer
D
Question. Given pedigree represents inheritance of myotonic dystrophy which is an autosomal dominant disorder.
What will be genotype of parents ?
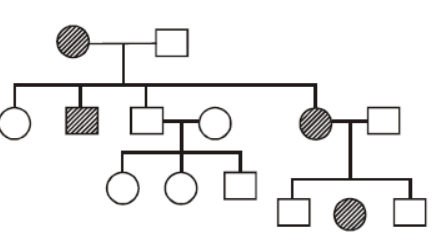
(a) Mother – aa Father – AA
(b) Mother – AA Father – aa
(c) Mother – Aa Father – aa
(d) Mother – aa Father – aa
Answer
C
Question. Given pedigree chart shows inheritance of autosomal recessive trait (for eg – sickle cell anaemia) then what will be genotype of parent ?
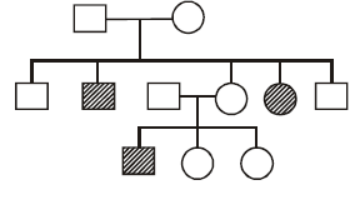
(a) Father – (Aa) Mother – (aa)
(b) Father – (aa) Mother – (aa)
(c) Father – (Aa) Mother – (Aa)
(d) Father – (AA) Mother – (AA)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following characters of Drosophila is not suitable for genetical studies ?
(a) They could be grown on simple synthetic medium in laboratory
(b) They complete their life cycle in about 2-weeks
(c) Single mating produces few number of progeny flies.
(d) They have many types of heredilaty variations that can be seen with low power microscope.
(e) Male & Female flies are not easily distinguishable
(1) a, b, c
(2) a, b, c, d, e
(3) d and e
(4) c and e
Answer
D
Question. Incomplete dominance can be seen in :
(a) Flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa
(b) Flower colour in Pisum sativum
(c) Size of starch grains in pea
(d) 1 and 3 both
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following cow breed comes in existance through artifical selection and domestication from ancestral wild cows
(a) Brown swiss
(b) Jamanapari
(c) Murrah
(d) Sahiwal
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following was/were applied first time to problems in biology during Mendel’s investigations into inheritance
(a) Statistical analysis
(b) Mathematical logic
(c) Computational devices
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer
D
Question. A true breeding line is that
(a) Having undergone continuous cross pollination
(b) Having undergone continuous self pollination
(c) Having undergone continuous vegetative propagation
(d) Obtain through tissue culture (Meristem)
Answer
B
Question. Variations are :
(a) Degree by which progeny differs from their parents
(b) Degree by which progeny similar to their parents
(c) Process by which characters are passed on from parent to progeny
(d) True breeding lines
Answer
A
Question. In any dihybrid cross segregation of one pair of characters is independent of other pair of characters, is known as
(a) Law of segregation
(b) Law of purity of gametes
(c) Law of independent assortment
(d) Law of dominance
Answer
C
Question. In dihybrid mendelian cross how many types of genotype and phenotype will be obtain
(a) 4 and 9 respectively
(b) 9 and 4 respectively
(c) 9 & 16 respectively
(d) 4 & 16 respectively
Answer
B
Question. Mendel found that the F1 always resembled either one of the parents and that the trait of the other parent was not seen in them. This is due to :
(a) Segregation
(b) Dominance
(c) Partial dominance
(d) Unit factor
Answer
B
Question. Study of family history about inheritance of a particular trait in several generations of a family called
(a) Phylogeny
(b) Ontogeny
(c) Pedigree analysis
(d) Cladistics
Answer
C
Question. Symbols 5 used in pedigree analysis, represents
(a) Five offspring with unspecified sex
(b) Five diseased offspring
(c) Five unaffected offspring
(d) Five affected offsprings
Answer
C
Question. It was found that sometimes the F1 – had a phenotype that did not resemble either of the two parents and was in between the two. This is the case of :
(a) Dominance
(b) Incomplete dominance
(c) Codominance
(d) Pleiotropism
Answer
B
Question. Theoratically, the modified allele could be responsible for the production of :
(a) less efficient enzyme
(b) A non functional enzyme
(c) Non enzyme at all
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. How many true breeding pea plant varieties were selected by Mendel
(a) 7
(b) 14
(c) 21
(d) 28
Answer
B
Question. Regarding to pair of dominant and recessive trait which of the following combination is wrong
(a) Flower colour – Violet / white
(b) Flower position – Axial / terminal
(c) Pod shape – Inflated / constricted
(d) Seed colour – Green / yellow
Answer
D
Question. If F1 individual of genotype (Tt) go through sexual reproduction, then it’s gamete (pollengrain) with genotype (T) have what chances to pollinate eggs of the genotype (T)
(a) 25 %
(b) 50 %
(c) 75 %
(d) 100 %
Answer
B
Question. Mendel proposed how many conclusions to consolidate his understanding of inheritance in monohybrid cross
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) None of the rules, he proposed laws / principles
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is correct ?
(a) When genes are grouped on the same chromosome, some genes are very tightly linked and showed very low recombination
(b) When genes are loosely linked show very low recombination
(c) When genes are tightly linked show higher recombination
(d) When genes are loosely linked show no recombination
Answer
A
Question. In Morgan’s experiment, what will be percentage of recombination in case of body colour and eye colour in Drosophila ?
(a) 37.2%
(b) 1.3%
(c) 98.7%
(d) 37.2%
Answer
B
Question. The law of dominance is used to explain the expession of only one of the parental characters in a monohybrid cross in ______ and the expression of both in _____.
(a) F1 and F2
(b) F2 and F3
(c) F1 and F3
(d) F2 and F1
Answer
A
Question. A diploid organism is heterozygous for 4 loci, how many types of gametes can be produced?
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 2
(d) 32
Answer
B
Question. When a cross is made between tall plant with yellow seed (TtYy) and tall plant with green seed (Ttyy), what proportion of phenotype in the offspring could be expected to be tall and green.
(a) 25%
(b) 12.5%
(c) 37.5%
(d) 50%
Answer
C
Question. The fact that the alleles donot show any blending and that both the characters are recovered as such in F2 generation, become the basis of
(a) Law of Dominance
(b) Law of paired factors
(c) Law of segregation
(d) Law of independent assortment
Answer
C
Question. If there are four allelic forms for the gene controlling ABO blood group then what will be the number of possible genotypes
(a) 6
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 14
Answer
B
Question. Multiple alleles can be found during study of
(a) Gametes
(b) Individual
(c) Population
(d) All above
Answer
C
Question. In sickle cell anaemia which of the following genotype will show disease phenotype
(a) HbA HbA
(b) HbS HbS
(c) HbS HbA
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not concerned with sickle cell anaemia
(a) Sixth position of b-chain
(b) a chain of Hb
(c) Valine
(d) Haemoglobin
Answer
B
Question. Shape of seed depends on starch granules size, so inheritance of seed shape show _____relationship while inheritance of starch grains show ____
(a) Dominant recessive, codominance
(b) Incomplete dominance, codominance
(c) Dominant – recessive, incomplete dominance
(d) Codominance, incomplete dominance
Answer
C
Question. Inheritance of starch grains size shows
(a) Dominant recessive relationship
(b) Codominance
(c) Incomplete dominance
(d) Multiple allelism
Answer
C
Question. The contrasting pairs of factors in Mendelian crosses are called
(a) multiple alleles
(b) alleles
(c) alloloci
(d) paramorphs
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following crosses will give tall and dwarf pea plants in same proportions?
(a) TT × tt
(b) Tt × tt
(c) TT × Tt
(d) tt × tt
Answer
B
Question. The F2 generation of a cross produced identical phenotypic and genotypic ratio. It is not an expected Mendelian result, and can be attributed to
(a) independent assortment
(b) linkage
(c) incomplete dominance
(d) none of the above
Answer
C
Question. Mendel selected pea as material for his experiments because
(a) it is an annual plant with comparatively short life cycle.
(b) the flowers are self-pollinated.
(c) the number of seeds produced is quite large.
(d) all of the above.
Answer
D
Question. Punnett square is used to know the
(a) outcome of a cross
(b) probable result of a cross
(c) types of gametes
(d) result of meiosis
Answer
B
Question. The test cross is used to determine the
(a) genotype of the plant
(b) phenotype of the plant
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. In humans, the dominance relationship between the A and B alleles of the ABO blood group gene is an example of
(a) complete dominance
(b) incomplete dominance
(c) codominance
(d) epistasis
Answer
C
Question. Linkage reduces the frequency of
(a) hybrids.
(b) all parental types.
(c) homozygous recessive parents.
(d) heterozygous recessive parents.
Answer
A
Question. HbA and HbS alleles of normal and sickle celled RBC are
(a) dominant-recessive alleles.
(b) polygenic alleles.
(c) codominant alleles.
(d) multiple alleles.
Answer
C
Question. The ‘X’ body of Henking was observed in
(a) all sperms during spermatogenesis.
(b) all eggs during oogenesis.
(c) half of the sperms during spermatogenesis.
(d) half of the eggs during oogenesis.
Answer
C
Question. In sickle-cell anaemia, shape of RBCs under oxygen tension becomes
(a) biconcave disc like
(b) elongated and curved
(c) circular
(d) spherical
Answer
B
Question. Sickel-cell anaemia is an example of
(a) sex-linked inheritance.
(b) deficiency disease.
(c) autosomal heritable disease.
(d) infectious disease.
Answer
C
Question. The number of phenotypes in ABO blood groups is
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer
B
Question. The person with Turner’s syndrome has
(a) 45 autosomes and X sex chromosome
(b) 44 autosomes and XYY sex chromosomes
(c) 45 autosomes and XYY sex chromosomes
(d) 44 autosomes and X sex chromosome
Answer
D
Question. Three children in a family have blood types O, AB and B respectively. What are the genotypes of their parents?
(a) IA i and IBi
(b) IAIB and i i
(c) IBIB and IAIA
(d) IAIA and IBi
Answer
A
Question. Mutations can be induced with
(a) infrared radiations
(b) I AA
(c) ethylene
(d) gamma radiations
Answer
D
Question. In XO type of sex determination
(a) females produce two different types of gametes.
(b) males produce two different types of gametes.
(c) females produce gametes with Y chromosomes.
(d) males produce single type of gametes.
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Question. Select the correct statement from the ones given below with respect to dihybrid cross.
(a) Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show higher recombinations.
(b) Genes far apart on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.
(c) Genes loosely linked on the same chromosome show similar recombinations as the tightly linked ones.
(d) Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is an incorrect statement regarding mutations?
(a) Deletion and insertion of base pairs cause frameshift mutations.
(b) Cancer cells commonly show chromosomal aberrations.
(c) UV and gamma rays are mutagens.
(d) Change in a single base pair of DNA does not cause mutation.
Answer
D
Question. Refer the given statements and select the correct option.
(i) Percentage of homozygous dominant individuals obtained by selfing Aa individuals is 25%.
(ii) Types of genetically different gametes produced by genotype AABbcc are 2.
(iii) Phenotypic ratio of monohybrid F2 progeny in case Mirabilis jalapa is 3 : 1.
(a) All the statements are true.
(b) Statements (i) and (ii) are true, but statement (iii) is false.
(c) Statements (i) and (iii) are true, but statement (ii) is false.
(d) Statements (ii) and (iii) are true, but statement (i) is false.
Answer
B
Question. Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) In male grasshoppers, 50% of the sperms have no sex chromosome.
(b) Usually female birds produce two types of gametes based on sex chromosomes.
(c) The human males have one of their sex chromosomes much shorter than the other.
(d) In domesticated fowls, the sex of the progeny depends on the type of sperm that fertilizes the egg.
Answer
D
Question. Choose the correct statements given below regarding Mendelian inheritance.
(i) Mendel’s experiments had small sample size which gave greater credibility to the data.
(ii) A true breeding line shows a stable trait inheritance and expression for several generations.
(iii) In a dissimilar pair of factors, one member of the pair dominates over the other.
(iv) A recessive parental trait is expressed only in its heterozygous condition.
(v) Two alleles of a gene are located on homologous sites on homologous.
(a) (ii) only
(b) (ii), (iii) and (v)
(c) (i), (iii) and (v)
(d) (i) and (v)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements are correct ?
(i) Incomplete or mosaic inheritance is an example of pre-Mendelian concept of blending inheritance.
(ii) Test cross is a special type of back cross.
(iii) Chromosomal aberrations are commonly observed in cancer cells.
(iv) Thalassaemia is a Mendelian disorder.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv) only
Answer
B
Assertion/Reason Type Questions Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Haemophilia is a recessive sex linked disease.
Reason : Haemophilia occurs due to mutation of a structural gene on chromosome 15.
Answer C
C
Question. Assertion : In humans, the gamete contributed by the male determines whether the child produced will be male or female.
Reason : Sex in humans is a polygenic trait depending upon a cumulative effect of some genes on X-chromosome and some on Y-chromosome.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Test cross is used to determine an unknown genotype within one breeding generation.
Reason : Test cross is a cross between F1 hybrid and dominant parent.
Answer
C
Matching Type Questions Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Question. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. ABO blood groups | I. Dihybrid cross |
| B. Law of segregation | II. Monohybrid cross |
| C. Law of Independent | III. Base pairs substitution assortment |
| D. Gene mutation | IV. Multiple allelism |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(b) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – II; C – I; D – III
(d) A – II; B – III; C – IV; D – I
Answer
C
Question. Match column-I with column-II and find the correct answer.
| Column -I | Column -II |
| A. Monoploidy | I. 2n – 1 |
| B. Monosomy | II. 2n + 1 |
| C. Nullisomy | III. 2n + 2 |
| D. Trisomy | IV. 2n – 2 |
| E. Tetrasomy | V. n |
| VI. 3n |
(a) A – V, B – I, C – IV, D – II, E – III
(b) A – V, B – II, C – IV, D – I, E – III
(c) A – VI, B – V, C – III, D – IV, E – II
(d) A – II, B – I, C – III, D – VI, E – V
Answer
A
Question. Match column-I with their name given in column-II and choose the correct answer.
| Column -I | Column -II |
| A. Alfred Sturtevant | I. Mapped position of genes |
| B. Henking | II. X-body |
| C. Meischer | III. Nuclein |
| D. Morgan | IV. Dihybrid crosses in Drosophila |
(a) A – I, B – III, C – IV, D – II
(b) A – I, B – II, C – III, D – IV
(c) A – IV, B – I, C – II, D – III
(d) A – III, B – II, C – IV, D – I
Answer
B
Question. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Autosomal | I. Down’s syndrome recessive trait |
| B. Sex-linked | II. Phenylketonuria recessive trait |
| C. Metabolic error | III. Haemophilia linked to autosomal recessive |
| D. Additional 21st | IV. Sickle cell anaemia chromosome |
(a) A – II; B – I; C – IV; D – III
(b) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(c) A – IV; B – III; C – II; D – I
(d) A – III; B – IV; C – I; D – II
Answer
C
Diagram Type Questions Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Question. Study the pedigree chart given below and choose its correct representation.

(a) Inheritance of a condition like phenylketonuria as an autosomal recessive trait.
(b) The pedigree chart is wrong as this is not possible.
(c) Inheritance of a recessive sex-linked disease like haemophilia.
(d) Inheritance of a sex-linked inborn error of metabolism like phenylketonuria.
Answer
A
Question. The given figure represents the inheritance pattern of a certain type of traits in humans.

Which one of the following conditions could be an example of this pattern?
(a) Thalassemia
(b) Haemophilia
(c) Phenylketonuria
(d) Sickle cell anaemia
Answer
B
Question. The experiment shown in the given figure has been carried out by Morgan to show the phenomenon of linkage and recombination. If in cross I, genes are tightly linked and in cross II, genes are loosely linked then what will be the percentage of recombinants produced in cross I and cross II respectively?

(a) 98.7% and 62.8%
(b) 1.3% and 37.2%
(c) 37.2 and 1.3%
(d) 62.8% and 98.7%
Answer
B
Question. Identify the type of inheritance shown in the diagram.

(a) dominant X-linked
(b) recessive X-linked
(c) dominant Y-linked
(d) recessive Y-linked
Answer
A
Critical Thinking Type Questions Class 12 Biology Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Question. In Mendelian dihybrid cross when heterozygous round yellow are self crossed, round green offsprings are represented by genotype
(a) RrYy, RrYY, RRYy
(b) RrYY, RRyy, rryy
(b) rrYy, rrYY
(c) RrYY, Rryy, RRyy
Answer
D
Question. Harmful mutations does not get eliminated from gene pool because
(a) they are recessive and carried by homozygous individuals.
(b) they are recessive and carried by heterozygous individuals.
(c) they are formed repeatedly.
(d) they show genetic drift.
Answer
B
Question. In a normal couple, half the sons are haemophilic while half the daughters are carriers. The gene responsible for it is located on
(a) X-chromosome of father.
(b) Y-chromosome of father.
(c) one X-chromosome of mother.
(d) both the X-chromosomes of mother.
Answer
C
Question. According to the law of independent assortment in a dihybrid cross
(a) there are four genotypes in F2.
(b) F2 contains 16 phenotypes.
(c) there is a single individual which is homozygous recessive for both the characters.
(d) it is not possible to forecast the different phenotypes.
Answer
C
Question. Inheritance of which of the following traits is shown in the above given cross?
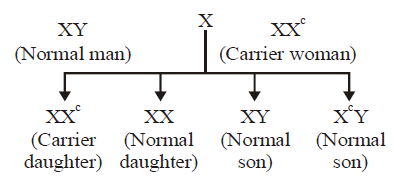
(a) X-linked dominant trait
(b) X-linked recessive trait
(c) Autosomal recessive trait
(d) Autosomal dominant trait
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following correctly represents the nature of blood in the ABO system of blood groups pertaining to the presence of antigens and antibodies?
(a) Blood group A –Antibody A and antigen B
(b) Blood group B–Antigen B and antibody A
(c) Blood group AB–Both antibodies A and B
(d) Blood group O–No antigens and no antibodies
Answer
B
Question. In Drosophila, XXY represents a female but in human it is an abnormal male. It shows that
(a) Y-chromosome is essential for male sex in human.
(b) Y-chromosome is essential for female sex determination in Drosophila.
(c) Y-chromosome is not essential for male sex determination in human.
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Multiple alleles are present
(a) at different loci in the same chromosome.
(b) in different chromosomes.
(c) at the same locus in one type of chromosomes.
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. A monohybrid cross is the one in which
(a) only a single plant is involved for the experiment.
(b) a single pair of contrasting characters is considered for the genetic results.
(c) a hybrid is crossed to a homozygous.
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. In genetics the term test cross means
(a) the crossing of F1 individual with homozygous recessive.
(b) crossing an F1 individual with either of the two parents.
(c) crossing F1 individual with another F1 individual.
(d) crossing F1 individual with that of F2.
Answer
A
Question. How would you test a pea plant whether it is a pure or hybrid for tallness ?
(a) Cross the pea plant with another tall pea plant of unknown genotype.
(b) Cross the pea plant with a pure tall pea plant.
(c) Cross the pea plant with a homozygous dwarf pea.
(d) Cross the pea plant with any pea plant.
Answer
C
Question. Mendel was successful in formulating the laws of inheritance whereas his predecessors were not because
(a) he studied one clear-cut character at a time.
(b) the characters studied by him were present on separate chromosomes.
(c) of the right choice of material.
(d) he kept accurate records of his experiments.
Answer
A
Question. The F2 generation offspring in a plant showing incomplete dominance, exhibit
(a) variable genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
(b) a genotypic ratio of 1 : 1.
(c) a phenotypic ratio of 3 : 1.
(d) similar phenotypic and genotypic ratios of 1 : 2 : 1.
Answer
D
Question. A man has enlarged breasts, sparse hairs on the body and sex chromosomal formula XXY. He then suffers from
(a) Down’s syndrome
(b) Edward’s syndrome
(c) Turner’s syndrome
(d) Klinefelter’s syndrome
Answer
D
Question. Two organisms that are true-breeding for a certain genetic characteristic are mated and their offspring were analysed.
Which of the following statements about this situation is correct?
(a) Both parents are homozygotes.
(b) The offspring are either all homozygotes or all heterozygotes.
(c) The offspring represent the F1 generation and the gametes produced by the offspring will carry only
one allele for this gene.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Sex determination in grasshoppers, humans, and Drosophila is similar because
(a) females are hemizygous.
(b) males have one X-chromosome and females have two X-chromosomes.
(c) all males always have one Y-chromosome in all three species.
(d) the ratio of autosomes to sex chromosomes is the same in all three organisms.
Answer
B
Question. Haemophilia is mentioned as a trait carried by the mother and passed to her sons. What is the pattern of inheritance for this trait ?
(a) Haemophilia is an allele carried on one of the mother’s autosomal chromosomes.
(b) Haemophilia is an allele carried on the Y-chromosome because more males have this genetic disorder than females.
(c) Haemophilia is an allele carried on the X-chromosome and can be directly inherited by the son from the father or the mother.
(d) Haemophilia is carried on the X-chromosome and can only be inherited by the son if the mother is a carrier.
Answer
D